Tutorial: Configure CLion on Windows
On Windows, configuring CLion requires setting up the environment: Cygwin, MinGW, WSL, or Microsoft Visual C++. You can have several environments installed on your system and create separate CLion toolchains for each of them. As a determining part of a toolchain, the environment provides C and C++ compilers, the make utility, and the debugger (in case of using default tools).
For details on Remote Host toolchains, see Full Remote Mode.
MinGW
MinGW-w64 (64- and 32-bit)
Download and run the MinGW-w64 installer. It provides both 64- and 32-bit options.
In the MinGW-w64 installation wizard, make sure to select the required architecture. Note that the default suggested option is 32-bit.

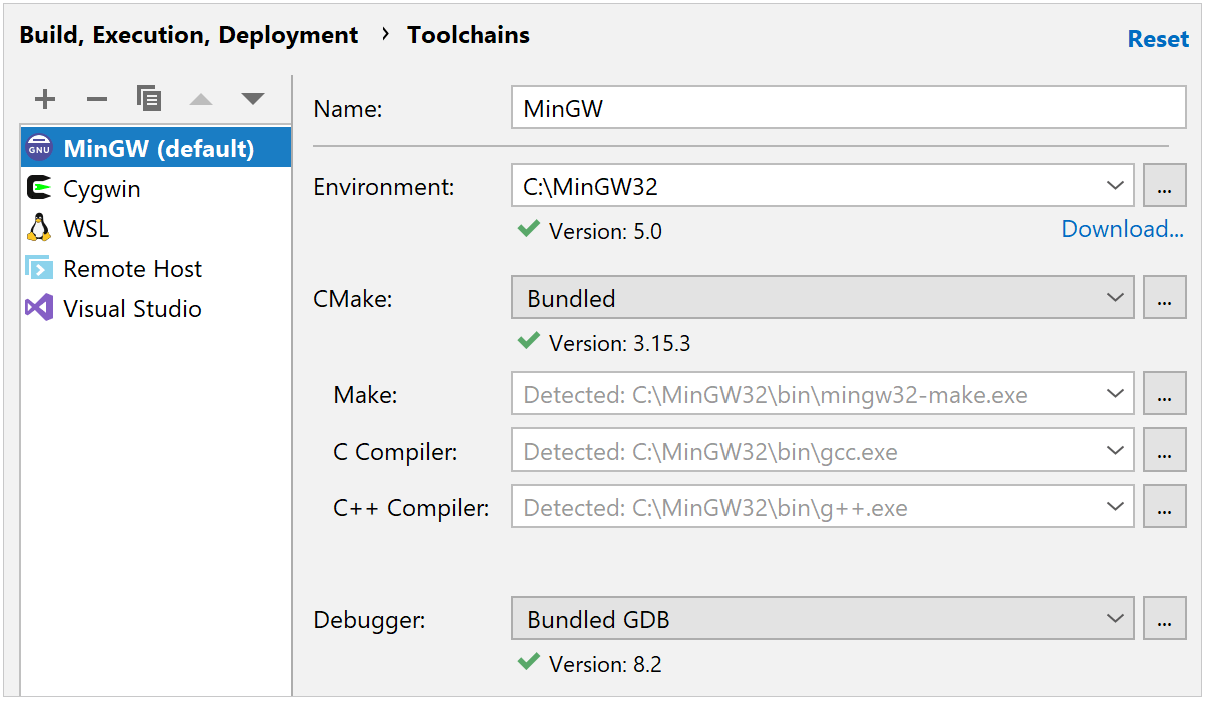
Once the installation is finished, open CLion and go to .
Choose the MinGW toolchain that you want to configure or create a new one using the
icon.
CLion will attempt to detect the MinGW installation automatically. Check the detection result in the Environment field, and specify the path manually if required.
Wait until the tools detection finishes.
Select the Debugger: you can use either MinGW-w64 GDB or a custom GDB binary.
Click Apply when all the tools are set correctly.
MinGW (32-bit only)
Although MinGW-w64 provides both 64- and 32-bit options, you can also install MinGW, the 32-bit-only version.
