Configuring Remote PHP Interpreters
The term remote PHP interpreter denotes a PHP engine installed on a remote host or in a virtual environment. The term remote PHP interpreter is used as the opposite of local PHP interpreters that are installed on your computer, see Configuring Local PHP Interpreters.
You can access a remote PHP interpreter through SSH, Docker, Docker Compose, Vagrant, or WSL:
By using SSH, you can access a PHP interpreter through the SSH access to the host where the PHP interpreter is installed.
Before you start:
Configure access to an ssh server on the target remote host and make sure this server is running.
Create an SSH configuration as described in Create SSH configurations.
Configure a PHP interpreter using SSH
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, click
in the left-hand pane, then choose From Docker, Vagrant, VM, WSL, Remote... from the popup menu.
In the Configure Remote PHP Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the SSH method.

From the SSH configuration list, choose one of the created SSH configurations, or click
and create a new configuration as described in Create SSH configurations.
To use an interpreter configuration, you need path mappings that set correspondence between the project folders, the folders on the server to copy project files to, and the URL addresses to access the copied data on the server. IntelliJ IDEA first attempts to retrieve path mappings itself by processing all the available application-level configurations. If IntelliJ IDEA finds the configurations with the same host as the one specified in the selected SSH configuration, the mappings from these configurations are merged automatically. If no configurations with this host are found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message informing you that path mappings are not configured.
To fix the problem, open the Languages and Frameworks | PHP page of the IDE settings Ctrl+Alt+S, click
in the Path mappings field and map local folders to the folders on the server.
- In the PHP interpreter path field, specify the location of the PHP executable file in accordance with the configuration of the selected remote development environment.
For remote hosts, IntelliJ IDEA by default suggests the /usr/bin/php location.
To specify a different folder, click
and choose the relevant folder in the dialog that opens. Note that the PHP home directory must be open for editing.
When you click OK, IntelliJ IDEA checks whether the PHP executable is actually stored in the specified folder.
If no PHP executable is found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message asking you whether to continue searching or save the interpreter configuration anyway.
If the PHP executable is found, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog where the installation folder and the detected version of the PHP interpreter are displayed.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog, click Show phpinfo
to have IntelliJ IDEA display a separate information window with the installation details and the list of loaded extensions and configured options. Note that the additional options specified in the Configuration Options field of the PHP Interpreters dialog are not listed.
By using the Docker configuration, you can access a PHP interpreter installed in a Docker container.
Before you start:
Make sure that Docker is downloaded, installed, and configured on your computer as described in Docker.
Make sure the Docker and PHP Docker plugins are installed and enabled. The plugins are not bundled with IntelliJ IDEA, but they can be installed on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page as described in Installing plugins from JetBrains repository. Once enabled, the plugins are available at the IDE level, that is, you can use them in all your IntelliJ IDEA projects.
Configure the PHP development environment in the Docker container to be used.
Learn more about using Docker with IntelliJ IDEA in Docker.
Configure a PHP interpreter in a Docker container
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, click
in the left-hand pane, then choose From Docker, Vagrant, VM, WSL, Remote... from the popup menu.
In the Configure Remote PHP Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the Docker method.
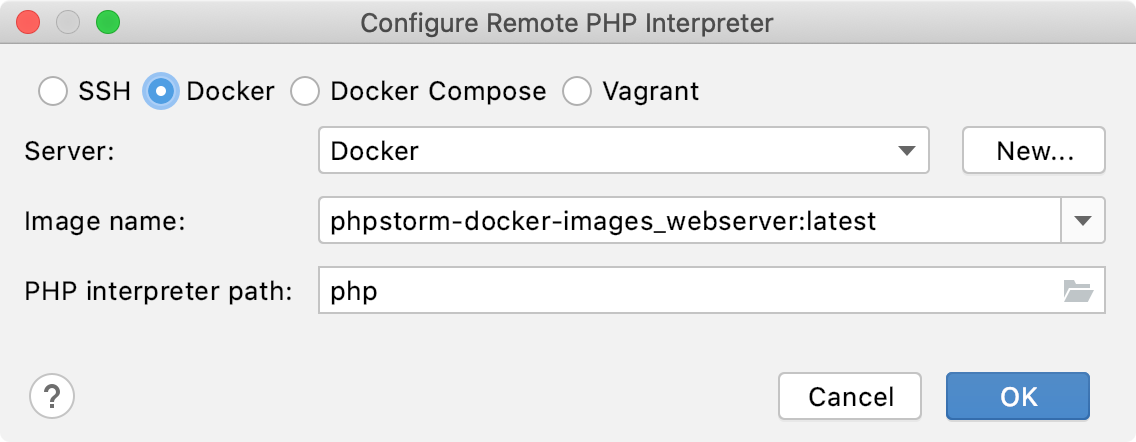
Provide the connection parameters:
In the Server field, specify the Docker configuration to use, see Configure the Docker daemon connection settings for details. Select a configuration from the list or click
and create a new configuration on the Docker page that opens.
