SAML 2.0 Auth Module
A SAML 2.0 authentication module lets you configure Hub as a SAML Service Provider (SAML SP). SAML supports single sign-on (SSO) across multiple domains.
When you enable an SAML 2.0 authentication module in Hub:
Your users log in to Hub with the credentials that are managed in a specified third-party identity provider (SAML IdP).
Your Hub users have fewer accounts and passwords to remember.
New users with accounts in the connected service can create their own accounts in Hub.
Hub can also be set up as a SAML IdP. However, the instructions for the identity provider setup are not described here. To learn how to use Hub as a SAML IdP, see SAML 2.0.
IdP-initiated SSO
The SAML 2.0 authentication module supports both service-provider (SP) and identity-provider (IdP) initiation for single sign-on (SSO). The login request is based on how the user signs in to Hub.
If the user signs in through an external login portal or access management provider (for example, OneLogin), the request is initiated by the IdP.
If the user signs in by clicking the button for the IdP on the Hub login page, Hub initiates the request as SP.
To support this behavior, the RelayState parameter for your SAML IdP can either be empty or a URL with the same hostname as the hostname of the service's home URL. If you set another value for this parameter in the configuration for your IdP, the redirection to the internal Hub service results in a Can't restore state error.
Add a SAML 2.0 Authentication Module
To add a SAML 2.0 authentication module to your Hub installation, follow these instructions. When finished, users will be able to log in to Hub using accounts that are managed in the connected SAML identity provider.
To add a SAML 2.0 Authentication module:
In a service that you plan to use as a SAML identity provider for Hub, retrieve its parameters as the IdP.
If the IdP service does not provide a fingerprint of their certificate, create it applying SHA256. For example, you can use SAML Tool
In Hub, click the Auth Modules link in the main navigation menu.
Click the New module button.
In the Select an identity provider dialog, select SAML 2.0 from the list.
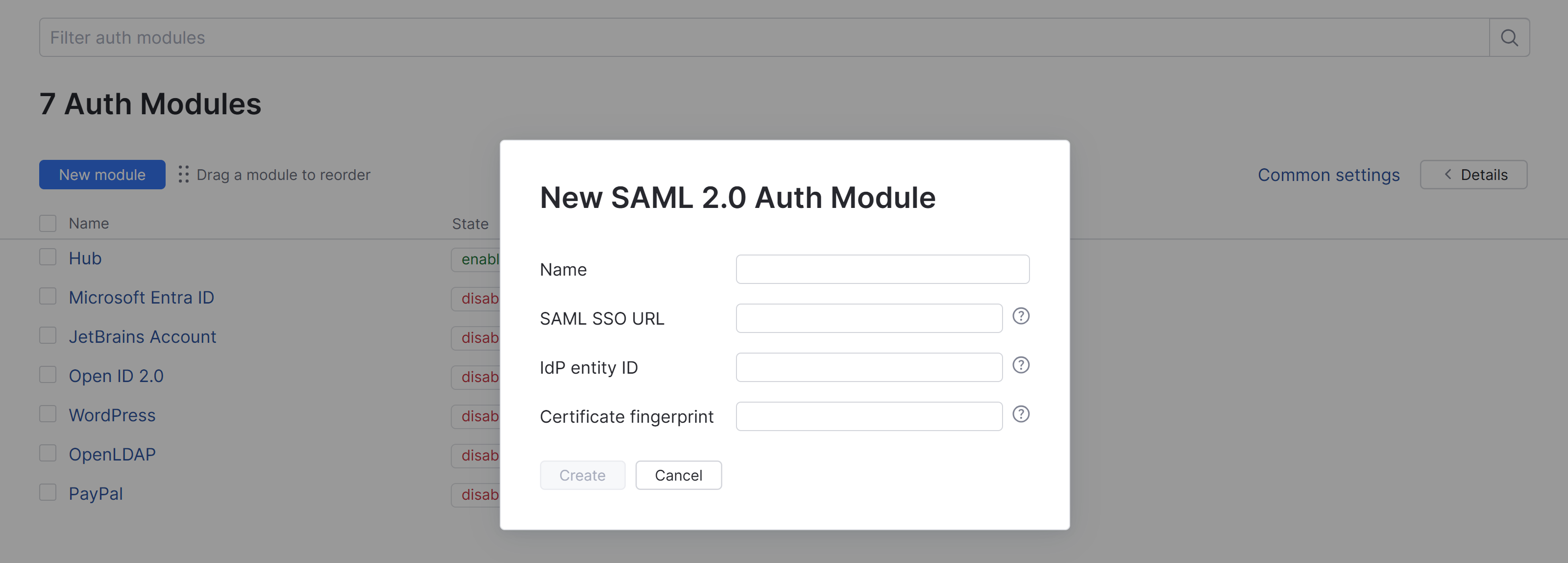
In the dialog, specify the parameters for the IdP service, then click the Create button.
The SAML 2.0 authentication module is created.
Configure the auth module by providing the names of the SAML attributes for user accounts in the Attributes section of the page.
To complete the setup:
Configure the optional settings for the authentication module. For more information, see Additional Settings.
Click the Save button to apply the settings.
Click the Enable button.
