Configure Big Data Tools environment
Before you start working with Big Data Tools, you need to install the required plugins and configure connections to servers.
Install the required plugins
Whatever you do in IntelliJ IDEA, you do it in a project. So, open an existing project () or create a new project ( ).
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Plugins | Marketplace.
Install the following plugins:
Big Data Tools
Scala
Also, check that the Python plugin is enabled. It should be installed by default for IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate.
Install the Big Data Tools plugin.
Restart the IDE. After the restart, the Big Data Tools tab appears in the rightmost group of the tool windows. Click it to open the Big Data Tools window.

Once the Big Data Tools support is enabled in the IDE, you can configure a connection to a Zeppelin, Spark, Google Storage, and S3 server. You can connect to HDFS, WebHDFS, AWS S3, and a local drive using config files and URI.
Configure a server connection
In the Big Data Tools window, click
 and select the server type. The Big Data Tools Connection dialog opens.
and select the server type. The Big Data Tools Connection dialog opens.In the Big Data Tools Connection dialog, specify the following parameters depending on the server type:
File Systems: FS | Local, FS | HDFS
Storages: AWS S3, Minio, Linode, Digital Open Spaces, GS, Azure
Monitoring: Spark, Hadoop
Notebooks: Zeppelin

Mandatory parameters:
Root path: a path to the root directory.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
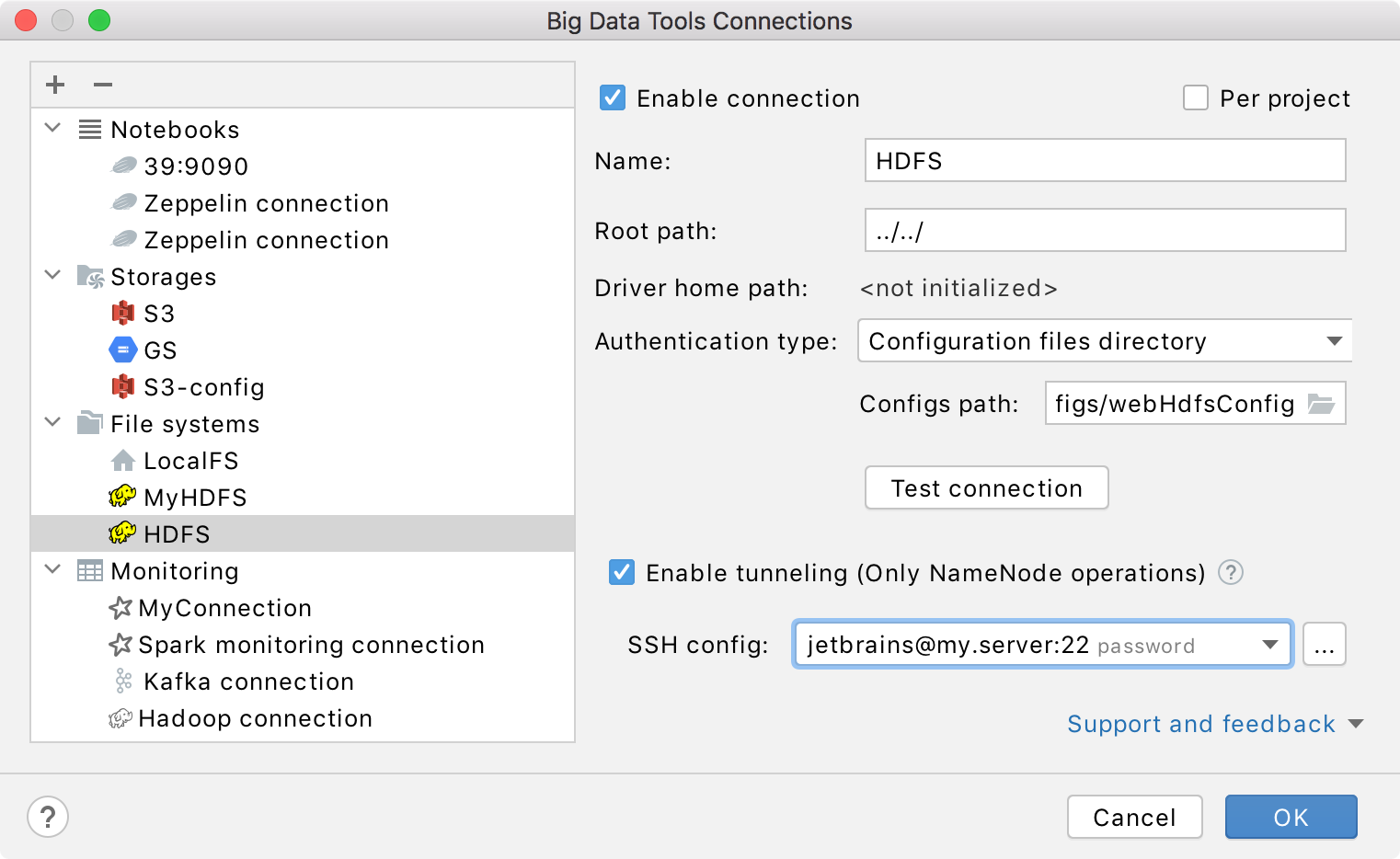
Mandatory parameters:
Root path: a path to the root directory on the target server.
When the connection is successfully established the Driver home path field shows the target IP address of connection including a port number. Example: hdfs://127.0.0.1:65224/.
Config path a path to the HDFS configuration files directory. See the samples of configuration files.
File system URI an explicit uri of an HDFS server. Once you select this option, you need to specify the file system URI, for example localhost:9000 and a username to connect.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Enable tunneling (Only NameNode operation). Creates an SSH tunnel to the remote host. It can be useful if the target server is in a private network but an SSH connection to the host in the network is available. SSH tunneling currently works only for operators with the following name nodes: list files, get meta info
