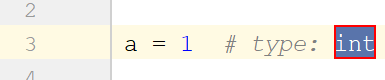Type hinting
DataSpell provides various means to assist inspecting and checking the types of the objects in your script. DataSpell supports type hinting in function annotations and type comments using the typing module and the format defined by PEP 484.
Adding type hints
Although DataSpell supports all methods for adding types supported in PEP 484, using type hints through intention actions is the most convenient way. Depending on the interpreter you use, the type is added as an annotation (Python 3) or as a comment (Python 2).
To add a type hint, follow these steps:
Select a code element.
Press Alt+Enter.
Select Add type hint for ....
Press Enter to complete the action or edit the type if appropriate.
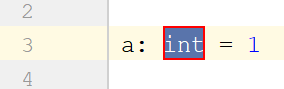
Example | Intention Action | Resulting Code for comments (Python 2) | Resulting Code for annotations (Python 3) |
|---|---|---|---|
Variables | |||
Functions | 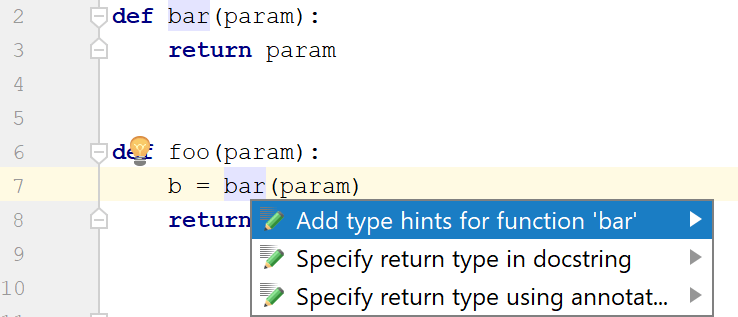 |  |  |
Class attributes | 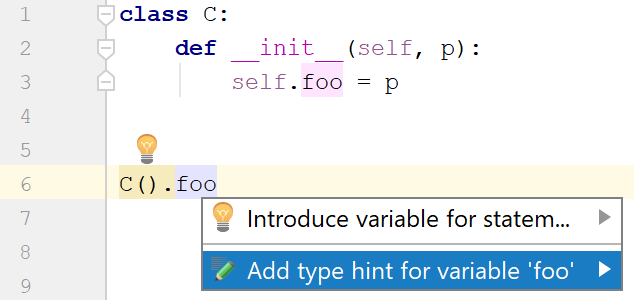 | 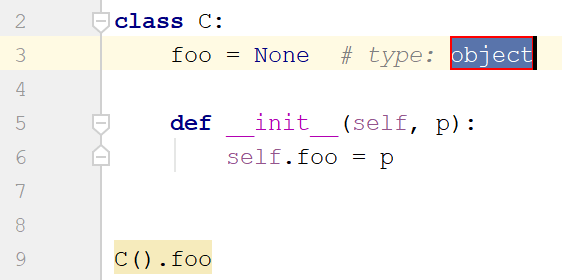 | 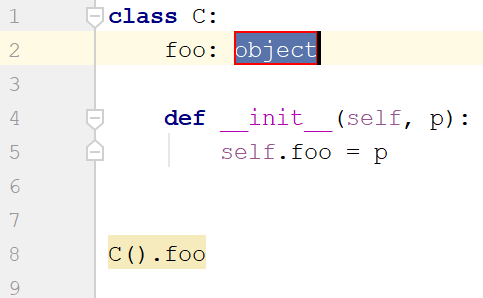 |
You can also use Python stubs or comments to specify the types of variables, functions, and class fields.