The SAML 2.0 authentication module is enabled.
The icon stored in the Button image setting is added to the login dialog window. Users can click this icon to log in to Hub with their SAML credentials.
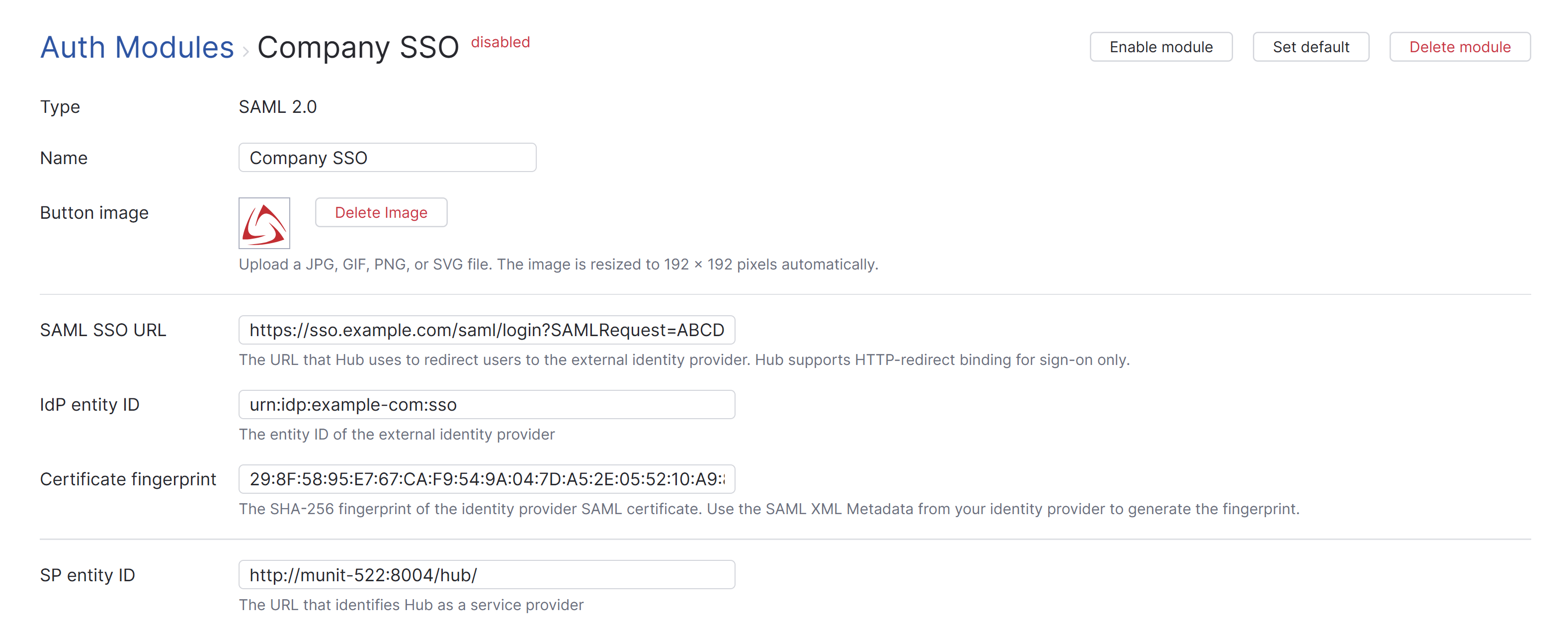
