Makefile projects
Full support for Makefile projects in CLion is still a work in progress. Use the tickets linked to CPP-494 to leave your feedback and vote for the desired features.
tip
Refer to Autotools if your Makefile project requires pre-configuration.
Select File | Open from the main menu.
Point CLion to a folder that contains the top-level Makefile or to that file directly:
In the dialog that opens, click Open as Project.
You will be prompted to clean the project:
Cleaning is required for the project load as the Make build is incremental and only the updated files are compiled. When run on an uncleaned project, reload will miss all the unchanged files and might perform incorrectly.
Clear the Clean project checkbox if you prefer to load without cleaning. You will be able to clean and reload your project later (for example, after performing the required bootstrapping).
At this point, CLion starts loading the project, displaying the progress and status in the Build tool window:
Warning messages may appear during the process, but if loading finishes with a green checkmark
next to the project name, this indicates a successful load. Take a look at the Troubleshooting section if your project fails to load correctly.
You can also open a project as a folder and load the Makefile later. This is helpful, for example, if your project requires some preconfigure step or launching a script to prepare the final Makefile, so you don't have it when opening your project in CLion.
To load the Makefile when ready, open it in the editor and click the Load Makefile project link in the notification:
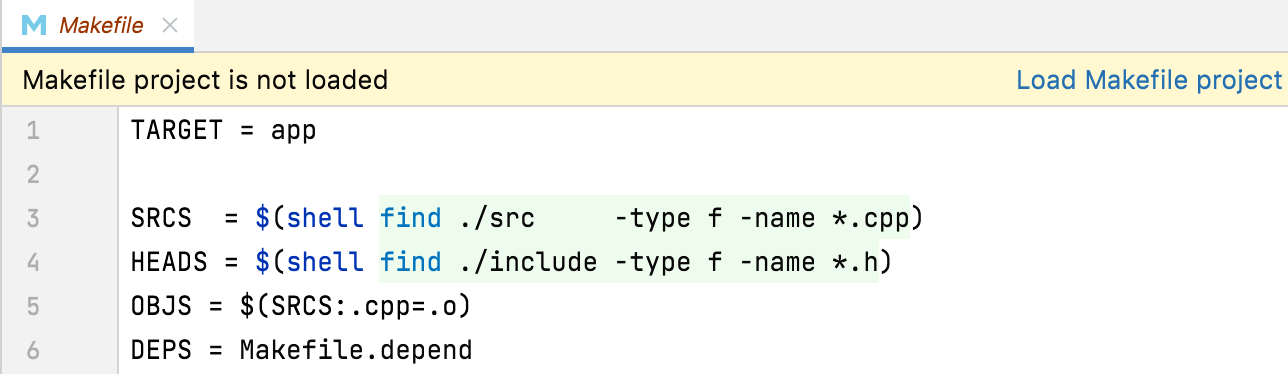
Alternatively, use the Load Makefile Project action from the file's context menu in the project tree.
note
When working with a Makefile project under VCS, consider not to share the .iml file, since it will be regenerated on import. See this instruction for more information.
By default, CLion doesn't update or reload your project automatically except for the cases of external events like VCS update. You can change this behavior in the Build Tools settings.
Go to Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Build Tools.
Select one of the auto-reload options:

Any changes - project reload will be triggered on any change in Makefiles.
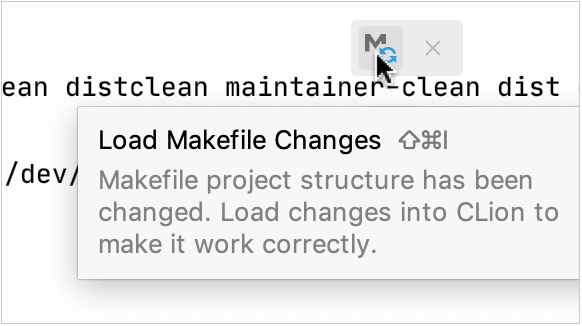
External changes (default) - your project will be reloaded only upon external events like VCS update. In case of other changes (for example, when you add a new file), you will get a notification on the Makefile:
tip
This setting works per-project. Auto-reload options should be configured for each of your Makefile, compilation database, or Gradle projects separately.
Apart from the automatic options, you can also reload your project manually:
Call Reload Makefile Project or Clean and Reload Makefile Project from Tools | Makefile on the main menu.