Specifying types by using comments
Use a # type: comment to specify the types of local variables and attributes:

Converting comments
For comment-based type hints, DataSpell suggests an intention action that allows you to convert comment-based type hint to a variable annotation. This intention has the name Convert to variable annotation, and works as follows:
Before | After |
|---|---|
from typing import List, Optional
xs = [] # type: List[Optional[str]]
|
from typing import List, Optional
xs: List[Optional[str]] = []
|
Type hints validation
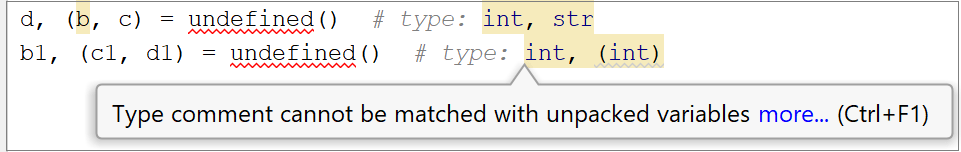
Any time you're applying type hints, DataSpell checks if the type is used correctly according to the supported PEPs. If there is a usage error, the corresponding warning is shown and the recommended action is suggested. Below are the validation examples.
Validation error | Suggested action |
|---|---|
Duplication of type declaration. 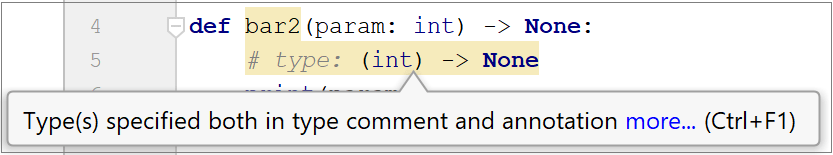 | Remove either of the type declarations. |
Number of arguments in the type declaration differs from the number of function arguments. 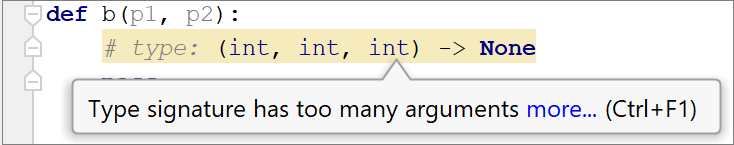 | Adjust the number of the arguments. |
Type comments with unpacking do not match the corresponding targets. | Check the target format and modify the type comment accordingly. |