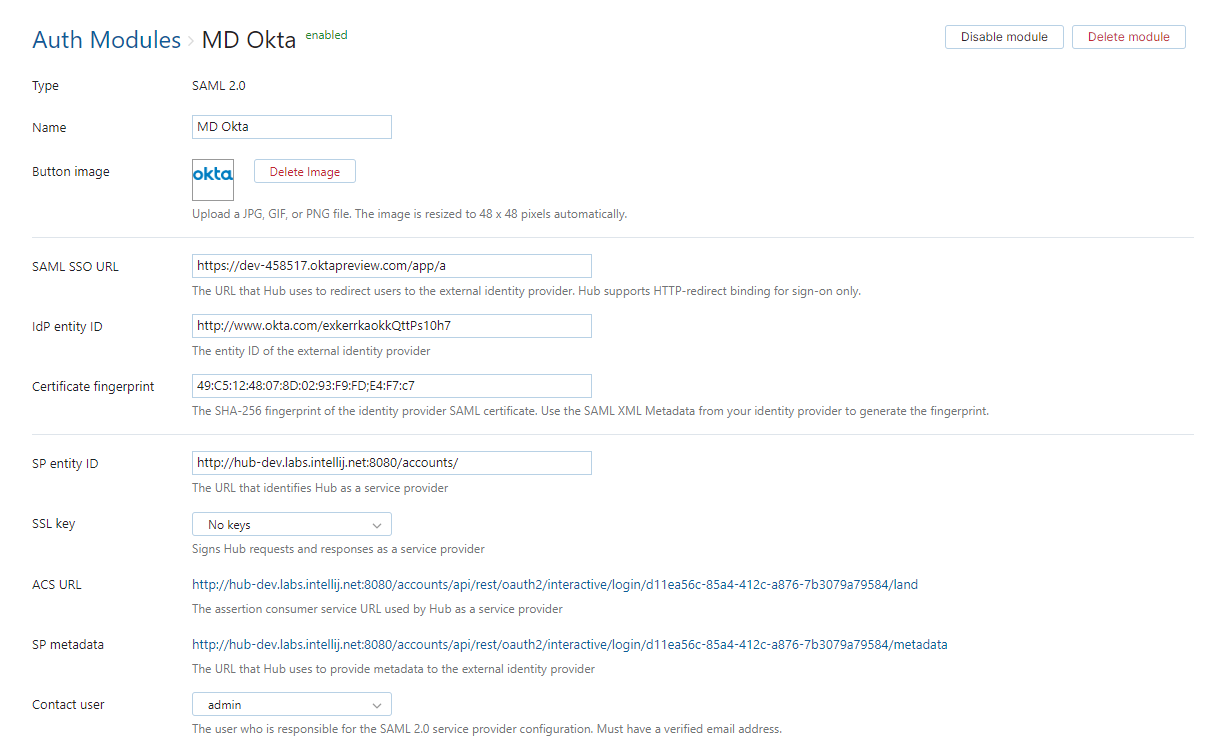
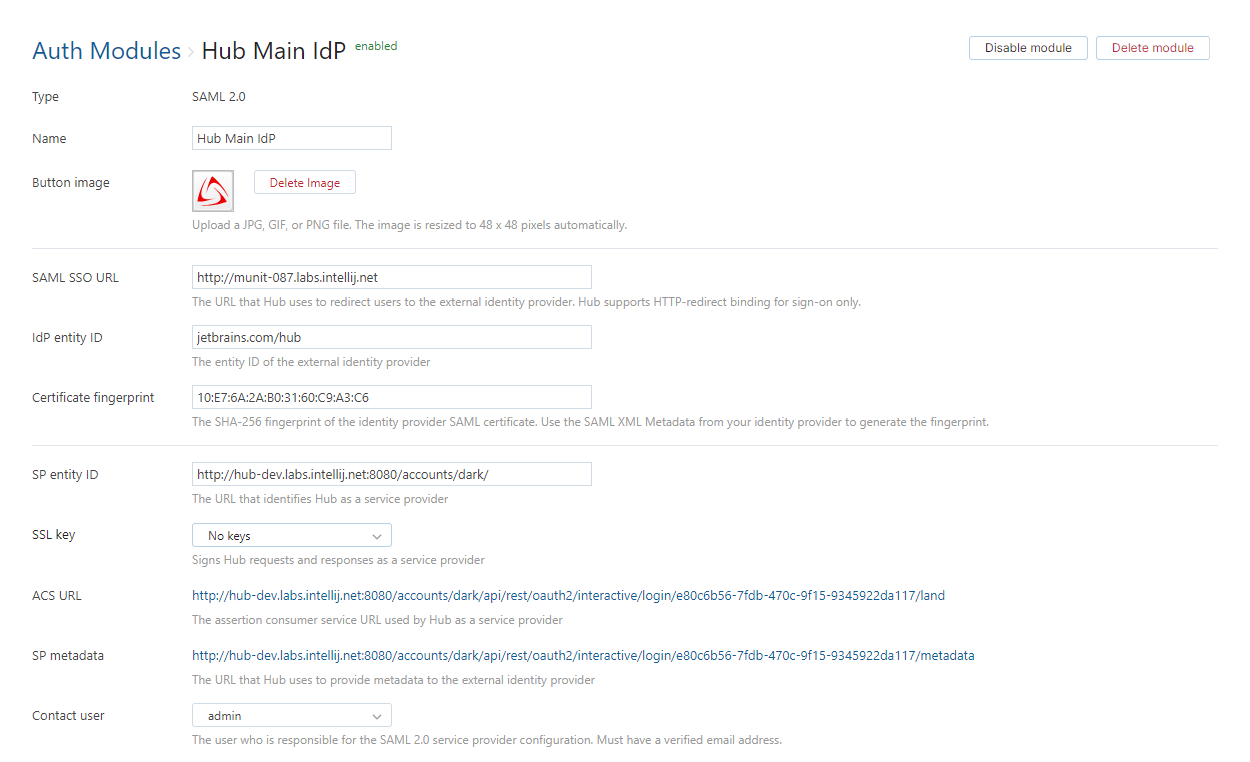
General Settings
The first section of the page displays settings that identify the authentication module and let you manage the connection to the SAML service.
