Attach to running Go processes with the debugger
In GoLand, you can attach the debugger to a running Go process on a local machine, on a remote machine, or in the Docker container.
Attach to a process on a local machine
You can debug an application that you launched from the command line. In this case, the application runs outside the IDE but on the same local machine. To debug the application, you need to open the project in the IDE and attach the debugger to the running process.
For example purposes, you can use the following Go code at github.com.
Step 1. Install the gops package
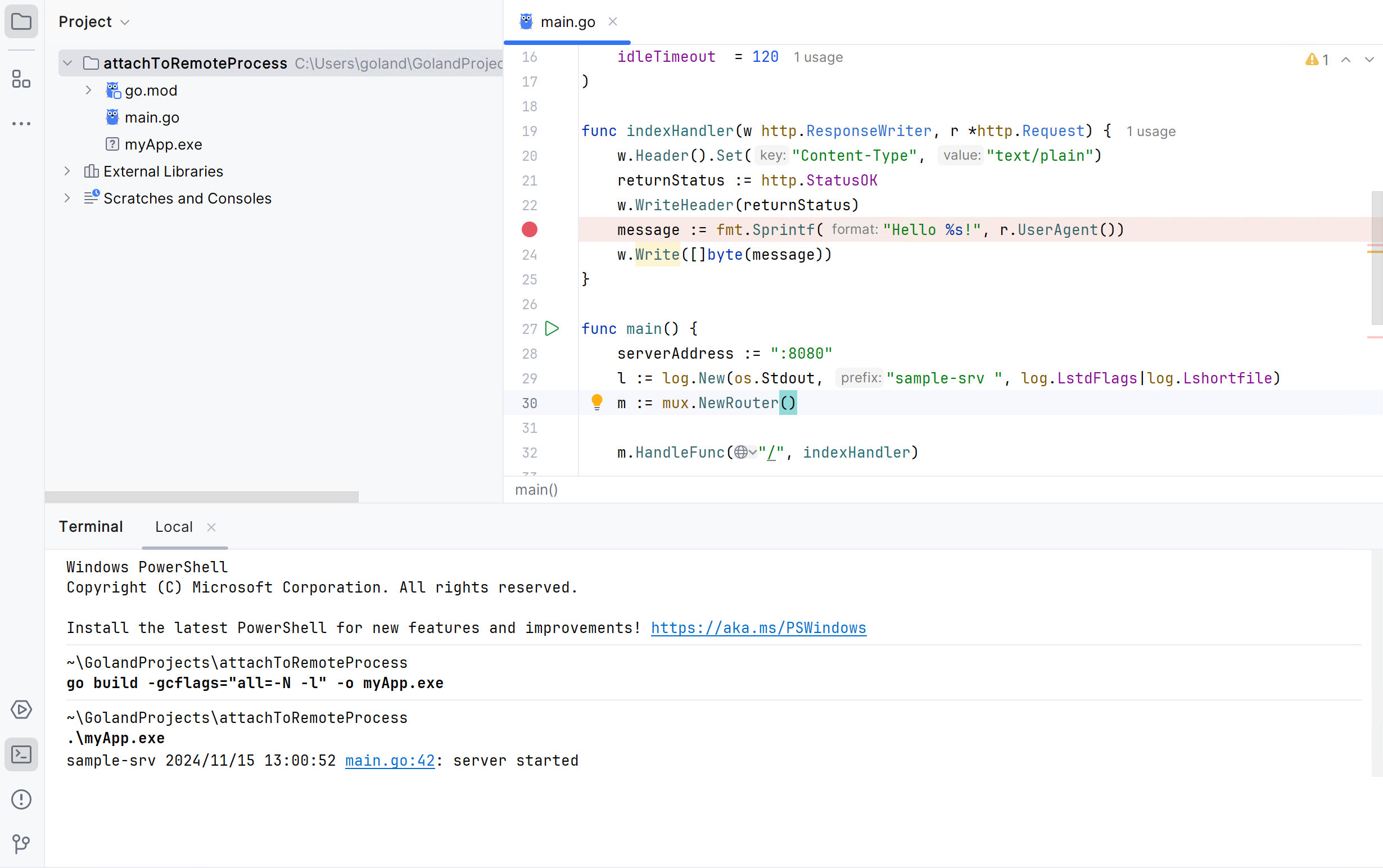
Open the Terminal tool window () and run the following command:
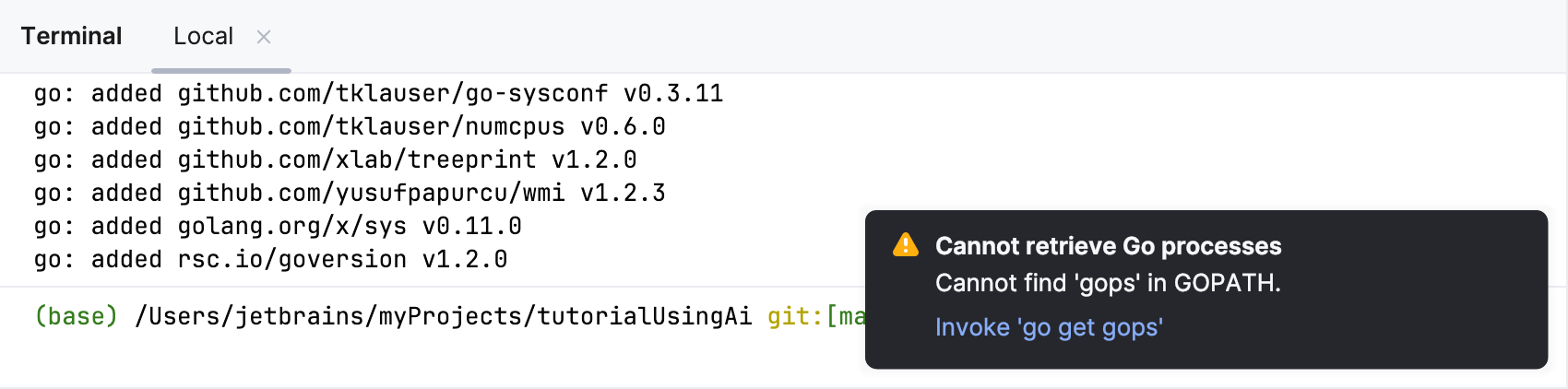
go install github.com/google/gops@latestClick (Ctrl+Alt+F5). In the notification window, click the Invoke 'go get gops' link.
Step 2. Build and run the application
Step 3. Attach to and debug the running process
Click the gutter next to the line of code where you want to set the breakpoint. In the provided example, place the breakpoint on the line 23 (
message := fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", r.UserAgent())). Read more about breakpoints in Breakpoints.Click or use the shortcut Ctrl+Alt+F5.
In the Attach with Debugger To window, select your application process and press Enter.
Trigger the event associated with the breakpoint in your application. If using the provided code example, open the http://localhost:8080/ link in a browser.
Attach to a process on a remote machine
You can connect to a remote computer and attach the debugger to the Go process running on it. The remote debugger (Delve) must be running on the remote computer.
