Run utPLSQL tests
utPLSQL is a testing framework for Oracle databases. You can use utPLSQL to test packages, functions, procedures, triggers, views, and other objects that can be used in PL/SQL.
To use utPLSQL, install the framework into your Oracle database. See the installation instructions in the official utPLSQL documentation.
To get a quick overview of utPLSQL and examples, see Getting started with TDD and utPLSQL at utplsql.org.
Step 1. Enable the utPLSQL schema
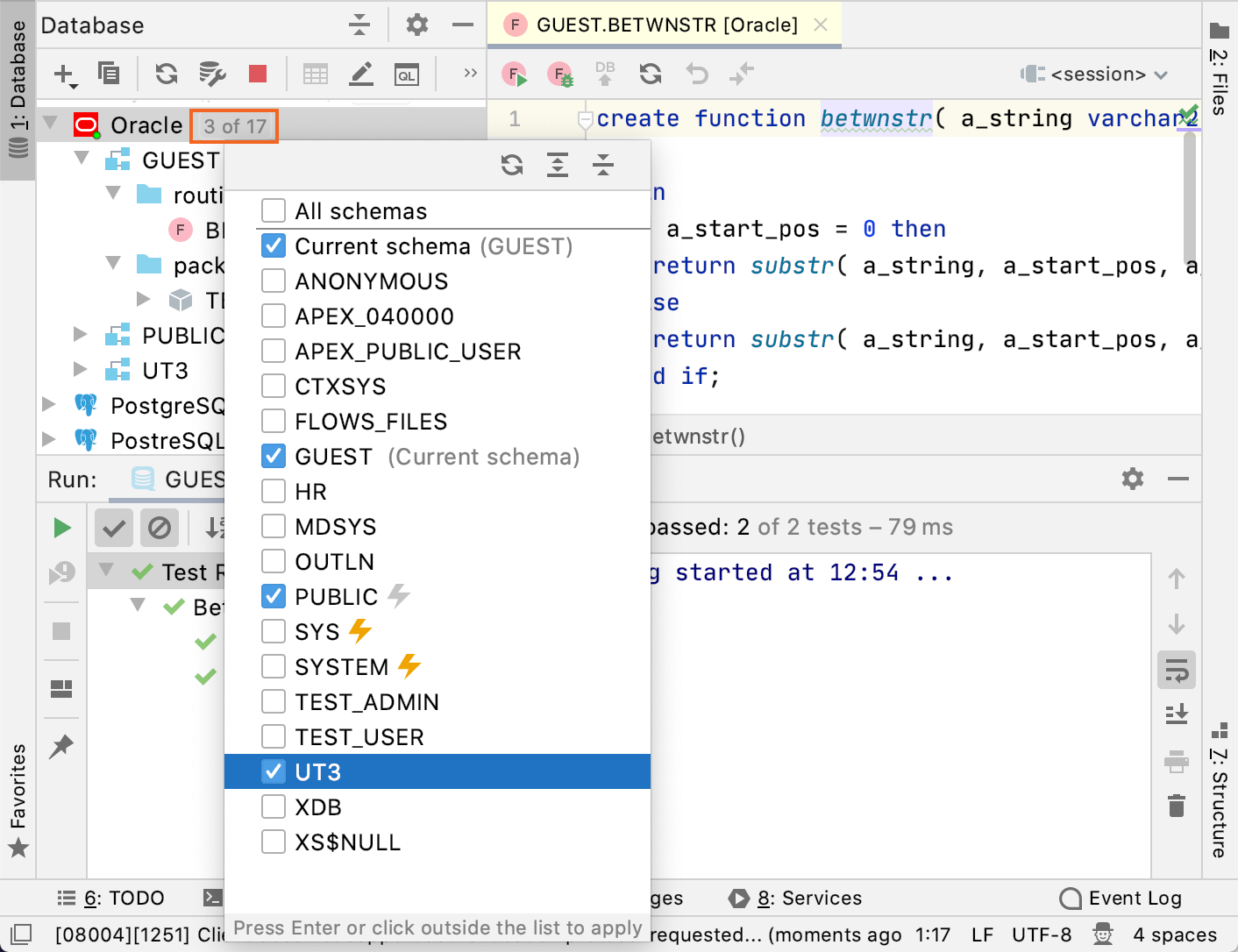
To use utPLSQL objects in your tests, enable the utPLSQL schema in DataGrip.