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Type | Displays the type of service that is enabled for authentication in Hub. Built-in Authorization means that this module is a part of Hub and is not installed separately. |
Name | Stores the name of the authentication module. Use this setting to distinguish this module from other authentication modules in the Auth Modules list. |
Button image | Displays the image used for the button that a user clicks to log in to Hub with their account in the connected authorization service. You can upload a JPG, GIF, or PNG file. The image is resized to 48 x 48 pixels automatically. |
SAML SSO URL | The URL that Hub uses to redirect to the external identity provider. Hub only supports HTTP-redirect binding for sign-on. |
IdP entity ID | The entity ID of the external identity provider. |
Certificate fingerprint | The SHA-256 fingerprint of the identity provider SAML certificate. Use the SAML XML Metadata from your identity provider to generate the fingerprint. |
SP entity ID | The URL that identifies Hub as a service provider. |
SSL key | Selects an SSL key that can be used to verify the identity of your Hub installation to the authentication service. When used, all requests that are sent to the identity provider from Hub are signed using the corresponding SSL certificate. This list displays only keystores that have been imported into Hub. For more information, see SSL Keys. |
ACS URL | The assertion consumer service URL used by Hub as a service provider. |
SP metadata | The URL that Hub uses to provide metadata to the external identity provider. |
Contact user | The user who is responsible for the SAML 2.0 service provider configuration. The email address associated with this user account must be verified in Hub. |
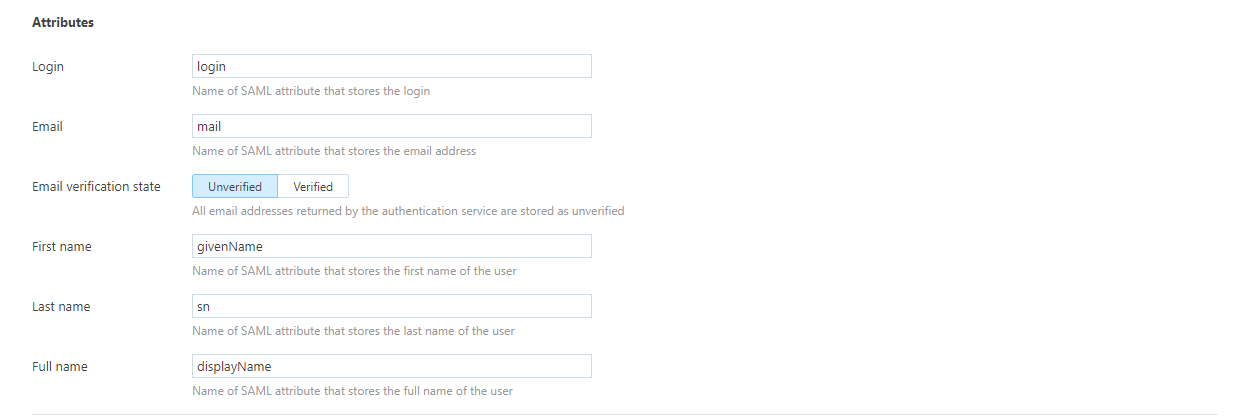
Attribute Mapping Settings
Settings in the Attributes section of the page let you map attributes for user accounts in the SAML service to fields that are stored in Hub accounts.
Option | Description |
|---|---|
Username | The name of the SAML attribute that stores the username. |
The name of the SAML attribute that stores the email address. | |
First name | The name of the SAML attribute that stores the first name of the user. |
Last name | The name of the SAML attribute that stores the last name of the user. |
Full name | The name of the SAML attribute that stores the full name of the user. |
Groups | Maps to the attribute that stores group membership assignments in the connected authorization service. When this value is specified, you can map and sync group memberships in the authorization service with corresponding groups in Hub. For details, see Group Mappings. |
Additional Settings
The following options are located at the bottom of the page. Use these settings to manage Hub account creation and group membership and to reduce the loss of processing resources consumed by idle connections.
Option | Description |
|---|---|
User creation | Enables creation of Hub accounts for unregistered users who log in with an account that is stored in the connected authorization service. Hub uses the email address to determine whether the user has an existing account. |
Email auto-verification | Determines how Hub sets the verification status of an email address when the authentication service does not return a value for this attribute. |
Auto-join groups | Adds users to a group when they log in with an account that is stored in the connected authorization service. You can select one or more groups. New users that auto-join a group inherit all the permissions assigned to this group. We recommend that you add users to at least one group. Otherwise, a new user is only granted the permissions that are currently assigned to the All Users group. |
Connection timeout | Sets the period of time to wait to establish a connection to the authorization service. The default setting is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds). |
Read timeout | Sets the period of time to wait to read and retrieve user profile data from the authorization service. The default setting is 5000 milliseconds (5 seconds). |
Audit | Links to the Audit Events page in Hub. There, you can view a list of changes that were applied to this authentication module. |
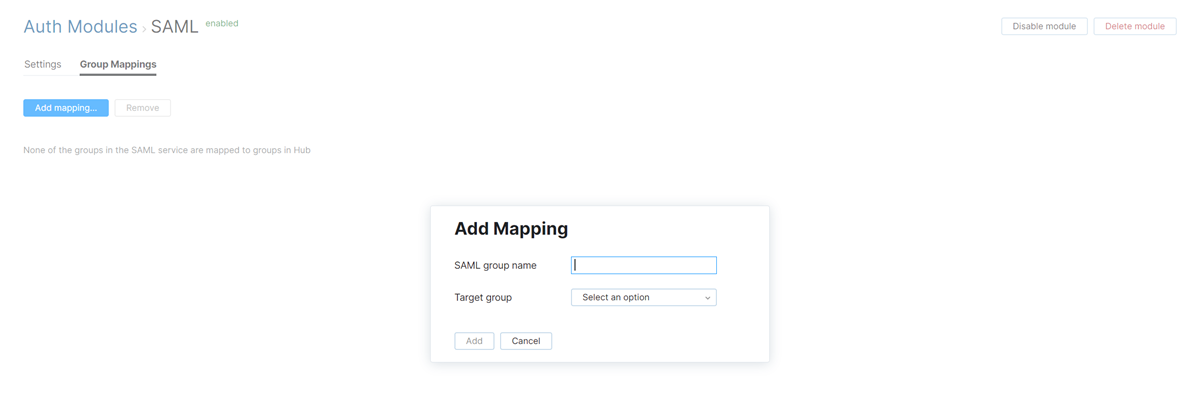
Group Mappings
On the Group Mappings tab, you can map existing groups in the SAML service to the groups in Hub.