Select the checkbox and specify a configuration of an SSH connection (press ... to create a new SSH configuration).
Note that the Big Data Tools plugin uses the
HADOOP_USER_NAMEenv variable to login to the server. It this variable is not defined then theuser.nameproperty is used.See more examples of the Hadoop File System configuration files.
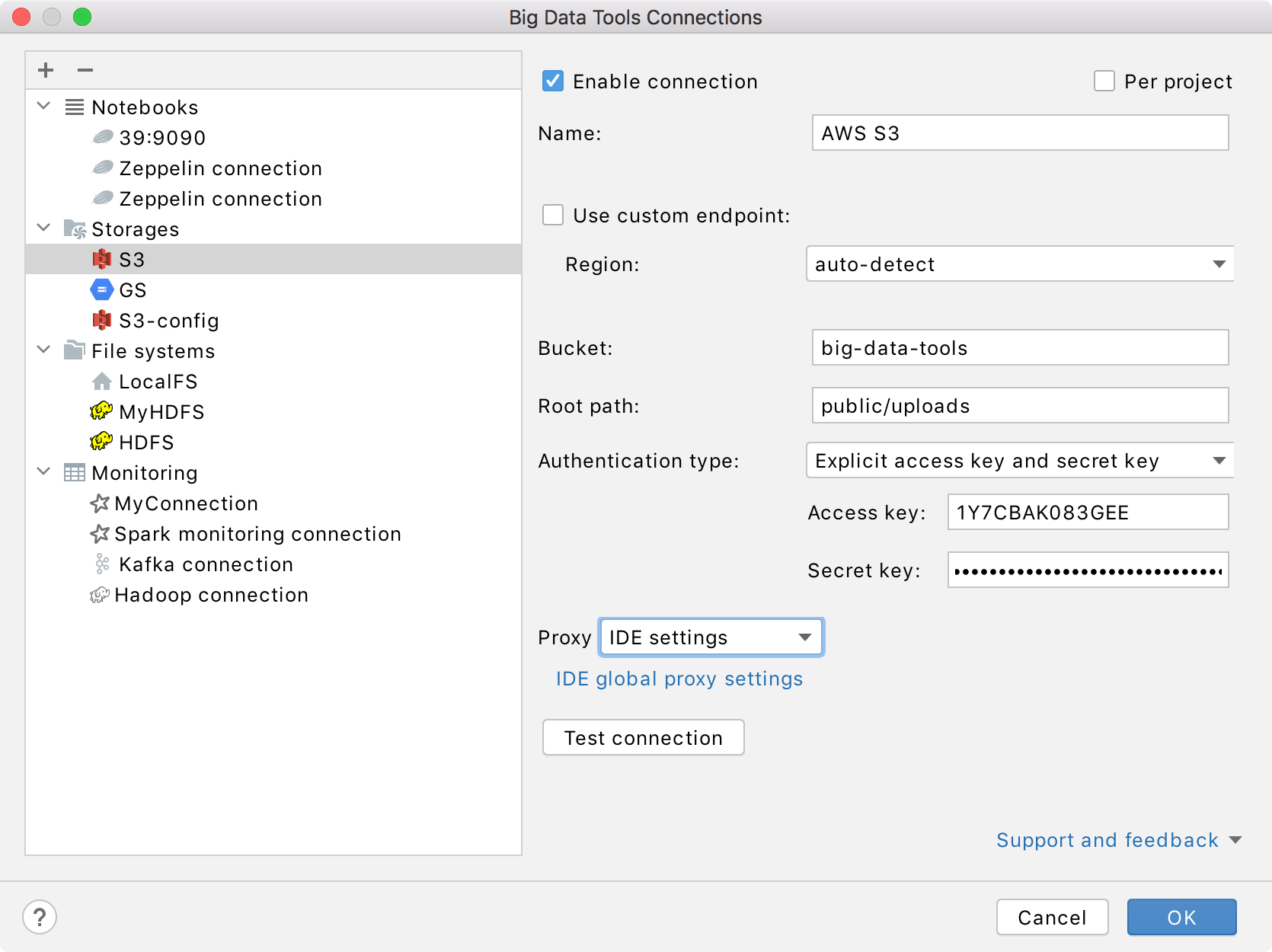
Mandatory parameters:
Bucket: a globally unique Amazon S3 bucket name.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Region: an AWS region of the specified bucket. You can select one from the list or let IntelliJ IDEA to auto detect it.
Root path: a path to the root directory in the specified bucket.
Authentication type: the authentication method. You can use your AWS account credentials (by default), or opt to entering the access and secret keys.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Use custom endpoint: select if you want to specify a custom endpoint and a signing region.