In the Image name field, specify the base Docker image to use. Choose one of the previously downloaded or your custom images from the list or type the image name manually, for example,
php:latestorphp:7.0-cli. When you later launch the run configuration, Docker will search for the specified image on your machine. If the search fails, the image will be downloaded from the Docker Official Images repository on the Docker Registry page.
- In the PHP interpreter path field, specify the location of the PHP executable file in accordance with the configuration of the selected remote development environment.
For Docker containers, IntelliJ IDEA by default suggests the php location.
When you click OK, IntelliJ IDEA checks whether the PHP executable is actually stored in the specified folder.
If no PHP executable is found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message asking you whether to continue searching or save the interpreter configuration anyway.
If the PHP executable is found, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog where the installation folder and the detected version of the PHP interpreter are displayed.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog, click Show phpinfo
to have IntelliJ IDEA display a separate information window with the installation details and the list of loaded extensions and configured options. Note that the additional options specified in the Configuration Options field of the PHP Interpreters dialog are not listed.
By using the Docker Compose configuration, you can access a PHP interpreter running in a multi-container Docker Compose environment.
Before you start:
Make sure that Docker is downloaded, installed, and configured on your computer as described in Docker.
Make sure the Docker and PHP Docker plugins are installed and enabled. The plugins are not bundled with IntelliJ IDEA, but they can be installed on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page as described in Installing plugins from JetBrains repository. Once enabled, the plugins are available at the IDE level, that is, you can use them in all your IntelliJ IDEA projects.
Configure the PHP development environment in the Docker container to be used.
Learn more about using Docker Compose with IntelliJ IDEA in Using Docker Compose.
Configure a PHP interpreter using Docker Compose
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, click
in the left-hand pane, then choose From Docker, Vagrant, VM, WSL, Remote... from the popup menu.
In the Configure Remote PHP Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the Docker Compose method.
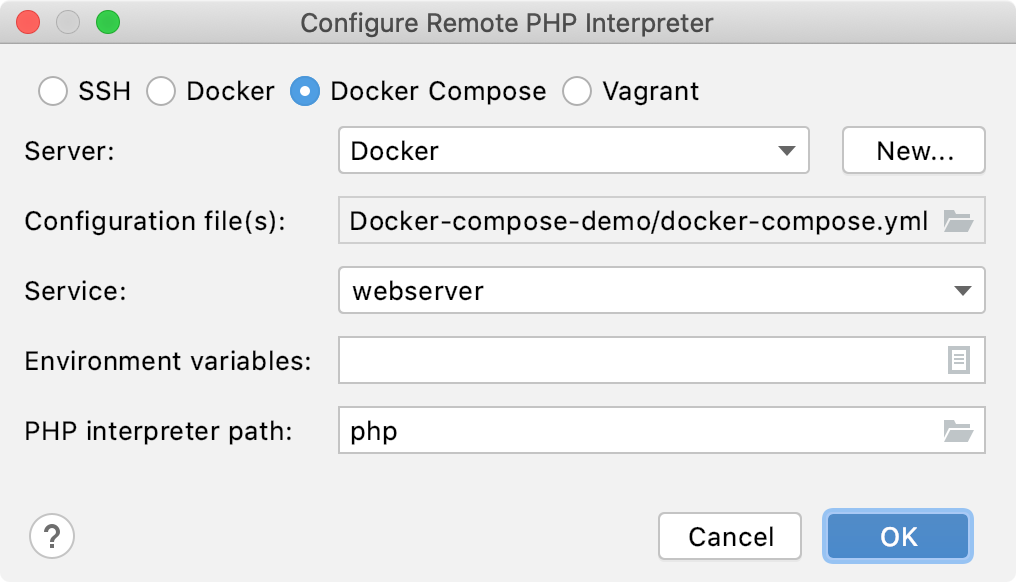
Provide the connection parameters:
In the Server field, specify the Docker configuration to use, see Configure the Docker daemon connection settings for details. Select a configuration from the list or click
and create a new configuration on the Docker page that opens.