If you want to map groups in the SAML service to groups in Hub, you need to specify the Groups attribute that stores SAML group memberships in the Attributes section of the settings for this auth module.
When group mappings are configured, Hub checks for group memberships when users log in with accounts that are managed in the SAML service. Hub performs the following operations for each group from the SAML service that is mapped to a Hub group:
Users who are members of a mapped SAML group and are not members of the mapped Hub group are added to the group in Hub.
Users who are not members of a mapped SAML group and are members of the mapped Hub group are removed from the group in Hub.
Changes to group memberships in the authorization service are only applied in Hub when users log in using their accounts from the SAML service.
You can map multiple groups from the SAML service to a single target group in Hub. You can't map groups from the SAML service to more than one Hub group.
To map a group from the SAML service to a group in Hub:
SCIM Provisioning
SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) automates the provisioning and deprovisioning of user accounts and groups, ensuring your identity provider stays in sync with your application. This reduces manual account management, improves security by promptly removing access when users leave, and ensures accurate, up-to-date user data across systems.
Hub supports SCIM 2.0 to automate user and group provisioning alongside your SAML SSO setup. When configured, the SAML authentication module lets users log in to Hub, and SCIM provisioning keeps Hub accounts in sync with the identity provider.
SCIM 2.0 support is available by default in Hub. To enable SCIM provisioning, store the following information in the SCIM provisioning settings for your IdP:
The SCIM endpoint URL for your Hub installation. This endpoint is:
<hub-base-url>/api/rest/scim2To locate the base URL for your Hub site, refer to the Settings tab on the Services page for the Hub service. If the Base URLs setting is empty, use the Home URL. For additional information, see Settings.
Authentication credentials in the form of a permanent token. To learn how to generate a permanent token for your Hub account, see Manage Permanent Tokens
Actions
The following actions are available in the header:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Set default | Designates the authentication module as the default for your installation. Only one authentication module can be set as the default at any time. If another module is currently set as the default, that state is cleared. This option is only shown when the current authentication module is not designated as the default. |
Clear default | Removes the authentication module as the default for your installation. If none of the available authentication modules are designated as the default, unauthenticated users are always directed to the Hub login page. This option is only shown when the current authentication module is designated as the default. |
Disable module | Disables the authentication module. This option is only shown when the authentication module is currently enabled. |
Enable module | Enables the authentication module. This option is only shown when the authentication module is currently disabled. |
Delete module | Removes the authentication module from Hub. Use only when you have configured additional authentication modules that let users log into your Hub installation. |
Sample Configurations
The following sample configurations show you how to use the SAML 2.0 authentication module to support different user management scenarios.
Okta as SAML Identity Provider for Hub
Due to a "URL Loop" in both applications' setup processes, a non-straightforward process is required to configure Okta as a SAML IdP in Hub. Setting up an Auth Module in Hub requires a unique URL from the IdP, and creating an IdP URL in Okta requires a unique URL from the SAML SP, Hub. You must create an application in Okta with a fake URL for YouTrack to generate the IdP URL, then you create an auth module in Hub to generate the SP URL that can be used in the Okta application.
Okta supports two protocols for handling federated single sign-on, both of which are supported for authentication with Hub.
The setup described here uses the SAML protocol. The settings for this module are preconfigured for generic connections with various SAML providers. Additional configuration for SAML authentication with Okta is required.
The Okta Auth Module supports the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol. The settings for this module are preconfigured to support direct connections with the Okta service. With this module, you need to register Hub as a client application in Okta, but everything else is relatively easy to set up.
Your choice of protocol depends mainly on your use case, but OIDC is generally recommended for new integrations.
To use Okta as IdP for Hub:
In Okta, create a new application for Hub service. Use any URLs for Hub as the SP. You need to correct it later. See the Okta documentation for setting up SAML application.
