Open and create projects
Open a project
To open an existing CMake project in CLion, do one of the following:
Select File | Open and locate the project directory. This directory should contain a CMakeLists.txt file.
Select File | Open and point CLion to the top-level CMakeLists.txt file, then choose Open as Project.
Select File | Open and locate the CMakeCache.txt file, then choose Open as Project.
When you open a project for the time, CLion displays the CMake Profiles dialog with the initial configuration. You can edit the profile or close the dialog without editing. To disable this initial profile configuration, go to and clear the corresponding checkbox: 
Create a new project
If no project is currently opened in CLion, click New Project on the Welcome screen. Otherwise, select on the main menu.
In the New Project dialog that opens, select the target type of your project (executable or library), and the language to be used (pure C or C++).
CLion will generate the top-level CMakeLists.txt file based on the provided settings. See CMakeLists.txt file templates for details.
New project example
As an example, let's create a simple shared library assuming the C++14 standard.
Click New Project from the Welcome screen or the File menu.
In the left pane, choose C++ Library.
In the right pane, set the location and the name of your project. You can type the path in the text field or click
to browse for the desired folder.
Click the Language standard control and select the standard from the drop down list (C++14 in our example).
Use the Library type control to select the library type (shared in our example).
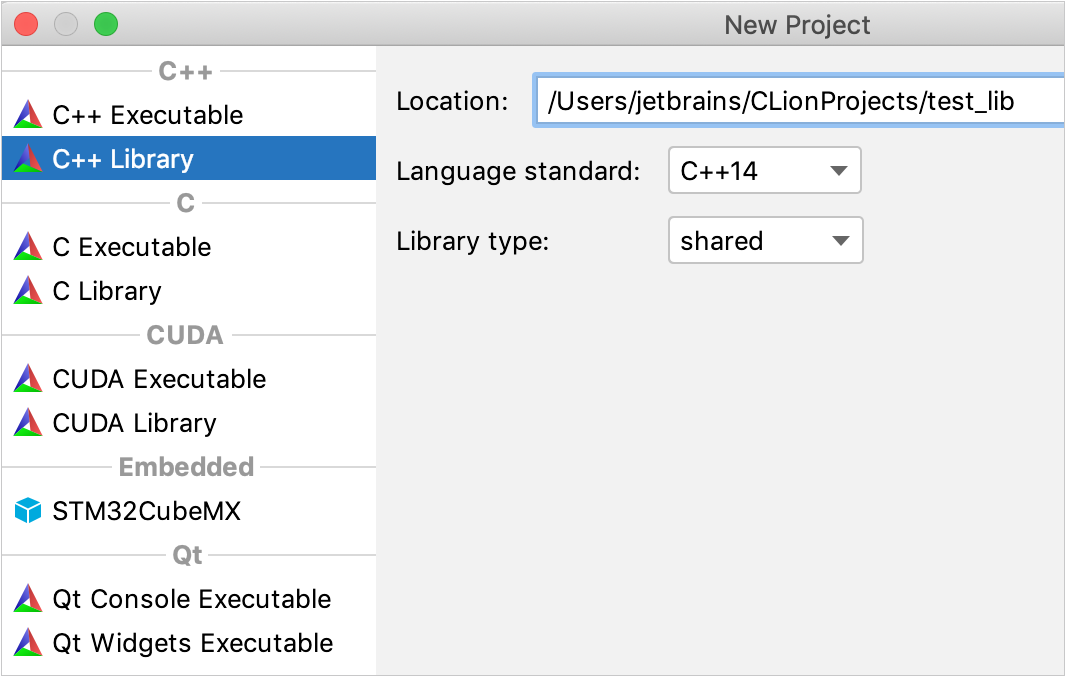
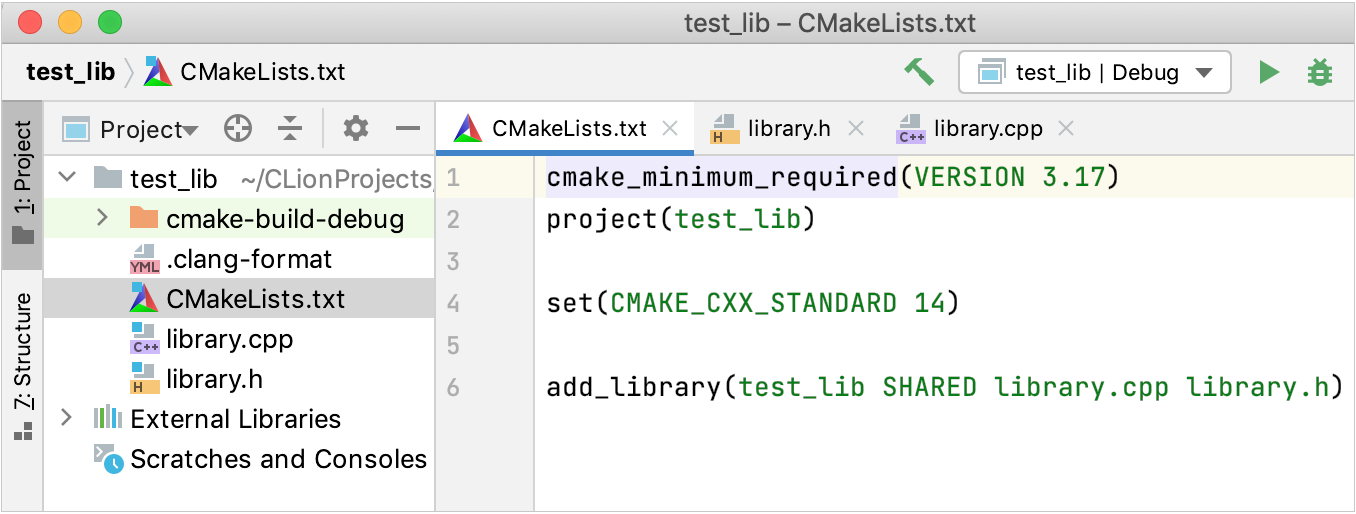
Click Create to create a project and generate the corresponding CMakeLists.txt file:
Create a CMake project from sources
To work with non-CMake sources in CLion, you can convert them into a CMake project structure.
On the main menu, choose and select the project root folder.
Open a source file in the editor.
If there is no top-level CMakeLists.txt file, CLion will suggest creating it:

In the Create CMakeLists.txt dialog, specify the following:
Select project files- select the files to be imported as project files. Use the subdirectories checkboxes to import their entire contents or clear the checkboxes to import the contents selectively.
User Include Directories- select the directories to be included in the project and specified in the CMake include_directories command. CLion includes a directory automatically when it contains at least one header file, if it is named include, or when it has subdirectories that contain header files only.
Note that directories not selected in the Select Project Files pane are not presented in the User Include Directories list - select them first, and then the available include directories will appear in the list.

Work with a monorepo
Monorepos are repositories that combine multiple projects, usually without a top-level CMake script. Instructions below describe how to work with a monorepo in CLion using LLVM Project as an example.
Call and point CLion to CMakeLists.txt in the required subdirectory. For the case of LLVM, select llvm-project/llvm/CMakeLists.txt.
In the dialog that opens, click Open as Project.
Go to and use the CMake options field to add the sub-projects that you want to build additionally.
For example, to add clang and clang-tools-extra, specify
-DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS=“clang;clang-tools-extra”:
Project reload should perform successfully at this point.
To be able to view the entire repository in the Project tree, change the project root: call from the main menu and select the top-level repository folder, llvm-project.
We also recommend that you build the project. This way, resolve will work on the entire codebase, including the parts generated at build time.