Git in DataSpell
DataSpell allows using Git to track changes in Jupyter notebooks and interact with remote repositories.
Sync workspace directories with Git
DataSpell lets you attach Git repositories to the workspace as directories.
Attach a Git repository
Do one of the following:
From the main menu, select .
Right-click the workspace tree or a directory and select from the context menu
Select Git:

Specify the path to the repository and select the directory to which it will be cloned. Do not select the default DataSpell installation directory as the target local directory. Alternatively, you can select GitHub on the left, login using your credentials, and select any repository you want to work with.
Click Clone.
Also, you can create a remote repository for a local directory in the DataSpell workspace.
Add a workspace directory to Git
Right-click the directory in the Workspace tool window and select Enable VCS integration:
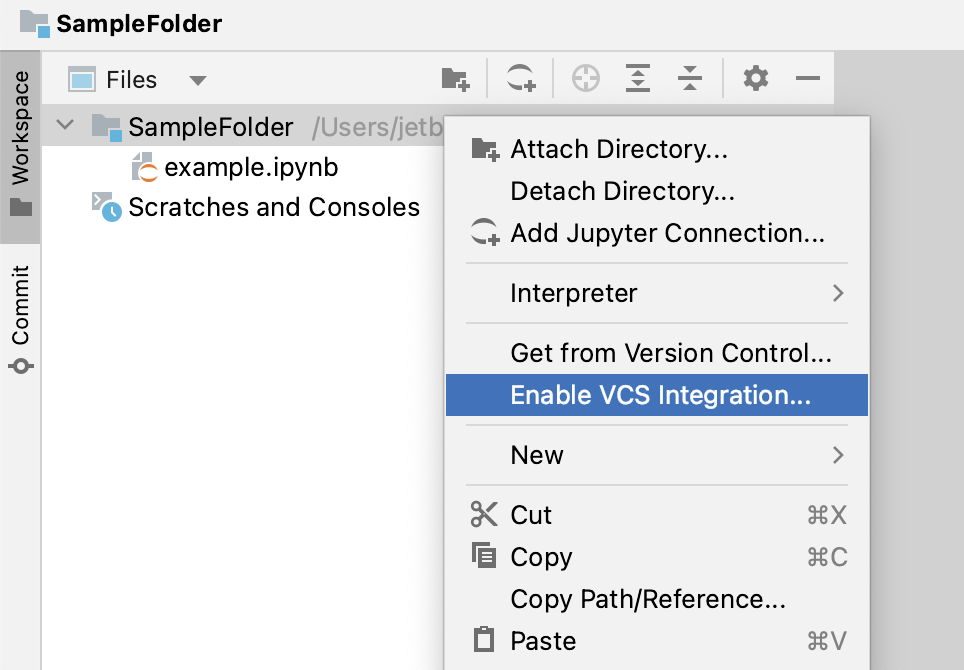
In the Enable Version Control Integration dialog that opens, select Git.
Open the Commit tool window Alt+0.
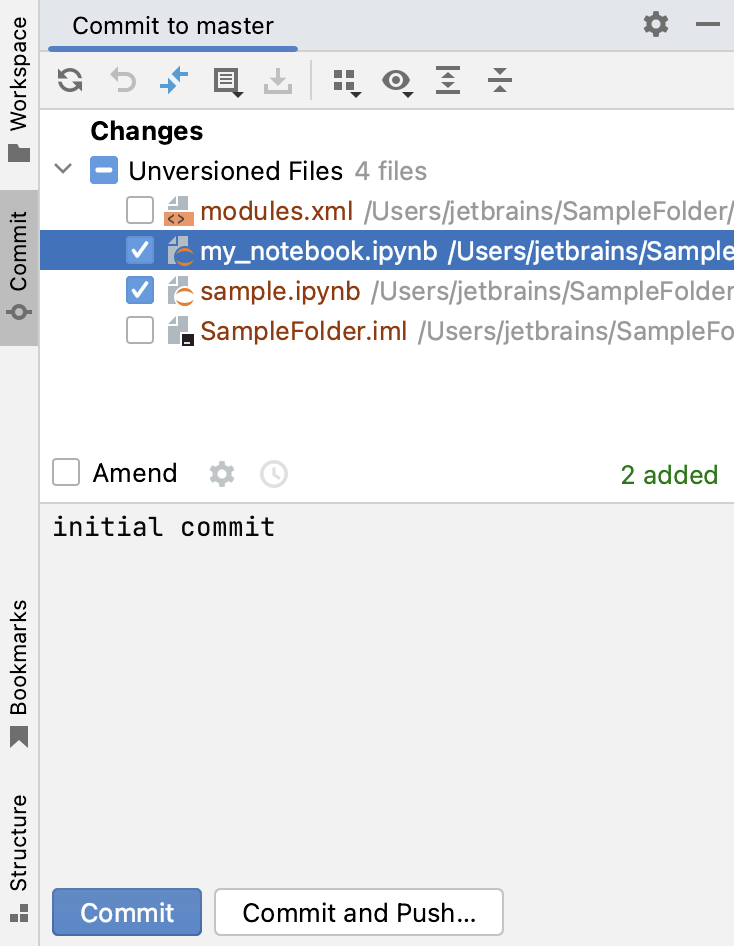
Select the files from the directory that should be added to Git, type the commit message, and click Commit and Push:
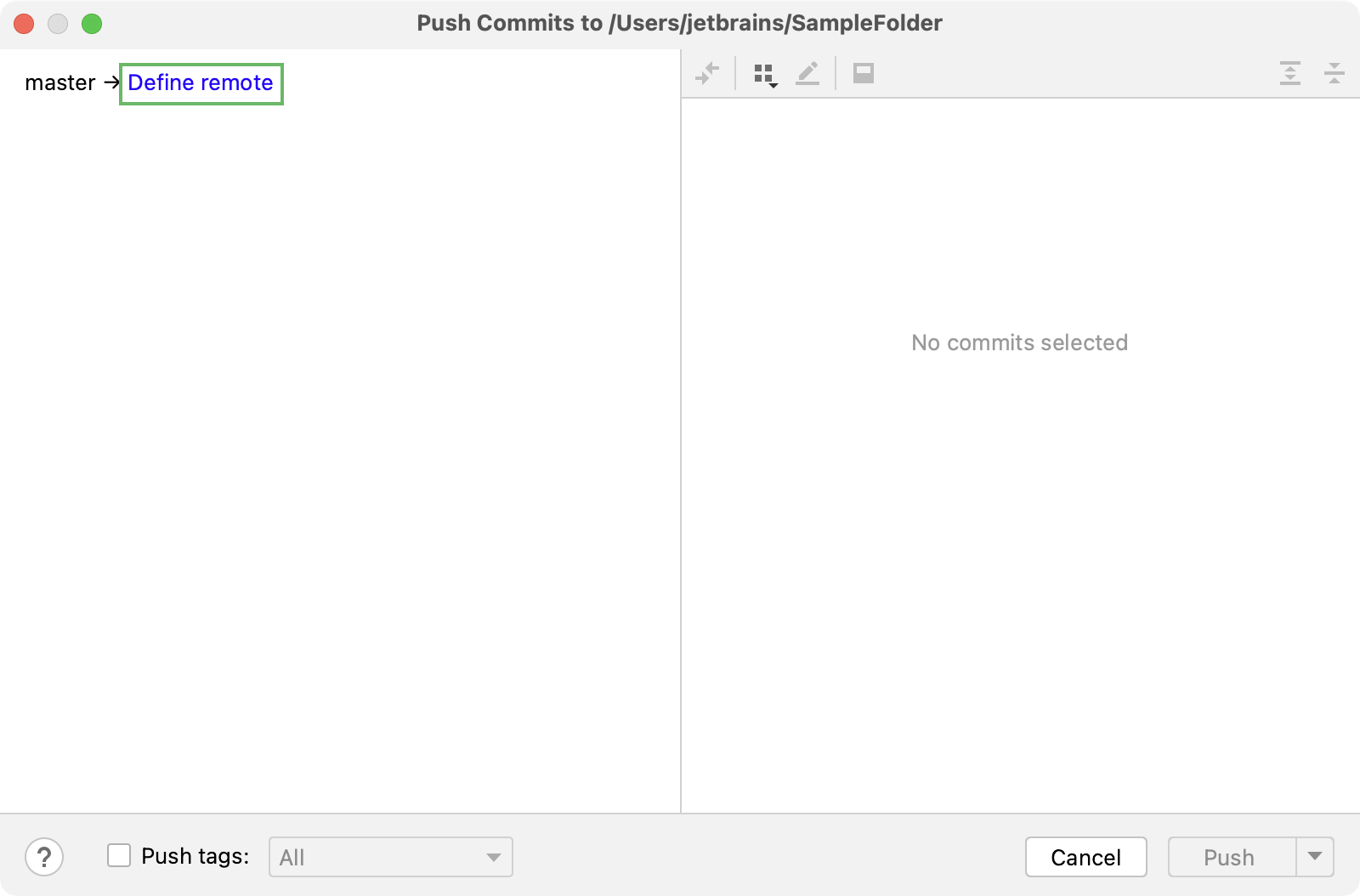
In the dialog window, click Define remote:
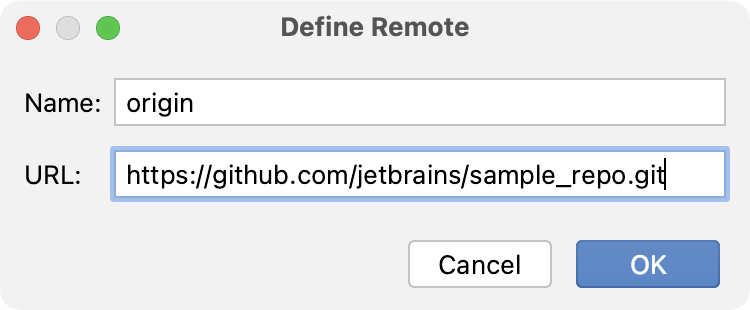
Specify the name of the remote and the URL of the repository:
Click Push.
The directory is added to the remote repository. Now you can sync the changes to files in this directory with Git.
Sync workspace directories with Github
You can clone a repository that you want to contribute to directly from DataSpell and create a new directory based on it.
