Cannot find a database object in Database Explorer
If you see no objects below the schema level, cannot find changes in objects, experience broken tables or any other visualization problems, try the following steps to resolve the problem.
note
If steps 1, 2, 3, and 4 did not resolve your problem, inform JetBrains of your situation by creating a YouTrack ticket. After you have created the ticket, try step 5 as a workaround.
If someone changed the remote database data or view, the local view of the database might differ from the actual state of the database.
To synchronize the database state automatically, in the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer), click the Data Source Properties button
and select the data source that you want to change. On the Options tab, select the Auto sync checkbox.
If the Auto sync checkbox is cleared, the view of the data source in the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) is synchronized with the actual state of the database only when you click the Refresh icon
or press CtrlF5.

note
If you see no schemas in the popup, check whether a connection to a data source is available. For more information, refer to this troubleshooting article or report the situation to us.
When you create a data source, the data source is created with no schemas selected. You need to select schemas with which you plan to work.

To select the schemas, do one of the following:
In the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a data source and navigate to Tools | Manage Shown Schemas. Select or clear checkboxes of schemas that you want to display or hide. Press Enter.
Click the N of M link near the data source name. In the database and schema selection window, select or clear checkboxes of schemas that you want to display or hide. Press Enter.

The Default schema or Default database is a schema or a database that will be current in connection to a data source. The current schema is a schema that is current in a session. You can change the current schema by using SET CURRENT_SCHEMA. The default schema depends on database settings and data source settings that you set in the JDBC URL.
You can change this default in connection settings of a data source. To change the default, click the Data Source Properties icon in the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer). From the list of data sources, select your data source. In the Database field, type the name of a schema or a database that you want to use as a default.