Proxy: select if you want to use IDE proxy settings or if you want to specify custom proxy settings. When configuring custom proxy settings, you can specify NTLM proxy options and enable proxy authentication.
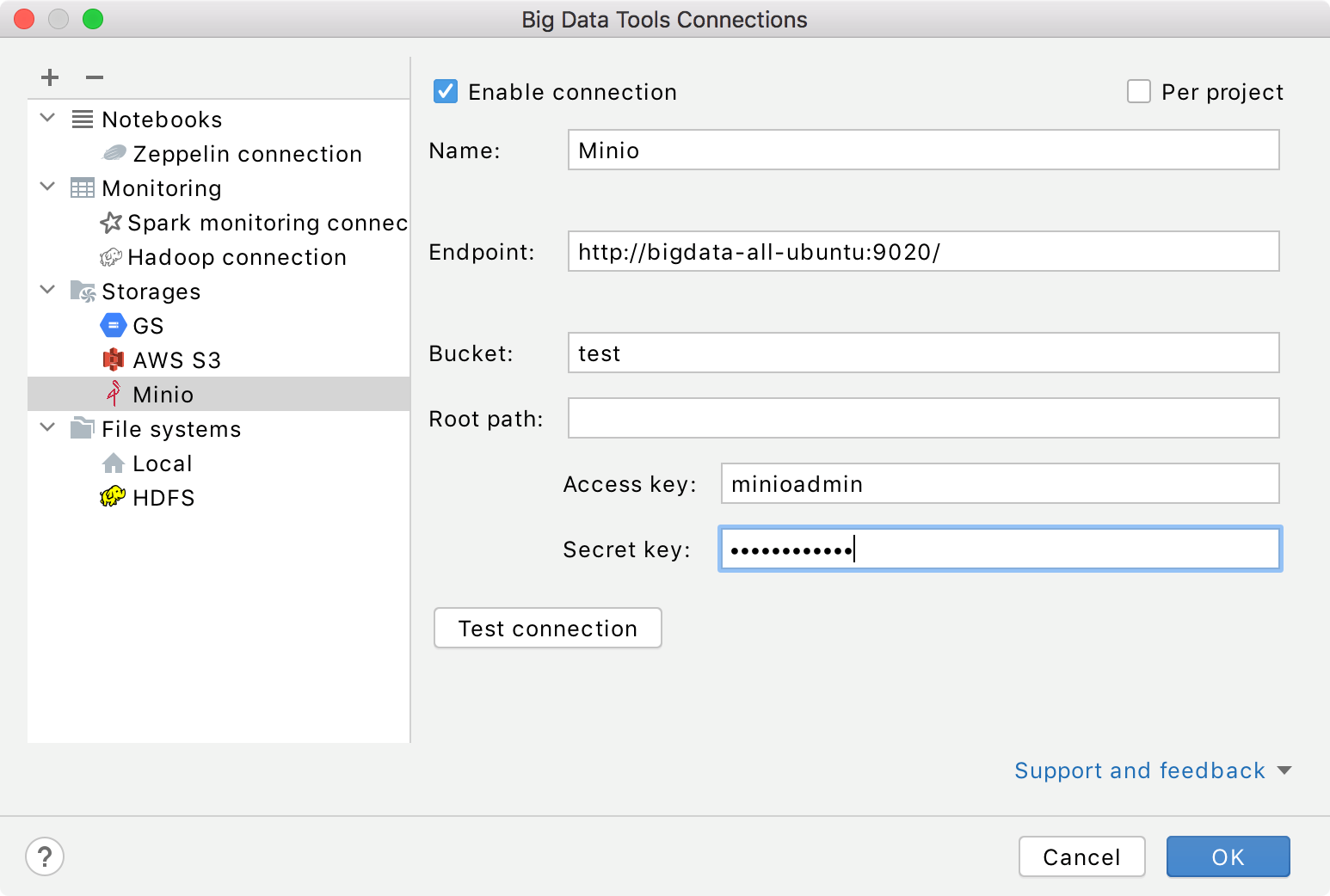
Mandatory parameters:
Endpoint: specify an endpoint to connect to.
Bucket: a globally unique Minio bucket name.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Root path: a path to the root directory in the specified bucket.
Access credentials: Access Key and Secret Key.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
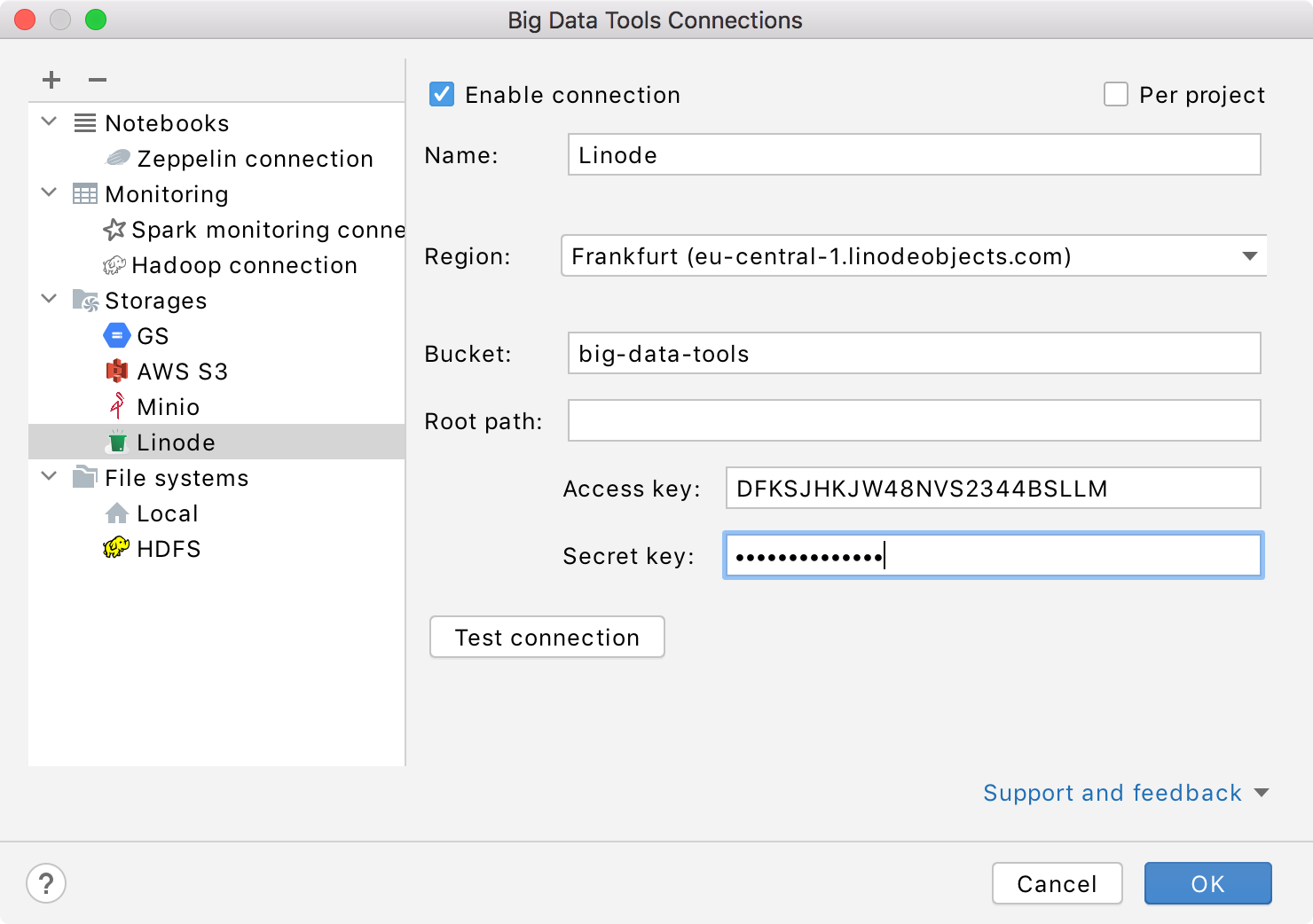
Mandatory parameters:
Bucket: a globally unique Linode bucket name.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Region: a region of the specified bucket. You can select one from the list or let IntelliJ IDEA to auto detect it.
Root path: a path to the root directory in the specified bucket.
Access credentials: Access Key and Secret Key.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
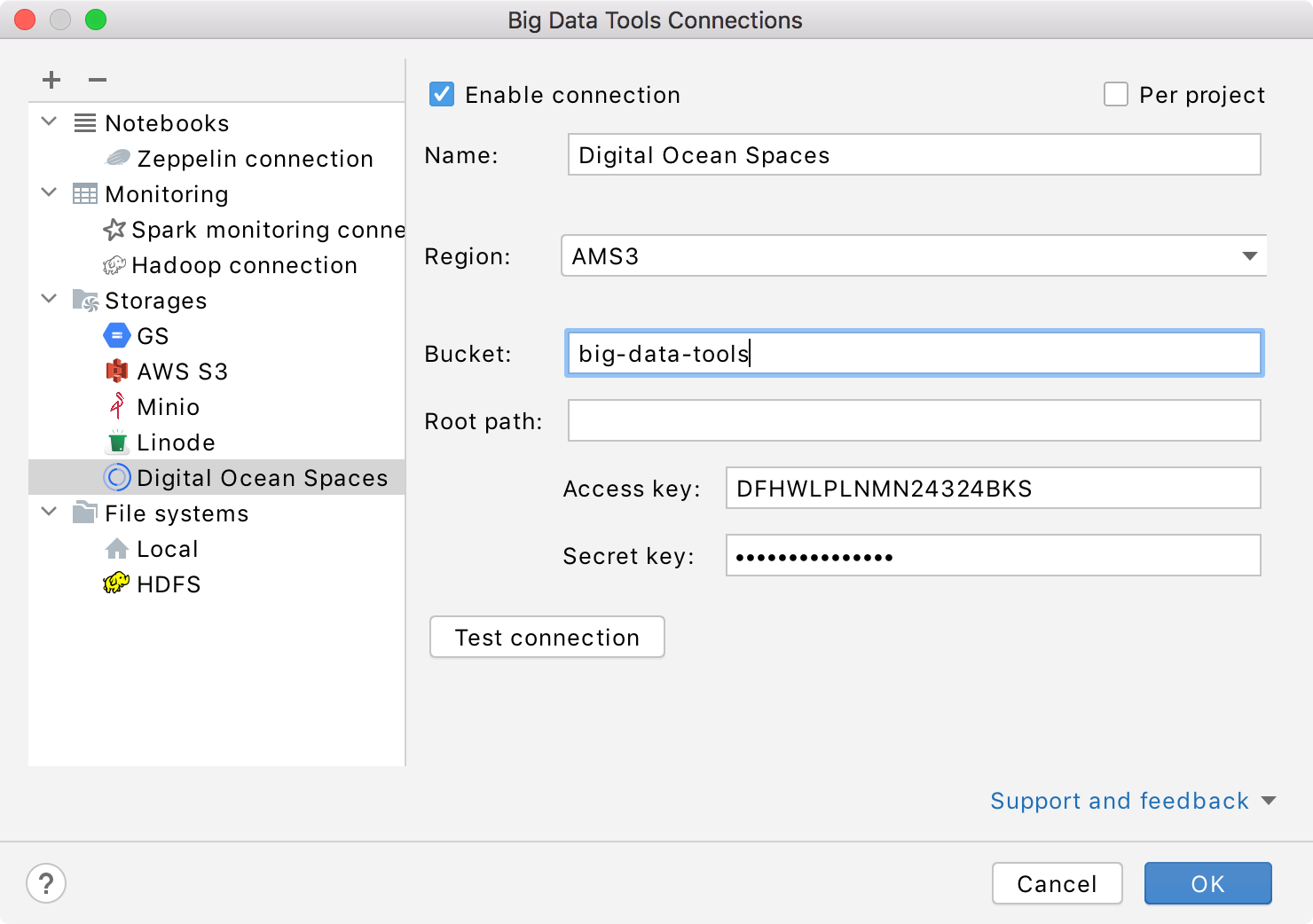
Mandatory parameters:
Bucket: a globally unique Digital Ocean bucket name.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Region: a Digital Ocean region of the specified bucket. You can select one from the list or let IntelliJ IDEA to auto detect it.
Root path: a path to the root directory in the specified bucket.
Access credentials: Access Key and Secret Key.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
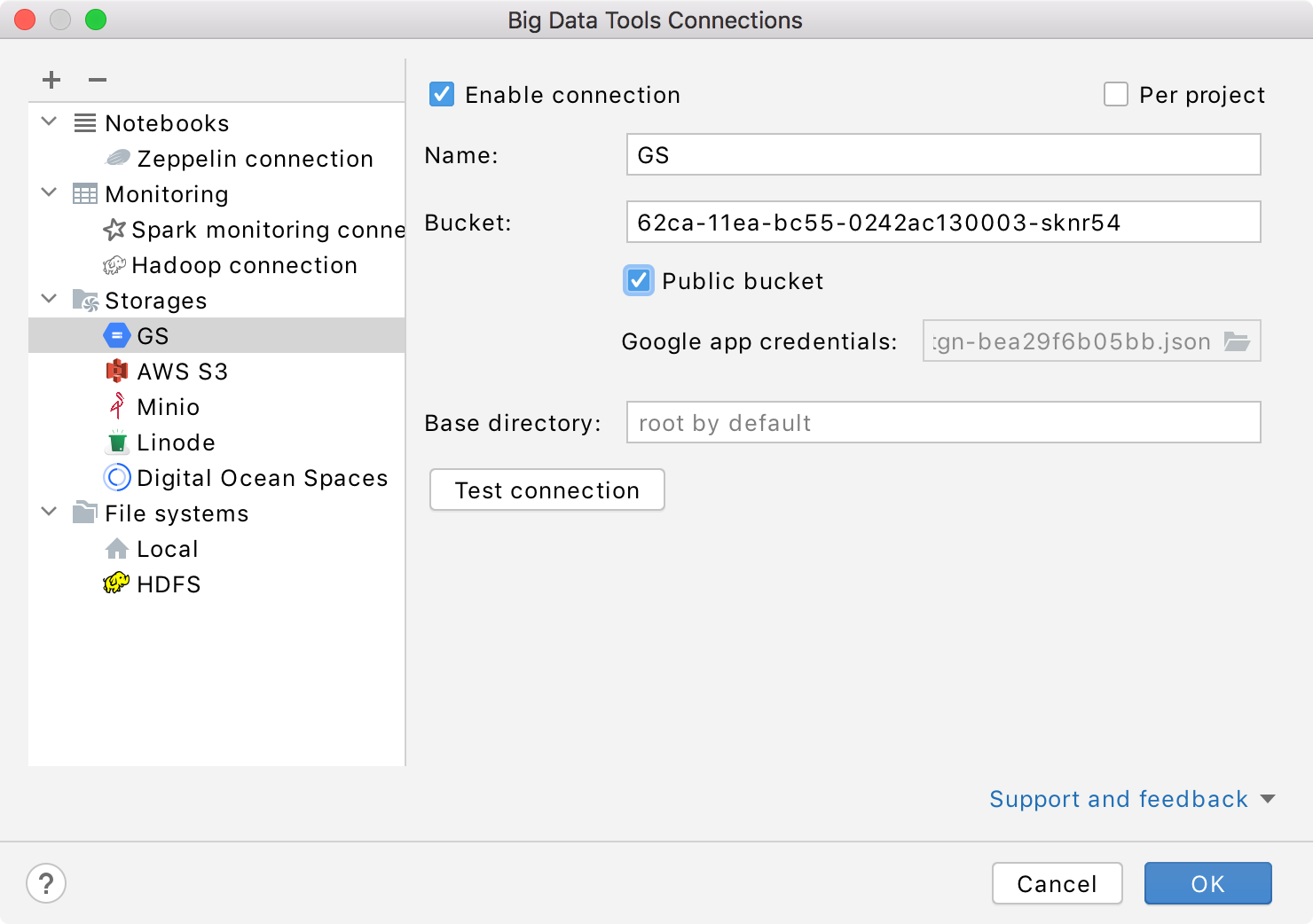
Mandatory parameters:
Bucket: a name of the basic container to store your data in Google Storage.
Cloud store JSON location: a path to the Cloud Storage JSON file. You don't need to specify the credentials if the Public bucket is selected.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Base directory (root by default): storage base directory.
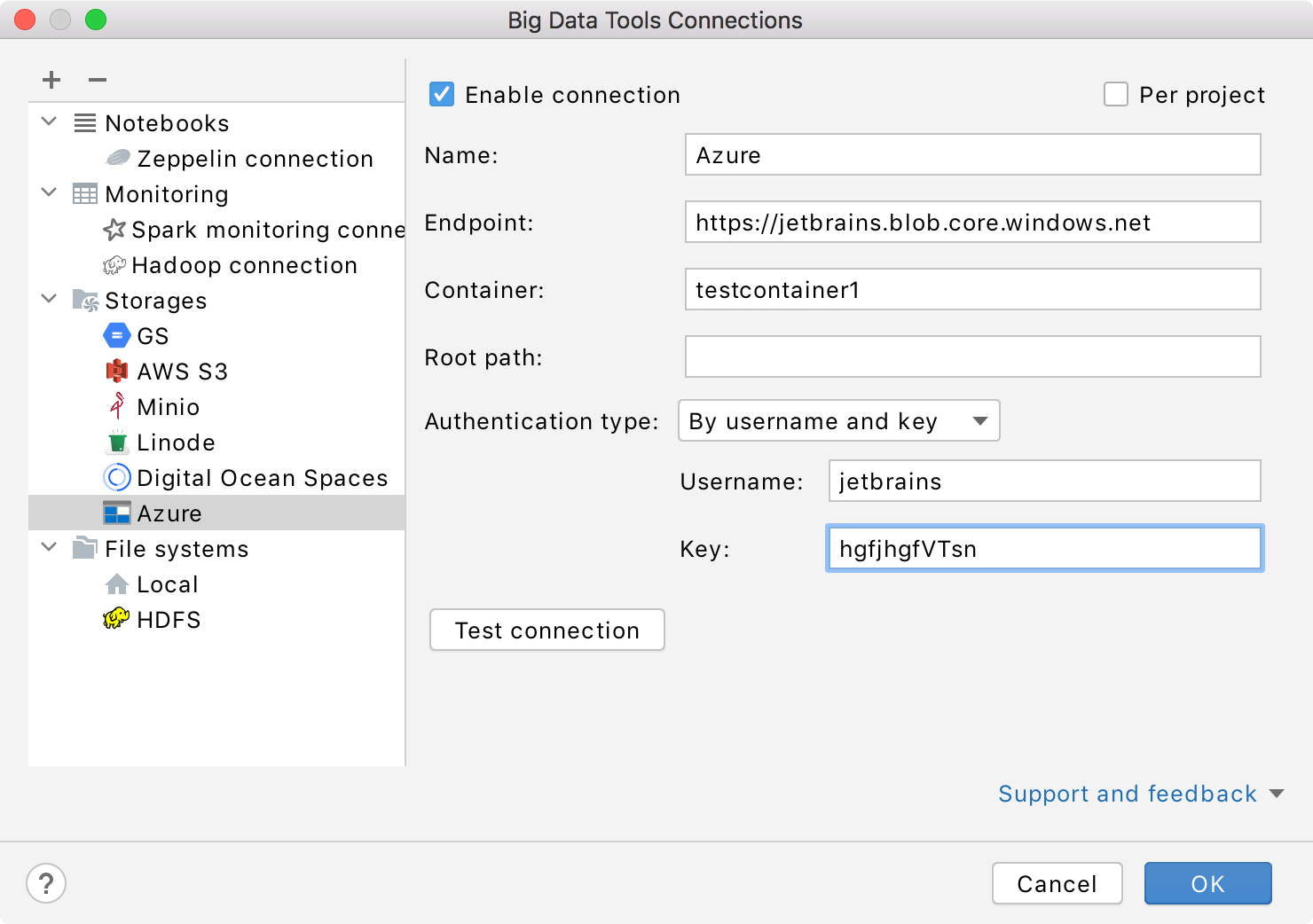
Mandatory parameters:
Endpoint: specify an endpoint to connect to.
Container: a name of the basic container to store your data in Microsoft Azure.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Root path: a path to the root directory in the specified bucket.
Authentication type: the authentication method. You can access the storage by username and key, by a connection string, or using a SAS token.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.

