Configure the SQL code style
You can apply and customize the SQL code style that satisfies code guidelines of your company. To see the description of SQL style options, see Code Style. SQL.
Change code style settings
Customize formatting rules for the SQL code: alignment, wrapping, and indentation.
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Expand the SQL node and select a dialect.
Select all the necessary code style settings on the available tabs.
Click Apply.

Create a code style for a dialect
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Expand the SQL node and select a dialect.
Click the Show Scheme Actions icon (
), and select Duplicate.
Type a name for a new style, and press Enter.
Select all the necessary code style settings, and click Apply.

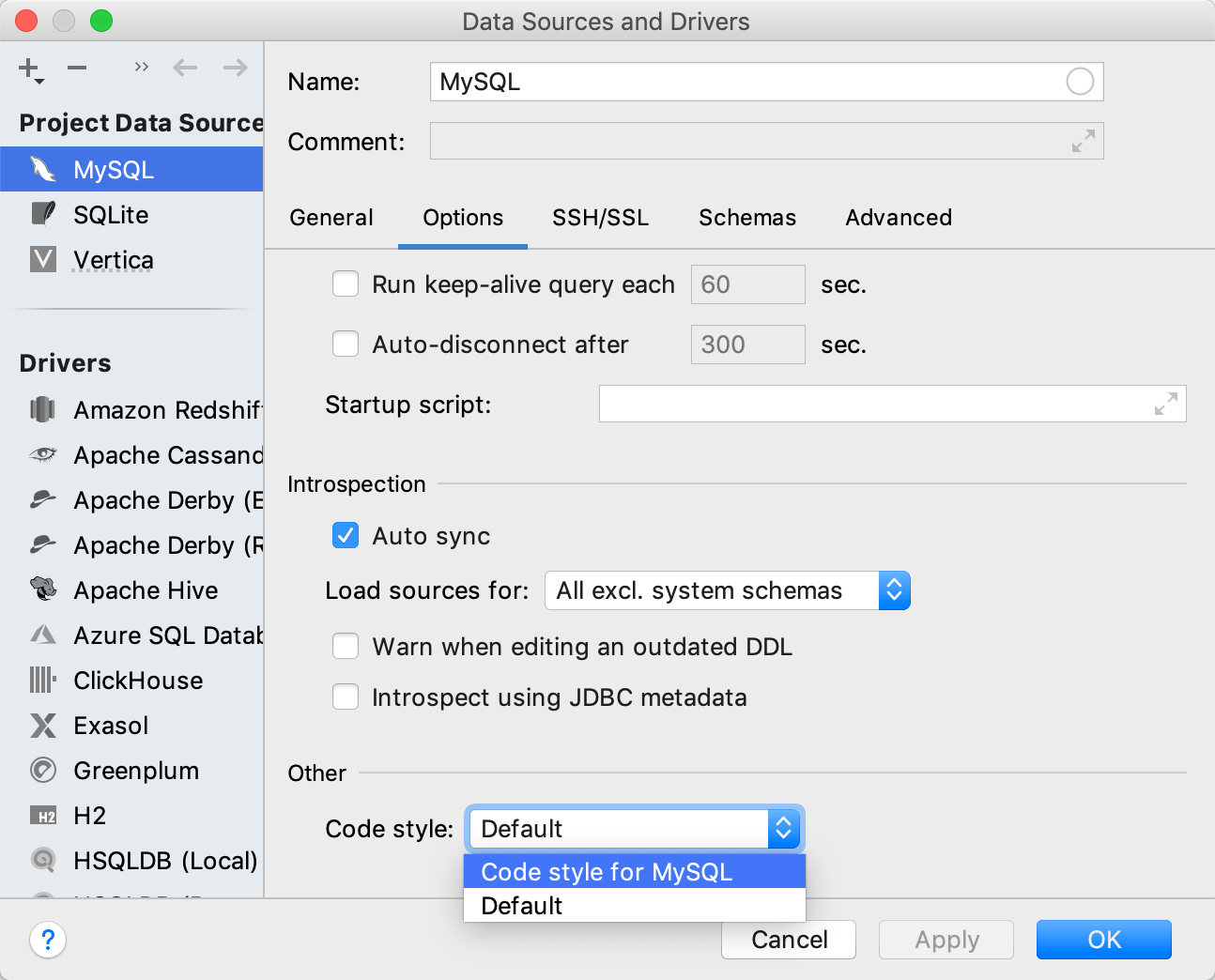
Configure code styles per data source
After you created a style for a dialect, you can apply this style to the data source that uses this dialect.
