Tables
A database table is a structure that organizes data into rows and columns. Data in a table is stored in a cell that is an intersection of a vertical column and horizontal row. The table has a specified number of columns, but can have any number of rows. With DataGrip, you can perform data manipulation and data definition operations with tables.
In DataGrip, you can work with a table in data editor. When you double-click a table in the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , the table is opened in the Table viewing mode of data editor.
Tables can be seen in the Database Explorer. You can see a reference on node and object icons in the Data sources and their elements chapter of Database Explorer topic.
For the table column icons, refer to Possible icon combinations for columns.
In DataGrip, each table opens in a separate tab. The following rules are applied to long tab titles:
The Always show qualified names for database objects option is now turned off by default. Tab names for objects are qualified if you open two tabs of objects with the same name. For example, if you open two
actortables from different schemas, the schema name is added in the tab name.If the data source has a name that is longer than 20 symbols, the name is truncated.
If you have only one data source, DataGrip does not display the data source name in the tab name.
If a qualified object name has more than 36 symbols, it is truncated.

In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , expand the data source tree until the nodes of databases or schemas.
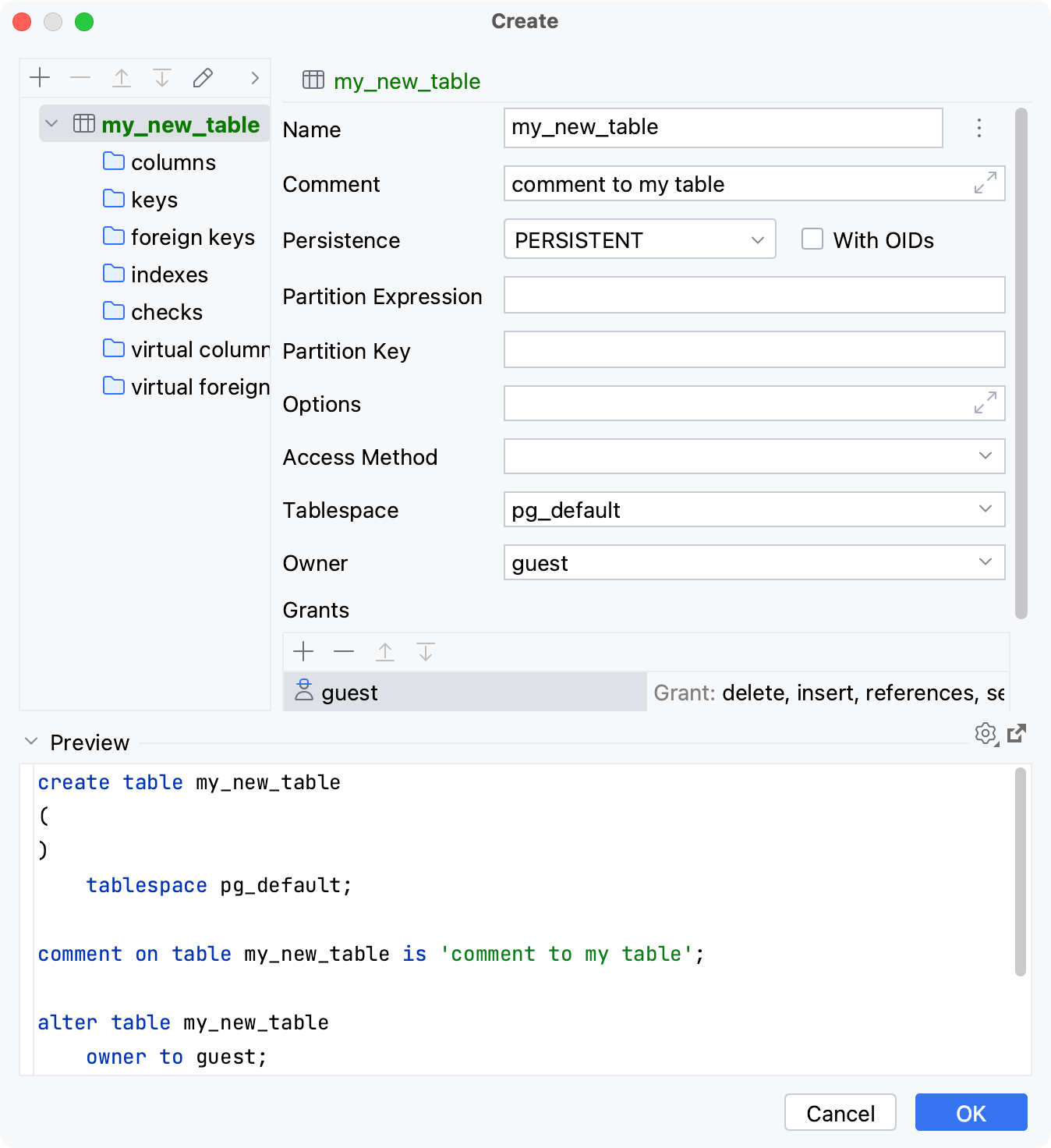
Right-click the database or schema node and select New | Table.