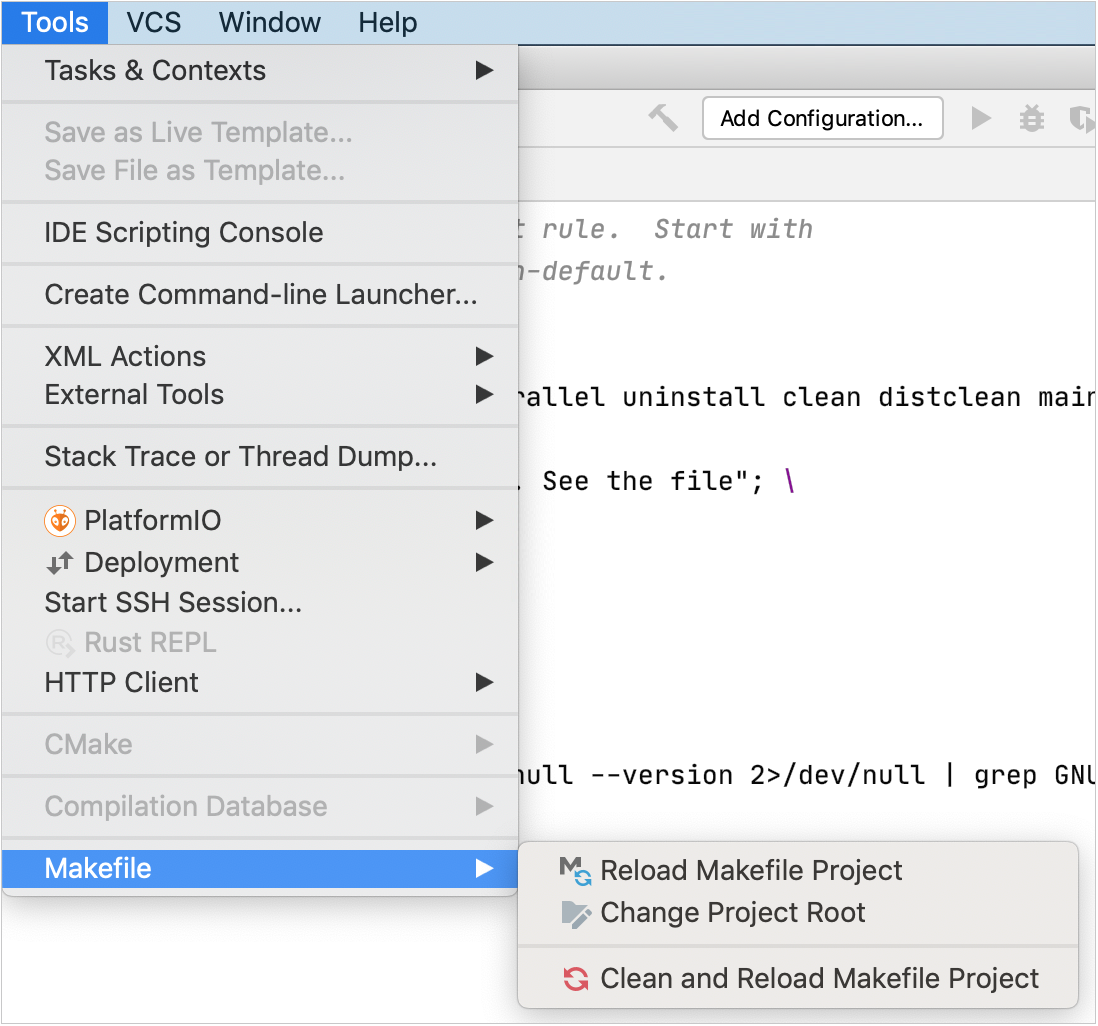
Alternatively, click
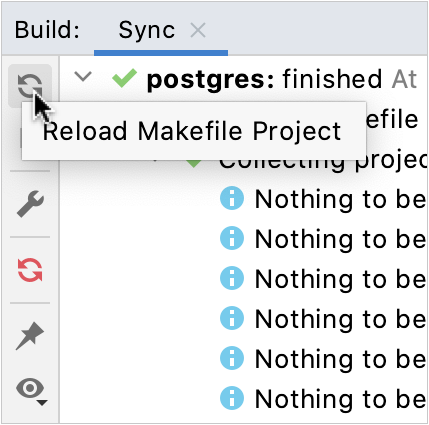
or
in the Build tool window:
note
Your project may also require the ./configure step to be performed after modifications in order to get the updated Makefiles.
Use the Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Makefile dialog to control your project settings.