In the MinGW installation wizard, select the following packages from the Basic Setup list: mingw-developer-tool, mingw32-base, mingw32-gcc-g++, mingw32-msys-base.
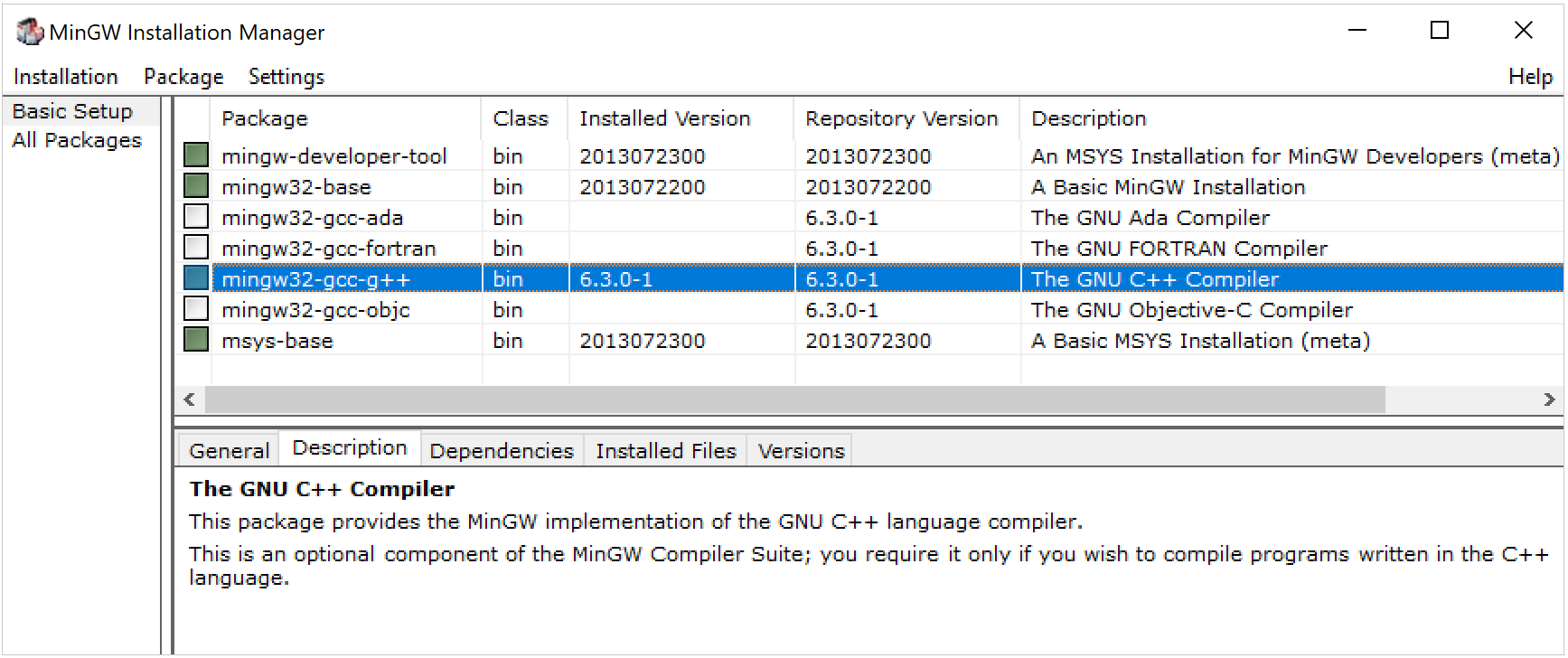
Follow the steps 3-7 for MinGW-w64.
When configuring the toolchain, if CLion cannot detect compilers or make, double-check the installed packages in MinGW Installation Manager.
In the Debugger field, you can choose between the bundled GDB, MinGW GDB, or your custom GDB executable.
The recommended option is bundled GDB, since it is guaranteed to include Python support required for CLion data renderers.
Cygwin
Download the Cygwin installer, version 2.8 or later.
Run the installer and select the following packages:
gcc-g++
make
gdb
To select a package, type its name in the Search field and set the version in the New column:

Once the installation is finished, open CLion and go to . Choose the toolchain that you want to configure.
Select Cygwin from the Environment list. CLion will attempt to detect the Cygwin installation automatically. Check the detection result, and specify the path manually if required.
Wait until the tools detection finishes, and click Apply.

Windows Subsystem for Linux
You can use WSL, Windows Subsystem for Linux, as your working environment in CLion on Windows 10 (starting the Fall Creators Update version 1709, build 16299.15).
WSL toolchain enables you to build projects using CMake and compilers from Linux and run/debug on WSL without leaving CLion running on your Windows machine.