When you create the application, click the View Setup Instructions button to open a page with the parameters of your Okta IdP:
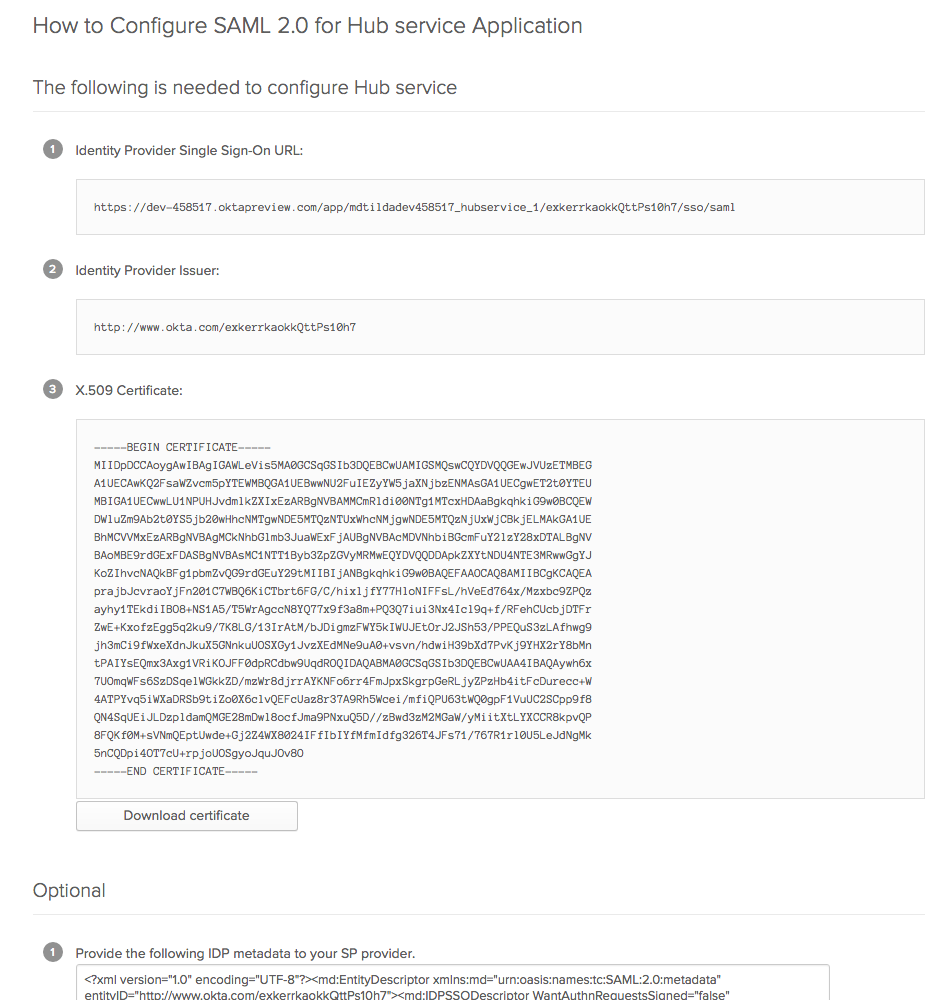
Download the certificate of your Okta IdP.
Create a fingerprint for the Okta certificate applying SHA256. For example, you can use SAML Developer Tools.
In Hub, open the page.
Click the New module button, then select SAML2.0 in the drop-down list.
A New SAML 2.0 Auth Module dialog opens.
In the displayed dialog, specify the parameters of your Okta IdP, then click the Create button.
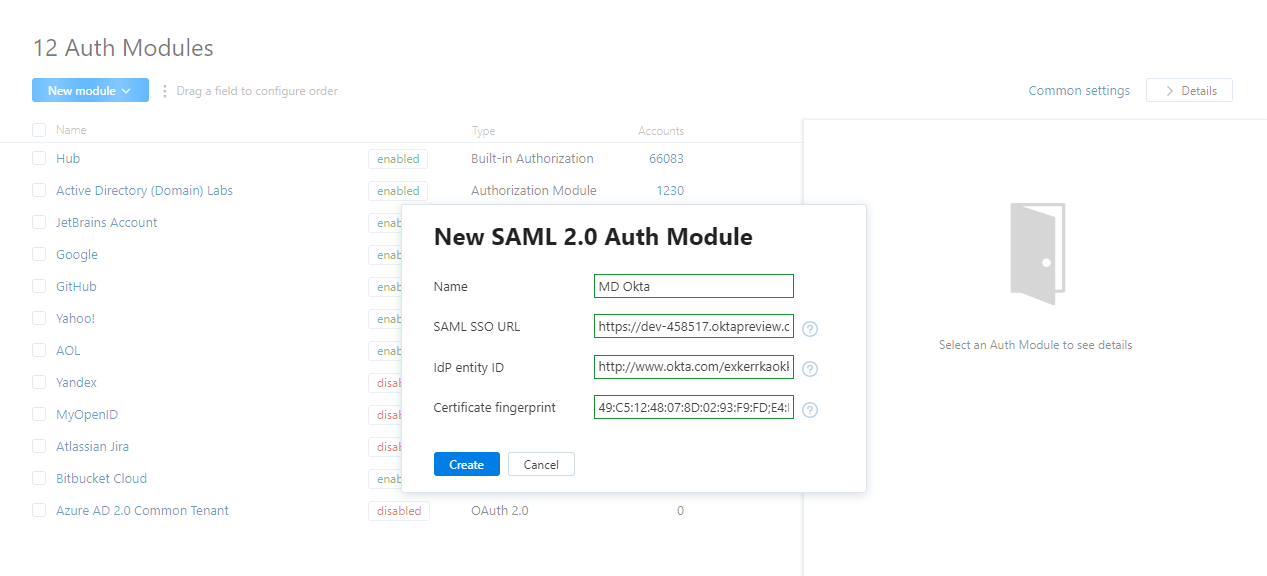
Configure the new module: Set up the SAML attributes.