In the Configuration file(s) field, specify the docker-compose configuration files to use. The base configuration file located in the project root is selected by default. To select a different file or several files, click
and select the desired configuration file in the Docker Compose Configuration Files dialog that opens.
From the Service list, choose the service corresponding to the container the PHP development environment is set up in.
If necessary, in the Environment Variables field, provide the environment variables. See Using Environment Variables for details.
- In the PHP interpreter path field, specify the location of the PHP executable file in accordance with the configuration of the selected remote development environment.
For Docker containers, IntelliJ IDEA by default suggests the php location.
When you click OK, IntelliJ IDEA checks whether the PHP executable is actually stored in the specified folder.
If no PHP executable is found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message asking you whether to continue searching or save the interpreter configuration anyway.
If the PHP executable is found, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog where the installation folder and the detected version of the PHP interpreter are displayed.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog, click Show phpinfo
to have IntelliJ IDEA display a separate information window with the installation details and the list of loaded extensions and configured options. Note that the additional options specified in the Configuration Options field of the PHP Interpreters dialog are not listed.
- In the Lifecycle area of the CLI Interpreters dialog, choose how the Docker container for the selected service should be managed by IntelliJ IDEA.
Always start a new container ('docker-compose run'): choose this option to have the container started via the run command. The container will be restarted upon each run.
Connect to existing container ('docker-compose exec'): choose this option to have the container started once, and then connect to it via the exec command.
By using the Vagrant configuration, you can access a PHP interpreter installed on the corresponding Vagrant instance.
Before you start:
Make sure that Vagrant and Oracle's VirtualBox are downloaded, installed, and configured on your computer as described in Vagrant.
Make sure the Vagrant plugin is installed and enabled. The Vagrant plugin is not bundled with IntelliJ IDEA, but it can be installed on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page, tab Marketplace, as described in Installing plugins from JetBrains repository.
- Make sure that the parent folders of the following executable files are added to the system PATH variable:
vagrant.bat or vagrant from your Vagrant installation. This should be done automatically by the Vagrant installer.
VBoxManage.exe or VBoxManage from your Oracle's VirtualBox installation.
Configure the PHP development environment in the Vagrant instance to be used.
Learn more about using Vagrant with IntelliJ IDEA in Vagrant.
Configure a PHP interpreter in a Vagrant instance
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, click
in the left-hand pane, then choose From Docker, Vagrant, VM, WSL, Remote... from the popup menu.
In the Configure Remote PHP Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the Vagrant method.
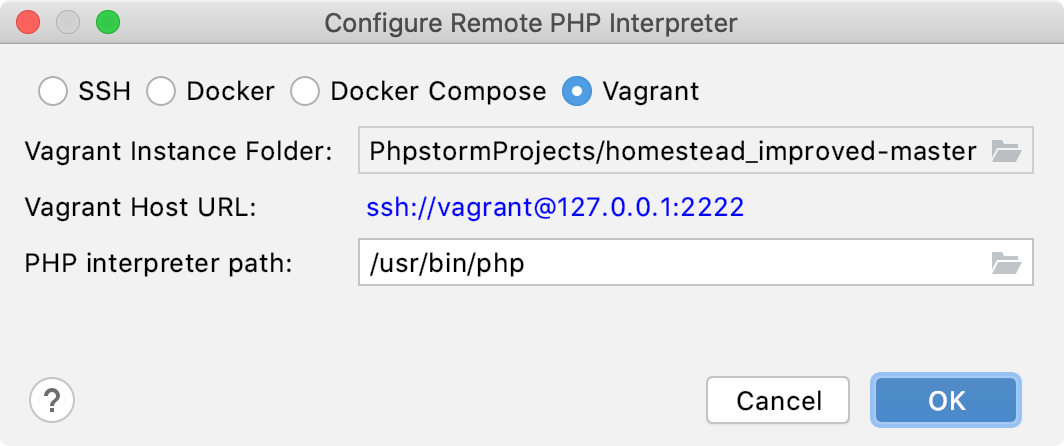
Provide the connection parameters:
Specify the Vagrant instance folder which points at the environment you are going to use. Technically, it is the folder where the VagrantFile configuration file for the desired environment is located. Based on this setting, IntelliJ IDEA detects the Vagrant host and shows it as a link in the Vagrant Host URL read-only field.