Click the N of N link near the data source name. In the schema selection window, select the utPLSQL schema (for example,
UT3).Press Enter.
Step 2. Create a function to be tested
In the Database Explorer () , right-click the Oracle data source and select .
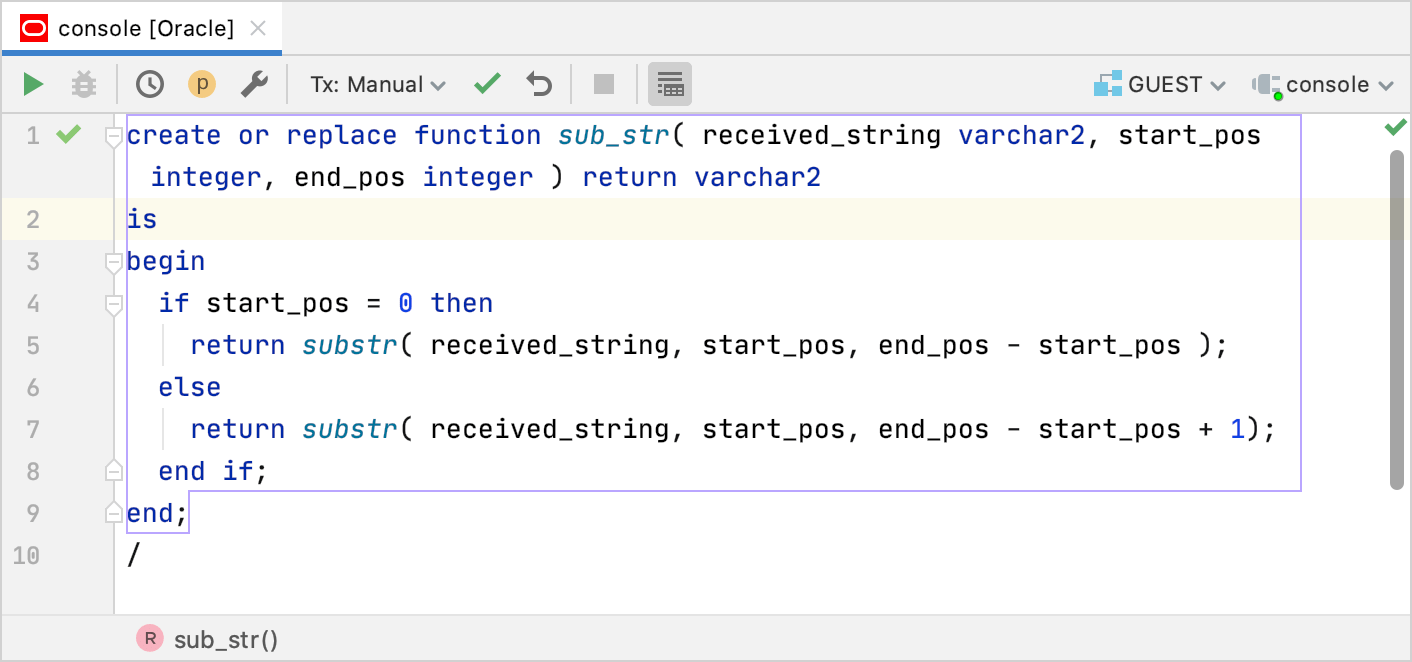
Write the code of a function that you want to test. Consider the following example:
create or replace function sub_str( received_string varchar2, start_pos integer, end_pos integer ) return varchar2 is begin if start_pos = 0 then return substr( received_string, start_pos, end_pos - start_pos ); else return substr( received_string, start_pos, end_pos - start_pos + 1); end if; end; /Click the Execute button (
) or press Ctrl+Enter.
Step 3. Create a testing package
In the Database Explorer () , right-click the Oracle data source and select .