Mandatory parameters:
URL: the path to the target server.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Enable tunneling. Creates an SSH tunnel to the remote host. It can be useful if the target server is in a private network but an SSH connection to the host in the network is available.
Select the checkbox and specify a configuration of an SSH connection (press ... to create a new SSH configuration).
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Enable HTTP basic authentication: connection with the HTTP authentication using the specified username and password.
Enable HTTP proxy: connection with the HTTP proxy using the specified host, port, username, and password.
HTTP Proxy: connection with the HTTP or SOCKS Proxy authentication. Select if you want to use IDEA HTTP Proxy settings or use custom settings with the specified host name, port, login, and password.
- Kerberos authentication settings: opens the Kerberos authentication settings.

Specify the following options:
Enable Kerberos auth: select to use the Kerberos authentication protocol.
Krb5 config file: a file that contains Kerberos configuration information.
JAAS login config file: a file that consists of one or more entries, each specifying which underlying authentication technology should be used for a particular application or applications.
Use subject credentials only: allows the mechanism to obtain credentials from some vendor-specific location. Select this checkbox and provide the username and password.
To include additional login information into IntelliJ IDEA log, select the Kerberos debug logging and JGSS debug logging.
Note that the Kerberos settings are effective for all you Spark connections.

Mandatory parameters:
URL: the path to the target server.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Enable tunneling. Creates an SSH tunnel to the remote host. It can be useful if the target server is in a private network but an SSH connection to the host in the network is available.
Select the checkbox and specify a configuration of an SSH connection (press ... to create a new SSH configuration).
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Enable HTTP basic authentication: connection with the HTTP authentication using the specified username and password.
Enable HTTP proxy: connection with the HTTP proxy using the specified host, port, username, and password.
HTTP Proxy: connection with the HTTP or SOCKS Proxy authentication. Select if you want to use IDEA HTTP Proxy settings or use custom settings with the specified host name, port, login, and password.
- Kerberos authentication settings: opens the Kerberos authentication settings.