Switch back to Okta. Edit the Hub application by storing the URLs that are generated during the creation of the authentication module. The settings in Okta should be configured as follows:
Setting
Description
Single Sign On Url
Enter the ACS URL from the authentication module in Hub.
Use this for recipient and destination URL
Enable this option.
Audience URI
Enter the SP entity ID from the authentication module in Hub.
Assign the Hub application to groups and users that should be able to log in to Hub with Okta credentials.
That's it. Now the users can log in to Hub and connected services with their Okta credentials.
Hub as SAML Identity Provider for Another Hub Service
If you have two Hub services, you can use one of them as a SAML Identity Provider and another one as the service provider.
In the Hub installation that you use as the SAML IdP, open the page.
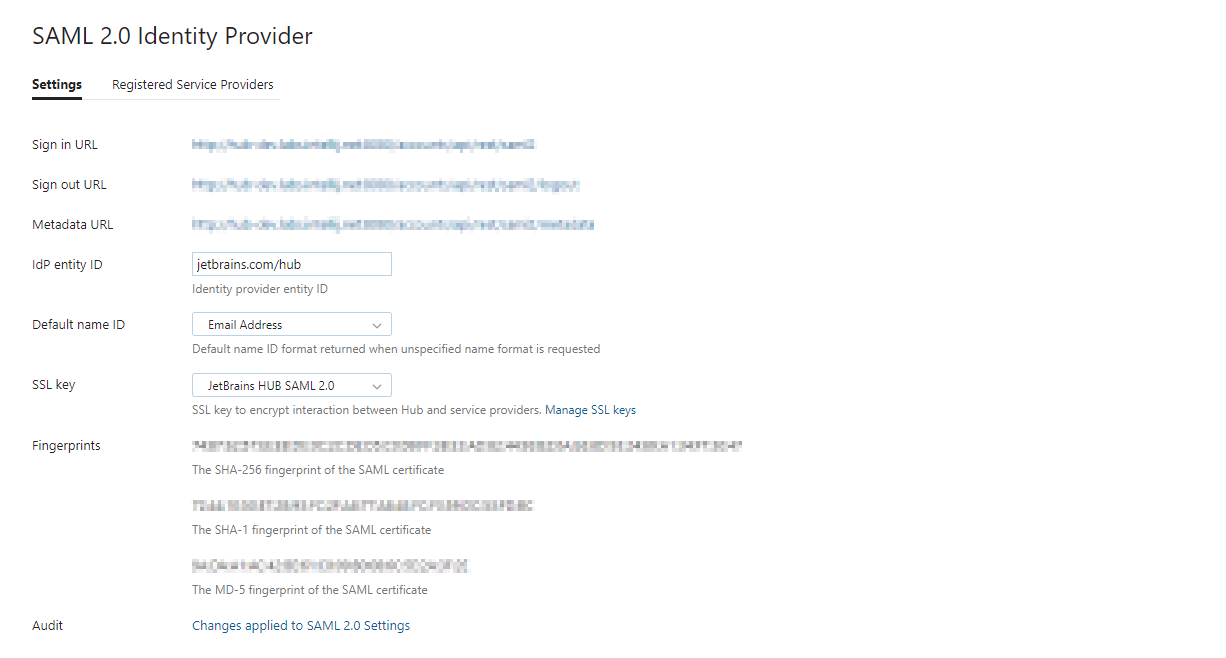
For details about Hub as a SAML 2.0 Identity Provider, see SAML 2.0 Identity Provider Parameters.
In the Hub installation that you use as the SAML service provider, open the Auth Modules page.
Click the New module button, then select SAML2.0.
A New SAML 2.0 Auth Module dialog opens.