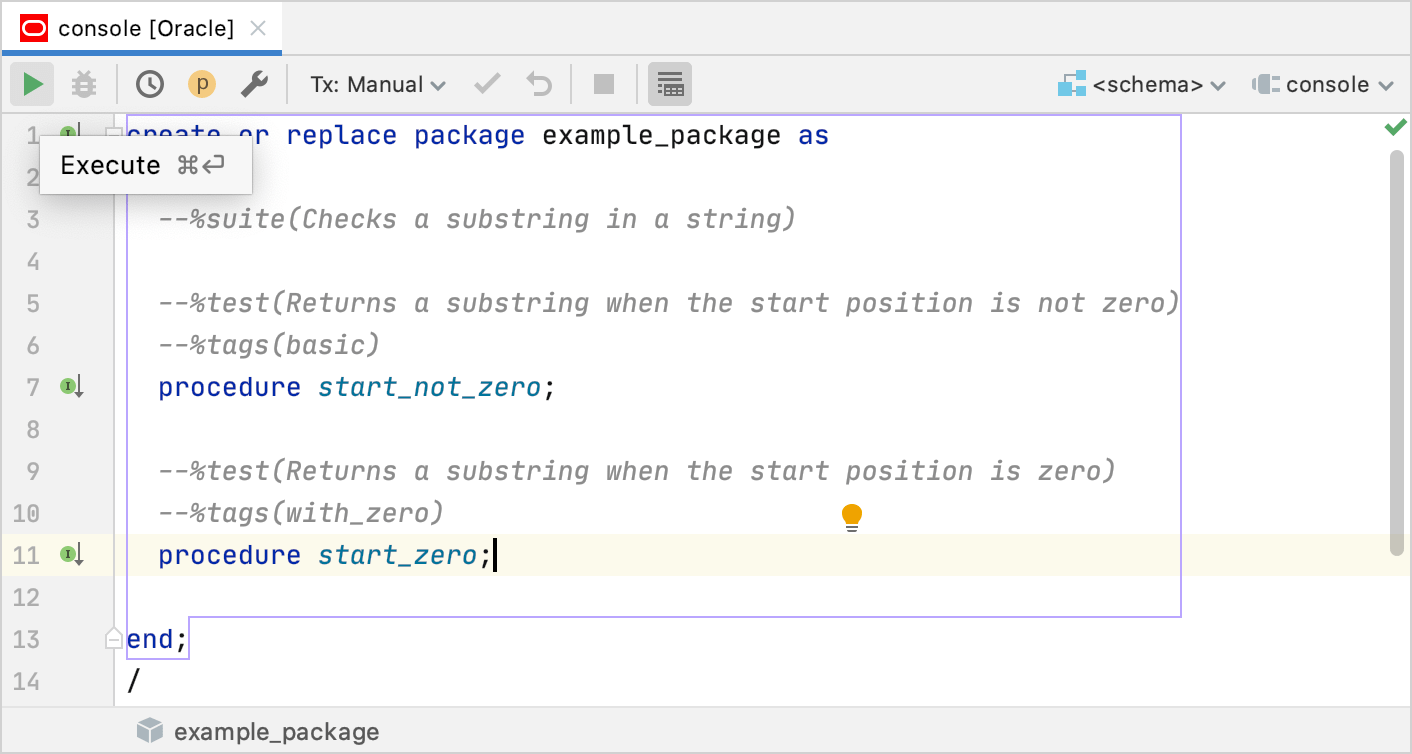
In the editor, type code of a package that lists all your tests. Consider the following example:
create or replace package example_package as --%suite(Checks a substring in a string) --%test(Returns a substring when the start position is not zero) --%tags(basic) procedure start_not_zero; --%test(Returns a substring when the start position is zero) --%tags(with_zero) procedure start_zero; end; /Click the Execute button (
) or press Ctrl+Enter.
Step 4. Create test procedures in the testing package
In the Database Explorer () , right-click the Oracle data source and select .