To install Delve, you can use the following command:
Step 1. Build the application on the remote computer
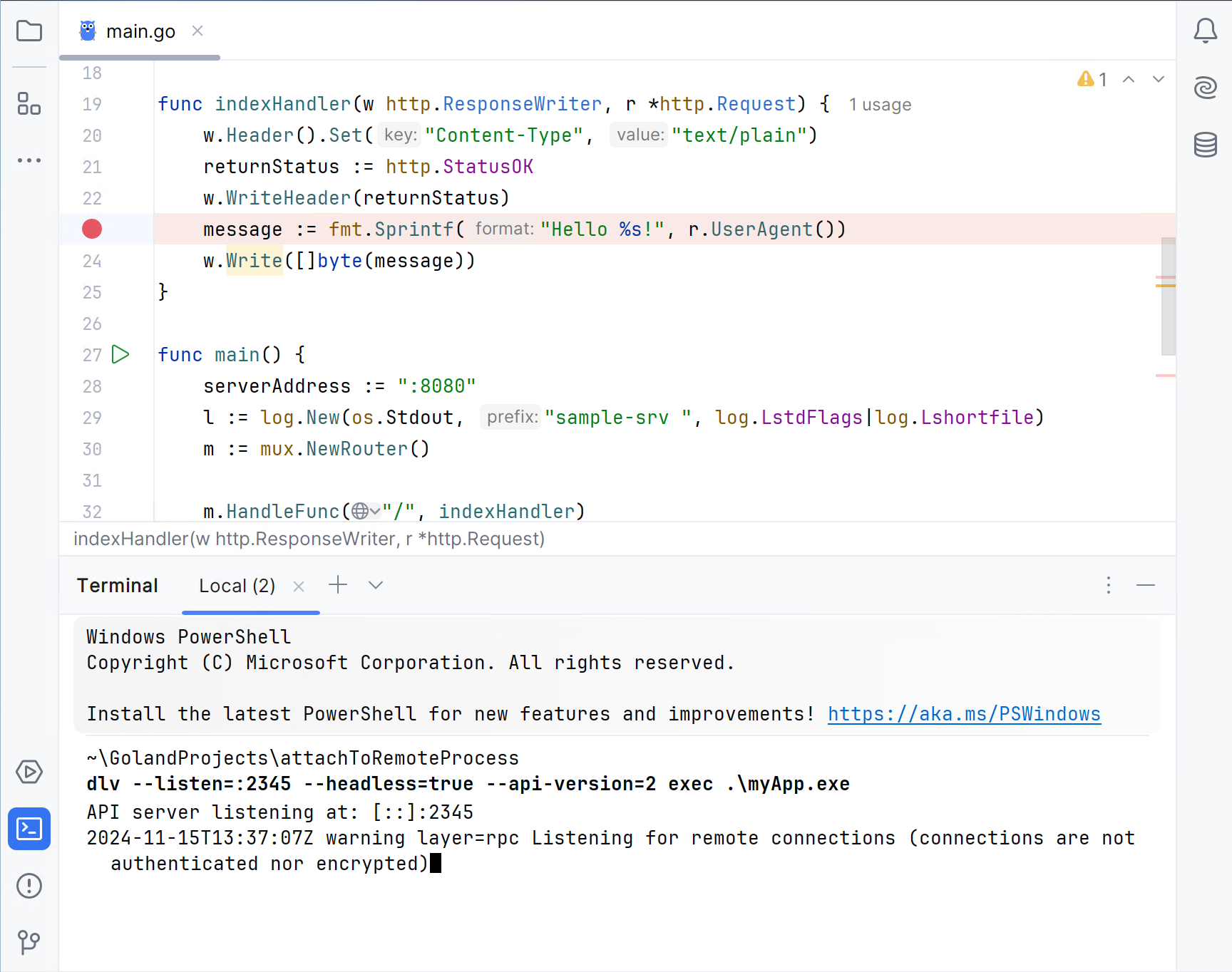
Open the Terminal tool window () and run the following command:
go build -gcflags="all=-N -l" -o myApp.exeThis command compiles the
myApp.exeexecutable and disables compiler optimizations and inlining.
Step 2. Run Delve on the remote machine
You have two options to launch the debugger on the host machine:
The debugger runs the process for you. If you use a firewall, expose the port that is used in the configuration (for example,
2345). You can use any port number that is not occupied.myAppis the name of the executable that was built on Step 1.dlv --listen=:2345 --headless=true --api-version=2 exec ./myAppIf you need to pass arguments to the binary as-is, add the double dash sign (
--) to the previous command and then necessary options (for example,-- --config=/path/to/config/file).You run the process, and the debugger attaches to the running process.
