Docker connection settings
Specify the settings for accessing the Docker Engine API from DataGrip. For more information about using the Docker integration with DataGrip, refer to Docker.
Enable the Docker plugin
This functionality relies on the Docker plugin, which is bundled and enabled in DataGrip by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Installed tab, find the Docker plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
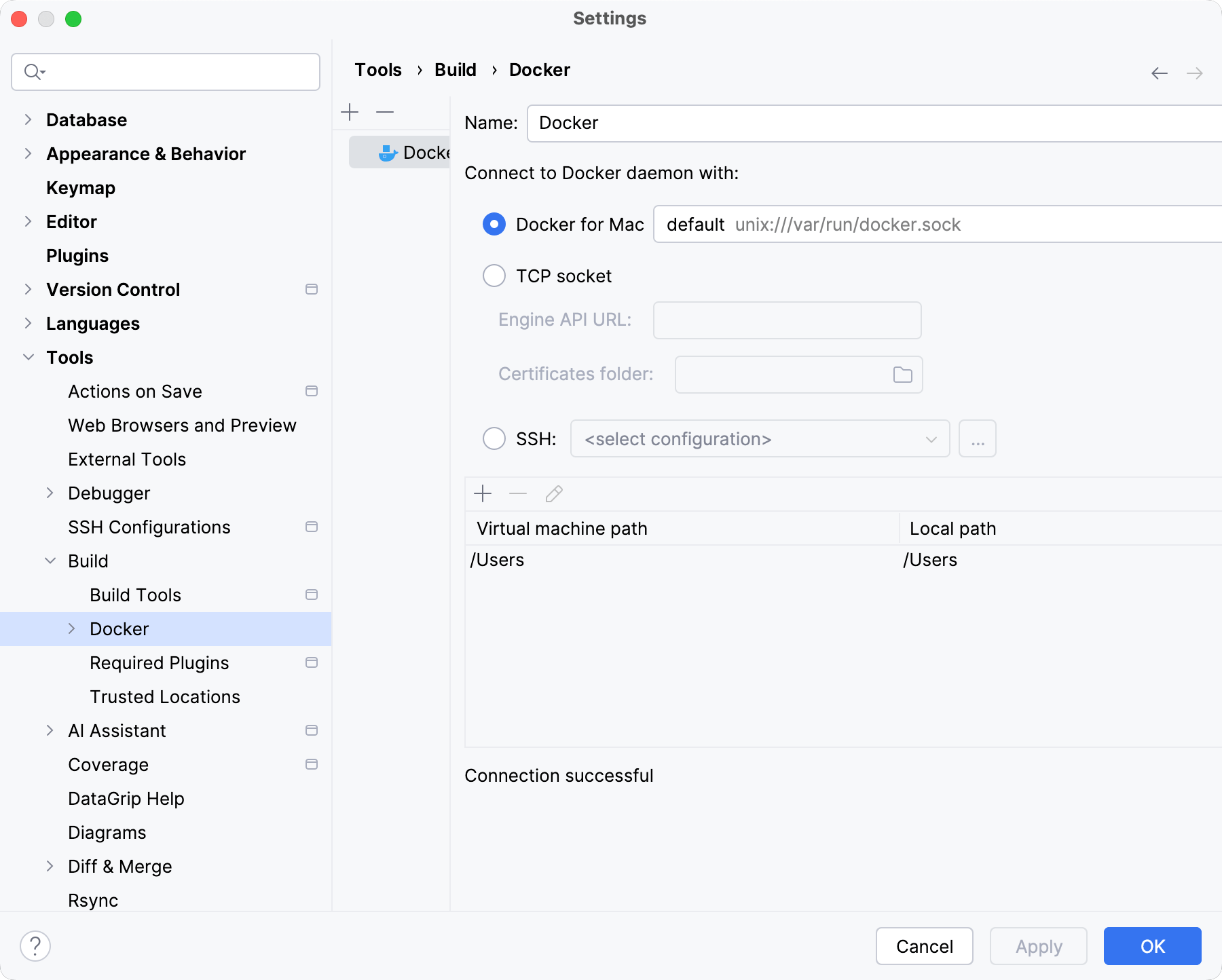
You can add multiple Docker configurations, each representing a connection to a separate Docker daemon:
Docker
Add a new Docker configuration.