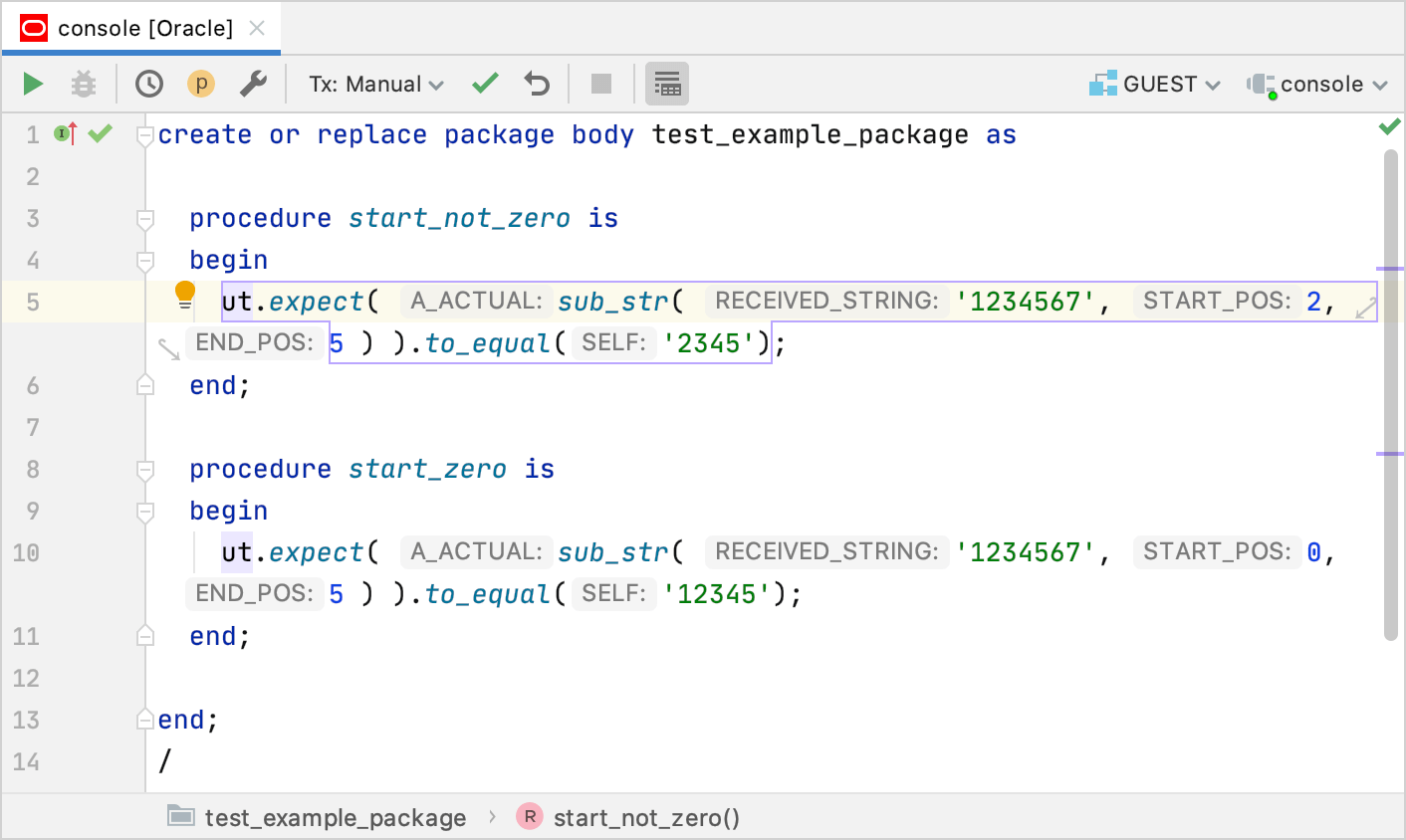
In the editor, type code of test procedures. Consider the following example:
create or replace package body example_package as procedure start_not_zero is begin ut.expect( sub_str( '1234567', 2, 5 ) ).to_equal('2345'); end; procedure start_zero is begin ut.expect( sub_str( '1234567', 0, 5 ) ).to_equal('12345'); end; end; /Click the Execute button (
) or press Ctrl+Enter.
Step 5. Run utPLSQL tests by using a run configuration
Open the Run/Debug Configuration dialog in one of the following ways:
Select from the main menu.
With the Navigation bar visible (), choose from the run/debug configuration selector.
Press Alt+Shift+F10 and then press 0.
