Configure an interpreter using WSL
You can use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to work with a Python interpreter available in your Linux distribution.
Fulfill the preliminary steps
Ensure that you have downloaded and installed Python on your computer.
Click the Windows button in the lower-left corner of the screen and start typing
System Information. To ensure that your system works well with WSL, upgrade your Windows to the latest available version.Install the Windows Subsystem for Linux and initialize your Linux distribution as described in the WSL Installation Guide.
If your Linux distribution doesn't come with rsync, you need to install it:
sudo apt install rsyncsudo pacman -S rsync
Configure remote interpreter via WSL
Do one of the following:
Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Add New Interpreter.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the project Settings/Preferences and go to . Click the Add Interpreter link next to the list of the available interpreters.
Select On WSL from the list of available interpreter types:
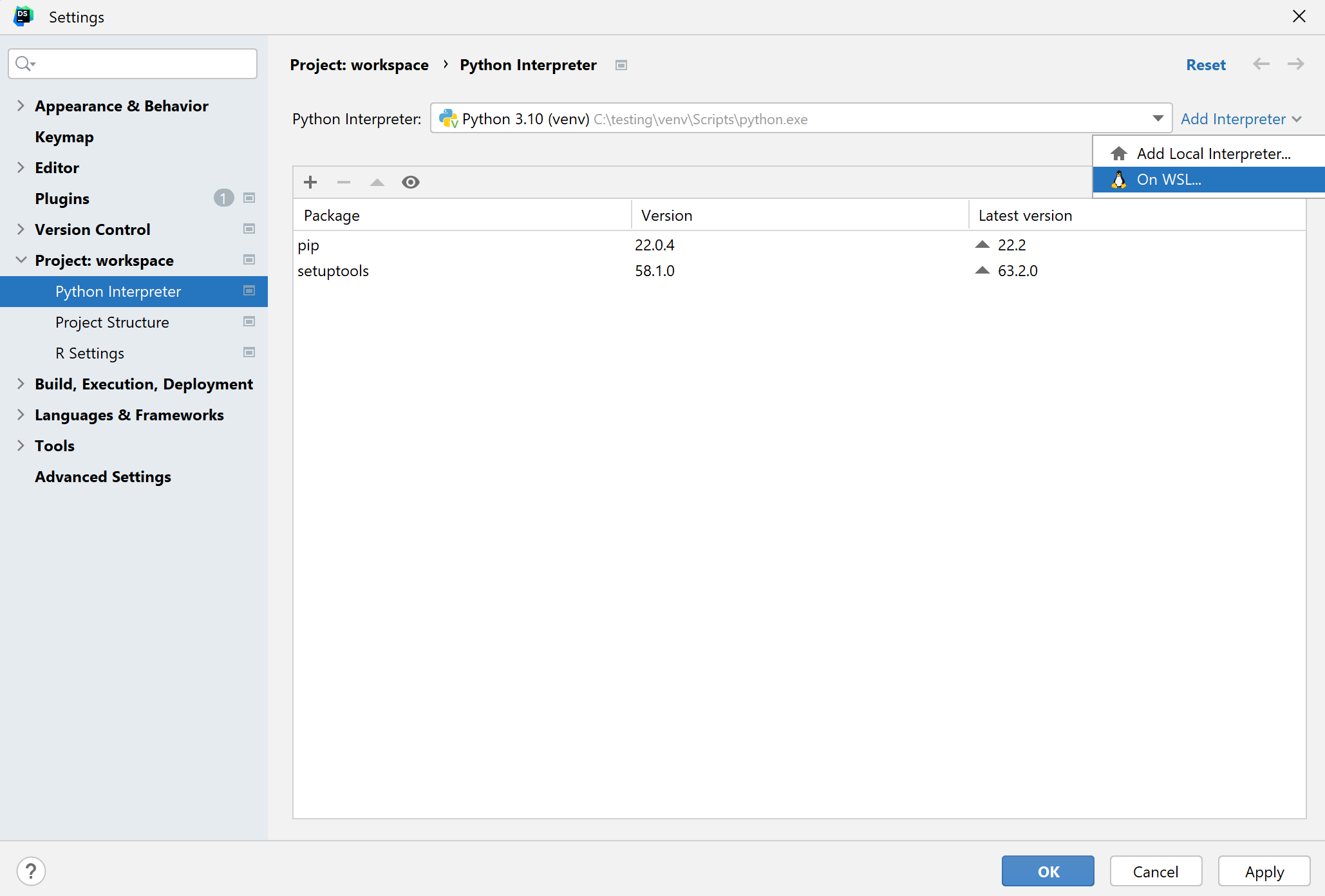
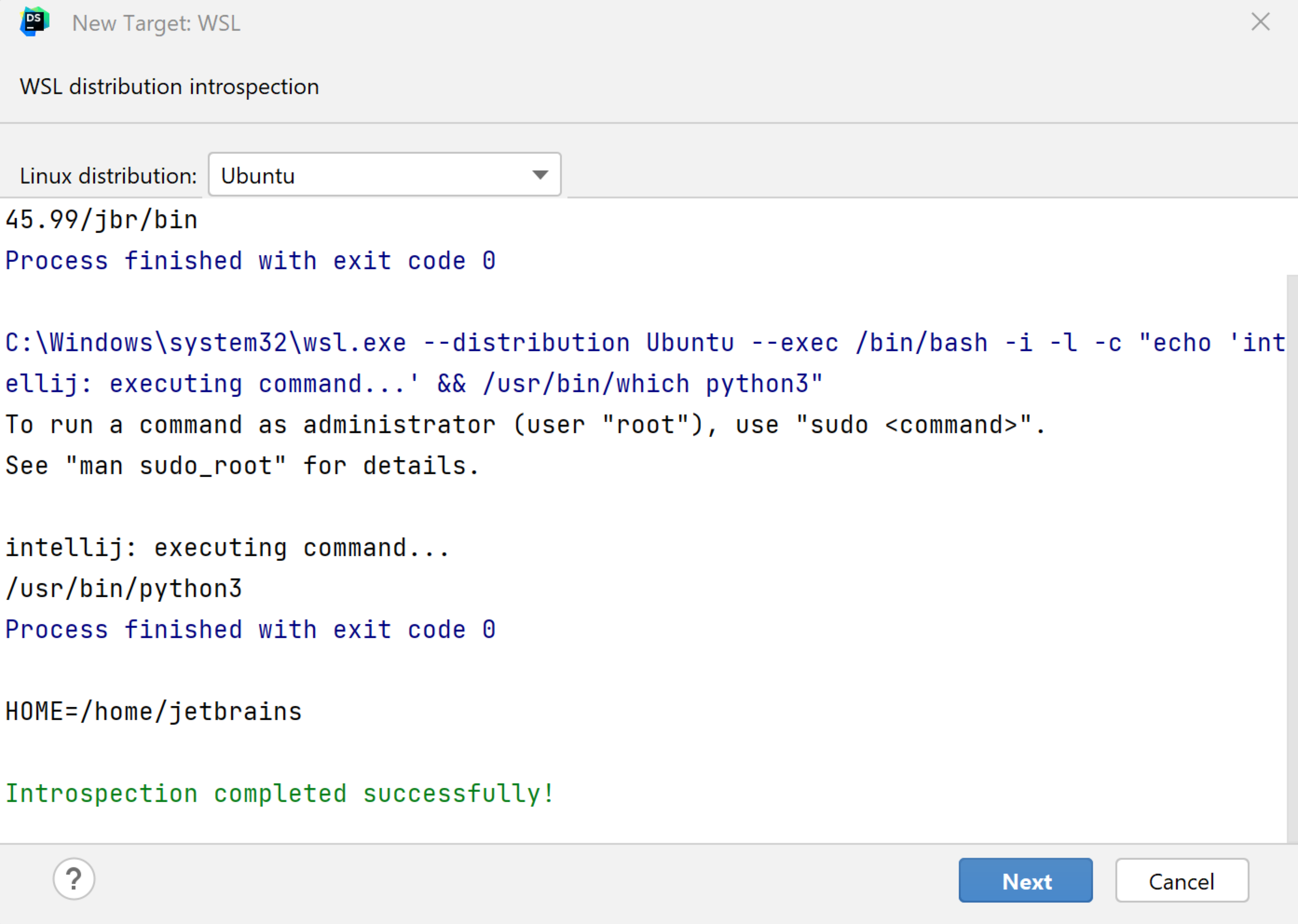
Wait until DataSpell detects Linux on your machine and completes introspection. Press Next to proceed:
In the left-hand pane of the dialog, select the type of the WSL interpreter you want to create: Virtual Environment or System Interpreter.