<PID>is the process identifier of your application. You can get the process identifier by using the Attach to Process command.dlv --listen=:2345 --headless=true --api-version=2 attach <PID>
Step 3. Start the debugging process on your local computer
Open the code of your application and place a breakpoint. In the provided code example, set the breakpoint on line 23 (
message := fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", r.UserAgent())). Read more about breakpoints in Breakpoints.Click . Alternatively, click the list of run/debug configurations on the toolbar and select Edit Configurations.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click the Add button (
) and select Go Remote.
In the Host field, type the host IP address (for example,
localhostor192.168.1.33).In the Port field, type the debugger port that you configured on Step 2 (for example,
2345).Click Debug.
Trigger the event at the breakpoint in your application. If you used the provided code example, open the
http://<host_address>:8080/link in a browser.On the following video, there are two IDE instances: the IDE using the dark theme is the local computer, and the IDE with the light theme is a remote computer.
Attach to a process in the Docker container
You can attach the debugger to a Go process that runs inside a Docker container. For more information about Docker, refer to Docker.
For example purposes, you can use the following Dockerfile for this Go application.
Step 1. Create a Dockerfile configuration
Click . Alternatively, click the list of run/debug configurations on the toolbar and select Edit Configurations.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click the Add button (
) and select .
In the Dockerfile field, click the Browse icon (
) and navigate to Dockerfile in the file browser. If you use the example from this section, navigate to this Dockerfile.
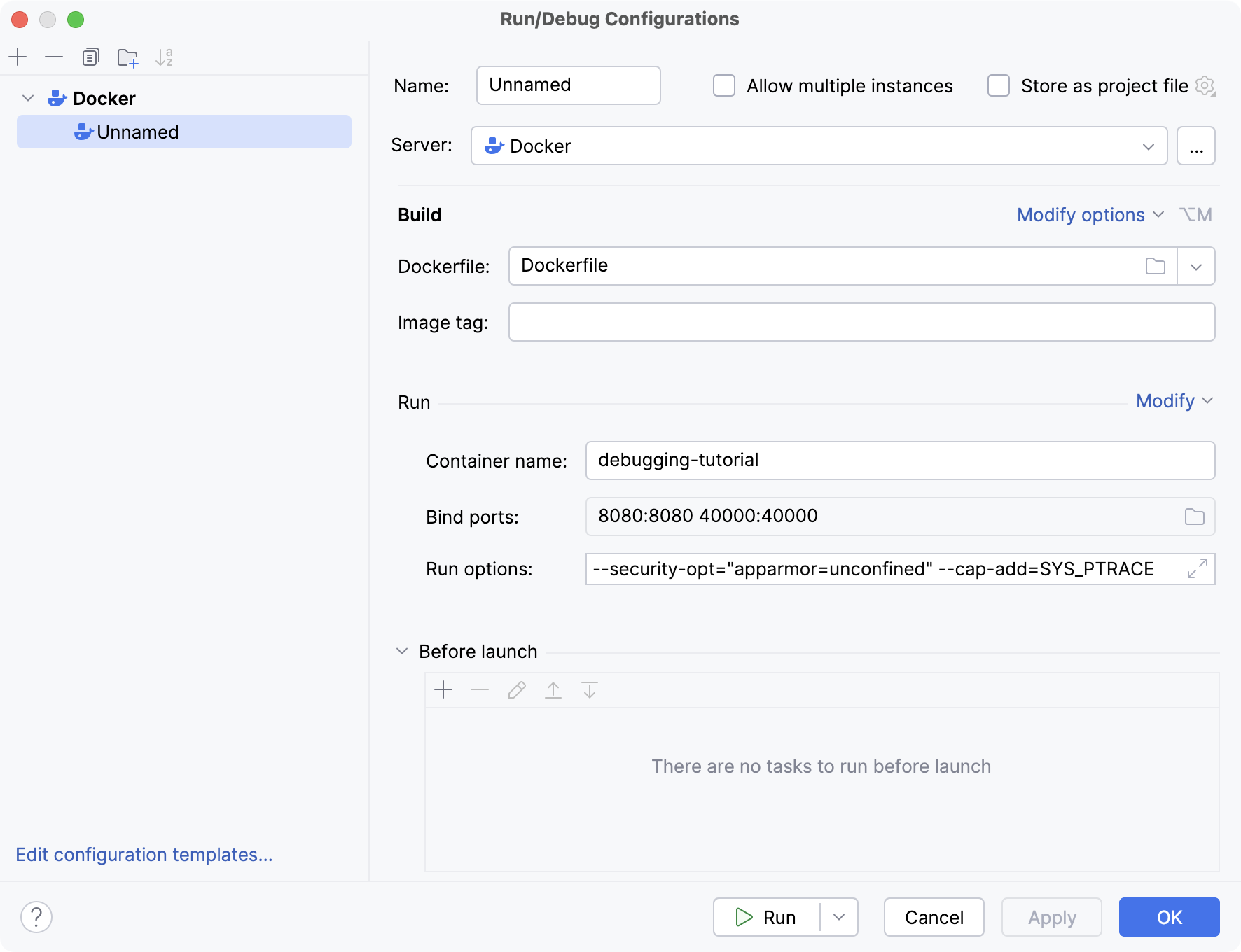
In the Container name field, type the container name (for example,