To use an interpreter configuration, you need path mappings that set correspondence between the project folders, the folders on the server to copy project files to, and the URL addresses to access the copied data on the server. IntelliJ IDEA evaluates path mappings from the VagrantFile configuration file.
- In the PHP interpreter path field, specify the location of the PHP executable file in accordance with the configuration of the selected remote development environment.
For Vagrant instances, IntelliJ IDEA by default suggests the /usr/bin/php location.
To specify a different folder, click
and choose the relevant folder in the dialog that opens. Note that the PHP home directory must be open for editing.
When you click OK, IntelliJ IDEA checks whether the PHP executable is actually stored in the specified folder.
If no PHP executable is found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message asking you whether to continue searching or save the interpreter configuration anyway.
If the PHP executable is found, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog where the installation folder and the detected version of the PHP interpreter are displayed.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog, click Show phpinfo
to have IntelliJ IDEA display a separate information window with the installation details and the list of loaded extensions and configured options. Note that the additional options specified in the Configuration Options field of the PHP Interpreters dialog are not listed.
By using WSL, you can access a PHP interpreter installed in a Linux environment through the Windows Subsystem for Linux compatibility layer.
Before you start, make sure the following prerequisites are met:
On your Windows 10 machine, make sure the WSL feature is enabled, and the preferred Linux distribution is installed. Refer to the Windows Subsystem for Linux Installation Guide for Windows 10 for details.
Inside the Linux installation, make sure PHP is installed. For the detailed installation instructions, refer to Debian GNU/Linux installation notes. If you are using Ubuntu, you can run this command in the Terminal to quickly install PHP:
sudo apt install php php-mbstring php-dom php-xml php-zip php-curl php-xdebug
Configure a PHP interpreter using WSL
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog that opens, click
in the left-hand pane, then choose From Docker, Vagrant, VM, WSL, Remote... from the popup menu.
In the Configure Remote PHP Interpreter dialog that opens, choose the WSL method.
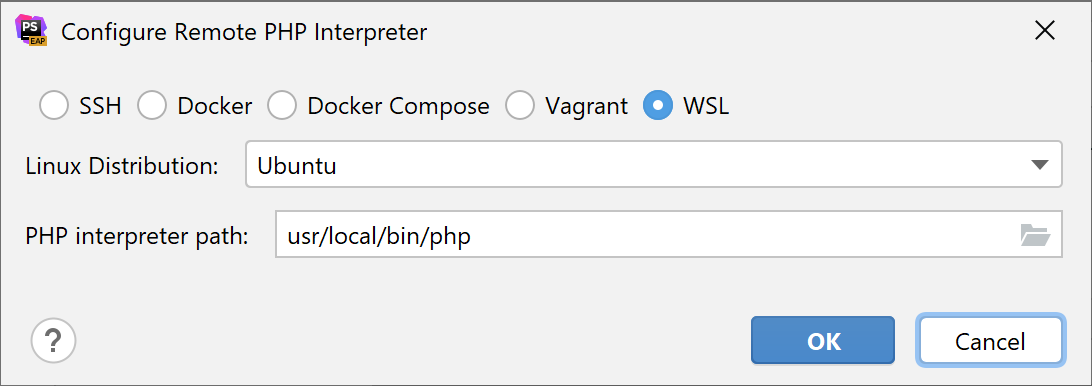
From the Linux distribution list, choose one of the installed Linux distributions to use.