From the main menu, choose . If the Git menu is not available, choose .
In the Get from Version Control dialog, choose GitHub on the left.
Log in to GitHub by doing one of the following:
If you have a token, click Use token, then paste the token in the Token field, and click Log In.
Otherwise, click Log In via GitHub.
Enter your GitHub credentials in the browser window that opens. If you have two-factor authentication enabled, you will be asked to enter a code that will be sent to you by SMS or through the mobile application.
Select a repository from the list of all GitHub projects associated with your account and the organization that your account belongs to.
In the Directory field, enter the path to the folder where your local Git repository will be created.
Click Clone.
You can add a remote GitHub repository for a workspace directory you are developing locally, so that others can view it or contribute to it.
Open the directory you want to share.
From the main menu, choose .
If you have already registered your GitHub account in DataSpell, connection will be established using these credentials.
If you have not registered your account in DataSpell, the Login to GitHub dialog opens. Specify your access token or request a new one with your login and password.
When connection to GitHub has been established, the Share Project on GitHub dialog opens. Specify the new repository name, the name of the remote , and enter a description of your project.
You can select the Private option if you do not want to allow public access to your repository for other GitHub users.
Click Share to initiate a new repository and upload directory sources to it.
You can jump from DataSpell to the GitHub version of a file. DataSpell detects which branch is currently active as well as the latest revision of the file, and opens the GitHub copy of the selected file in the corresponding commit in your web browser.
Do one of the following:
Select from the main menu.
Select a file in the editor or in the Project view, and choose from the context menu.
Select the file in the Project view, press Ctrl+Shift+A, and type
Open on Github.
If you are signed in to GitHub, the remote version of the file will open in the browser.
Otherwise:
Enter your GitHub credentials in the browser window that opens. If you have two-factor authentication enabled, you will be asked to enter a code that will be sent to you by SMS or through the mobile application.
If you are opening the GitHub file version from the editor, the file will be also automatically scrolled to the current line.
If the file points to more than one remote, you will be prompted to select the appropriate repository.
View changes
When you modify Jupyter notebooks under version control, you may want to review the changes before committing and pushing them to a remote repository.
Compare a modified file with its repository version
Open the Commit tool window Alt+0.
Locate the required file in a changelist and do one of the following:
Select the file and click
on the toolbar or press Ctrl+D
Double-click the file
The diff view opens where changes to the file are highlighted.
The right pane contains the modified version of the file. You can edit it in the diff view.
The left pane contains the initial version of the file. It is read-only. You can click
(Revert) to undo a change.
For more information on comparing Jupyter notebooks, see Compare file and folder versions.