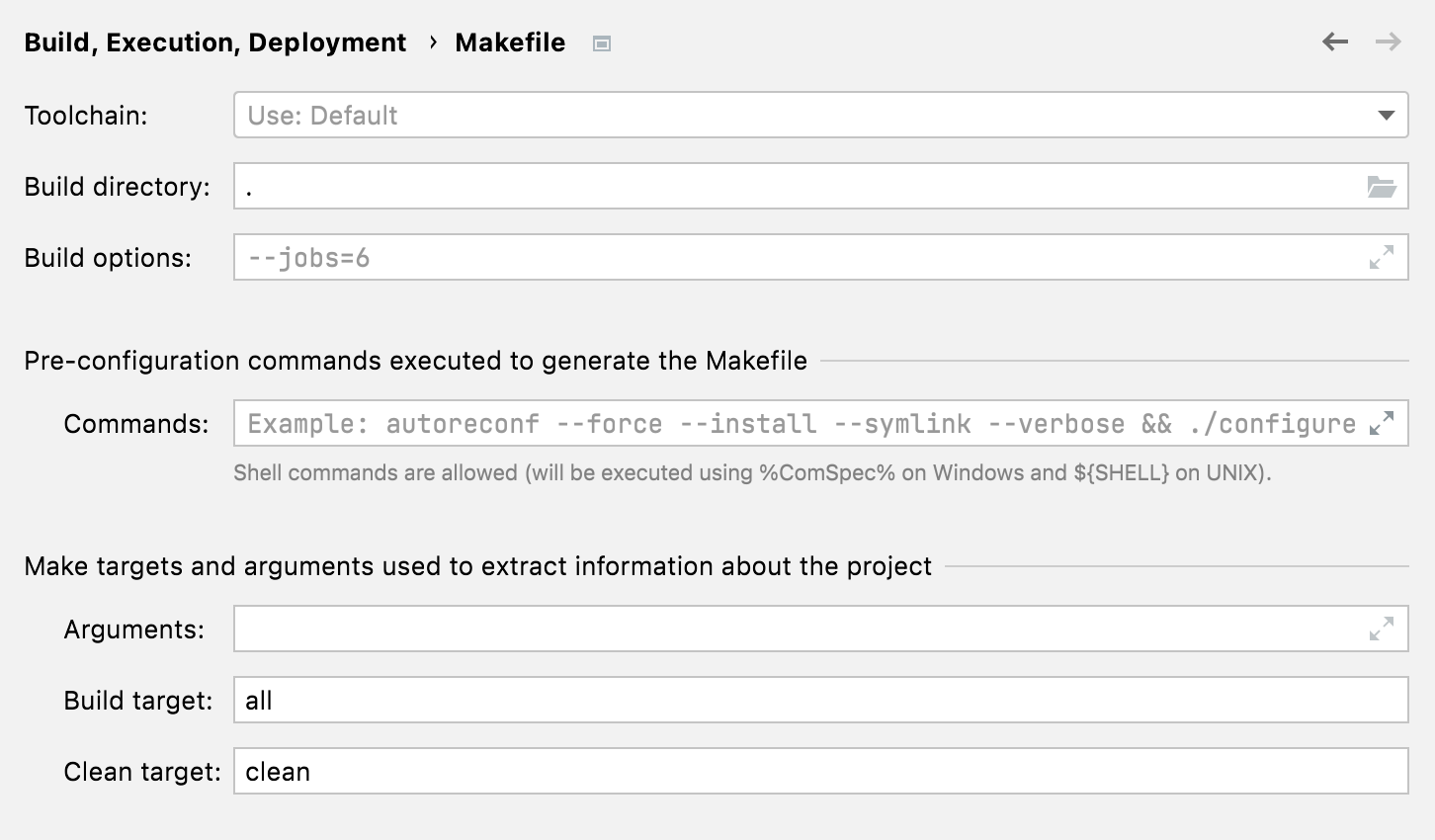
Toolchain
Here you can select the toolchain to be used for loading your Makefile project.
Note that NMake is not supported currently, so you can't use the Visual Studio toolchain directly. In order to work with it, you need to build the project separately using GNU Make.
If the toolchain you selected includes non-default compilers (configured explicitly in the C Compiler and C++ Compiler fields), they will be passed to
makeas well.note
Windows-specific details:
Your Makefile may include full paths to the tools. In this case, make sure to select the corresponding toolchain with the same paths.
When working with a MinGW toolchain, check that the paths don't contain spaces. Use the
~notation if necessary, for example, C:\PROGRA~1 .\mingw-w64 \...
Build options
In this field, you can provide additional make options for the project build. These options don't affect the project reload.
Commands
In this field, you can adjust preconfiguration parameters. See Pre-configuration (GNU Autoconf).
Arguments
These arguments are used by CLion when calling the