Right-click a data source and select Properties.
Click the Options tab.
In the Code style drop-down menu, select a style that you want to apply.
Click Apply.
Apply a code style in the editor
Right-click any area in the editor and select Reformat. Alternatively, press Ctrl+Alt+L.

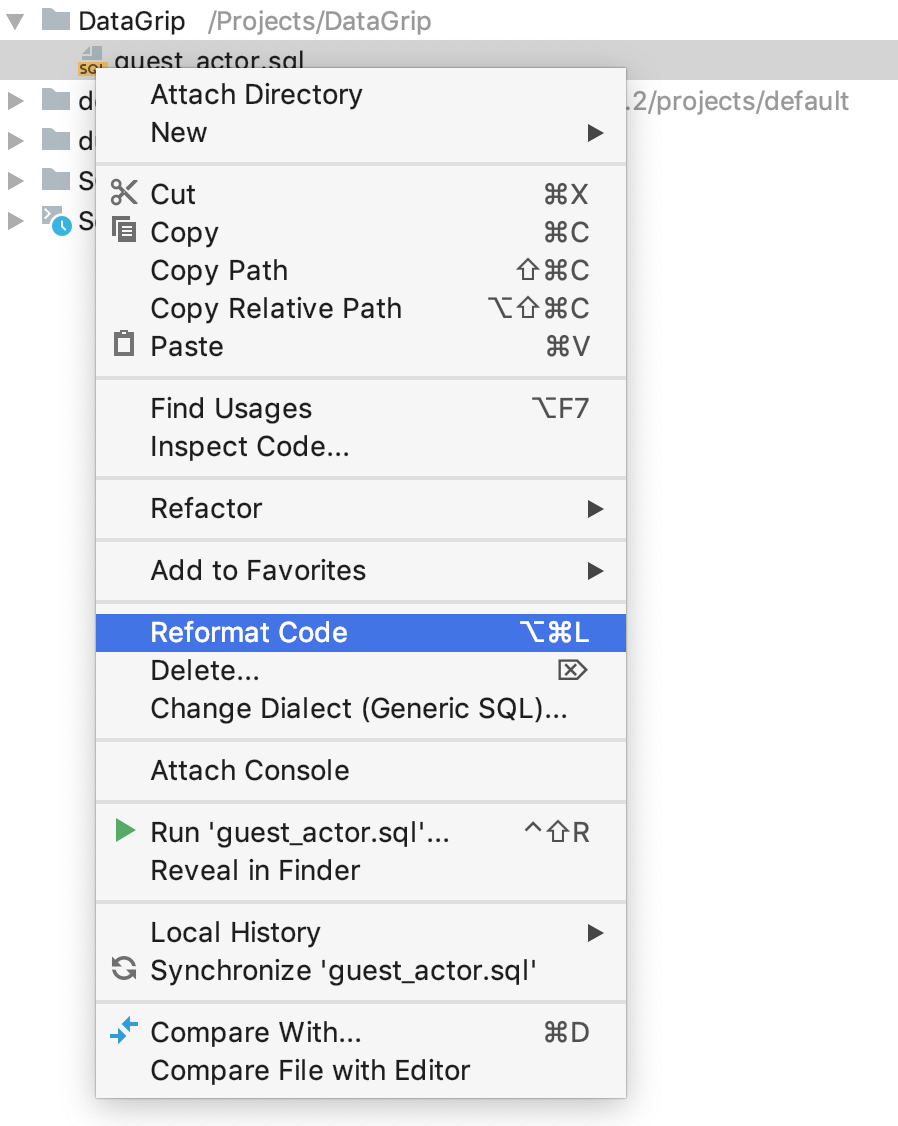
Apply a code style to a file from the context menu
You can format files from the context menu without opening them.
In the Files tool window (), right-click a directory and select Reformat Code.
Import code style settings
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Expand the SQL node and select a dialect.
Click the Set from link and select the style that you want to import.
You can select preconfigured styles like Modern, Joe Celko, Allman (DDL only)), Whitesmiths (DDL only)), Egypt, Old Idea. Or, import settings from the dialect that you configured.