Resolve conflicts
When you push your changes to a remote repository, conflicts may arise. It happens when you modify the same lines that have been modified on the remote, for example, by other users of the repository. In this case, you will see the following window:
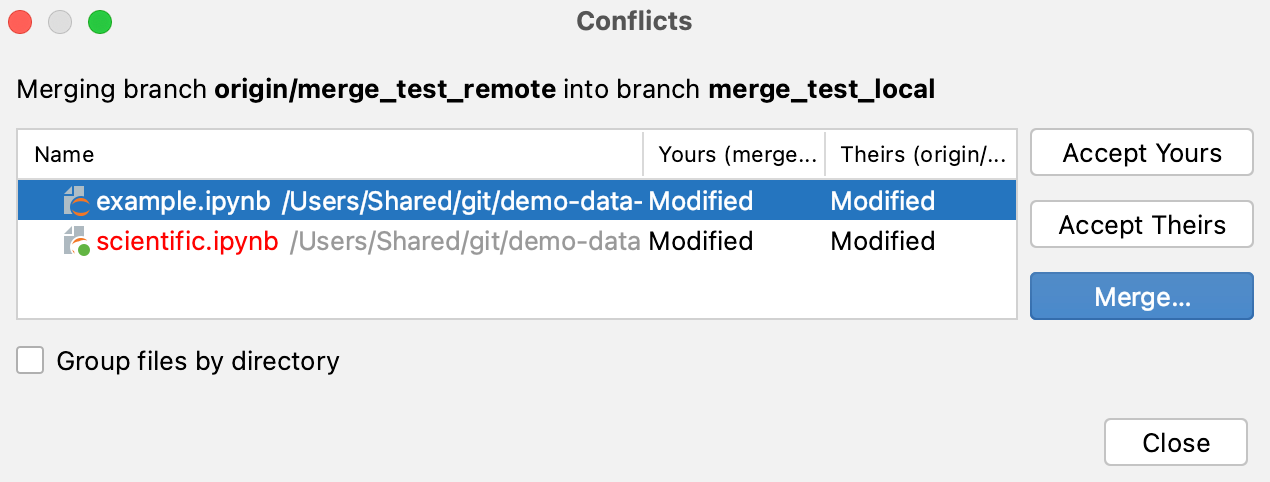
You need to resolve the conflicts to continue syncing with the remote repository. To do that, perform the following steps:
Resolve conflicts
Click Merge in the Conflicts dialog, the Resolve link in the Local Changes view, or select the conflicting file in the editor and choose Git | Resolve Conflicts from the main menu.
To automatically merge all non-conflicting changes, click
(Apply All Non-Conflicting Changes) on the toolbar. You can also use the
(Apply Non-Conflicting Changes from the Left Side) and
(Apply Non-Conflicting Changes from the Right Side) to merge non-conflicting changes from the left/right parts of the dialog respectively.
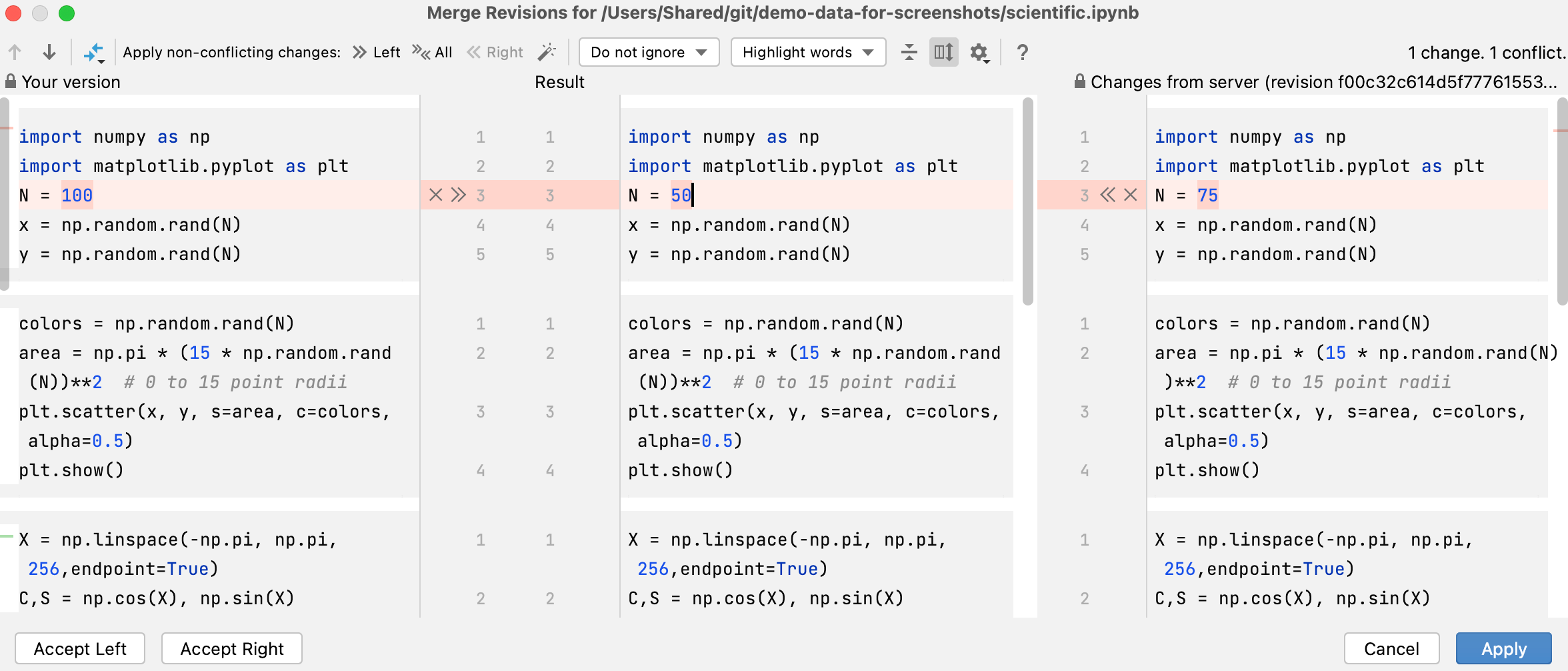