Microsoft Visual C++
Install Visual Studio 2013, 2015, 2017, or 2019 on your system.
In CLion, go to .
Click
and select Visual Studio from the list of toolchain templates.
Check the Environment field. CLion will attempt to automatically detect the installed Visual Studio distribution. If the detection fails, set the path to Visual Studio manually.
If required, specify the Architecture (x86, amd64, x86_arm, or another), Platform (store, uwp, onecore, or leave it blank), and Version. To build your project for the selected architecture, CLion will call the script to configure the environment with the specified parameters.
Wait until the tools detection is finished
:

MSVC compiler
CLion supports the Microsoft Visual C++ compiler that ships with Visual Studio 2013, 2015, 2017, and 2019.
Note that msbuild is not supported: CLion runs CMake with the NMAKE generator instead.
For the case when your code includes MSVC extensions, CLion provides the support for:
__uuidof,__forceinline,__unaligned, and__alignofkeywords;pointer type attributes:
__ptr32,__ptr64,__uptr,__sptr;MSVC built-in data types:
(unsigned) __int8,(unsigned) __int16,(unsigned) __int32,(unsigned) __int64,__wchar_t;additional format specifiers, such as
%I32and%I64;the clang 's
-fms-extensionsflag.
Clang-cl compiler
As an alternative compiler, you can use clang-cl- the MSVC-compatible compiler driver for Clang. CLion supports clang-cl version 8.0 and later.
Install clang-cl from the LLVM site or along with the Visual Studio tools.
When installed from the LLVM site, the clang-cl binary can be found at the standard location C:\Program Files\LLVM\bin\clang-cl.exe for the 64-bit version or C:\Program Files (x86)\LLVM\bin\clang-cl.exe for the 32-bit version.
In CLion, go to and select the Visual Studio toolchain that you want to configure, or create a new one.
Point the C Compiler and C++ Compiler fields to clang-cl.exe. CLion will suggest the paths detected automatically.

Note that currently the -T clangcl options can't be picked up if the bundled CMake is in use along with the Visual Studio toolchain setup (CPP-18848).
MSVC debugger
The MSVC toolchain debugger is implemented on top of LLDB, and it can work with native visualizers from the Visual Studio installation or from your project.
To enable native visualizers support and set the desired diagnostics level, select the Enable NatVis renderers for LLDB checkbox in : 
CLion automatically generates one-line summaries for all structures not covered by Natvis and highlights them to increase readability. Also, the built-in formatters provide visualization for wide/Unicode strings (wchar_t, char16_t, char32_t).
If you have custom native visualizers in your project, CLion will use them as well. 
CLion supports most of the Natvis customization features, such as ArrayItems, IndexListItems, LinkedListItems, TreeItems, Inheritable attribute, Format specifiers, and CustomListItems.
Clang compiler on Windows
With CMake 3.15, it has become possible to use the Clang compiler on Windows with the MinGW-w64/MinGW toolchain.
However, the LLVM Clang for Windows is built using Microsoft Visual Studio, and all the built-in macros and include search paths are set up for use with Visual Studio. So if you take Clang from the LLVM repository, it will not work correctly when configured with the MinGW toolchain. One of the possible workarounds is described below.
Set up the Clang compiler for MinGW
Install MSYS2.
Download the following packages with the pacman tool (use the
pacman -S package_namecommand):mingw-w64-x86_64-gcc
mingw-w64-x86_64-clang
mingw-w64-x86_64-lld
mingw-w64-x86_64-gdb
mingw-w64-x86_64-make
mingw-w64-x86_64-polly
mingw-w64-x86_64-compiler-rt
This way, you will get the Clang compiler which is built with mingw-w64 and has paths and macros that correspond to this toolchain.
Go to , create a MinGW toolchain, and set up the tools from MSYS.
After specifying the Environment, check the automatically detected tools and make sure to switch to Clang in the C Compiler and C++ Compiler fields.

GDB on Windows
In the case of MinGW, CLion includes the bundled GDB (version 10.2). For Cygwin, you need to install the GDB package in the Cygwin Package Manager, as described in the Cygwin section of this guide.
You can also switch to a custom GDB binary. In this case, the supported GDB versions are 7.8.x-10.2.
Note that for GDB 8.0 and later, debugger output is redirected to CLion console by default. To enable opening an external console window for application input/output, go to Help | Find Action or press Ctrl+Shift+A, search for Registry, and set the following key: cidr.debugger.gdb.workaround.windows.forceExternalConsole.