In the Create dialog that opens, enter the name of your table in the Name field.
Specify table settings (columns, keys, indexes, foreign keys, grants).
In the Preview pane, you can view and change the generated SQL code.
Click OK.
Right-click a table and select Drop…. Alternatively, press Delete.
Click OK.
For more information about the dialog options, refer to Confirm Drop dialog.
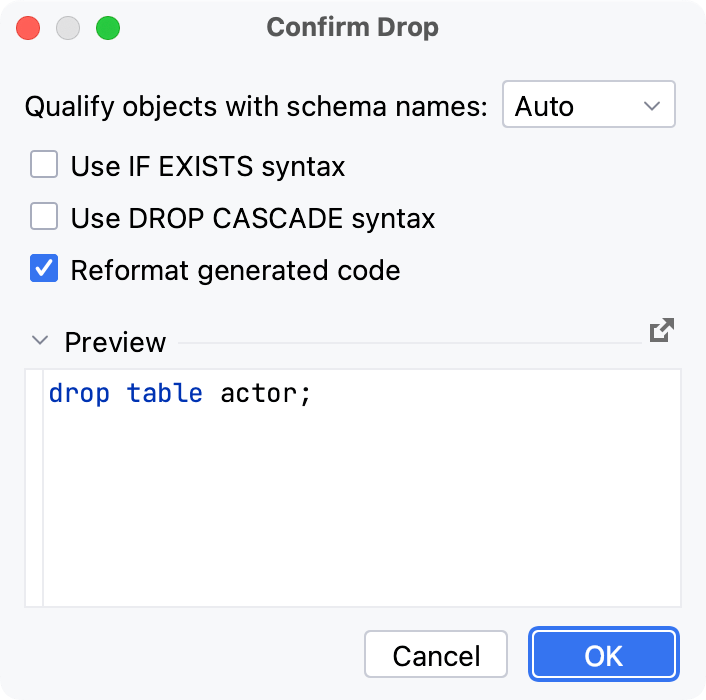
tip
Use the Qualify objects with schema names option if you want to compose the
DROPstatement and use it later. If you plan to execute theDROPstatement right away, ignore this option as the table has already been identified.