In the dialog, enter the parameters of the Hub service that you use as IdP:
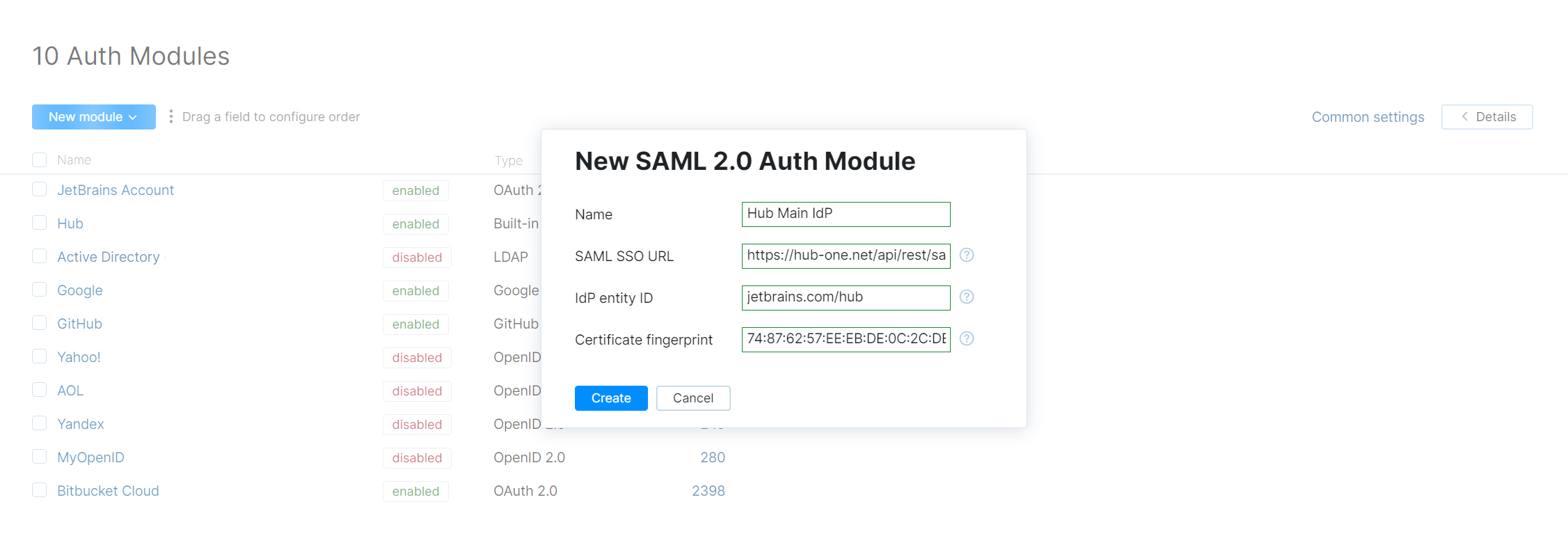
Click the Create button.
The new module is created. You are navigated to the settings page for the new module:
Configure SAML attributes:
In the Hub service that you are using as IdP, open the SAML 2.0 page from the Access Management section of the Administration menu, select the Registered Service Providers tab, then click the New service provider button.
Register the second Hub service as the SAML service provider:
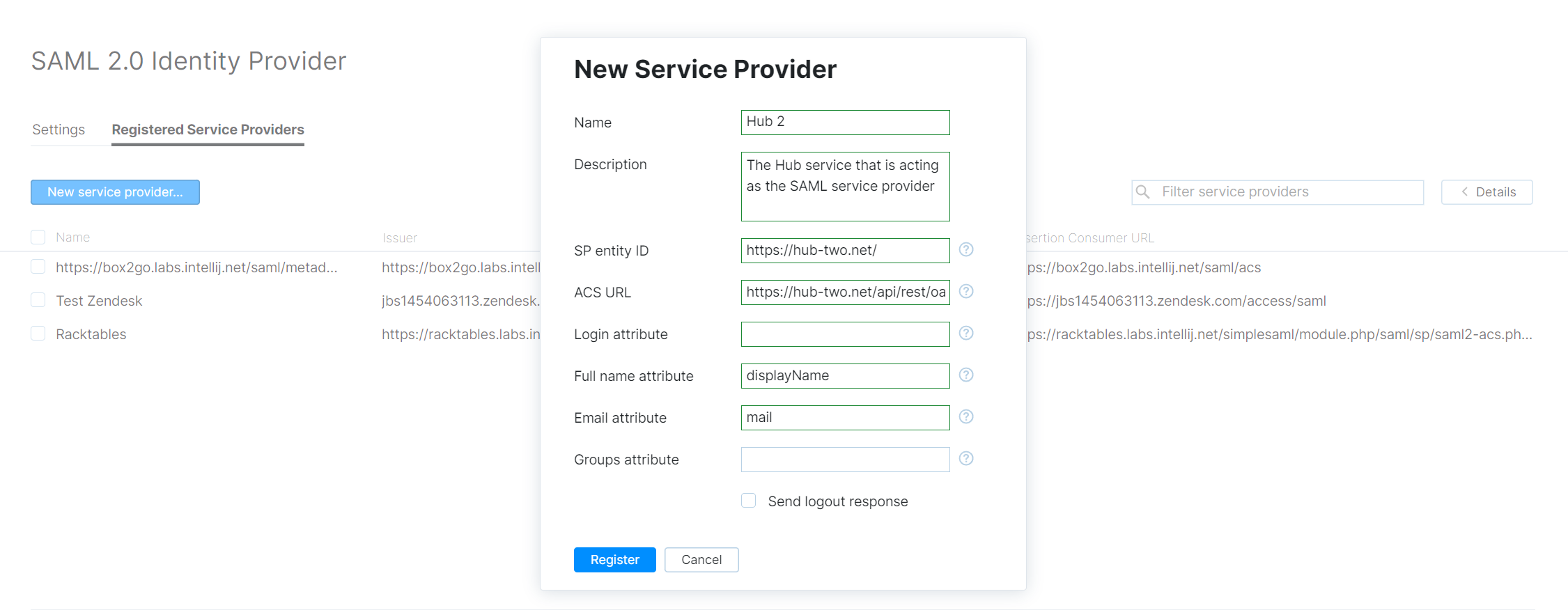
To register the service provider, enter the same values that are currently stored in the settings for the SAML 2.0 authentication module. For more details, see Register a Service Provider.
You are all set! Now your users can log into the Hub SP with the credentials from the Hub service that you use as SAML IdP.