To resolve a conflict, you need to select which action to apply (accept
or ignore
) to the left (local) and the right (repository) version, and check the resulting code in the central pane:
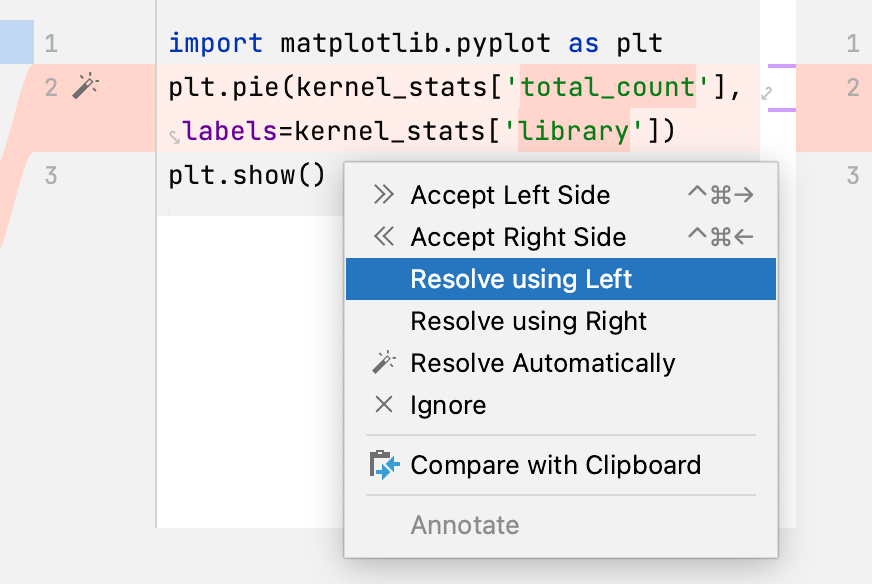
You can also right-click a highlighted conflict in the central pane and use the commands from the context menu. The Resolve using Left and Resolve using Right commands provide a shortcut to accepting changes from one side and ignoring them from the other side respectively:
For simple conflicts (for example, if the beginning and the end of the same line have been modified in different file revisions), the Resolve simple conflicts
button that allows merging the changes in one click becomes available.
Such conflicts are not resolved with the Apply All Non-Conflicting Changes action since you must make sure that they are resolved properly.
Review merge results in the central pane and click Apply.
For more details, see Resolve conflicts.