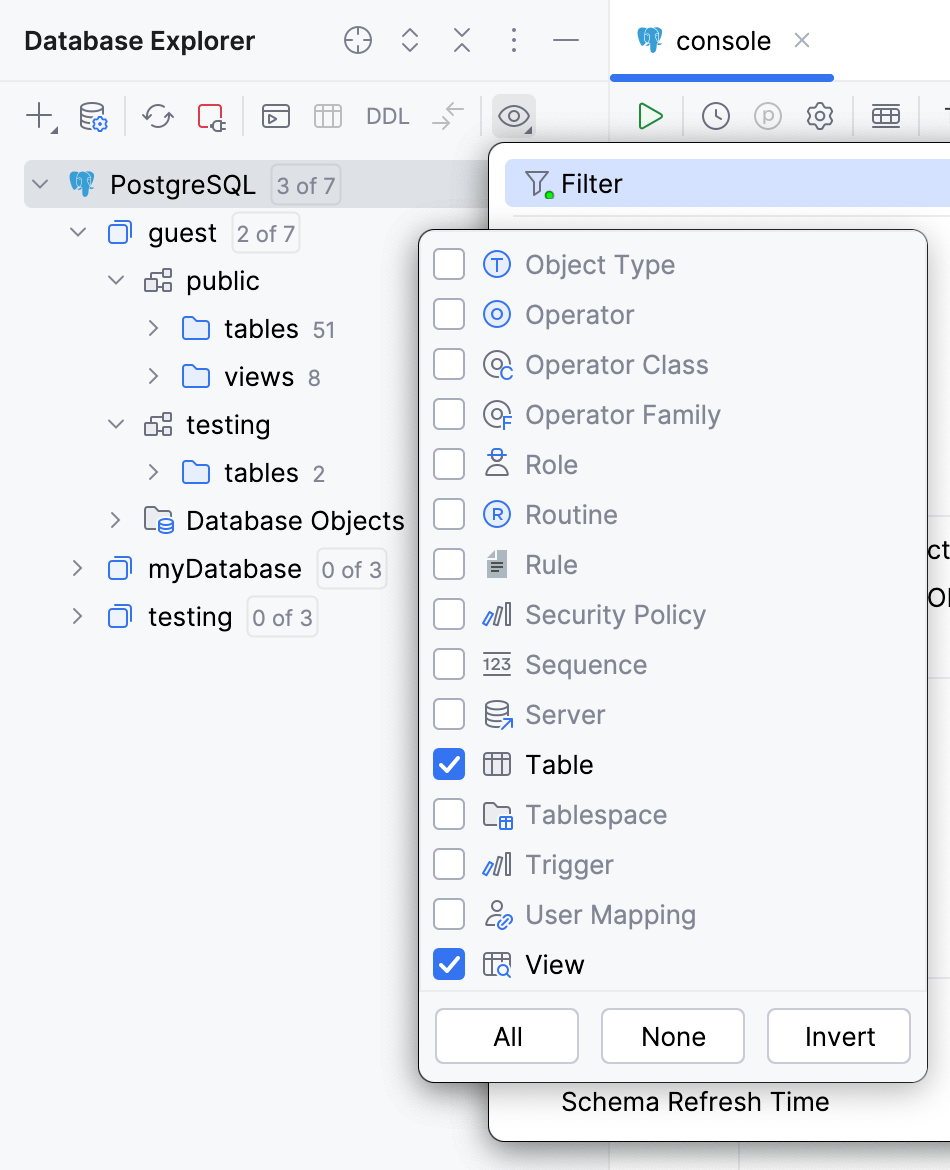
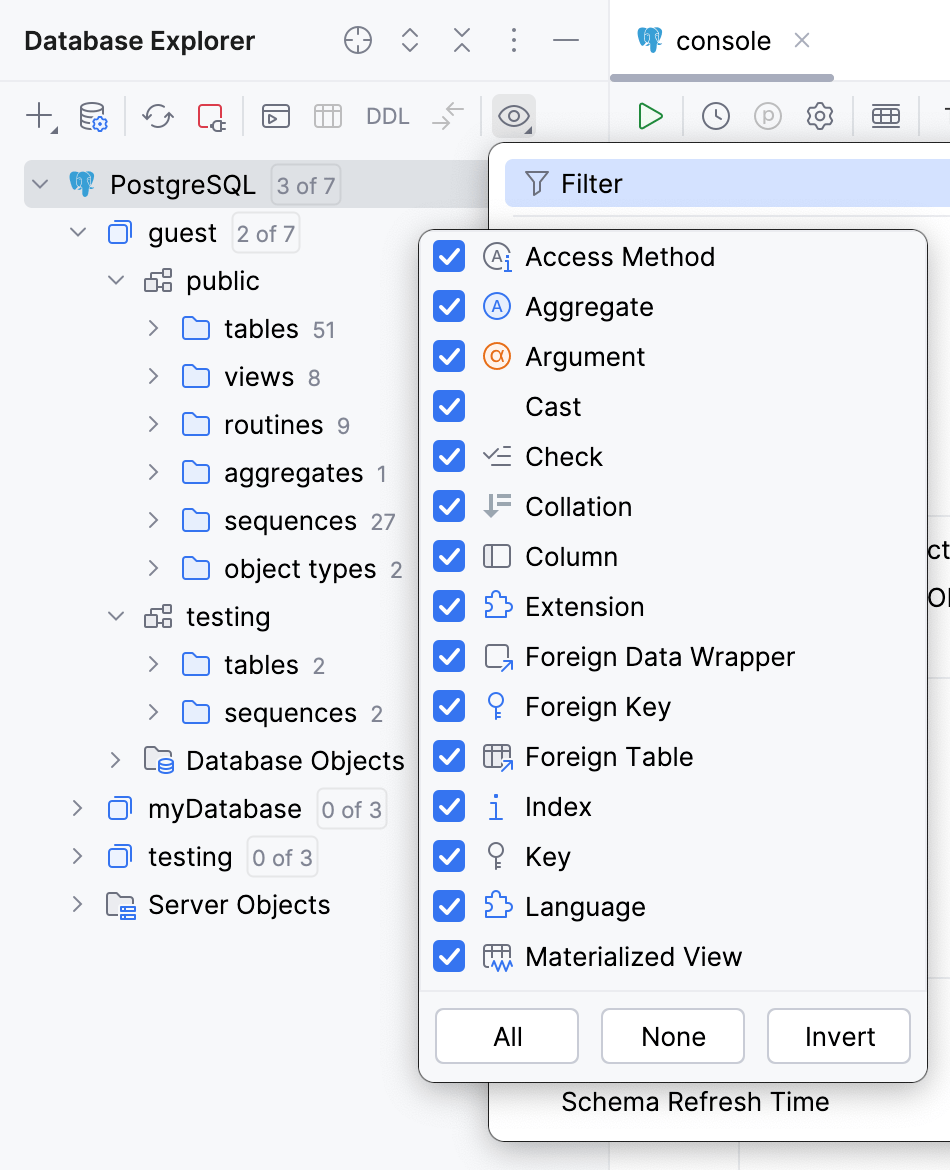
If the items of the object kind are filtered out from the view, the objects wil be hidden in the Database Explorer.
To make sure the database object is not filtered out from the view, do the following:
In the Database Explorer toolbar, click
View Options.
Select
Filter.
Navigate to the database object kind and make sure that the checkbox is ticked.
The green dot in the corner of filter icon indicates that the filter is on and some objects are filtered out.
The Force Refresh action clears the data source information from cache and loads it again from scratch.
In the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer) , right-click a data source and select Diagnostics | Force Refresh.