makecommand on the step of extracting project information, cleaning the project, or searching for build targets.Build target and Clean target
These targets are used along the
makecommand to extract the project information. If you leave the Build target field empty, CLion will take the first target specified in the project’s top Makefile.Also, the targets specified here are used when you call Build Project or Rebuild Project from the Build actions menu.
You can quickly access the Makefile settings dialog from the Build tool window. Select Makefile Settings from the context menu or click :
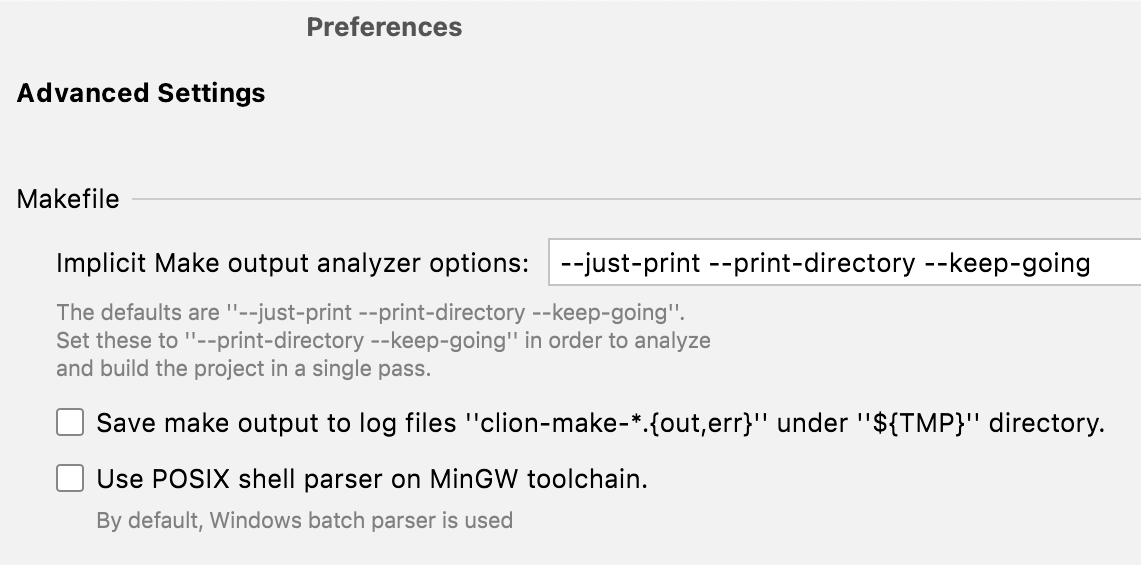
More settings for Makefile projects are available in Settings | Advanced Settings:
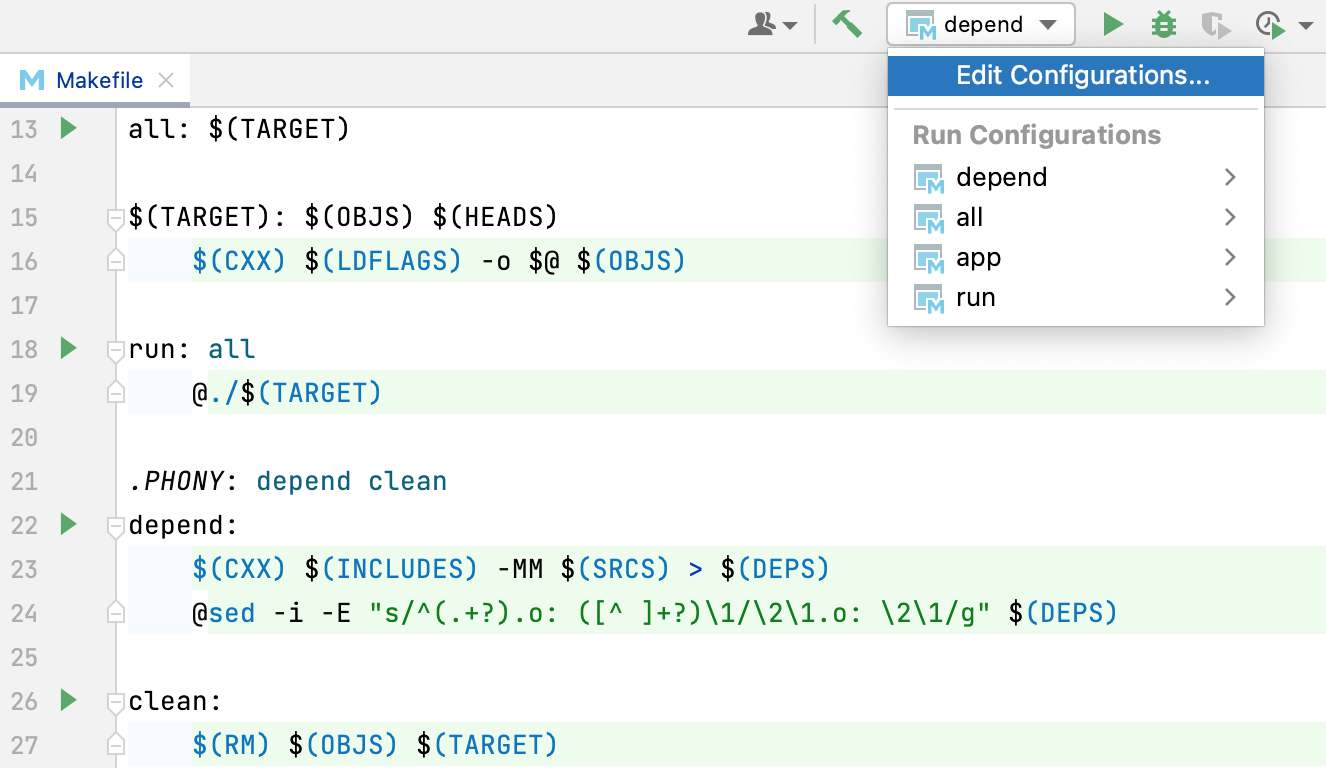
CLion automatically creates a Makefile Application configuration for each target from the top-level Makefile:
When creating configurations, CLion filters out the following targets:
The
cleantarget.Targets that correspond to object (.o) files.
Targets that end with unknown file extensions (for example, .d).
You can customize the automatically created configurations or create new ones in the Edit Configurations dialog (see below).