debugging-tutorial.In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click Modify and select Bind ports and Run options.
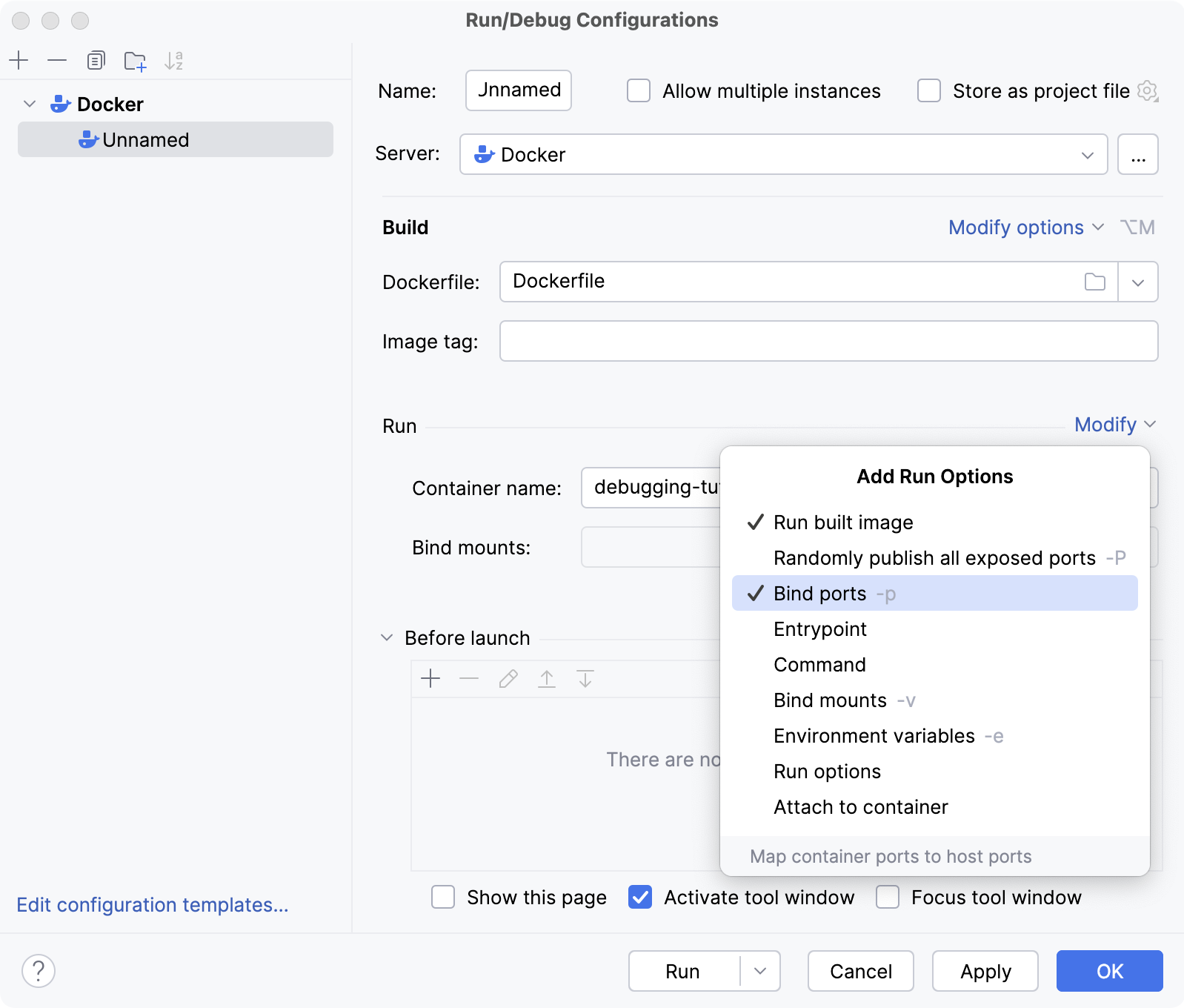
In the Bind ports field, click Browse (
).
In the Port Bindings dialog, click the Add button (
). In the Host port column, type
8080. Click the Container port column, type8080. Additionally, create the same binding for the port40000.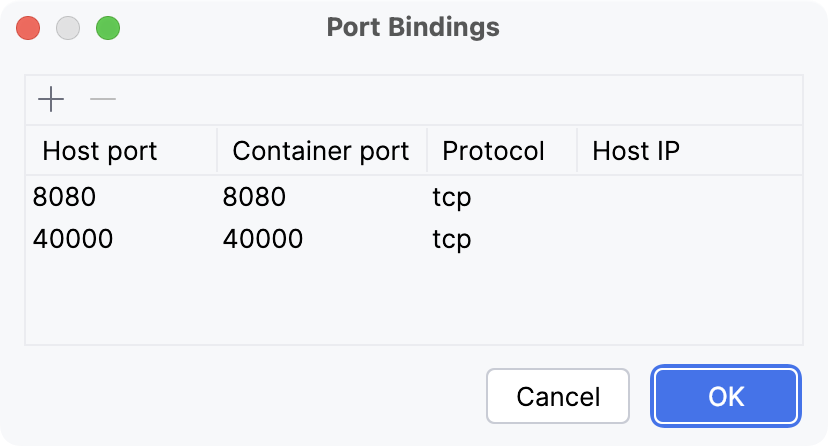
In the Run options field, specify command-line options for Docker. For the example provided in the Dockerfile, disable the security profile and add the
SYS_PTRACELinux capability.--security-opt="apparmor=unconfined" --cap-add=SYS_PTRACEClick Run.
Step 2. Create the Go Remote run/debug configuration
Click . Alternatively, click the list of run/debug configurations on the toolbar and select Edit Configurations.
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, click the Add button (
) and select Go Remote.