- In the PHP interpreter path field, specify the location of the PHP executable file in accordance with the configuration of the selected remote development environment.
For WSL, IntelliJ IDEA by default suggests /usr/local/bin/php.
To specify a different folder, click
and choose the relevant folder in the dialog that opens. Note that the PHP home directory must be open for editing.
When you click OK, IntelliJ IDEA checks whether the PHP executable is actually stored in the specified folder.
If no PHP executable is found, IntelliJ IDEA displays an error message asking you whether to continue searching or save the interpreter configuration anyway.
If the PHP executable is found, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog where the installation folder and the detected version of the PHP interpreter are displayed.
In the CLI Interpreters dialog, click Show phpinfo
to have IntelliJ IDEA display a separate information window with the installation details and the list of loaded extensions and configured options. Note that the additional options specified in the Configuration Options field of the PHP Interpreters dialog are not listed.
Provide additional configuration options
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
On the PHP page that opens, click
next to the CLI Interpreter list.
In the Additional area of the CLI Interpreters dialog, you can optionally customize the configuration settings of the PHP installation.
In the Debugger extension field, specify the path to Xdebug. This enables IntelliJ IDEA to activate Xdebug when it is necessary if you have disabled it in the php.ini file, see Configuring Xdebug for Using in the On-Demand Mode.
In the Configuration options field, compose a string of configuration directives to be passed through the -d command line option and thus add new entries to the php.ini file. The directives specified in this field override the default directives generated by IntelliJ IDEA, such as
-dxdebug.remote_enable=1,-dxdebug.remote_host=127.0.0.1,-dxdebug.remote_port=9001,-dxdebug.remote_mode=req.For example, if you specify the
-dxdebug.remote_mode=jitdirective it will override the default-dxdebug.remote_mode=reqdirective and thus switch Xdebug to the Just-In-Time (JIT) mode, see Debug in the Just-In-Time mode for details.To do that, click
next to the Configuration options field, and then create a list of entries in the Configuration Options dialog that opens.
- To add a new entry, click
. In the new line, that is added to the list, specify the name of the new entry and its value in the Name and Value fields respectively.
You can add as many entries as you need, just keep in mind that they will be transformed into a command line with its length limited to 256 characters.
To delete an entry, select it in the list and click
.
To change the order of entries, click
or
.
Upon clicking OK, you return to the CLI Interpreters dialog, where the entries are transformed into a command line.
- To add a new entry, click
Configure custom mappings
If you use an interpreter accessible through SSH connection or located on a Vagrant instance or in a Docker container, the mappings are automatically retrieved from the corresponding deployment configuration, Vagrantfile, or Dockerfile.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open IDE settings and select Languages and Frameworks | PHP.
From the Interpreter list, choose the remote interpreter for which you want to customize the mappings. The Path Mappings read-only field shows the path mappings retrieved from the corresponding deployment configuration, Vagrantfile, or Dockerfile. To specify the custom mappings, click
next to the Path Mappings field.
The Edit Project Path Mappings dialog shows the path mappings retrieved from the deployment configuration, Vagrantfile, or Dockerfile. These mappings are read-only.
To add a custom mapping, click
and specify the path in the project and the corresponding path on the remote runtime environment in the Local Path and Remote Path fields respectively. Type the paths manually or click
and select the relevant files or folders in the dialog that opens.
To remove a custom mapping, select it in the list and click
.
Switch between configured PHP interpreters on the fly
Press Ctrl+Shift+A and start typing
Change PHP interpreter. In the suggestions list, select the Change PHP interpreter action.If necessary, you can assign a keyboard shortcut for this action either directly in the suggestions list by pressing Alt+Enter, or at a later point as described in Configure keyboard shortcuts.
In the popup menu that opens, select one of the configured local or remote PHP interpreters.
The selected interpreter will be set as the default project interpreter on the PHP page of the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S. This will also affect the run/debug configurations, test frameworks', and quality tools' configurations that are set to use the default project interpreter.