Go to Run | Edit Configurations, click
, and select Makefile Application from the list of templates:
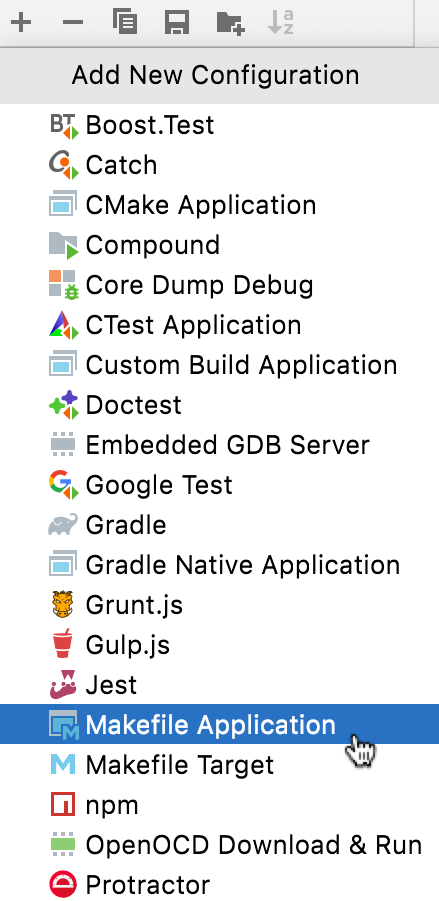
In the Target field, you can choose one of the detected targets:
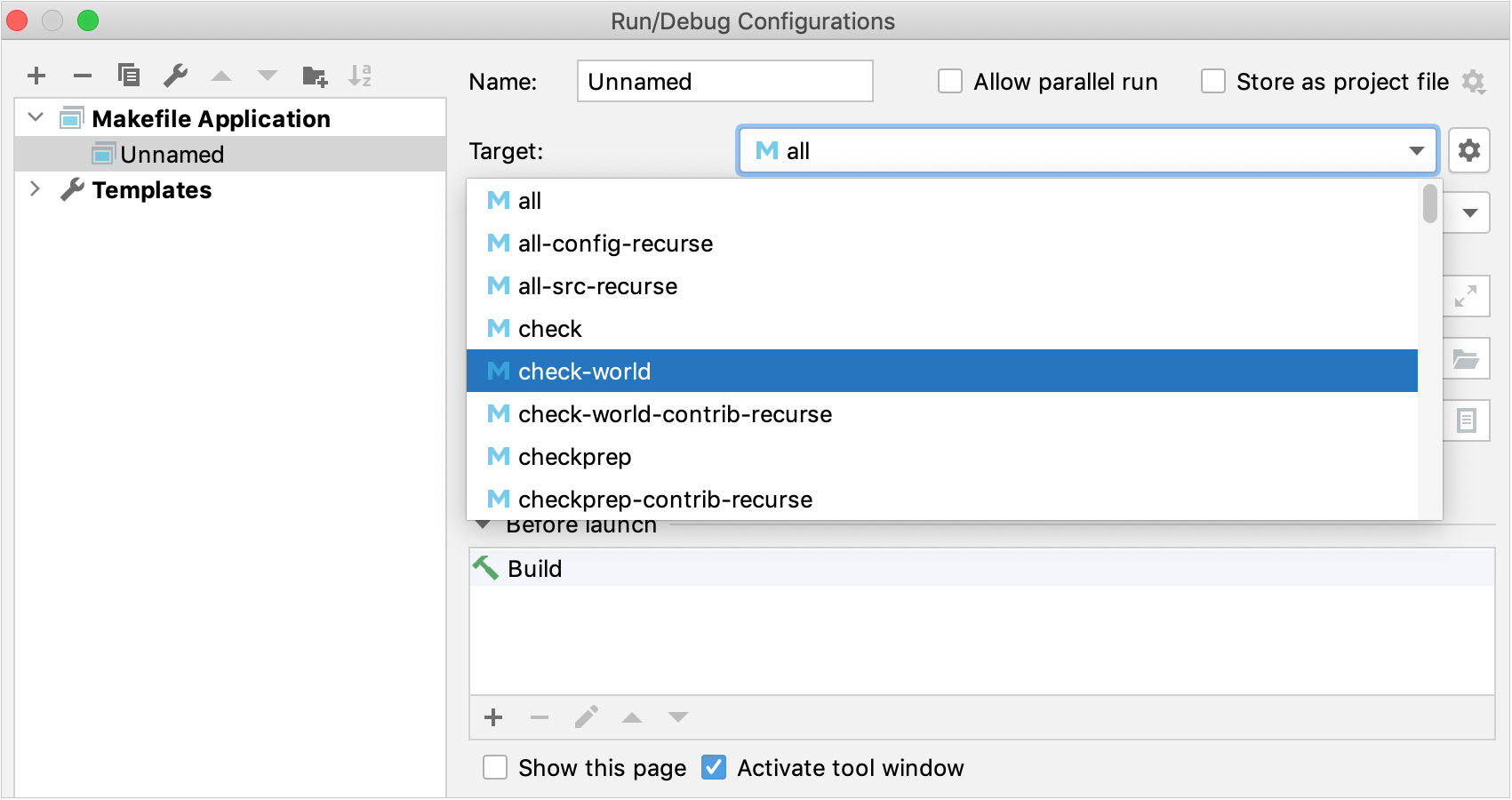
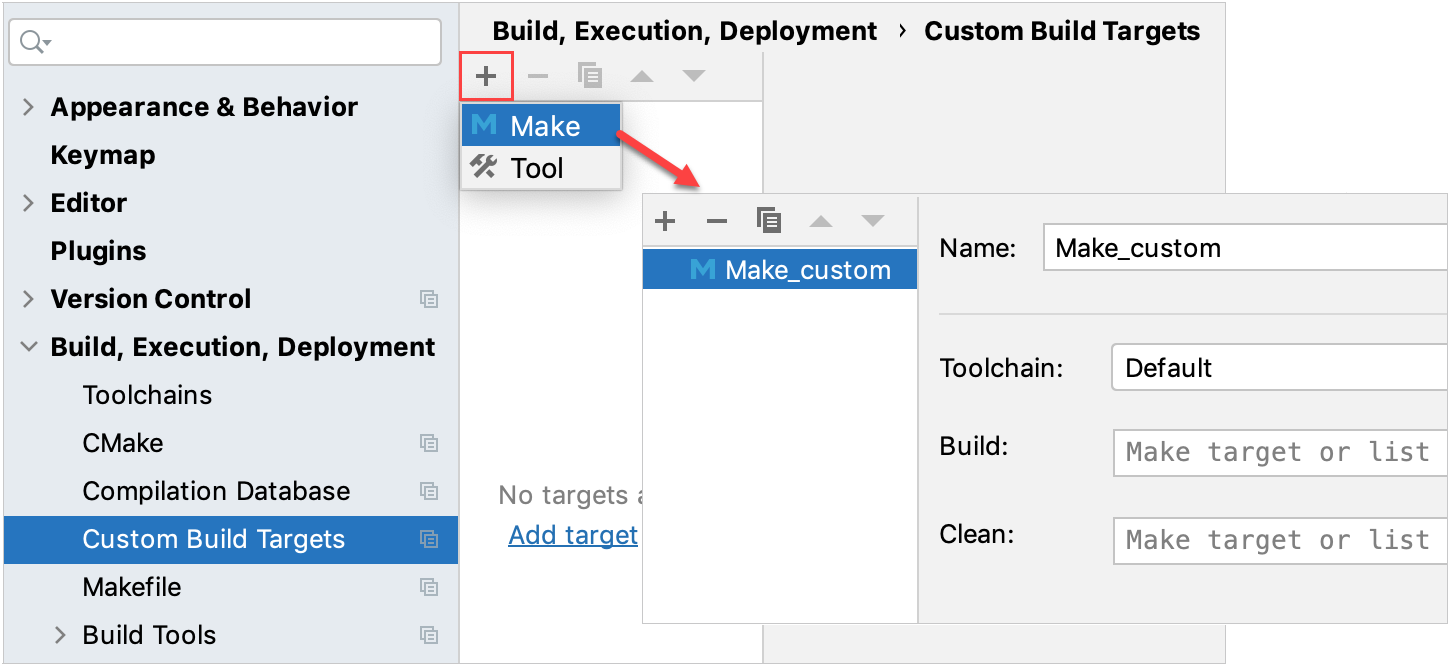
Another option is to set a custom build target with type Make. Click
next to the Target field, add (
) a new Make target, and fill in the parameters:
In the Executable field, provide the full path to the binary.
note
If you plan to debug the application, make sure the binary includes debug symbols. For example, you can add
-gtoCXXFLAGSin the Makefile.To run/debug remotely, provide the path to the binary on your remote machine. Note that remote path needs to be set manually.
Other settings of the Makefile Application template are described on the reference page.
Select the desired configuration in the switcher and then use one of the following options:
Click
.
Press ShiftF10.
Select Run | Run 'selected configuration' from the main menu.
Before you start a debug session, make sure the binary specified in the configuration includes debug symbols.
Select the desired configuration in the switcher and then use one of the following options:
Click
on the toolbar.
Press ShiftF9.
Select Run | Debug 'selected configuration' from the main menu.
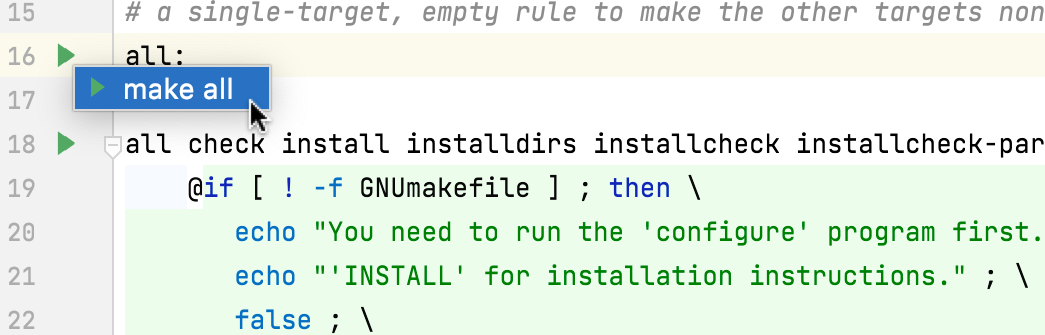
You can use the gutter menu to quickly call make for a particular target:
Alternatively, you can run targets from the Make tool window (View | Tool Windows | make). Double-click a target or select it and then click :
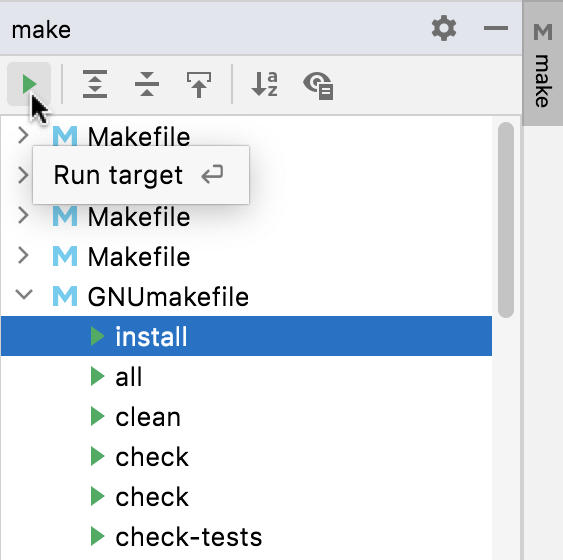
Upon any of these actions, CLion creates a temporary configuration of the Makefile Target type. You can customize it or create new configurations out of the same template in the Edit Configurations dialog (see below).