Clear the DataGrip schema cache (right-click a data source and select Diagnostics | Forget This Schema Cache). Synchronize the view (refer to Step 1. Synchronize the database state).
To profile the introspection and diagnose possible issues, DataGrip can generate three files that include information about the following:
dataSource.txt: the data source.
introspector.txt: a module that was used to load the metadata from the database.
model.xml: a part of the database model.
This information might be helpful when introspection works incorrectly. For example, when you see something outdated or do not see new objects.
Right-click a data source and navigate to Diagnostics | Generate Introspector Diagnostic Files.
DataGrip will generate three files with the introspector diagnostic info.

Click the link in the Diagnostic information collected notification message to navigate to the directory with generated files.
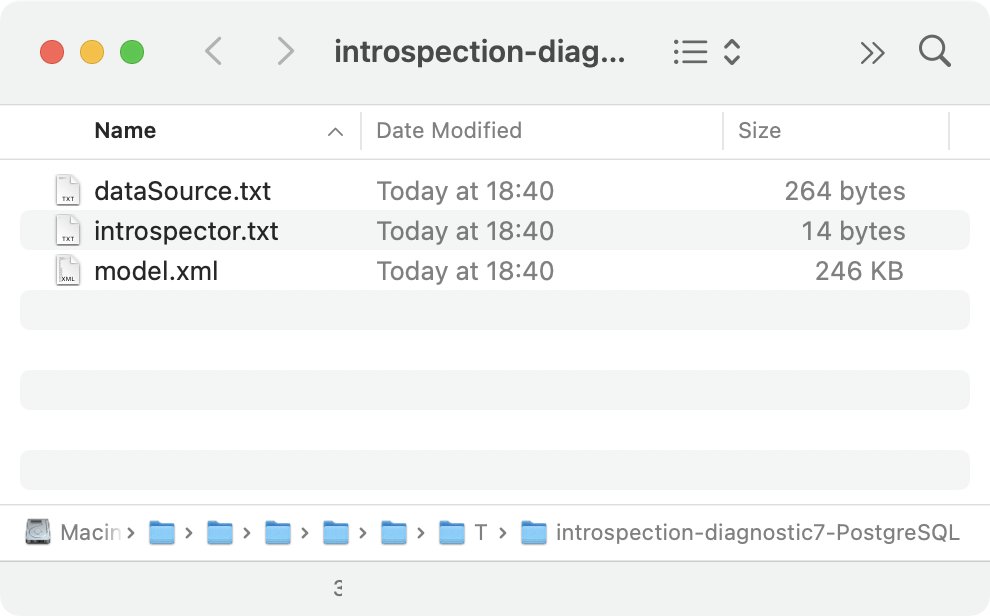
The following screenshots show the example output of these three files.
dataSource.txt

introspector.txt

model.xml

To report an issue, you can use any option that is described in the Where to report an issue section. But we recommend using the JetBrains Support Center.
Open the request form by doing one of the following:
Click Help | Contact Support.
The request form will contain prefilled fields about your product and OS.
Go to the Submit a request page.
Fill in the Submit a request form.
If it is possible, attach some troubleshooting materials.
Click Submit.
warning
Switch to the JDBC-based introspector with caution and when requested by the JetBrains support team. This step may lead to problems with code generation because some objects and properties become unavailable or return wrong values.
Consider this step as a temporary workaround. If you cannot see objects in the Database Explorer, you might have a bug. Collect troubleshooting materials and send them to our support team.
Open data source properties. You can open data source properties by using one of the following options:
Navigate to File | Data Sources....
Press CtrlAltShift0S.
In the Database Explorer (View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer), click the Data Source Properties icon (
).

On the Data Sources tab, select the data source that you want to modify.
Open the Advanced tab.
From the Expert options list, select the Introspect using JDBC metadata checkbox.
Synchronize the view (see Step 1. Synchronize the database state).
Thanks for your feedback!