ROS setup tutorial
ROS (Robot Operating System) is a set of libraries and tools designed for robot applications. It mainly targets C++ and Python development and uses catkin build system, which is based on CMake with Python scripts. ROS software distributions are available for Linux, Windows, and also for macOS in experimental mode.
You can use CLion as an IDE for your ROS projects. This tutorial describes how to set up the workflow and gives an example of creating a ROS package and working with it in CLion. Note that this setup procedure has been tested on Ubuntu.
Launch CLion in the sourced environment
CLion needs to be informed of the ROS-specific environment variables. These variables are retrieved in the current shell when you source the workspace by running the following command from the workspace directory:
The simplest way to provide CLion with ROS environment variables is to launch the IDE from the same shell. After the workspace is sourced, you can type in the same terminal:
Open a ROS project in CLion
After you have launched CLion in the sourced environment, do one of the following to open your ROS project:
Click and select CMakeLists.txt in the src directory of your ROS workspace, then choose Open as Project.
Click and select the src directory of the workspace to import the project from.
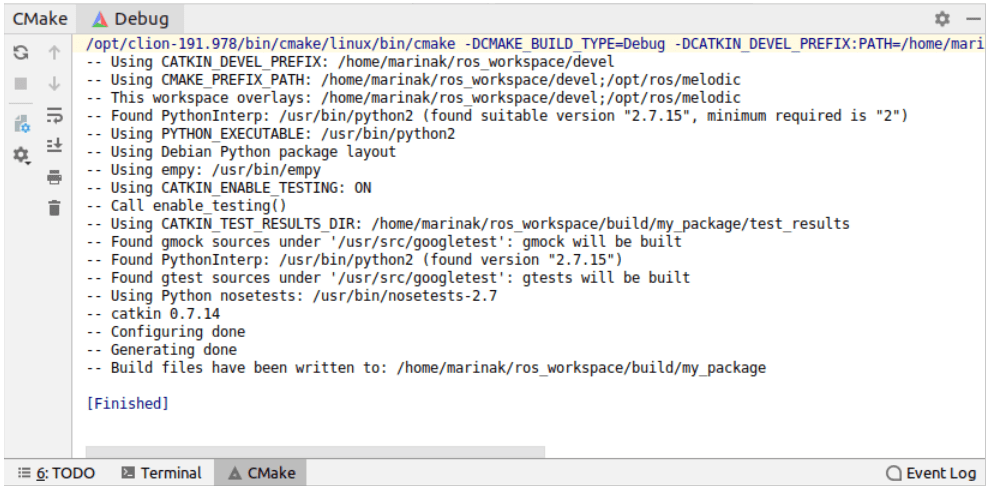
The CMake tool window will show the status of the project loading:
Set build paths to the catkin workspace
By default, CLion places build output in cmake-build-debug or cmake-build-release directory that is created automatically. For ROS development, it means that you will have two different builds in CLion and in the console where you run catkin_make.
To have a single build across the IDE and console, you need to set CLion build paths to the catkin workspace directories. For this, go to and change two fields:
In Build directory, set <WORKSPACE_DIRECTORY>/build.
In CMake options, add
-DCATKIN_DEVEL_PREFIX:PATH=<WORKSPACE_DIRECTORY>/devel.
Work with launch files
You can run and debug ROS nodes as regular applications in CLion.
Launch files cannot be executed directly, but you can edit them with XML syntax highlighting and completion, and attach the debugger to a running node.
Attach the debugger to a running node
Run your .launch file from the command line. For example
roslaunch roscpp_tutorials talker_listener.launchYou can check the list of currently running nodes by the
rosnode listcommand. In our example, the list will containtalkerandlistener: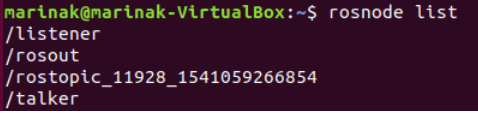
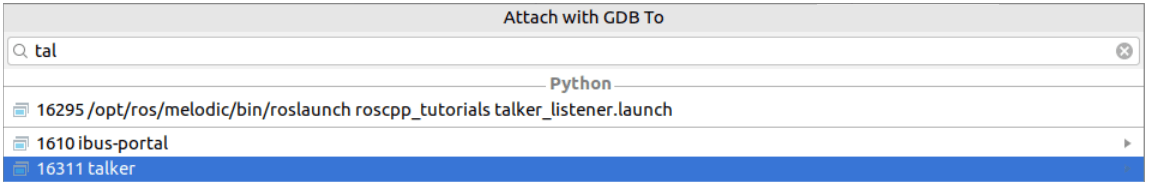
Call from the main menu or press Ctrl+Alt+F5.