Go to Run | Edit Configurations, click
, and select Makefile Target from the list of templates:
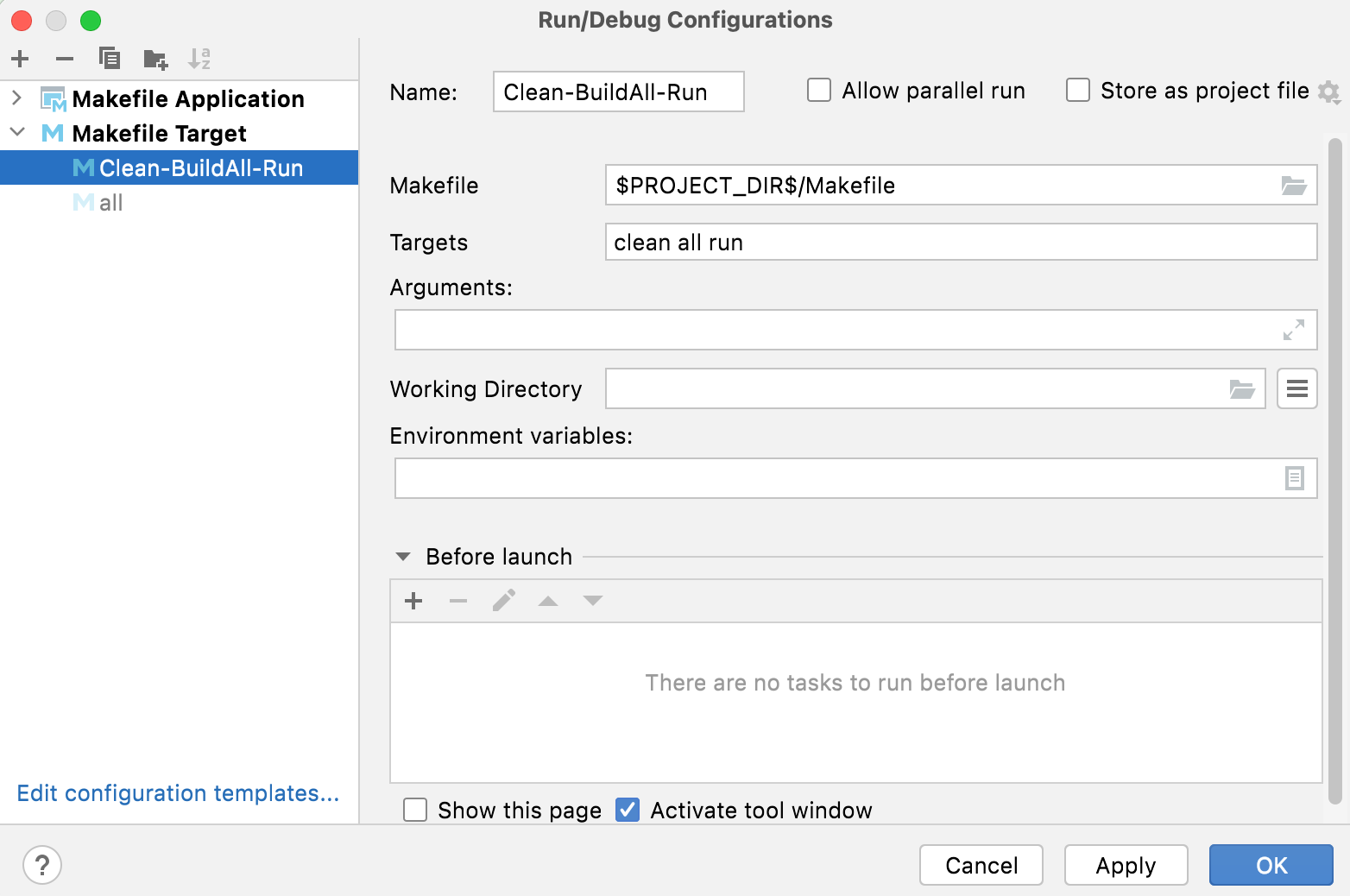
In the settings, you can set up several targets to run, provide additional arguments, and tune other parameters if required. See the reference page for details.
note
Unlike Makefile Applications, Makefile Target configurations use the path to
makefrom Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Build Tools | Make regardless of the currently selected toolchain.Makefile Target configurations can't be used with remote or Docker toolchains. See below for details on WSL.
When working with WSL, make sure to sync the per-project toolchain settings and the global Make settings:
Go to Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Build Tools | Make.