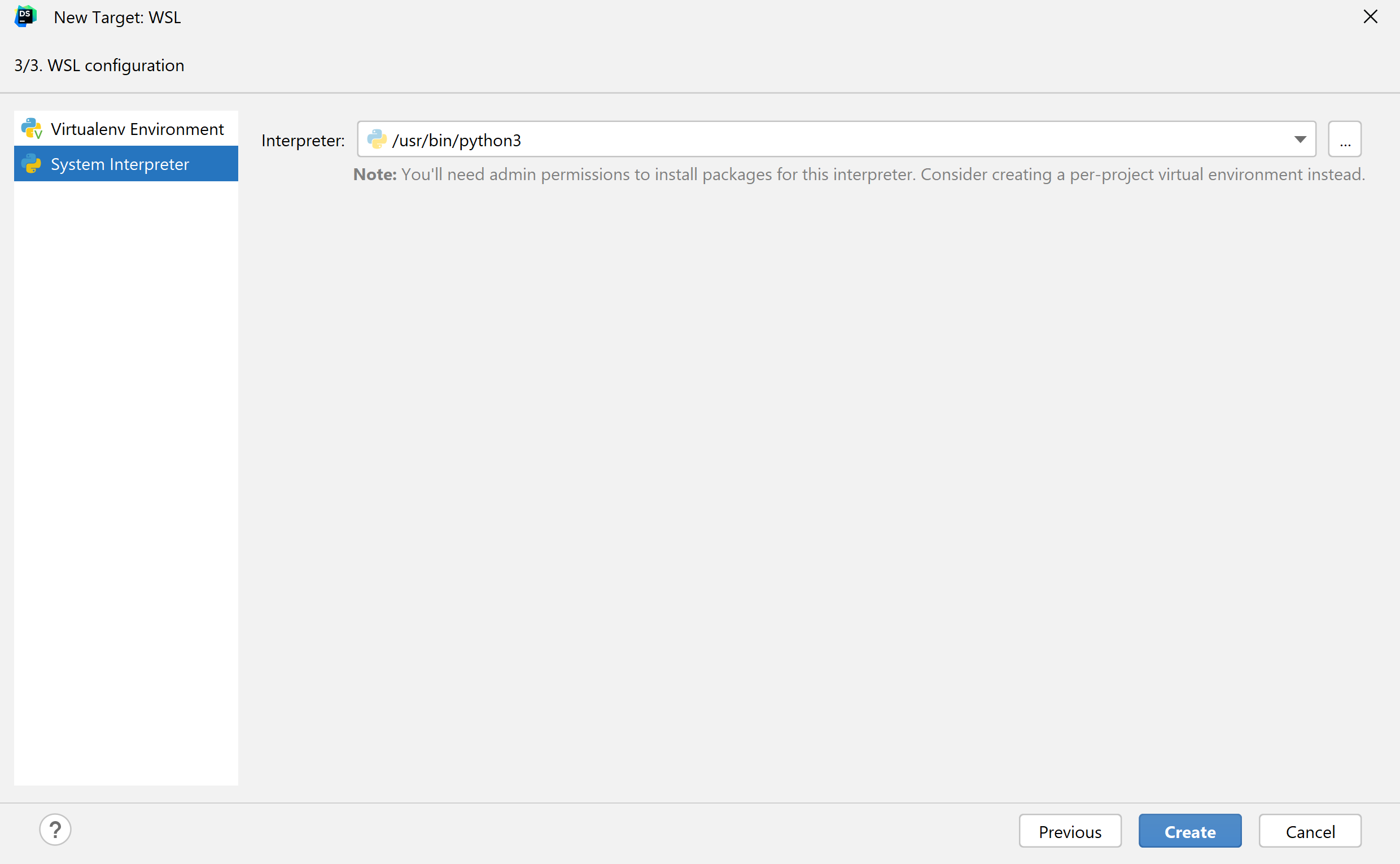
For a system interpreter, just provide the path to the Python executable in the selected Linux distribution.
For virtual environments, you can provide a path to a Python executable of an existing environment in the selected Linux distribution or create a new environment based on the specified Python.
Once done, the new interpreter will be added to your project, and the default mnt mappings will be set.
Configure Terminal in WSL
To run Terminal in WSL configuration, open project Settings/Preference (Ctrl+Alt+S) and go to .
Type
wsl.exein the Shell path field and click OK.
Switch to the Terminal tool window and type any command to inspect the output.