Specify the following options:
Enable Kerberos auth: select to use the Kerberos authentication protocol.
Krb5 config file: a file that contains Kerberos configuration information.
JAAS login config file: a file that consists of one or more entries, each specifying which underlying authentication technology should be used for a particular application or applications.
Use subject credentials only: allows the mechanism to obtain credentials from some vendor-specific location. Select this checkbox and provide the username and password.
To include additional login information into IntelliJ IDEA log, select the Kerberos debug logging and JGSS debug logging.
Note that the Kerberos settings are effective for all you Spark connections.
You can also reuse any of the existing Spark connections. Just select it from the Spark Monitoring list.

Mandatory parameters:
URL: the path to the target server.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Properties: the list of configurable connection parameters. See Kafka reference documentation for more details.
Enable tunneling. Creates an SSH tunnel to the remote host. It can be useful if the target server is in a private network but an SSH connection to the host in the network is available.
Select the checkbox and specify a configuration of an SSH connection (press ... to create a new SSH configuration).
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Click the question mark next to the Kafka support is limited message to preview the list of the currently supported features.
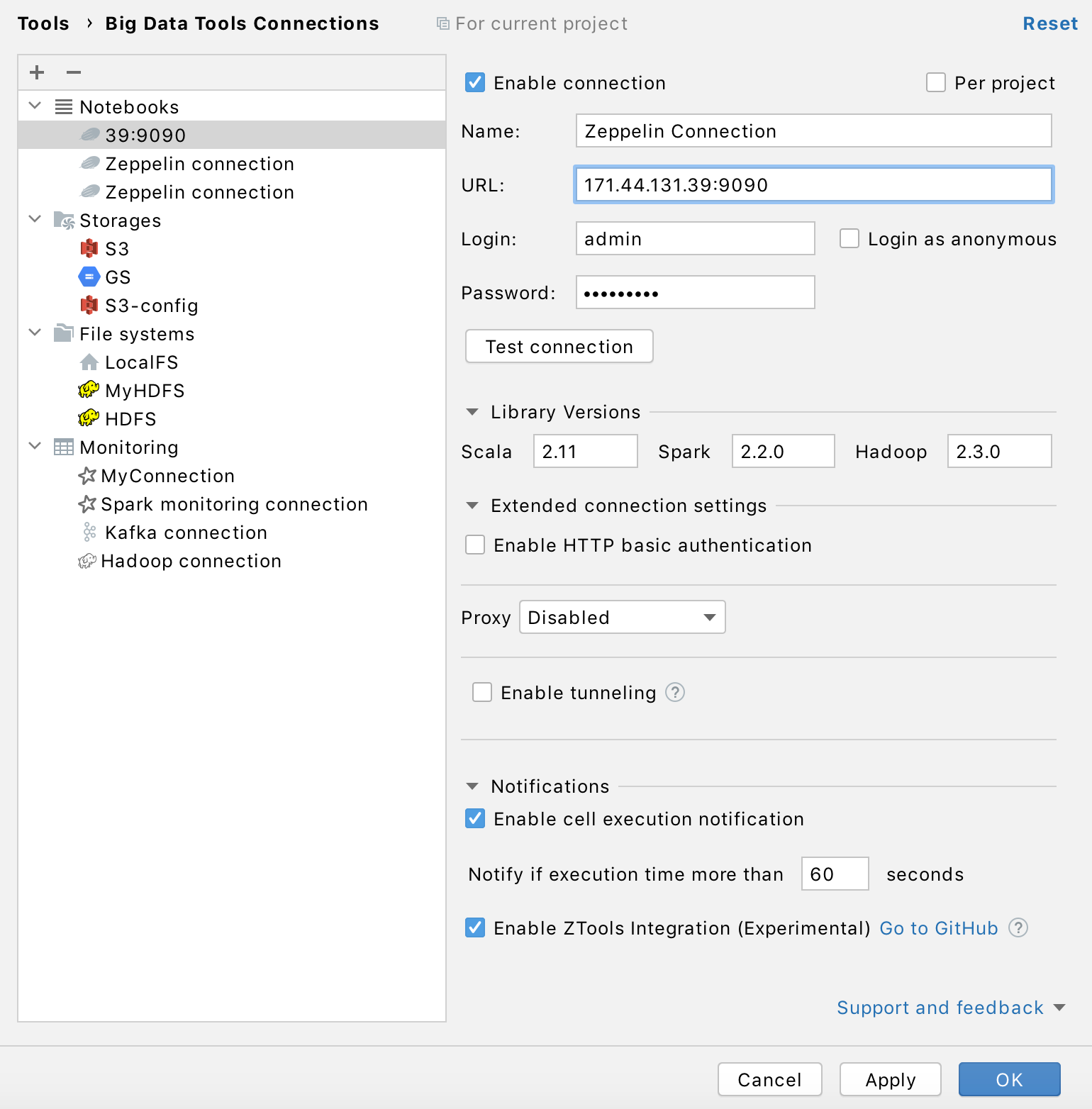
Mandatory parameters:
URL: the path to the target server.
Login and Password: your credentials to access the target server.
Name: the name of the connection to distinguish it between the other connections.
Optionally, you can set up:
Login as anonymous: select to login without using your credentials.
Per project: select to enable these connection settings only for the current project. Deselect it if you want this connection to be visible in other projects.
Enable connection: deselect if, for some reasons, you want to restrict using this connection. By default, the newly created connections are enabled.
Library Versions: Scala Version, Spark Version, and Hadoop Version: these values are derived from the plugin bundles. If needed, specify any alternative version values.
Enable HTTP basic authentication: connection with the HTTP authentication using the specified username and password.
Proxy: connection with the HTTP or SOCKS Proxy authentication. Select if you want to use IDEA HTTP Proxy settings or use custom settings with the specified host name, port, login, and password.
Enable tunneling. Creates an SSH tunnel to the remote host. It can be useful if the target server is in a private network but an SSH connection to the host in the network is available.
Select the checkbox and specify a configuration of an SSH connection (press ... to create a new SSH configuration).
Notifications. Select Enable cell execution notification if you want to be notified when execution time exceeds the specified time interval (60 seconds by default).
Enable ZTools Integration. Select this checkbox to preview local variables for the current Zeppelin session.
Once you fill in the settings, click Test connection to ensure that all configuration parameters are correct. Then click OK.
temporarly
You can disable any connection if you temporarily do not need it. Right-click the corresponding item in the BigDataTools window and select Disable Connection from the context menu. The server changes its visual appearance and behavior: you cannot preview its content. To restore the connection, right-click it and select Enable Connection from the context menu.
For your convenience, you can rename the server root and copy a path to it. To quickly access all the required actions, right-click the target server in the BigDataTools window and select the corresponding command from the context menu.
Now that you have established a connection to the server, you can start working with your notebooks. However, it might be a good practice to ensure that all the libraries and packages required for execution on a particular server are installed and available.
Configure notebook dependencies
From the main menu, select .
In the Project Structure dialog, select Modules in the list of the Project Settings. Then select any of the configured connections in the list of the modules and double-click System Dependencies.
Inspect the list of the added libraries. Click the list and start typing to search for a particular library.