Connect to the desired node by its PID or name:
Example: create a basic ROS node, edit and run it in CLion
In this example, we will create a simple ROS package, edit the source code, and run the node from CLion. We will use ROS Melodic on Ubuntu 18.04 and the basic publisher node from the Writing a Simple Publisher and Subscriber (C++) tutorial available on the ROS wiki.
Create a basic ROS package
Create and build a ROS workspace:
mkdir -p ros_workspace/src cd ros_workspace catkin_makeIn the workspace, create a package called my_package:
cd src catkin_create_pkg my_package roscpp rospy std_msgs
Launch CLion
Source the workspace:
cd ../../../ source ./devel/setup.bashAnd launch CLion in the same terminal:
sh /opt/clion-2018.2/bin/clion.sh
Open the package as a project in CLion
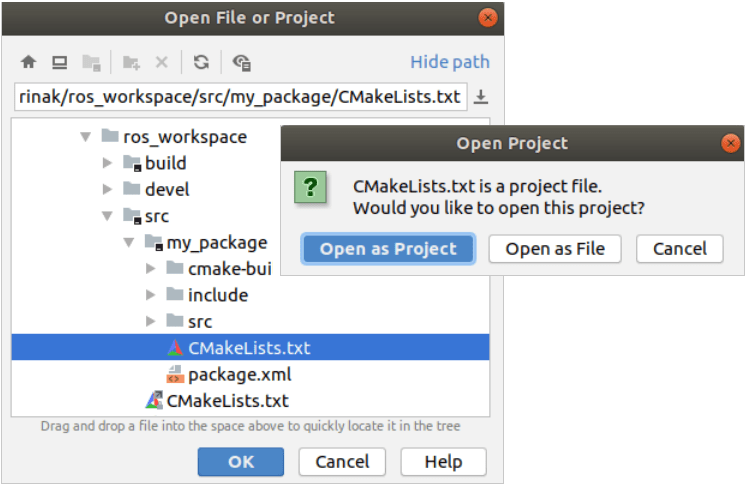
In CLion, go to File | Open in the main menu and select the CMakeLists .txt file located inside the package folder, and choose to open it as a project:
Add a source file and edit CMakeLists.txt