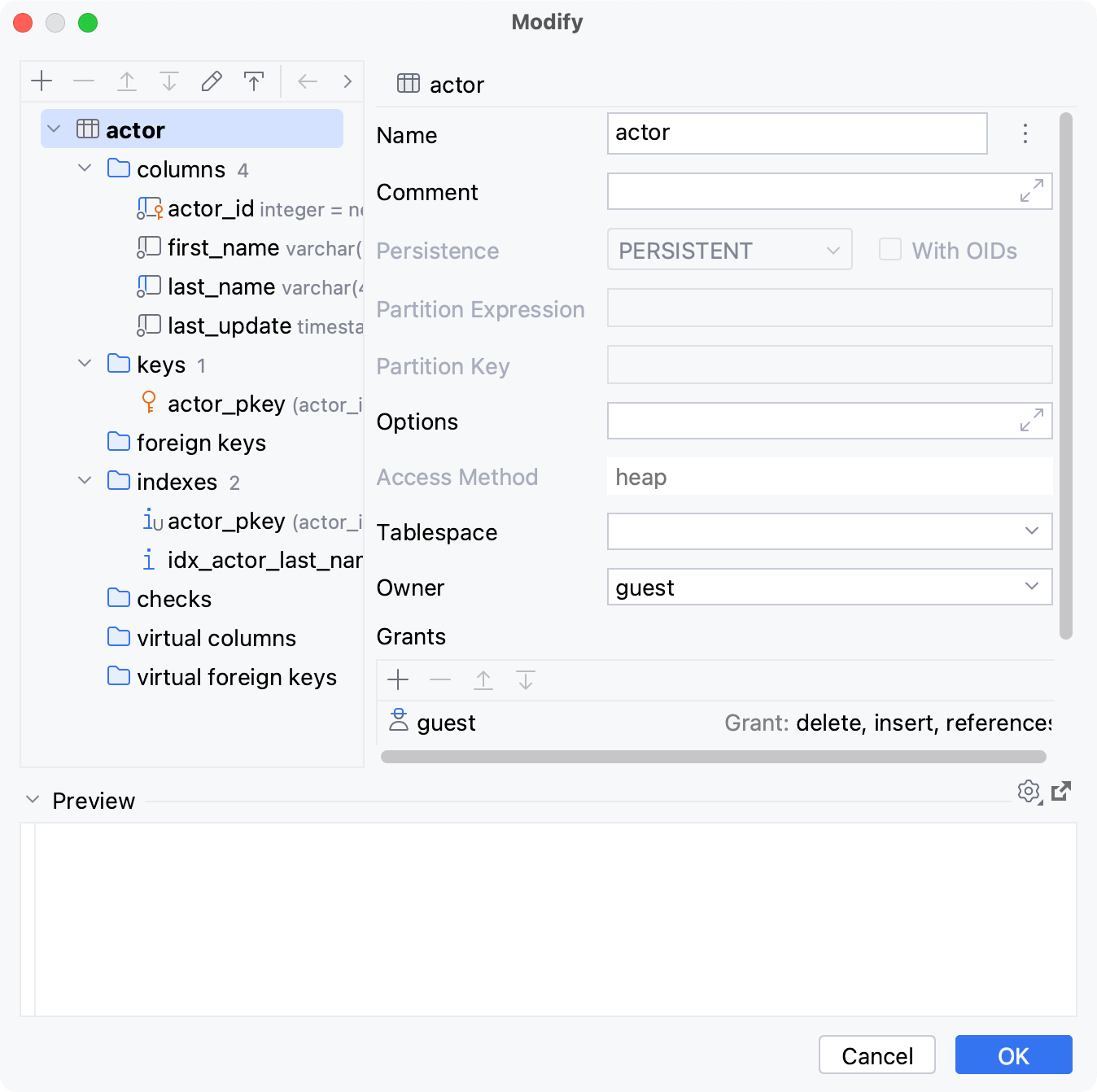
Starting with DataGrip 2022.1, you can change database-specific parameters of a table. The IDE generates fields for the Modify dialog automatically according to the properties received during the introspection. For example, by using this dialog in PostgreSQL, you can add and edit column check constraints.
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a table and select Modify Table.
In the Modify dialog, specify object settings that you need.
note
Column settings depend on the database vendor. For example, the Auto Increment checkbox is only available for SQLite, MySQL, and other vendors that allow it for a primary key column of an integer data type.
Click OK.