Click the selector next to Path to Make executable and set the path to WSL's
make: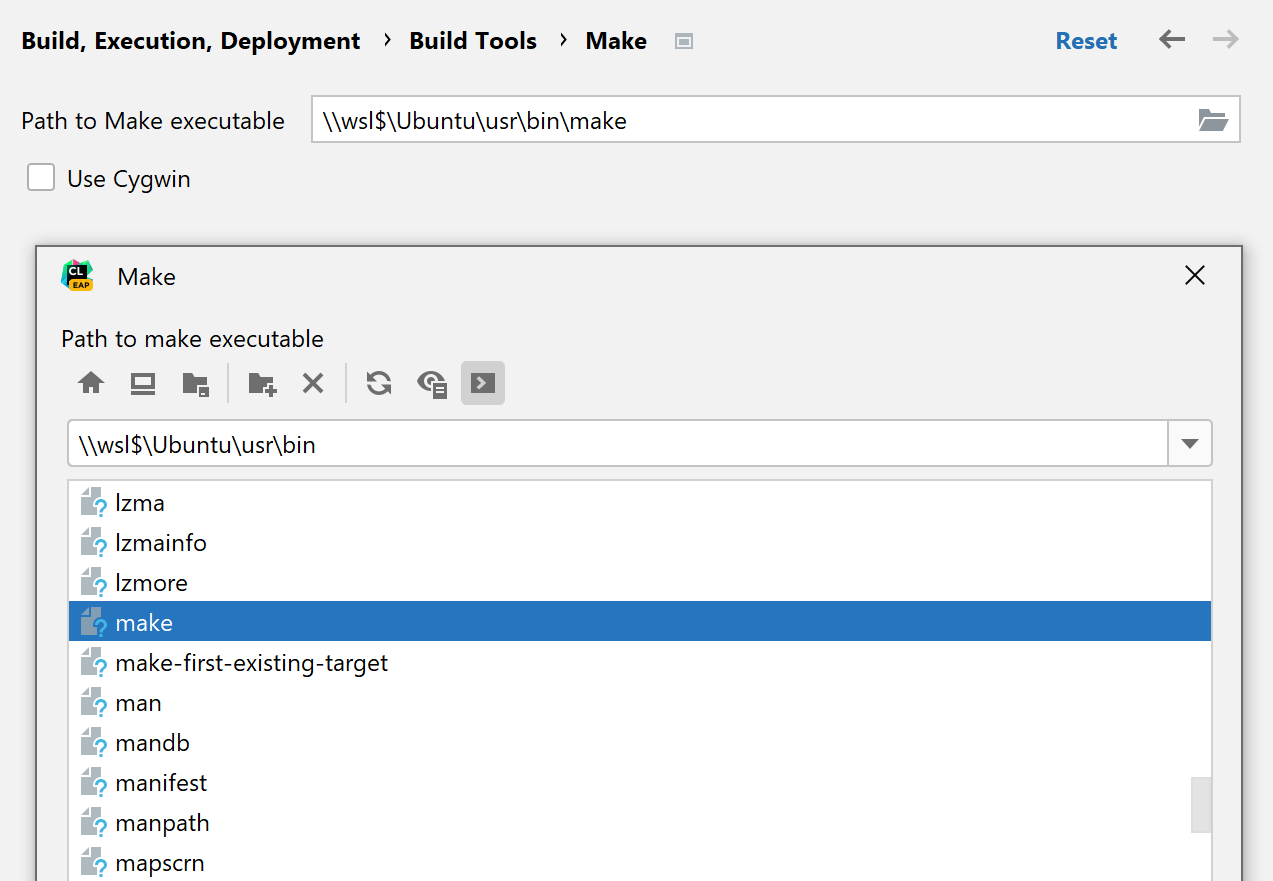
If you are working under a non-root WSL user, this user should be set as default in order to own the make process and all the files it may create.
Create a
/etc file inside your WSL guest and add the following lines:/wsl.conf [user] default=usernameHere,
usernameis the WSL guest username (which may be different from the Windows username).Find out more in WSL documentation.
Restart the WSL machine.
Make sure that both Makefile and Makefile Language plugins are enabled. Check the Installed tab in Settings | Plugins.

If your project fails to load correctly, try the following tips:
Check Makefile settings:
Make sure to select a proper toolchain. Your project should build successfully in the selected environment.
Arguments and Build target may need adjustments for the case of your project.
Call Tools | Makefile | Clean and Reload Makefile Project from the main menu or click
in the Build tool window.
If your project's Makefiles were generated by Premake, try removing the
--no-print-directoryarguments from the root Makefile.In case none of the above helps, try cleaning the project cache from /makefiles in the system directory (for example, ~
/Library ), then reload the project./Caches /JetBrains /CLion2020.2 /makefiles /postgrtipes.dc29ef09
CLion handles Makefile projects that use wrappers like ccache and libtool (as well as its alternative implementations like Dolt, slibtool, and jlibtool), but distcc is not yet supported (CPP-19305).
Non-GNU Makes like NMake or BSD Make are not supported at the moment (CPP-18723).
Unit testing configurations are not available for Makefile projects yet (CPP-20718).
Thanks for your feedback!