Incorrect syntax of 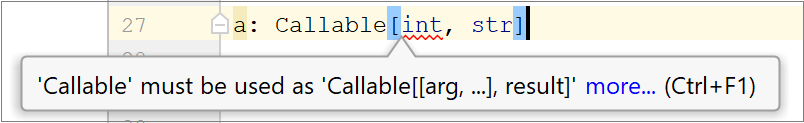 | Use the suggested format and add the required brackets to wrap |
Unexpected type in assignment expressions. 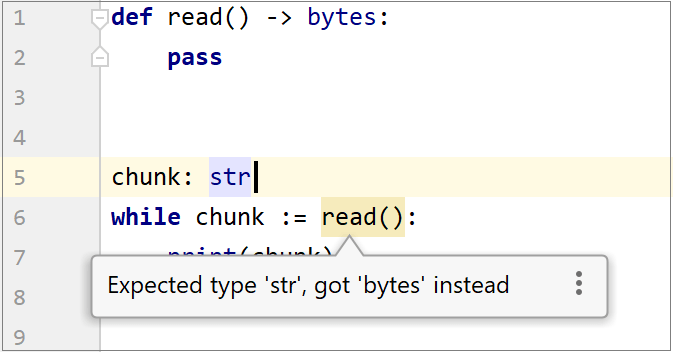 | Align the types to match the expected pattern. |
Assigning a value to a 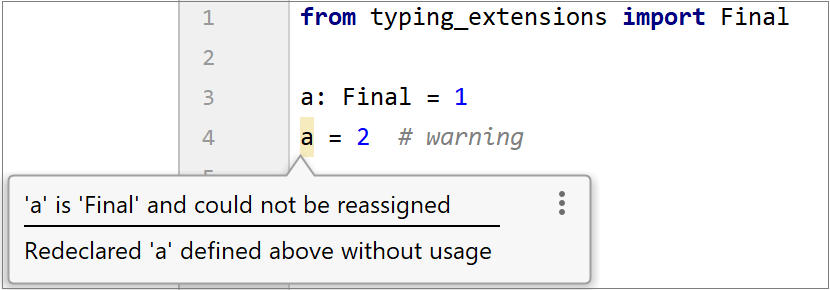 | You cannot alter a |
Inheriting a 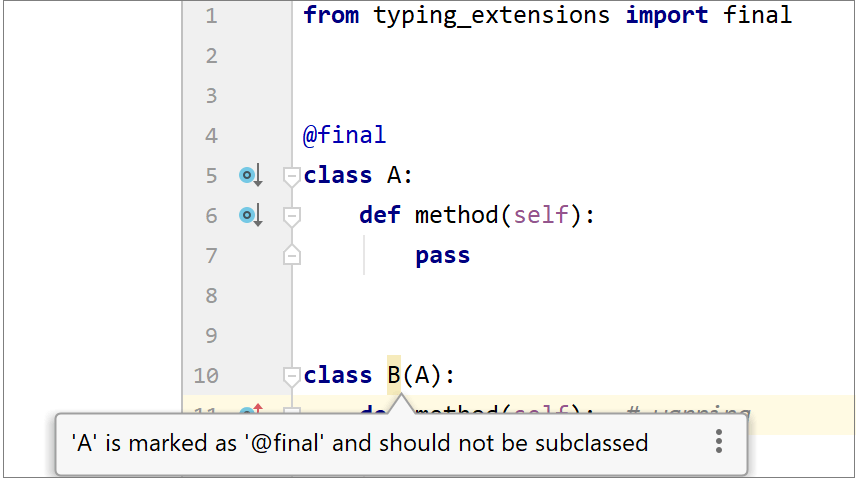 | You cannot inherit a |
Incorrect type of the function argument.  | Use the |
Incorrect usage of the 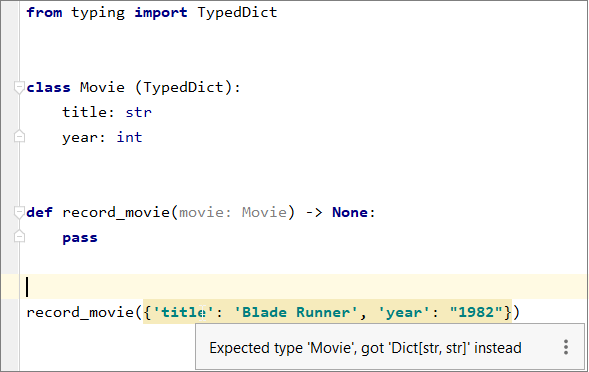 | Refer to the
|
Incorrect type of decorated methods. DataSpell can validate the type of decorated methods based on the types of their decorators as well as the type hints of their decorators: 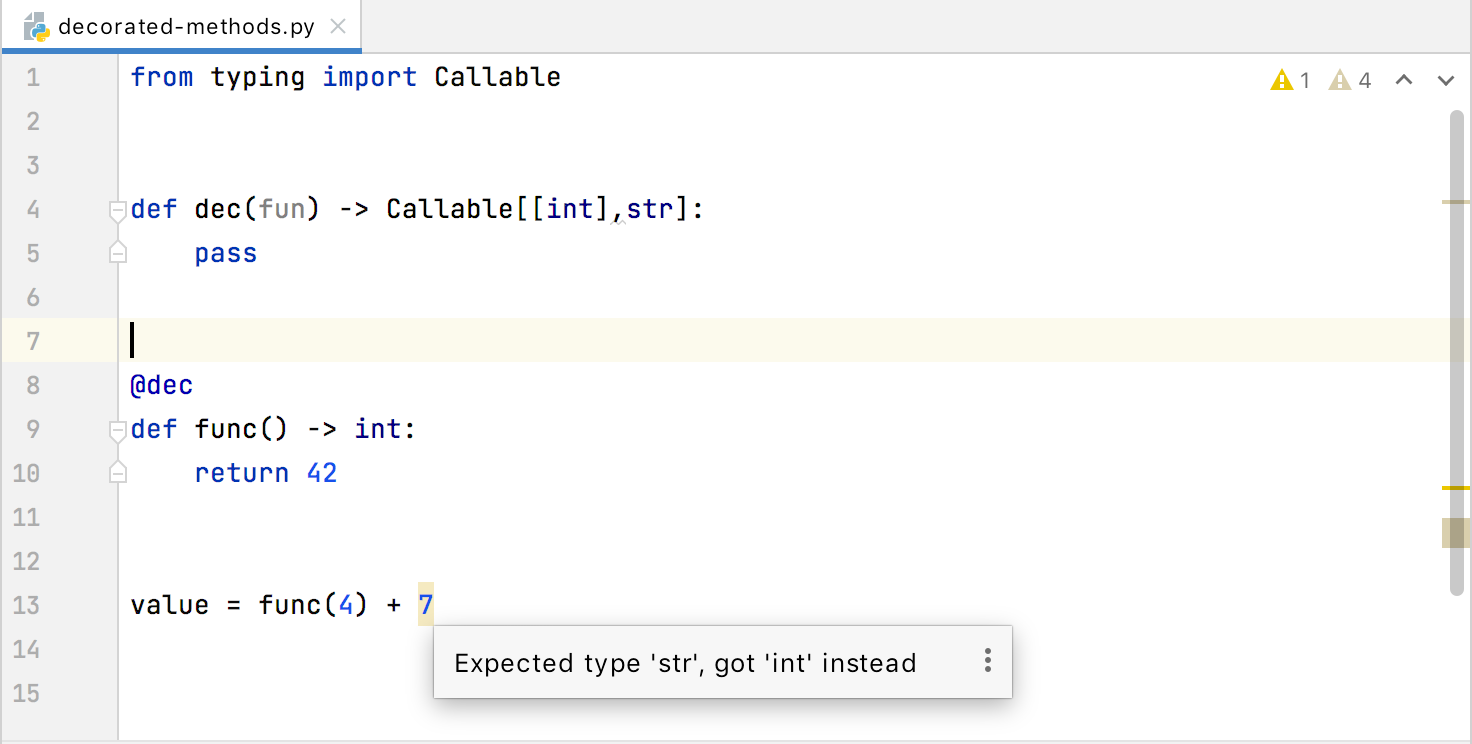 | Use the suggested type, in this example, |
You can add a # type: ignore comment to suppress a type validate warning or a missing import statement. 
Python stubs
As DataSpell supports Python stub files, you can specify the type hints using Python 3 syntax for both Python 2 and 3.
If any type hints recorded in the stub files, they become available in your code that use these stubs. For example, the following type hint for some_func_2 becomes available in the Python code:

If you're using a package for which a stub analog is detected, the following message will be shown:

You can install the stub package, ignore this message and continue working with the currently installed package, or even disable the corresponding inspection in the project Settings/Preferences.
Using Typeshed
Typeshed is a set of files with type annotations for the standard Python library and various packages. Typeshed stubs provide definitions for Python classes, functions, and modules defined with type hints. DataSpell uses this information for better code completion, inspections, and other code insight features.
DataSpell is switching to Typeshed, the common repository for Python stubs. The Typeshed stubs bundled with DataSpell are shown in the project view under the node External Libraries | <Python interpreter> | Typeshed Stubs. Note that DataSpell currently uses only a few of the bundled stubs (that is builtins.pyi, typing.pyi, and several others).
To override the bundled Typeshed repository with your own version, follow these steps:
Copy some or all the stubs into a directory in your project.
Mark a directory as a source root by choosing Mark Directory as | Sources Root from the context menu of the directory.
The Python skeletons repository https://github.com/JetBrains/python-skeletons is now deprecated.