Apply code style to the Generic dialect
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Clear the Inherit general SQL style checkbox.
Apply code style settings. For more information about code style settings, see Code Style. SQL.
Apply the original case from the declaration
DataGrip can format names of variables, procedures, and functions as you defined them initially. For example, if you defined the get_Amount function in the CREATE PACKAGE statement, you want the same case throughout your code, not GET_AMOUNT or get_amount.
To apply this case throughout the file, DataGrip must find the declaration of these variables, procedures, and functions (for example, in the CREATE PACKAGE statement). To apply the case in multiple files, create a DDL data source from these files.
Apply the declaration case for a file
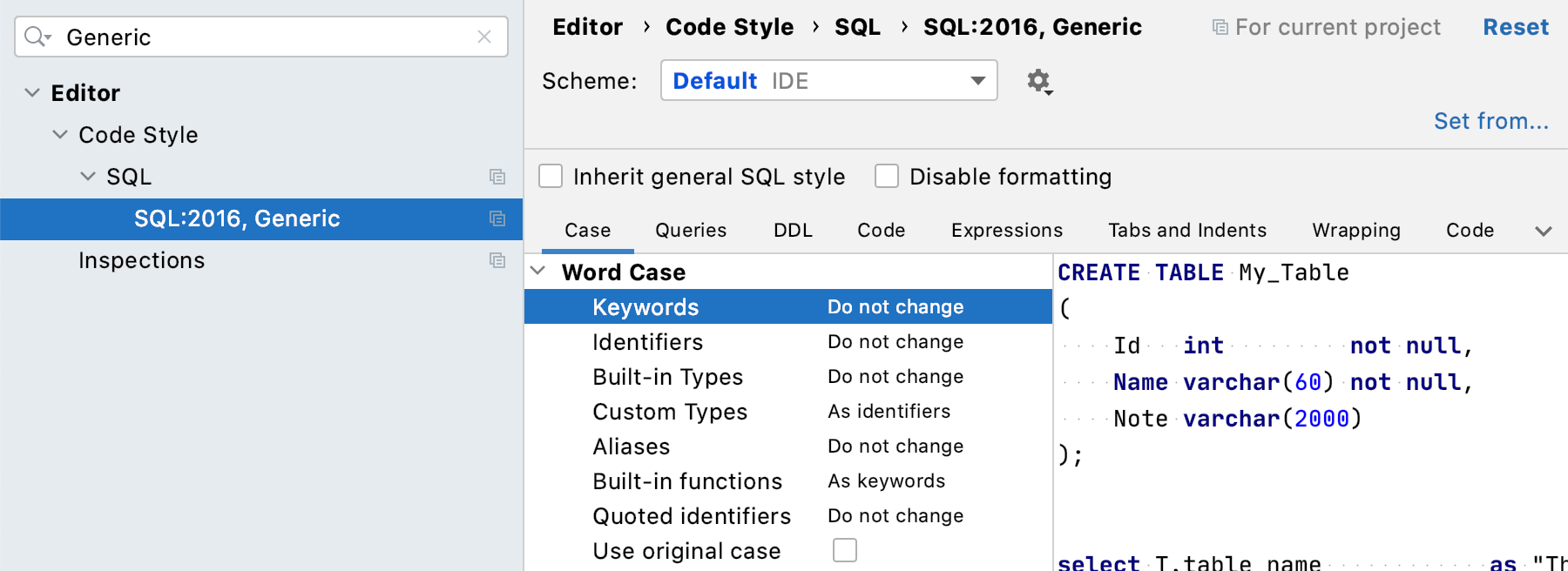
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Select the dialect in which you want to apply the original case from the declaration.
Click the Case tab and select the Use original case checkbox.
Click OK.
Click or press Ctrl+Alt+L.