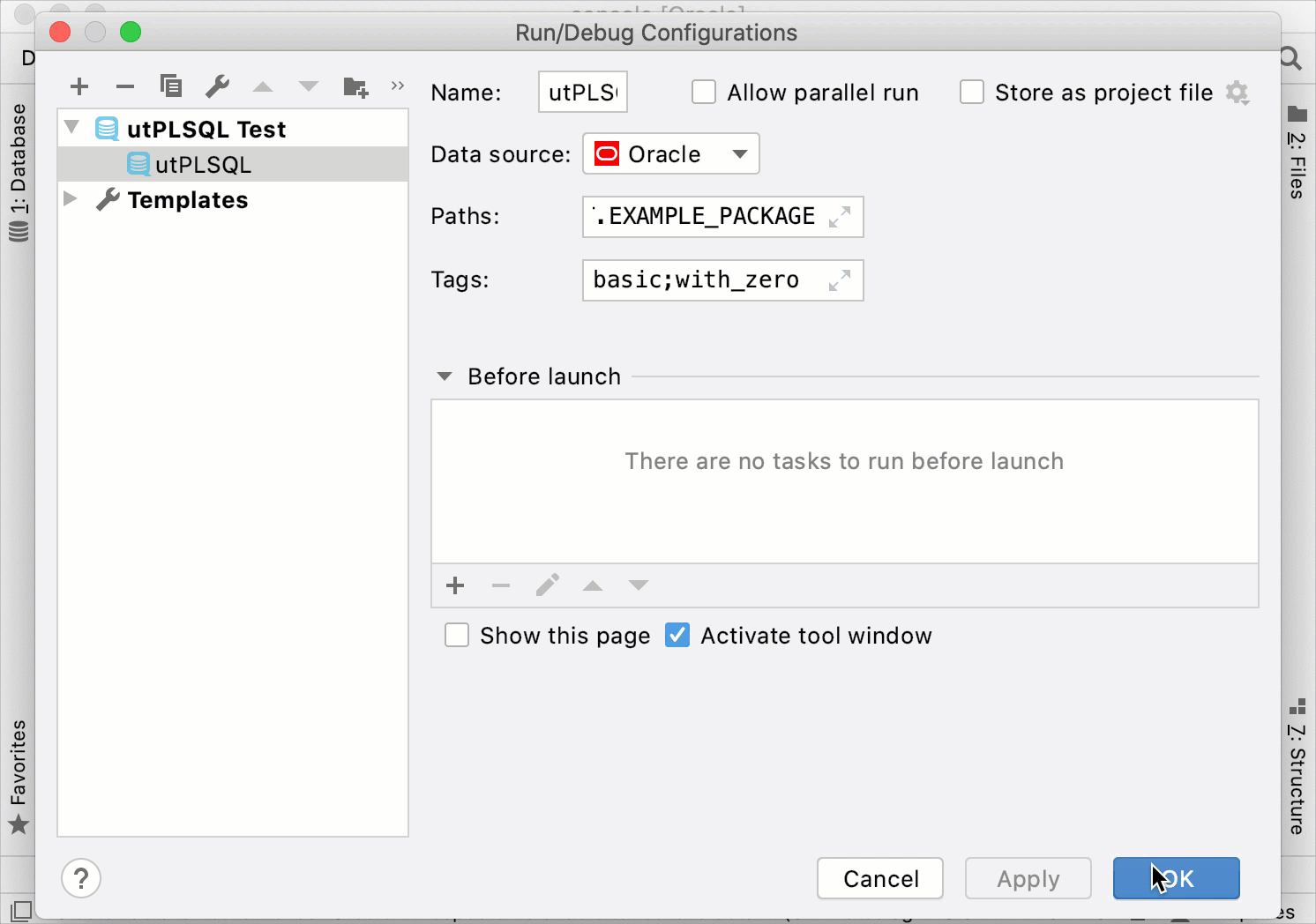
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click the Add New Configuration icon (
) and select utPLSQL Test.
Data source: a name of a data source. utPLSQL supports Oracle.
Paths: a qualified path to the testing package (for example,
GUEST.EXAMPLE_PACKAGE).Tags: tags of tests that you want to run. Use semicolon (
;) as separator (for example,basic;with_zero).
For more information about settings of the utPLSQL Test configuration type, refer to utPLSQL Test.
You can either run the configuration right away or save the configuration to run it later.