Delete Alt+Delete
Remove the selected Docker configuration.
For each Docker configuration, specify a name and choose the connection type depending on the operating system:
- Docker for Windows
This is the recommended option when using Docker Desktop for Windows.
- Docker for Mac
This is the recommended option when using Docker Desktop for macOS.
- Unix socket
This is the recommended option when using Docker Desktop for Linux.
- TCP socket
Configure the URL to the Docker Engine API manually.
In the Engine API URL field, you can specify a TCP connection to a remote Docker daemon or any Docker socket path, including a custom local socket. For example, in rootless mode, the Docker daemon runs via a
systemduser service with a unique identifier, so the socket path will be something likeunix:///run/user/1000/docker.sock.By default, on macOS and Linux, the Docker daemon listens for Docker Engine API requests on the Unix socket at
unix:///var/run/docker.sock.If you are using Docker Desktop for Windows, you can connect to the Docker Engine through a named pipe at
npipe:////./pipe/docker_engineor a TCP socket attcp://localhost:2375.You can also connect to Podman, which has an API that is equivalent to the Docker Engine API. For more information, refer to Podman.
- SSH
Connect to a remote Docker daemon via an existing SSH configuration or create a new one.
- WSL
Connect to a Docker daemon running in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
- Minikube
If you are running minikube, select this option to automatically detect and connect to the minikube's Docker Engine environment.
If DataGrip cannot detect minikube or if it is running remotely, run the
minikube docker-envcommand to get the necessary connection information and set the following under TCP socket:Engine API URL: the value of
DOCKER_HOST(withhttpsas the protocol instead oftcp)Certificates folder: the value of
DOCKER_CERT_PATH
Virtual machine path mappings for Windows and macOS hosts
The Docker Engine runs natively on Linux, so you can mount directories and files from a Linux host directly to the container. A Docker host on Windows or macOS uses a lightweight virtual machine with Linux to run the Docker Engine. Use the table below the Docker connection configuration options to configure the mappings between your local file system and the virtual machine running the Docker Engine.
Add Alt+Insert
Add a new mapping.
Remove Ctrl+Y
Remove the selected mapping.
Edit Enter
Edit the selected mapping.
- Virtual machine path
The path to the directory in the virtual machine used for running this Docker Engine.
- Local path
The path to the local folder that you want to map to the corresponding directory in the virtual machine. You will not be able to bind-mount anything outside of this folder to containers that this Docker Engine runs.
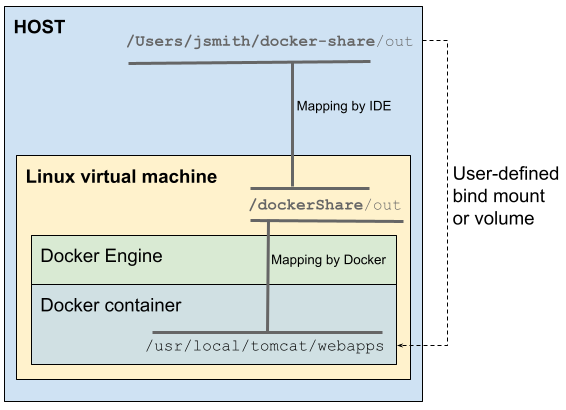
For example, let's say you keep all files that you bind-mount to Docker containers in /Users/jsmith/docker-share. You can map this directory to /dockerShare on the virtual machine for your Docker Engine connection. This Docker Engine will effectively bind-mount files to containers from /dockerShare, because that's where it can access the files that you mapped from /Users/jsmith/docker-share.
This does not affect you as a user running containers, because you still configure bind mounts and volumes as a mapping between some path on your host machine and some path inside the container. However, you can't mount anything outside of the directory that you mapped to the virtual machine.
Let's say you run a container and mount the directory with your application artifacts /Users/jsmith/docker-share/out on the host to /usr/local/tomcat/webapps in the container. In this case, the Docker Engine actually mounts /dockerShare/out, because that's where it has access to your files through virtual machine mapping.
For more information about volumes and bind mounts, refer to Manage data in Docker.