Add a new source file to the project: right-click src in the Project tree, select and call it my_package.cpp.
Copy the entire talker.cpp file from the Publisher and Subscriber tutorial into my_package.cpp.
Add the newly created source to CMakeLists.txt and link it against catkin libraries:
add_executable(my_package src/my_package.cpp) target_link_libraries(my_package ${catkin_LIBRARIES})After that, reload the CMake project, and notice my_package in the list of Run/Debug configurations:
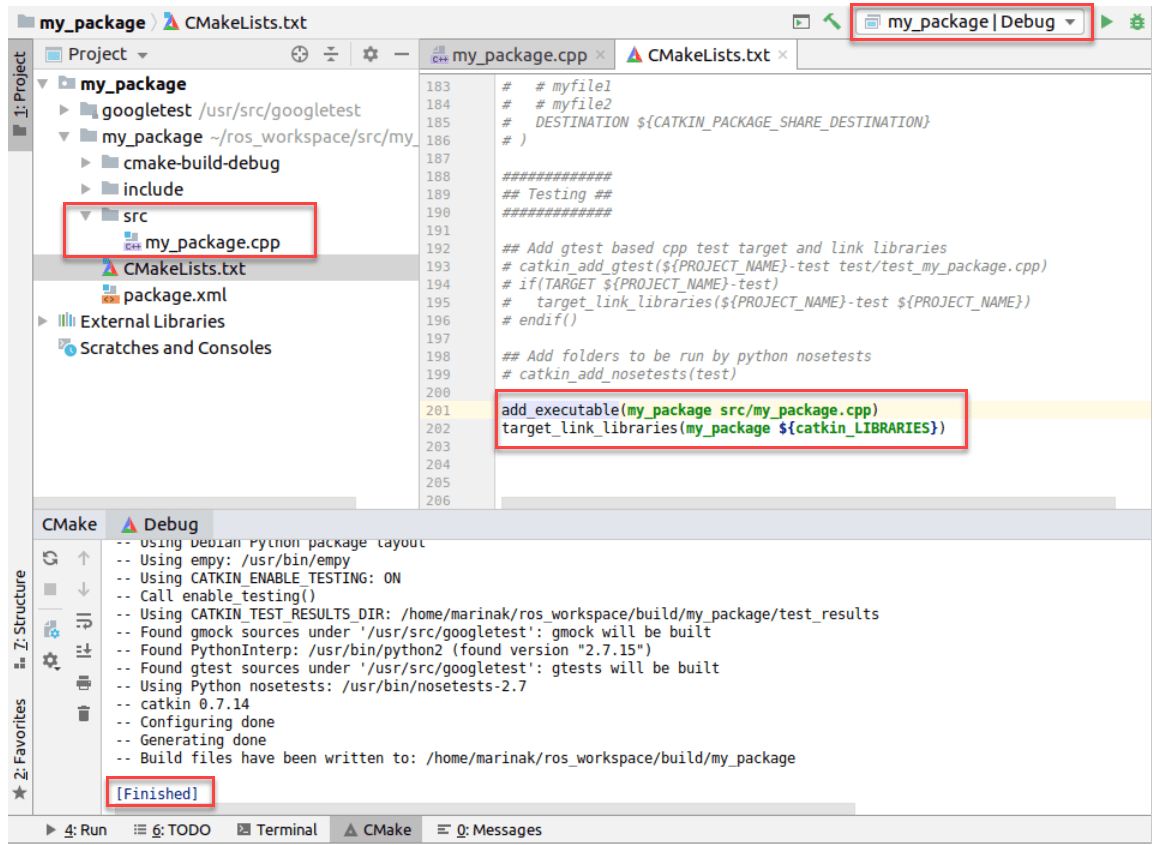
Run a ROS node
Before running the node from CLion, open the ROS master in a new terminal:
roscoreIn CLion, Run
the my_package configuration. Run tool window will show the node output:
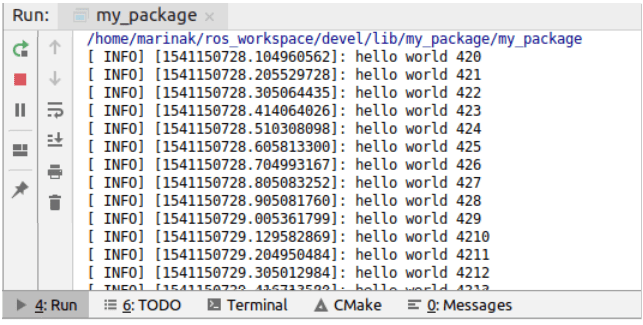
In a separate terminal, check the currently active ROS topics.
If we print the messages from
chatter, the output will be similar to what we can see in CLion: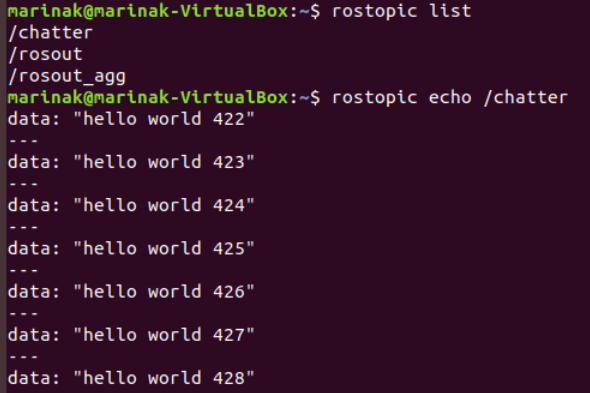
Now if we stop the application in CLion, the
rostopic echo /chattercommand will have no output.