To save the run configuration for later, click OK.
To run the configuration right away, click Run.
Productivity tips
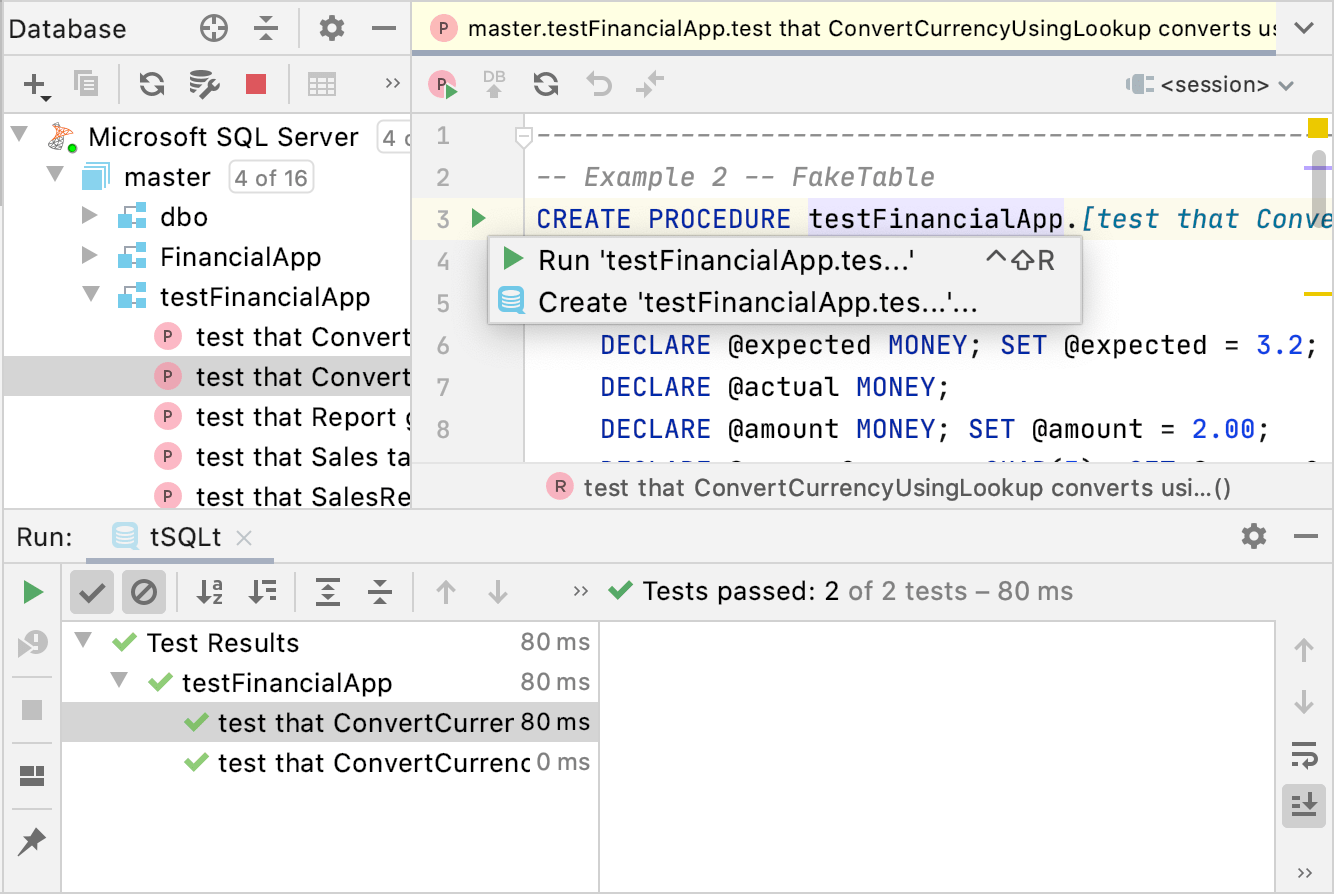
Run tests from the editor
In the Database Explorer () , double-click the test.
In the editor, click the Run icon
in the gutter and select Run <procedure_name>.
Rerun failed tests
In the Run tool window, click the Rerun failed tests button