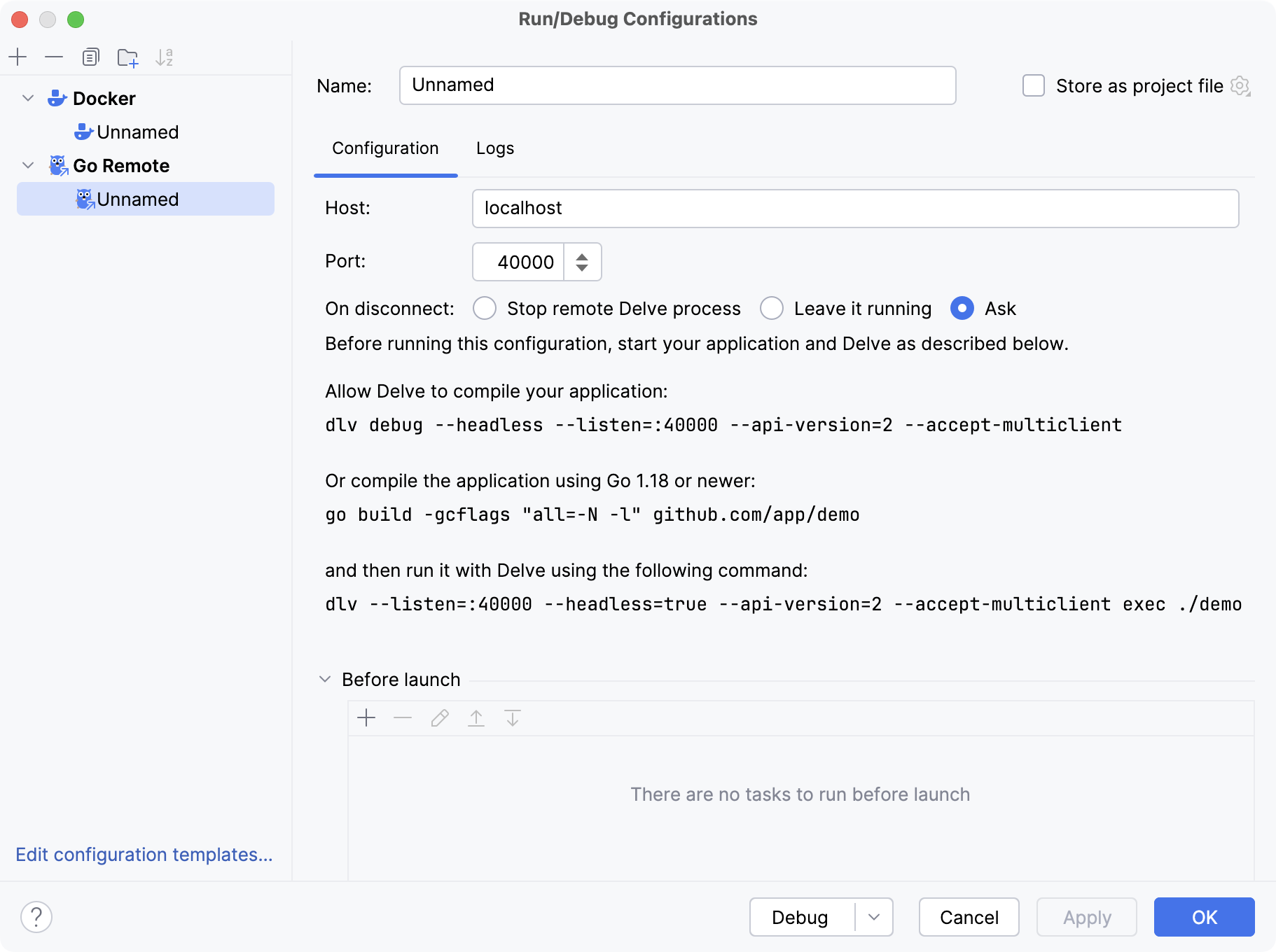
In the Host field, type the host IP address (for example,
localhost).In the Port field, type the debugger port that you configured. In this example, it is
40000.Click OK.
Step 3. Start the debugging process
In the Services tool window (), expand . Ensure that the created container is running and listens to the preconfigured debugger port.
Click the gutter near the line of code to place the breakpoint. For example, in the provided code example, put the breakpoint on the line 23 (
message := fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s!", r.UserAgent())).Read more about breakpoints in Breakpoints.
From the list of run/debug configurations on the toolbar, select the created Go Remote configuration and click the Debug <configuration_name> button (
). Alternatively, press Alt+Shift+F9 to select the created Go Remote configuration.
Trigger the event at the breakpoint in your application. If you used the provided code example, open http://localhost:8080/ in a browser.
The following video demonstrates how to run a container, create a remote run/debug configuration, and connect to the container for debugging.
Productivity tips
Terminate the remote process
You can press Ctrl+F2 to terminate the remote process during the remote debugging session. Note that you cannot reattach to the process when you terminated it.