If needed, modify the list of the libraries
Click
to add a new library.
Click
and specify the URL of the external documentation.
Click
to select the items that you want IntelliJ IDEA to ignore (folders, archives and folders within the archives), and click OK.
Click
to remove the selected ordinary library from the library or restore the selected excluded items. The items themselves will stay in the library.
Manage Zeppelin interpreters
You can configure interpreters on a Zeppelin server. Once an interpreter is added, it is available for all notes on this server.
Configure Zeppelin interpreters
Open interpreter settings using one of the following ways:
Click the
on the notebook toolbar.
Right-click a Zeppelin server in the BigDataTools tool window and select Open Interpreter Settings from the context menu.
Preview the list of the available interpreters in the Interpreter Settings window.

Note that the list of the interpreters is identical to the list that opens in the Interpreter Bindings dialog for Zeppelin 0.8 and earlier. For Zeppelin 0.9, Interpreter Bindings shows only interpreters in use. To filter out the list of the interpreters, type the target name in the Search field.
You can use the following actions of the interpreter toolbar:
Item Description 
Updates the list of the interpreters.

Opens a dialog to add a new interpreter. You can include a new interpreter to an existing group of interpreters and configure its settings.

Deletes the selected interpreter.

Restarts the selected interpreter.
Opens a dialog to add, remove, and modify interpreter repositories.
Preview the settings of the target interpreter.
When an interpreter has resolved all dependencies and it is ready for use, its status is shown as Ready.
If the selected interpreter is a root of the interpreter group, you should see the interpreters that are included in this group. For example, the
sparkgroup consists of%spark,%spark.sql,%spark.pyspark,%spark.ipyspark,%spark.r,%spark.ir,%spark.shiny,%spark.kotlinSelect SHARED, SCOPED, or ISOLATED interpreter binding modes. In shared mode, every note using this interpreter shares a single interpreter instance. Scoped and isolated mode can be used under per user or per note dimensions. In scoped per note mode, each note will create a new interpreter instance in the same interpreter process. In isolated per note mode, each note will create a new interpreter process.
Select the Set permission checkbox and specify the owner names, if you want to restrict access to the selected interpreter.
Select the Connect to existing process checkbox to provide a Host and Port on the target server.
You can add interpreter Properties or modify the predefined set of properties and their values. Properties are exported as environment variables on the system if the property name consists of upper-case characters, numbers, or underscores ([A-Z_0-9]). Otherwise, the property is set as a common interpreter property. See more details in the Apache Zeppelin documentation.
For example, you can add the zeppelin.SparkInterpreter.precode property and put some code into the Value field to execute on interpreter init.

This code is resolved in a note after initialization of the interpreter:

In the Dependencies area add any library you want to use with the selected interpreter. If needed, specify the files that should be excluded.
Click to update the list of the interpreters. To restart the selected interpreter, click
![]() .
.
Manage repositories
To open Repository Settings, click
on the interpreter toolbar.

You can refresh the list of the repositories (
 ), add a new repository (
), add a new repository ( ), and remove the selected repository (
), and remove the selected repository ( ).
).To add a new repository, click
 and fill in the repository settings:
and fill in the repository settings:Mandatory parameters:
Id: a unique name of the repository
Url: address of the repository
Optionally, you can set up:
Name: a username to access the repository
Password: a password to access the repository
Host: an HTTP or HTTPS server where the repository resides
Port: a port of the repository server
Name and Password: user credentials to access the repository server
Samples of Hadoop File System configuration files
| Type | Sample configuration |
|---|---|
| HDFS |
<?xml version="1.0"?>
-<configuration>
-<property>
<name>fs.hdfs.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.DistributedFileSystem</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://example.com:9000/</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|
| S3 |
<?xml version="1.0"?>
-<configuration>
-<property>
<name>fs.s3a.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.S3AFileSystem</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.s3a.access.key</name>
<value>sample_access_key</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.s3a.secret.key</name>
<value>sample_secret_key</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>s3a://example.com/</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|
| WebHDFS |
<?xml version="1.0"?>
-<configuration>
-<property>
<name>fs.webhdfs.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.web.WebHdfsFileSystem</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>webhdfs://master.example.com:50070/</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|
| WebHDFS and Kerberos |
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<configuration>
-<property>
<name>fs.webhdfs.impl</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.web.WebHdfsFileSystem</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>webhdfs://master.example.com:50070</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>hadoop.security.authentication</name>
<value>Kerberos</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>dfs.web.authentication.kerberos.principal</name>
<value>testuser@EXAMPLE.COM</value>
</property>
-<property>
<name>hadoop.security.authorization</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
</configuration>
|