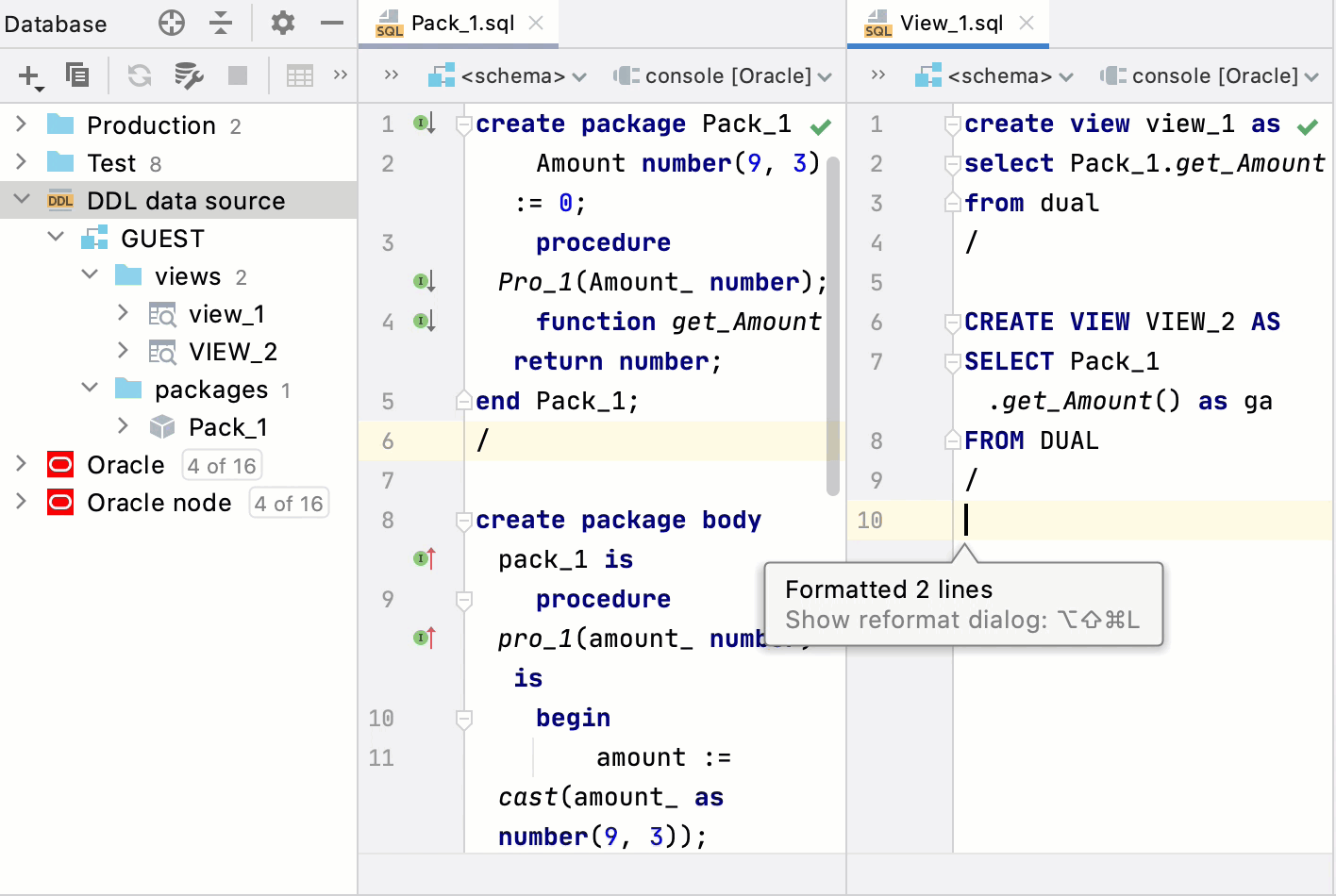
On the following image, you can see Pack_1.sql and Pack_2.sql with identical code. Pack_1.sql is not reformatted. Pack_2.sql was reformatted with the Use original case checkbox enabled. In Pack_2.sql, the case from the package declaration was applied throughout the whole file.

Apply the declaration case in multiple files
Create a DDL data source from the files for which you want to apply the declaration case.
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S and navigate to .
Select the dialect in which you want to apply the declaration case settings.
Click the Case tab and select the Use original case checkbox .
Click OK.
Click or press Ctrl+Alt+L to apply the declaration case in any file of the DDL data source. Alternatively, in the attached directory, select all the files that are in the DDL data source, right-click the selection and click Reformat Code.
On the following image, you can see Pack_1.sql and View_1.sql. Both files are in the DDL data source. With the Use original case checkbox enabled, when you reformat code in View_1.sql, the original case from the package declaration in Pack_1.sql is applied.