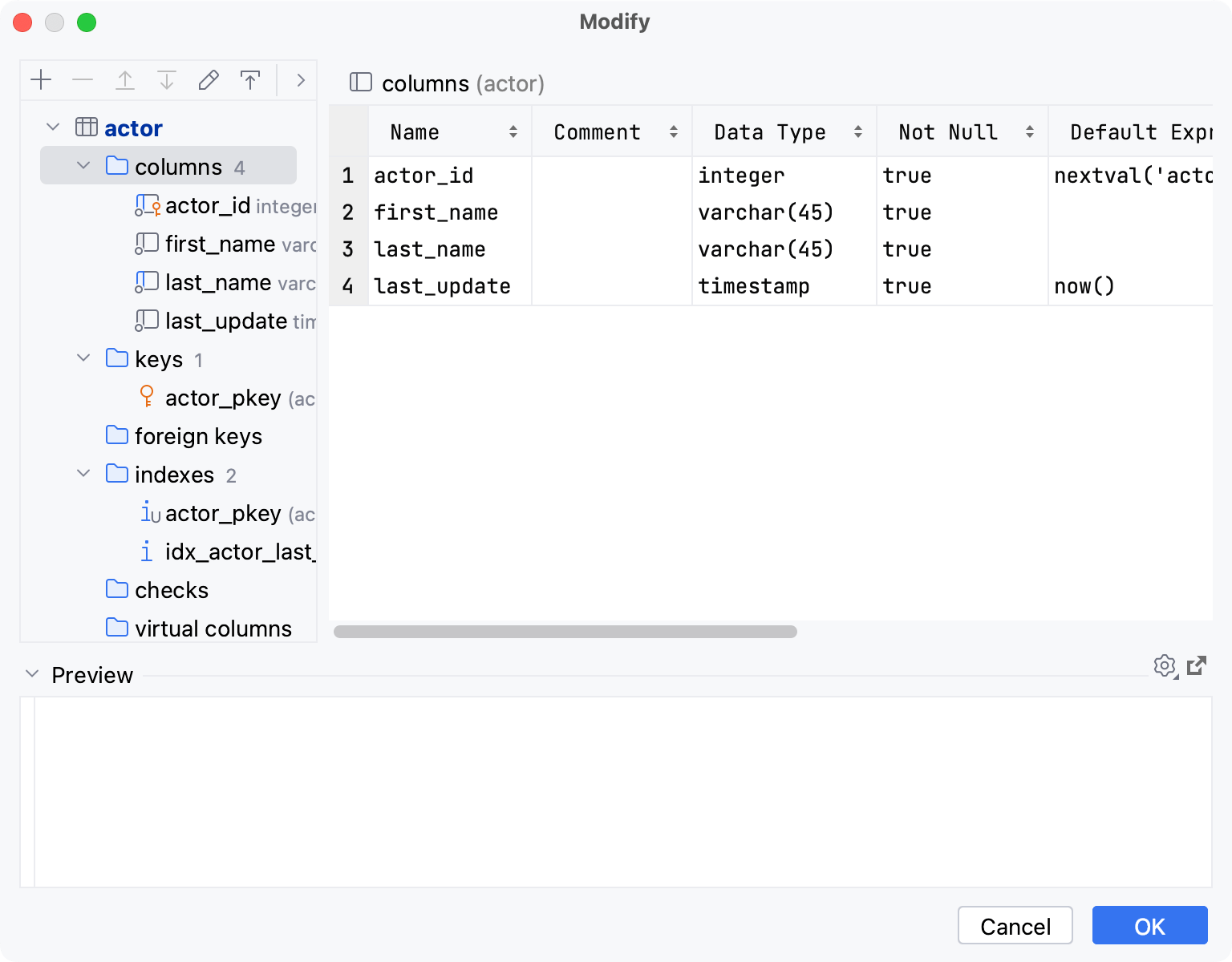
In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a table and select Modify Table.
In the Modify dialog, double-click the family node.
To protect a table from accidental modifications in the data editor, you can make the table read-only.
To enable read-only mode, click the Click to toggle the read-only attribute icon (
) in the lower-right corner of the editor.
To turn off read-only mode, click the Click to toggle the read-only attribute icon again.
note
Tables with the read-only status in the data editor can still be modified when using the database consoles or in the Database Explorer.
You can modify a table while you edit table data.
Double-click a table to open it in the data editor.
Press CtrlF6.
Modify data and click OK.
Press CtrlF5 to reload the page.
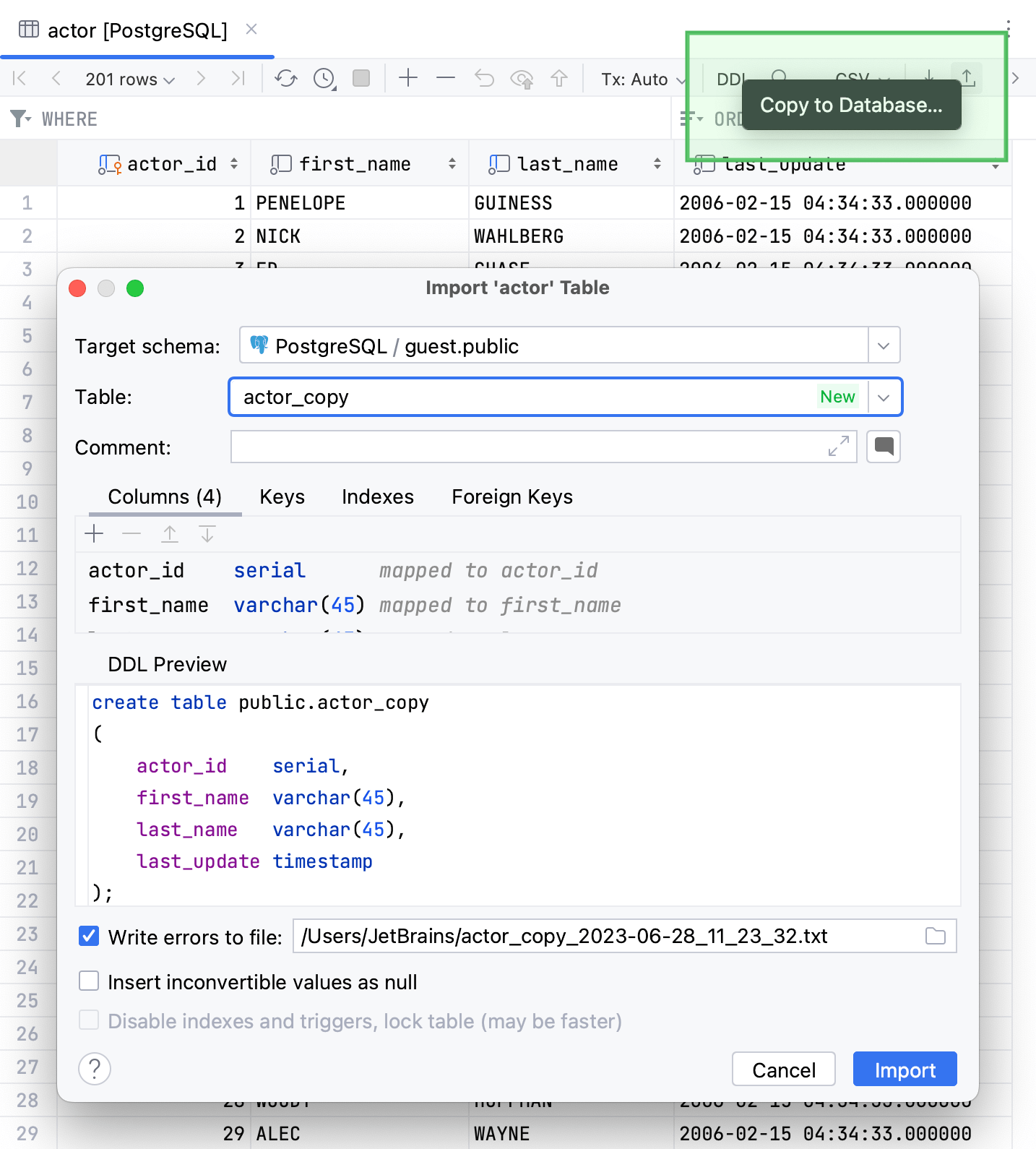
You can duplicate the table data in the current schema or copy it to another schema or data source.
Drag a table to the node in which you want to create a copy. In the Import <table_name> Table dialog, ensure that mappings are correct and click Import.
Right-click a table and select Import/Export | Copy Table to… (F5). In the Import <table_name> Table dialog, select the schema in which you want to create a copy, ensure that mappings are correct, and click Import.

In the data editor, click the Copy to Database… icon (
) and select a schema to which you want to copy the table.
Check the video at youtube.com to see the live example.
You can copy the table structure using SQL Generator. To do that, in the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer), right-click the table and select SQL Scripts | SQL Generator…. Alternatively, press .
For more information about the SQL Generator… controls, refer to Generate DDL definitions for database objects.

The quick documentation displays the information about table: data source, database, schema, name, auto-generated definition, and table preview. To see the table preview, click Show table preview.

For PostgreSQL and MySQL databases, table preview also contains information about the table size.
Thanks for your feedback!