Jupyter notebook support
With Jupyter Notebook integration available in IntelliJ IDEA through the Python plugin, you can easily edit, execute, and debug notebook source code and examine execution outputs including stream data, images, and other media.
Notebook support in IntelliJ IDEA includes:
Editing and preview:
Ability to present a notebook as source code with textual cell definitions and manipulate cells as regular code.
Live preview of the cell execution output and Markdown content.
Auto-saving changes that you make in your files. Saving is triggered by various events, for example, closing a file or a project, or quitting the IDE.
Coding assistance:
Error and syntax highlighting.
Ability to create line comments Ctrl+/.
Ability to run cells and preview execution results.
Dedicated Jupyter Notebook Debugger.
Shortcuts for basic operations with Jupyter notebooks.
Ability to recognize .ipynb files and mark them with the
icon.
Quick start with the Jupyter notebook in IntelliJ IDEA
To start working with Jupyter notebooks in IntelliJ IDEA:
Create a new project, specify a virtual environment, and install the jupyter package.
Open or create an .ipynb file.
Add and edit source cells.
Execute any of the code cells to launch the Jupyter server.
Analyze execution results in the Preview pane.
Get familiar with the user interface
Mind the following user interface features when working with Jupyter notebooks in IntelliJ IDEA.
Notebook editor
In IntelliJ IDEA, you can work with Jupyter notebook files using three viewing modes:
In this mode, you can add notebook cells and edit them.
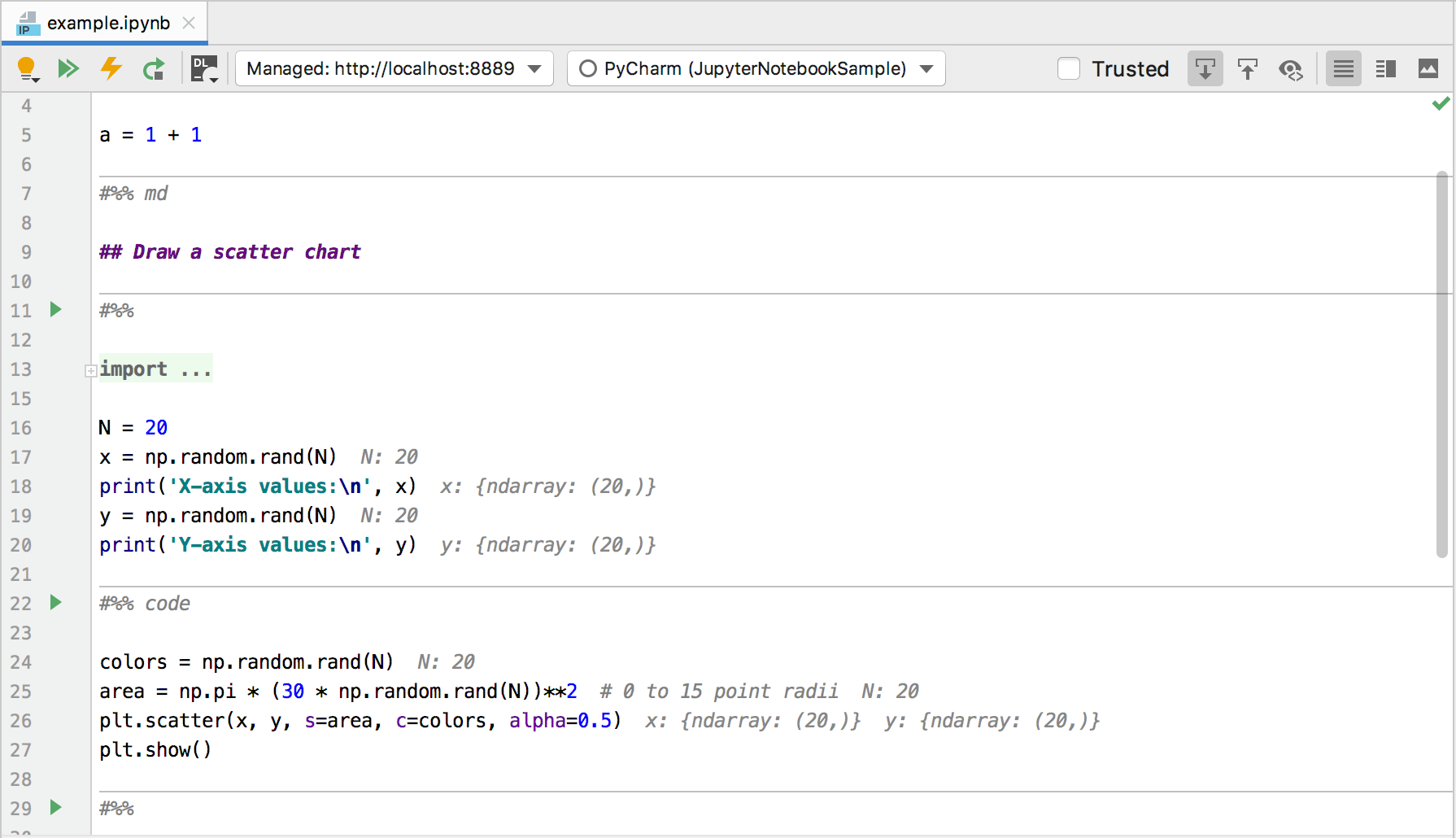
In this mode, you can both edit cells and preview their output. This is the default viewing mode for Jupyter notebooks in IntelliJ IDEA.
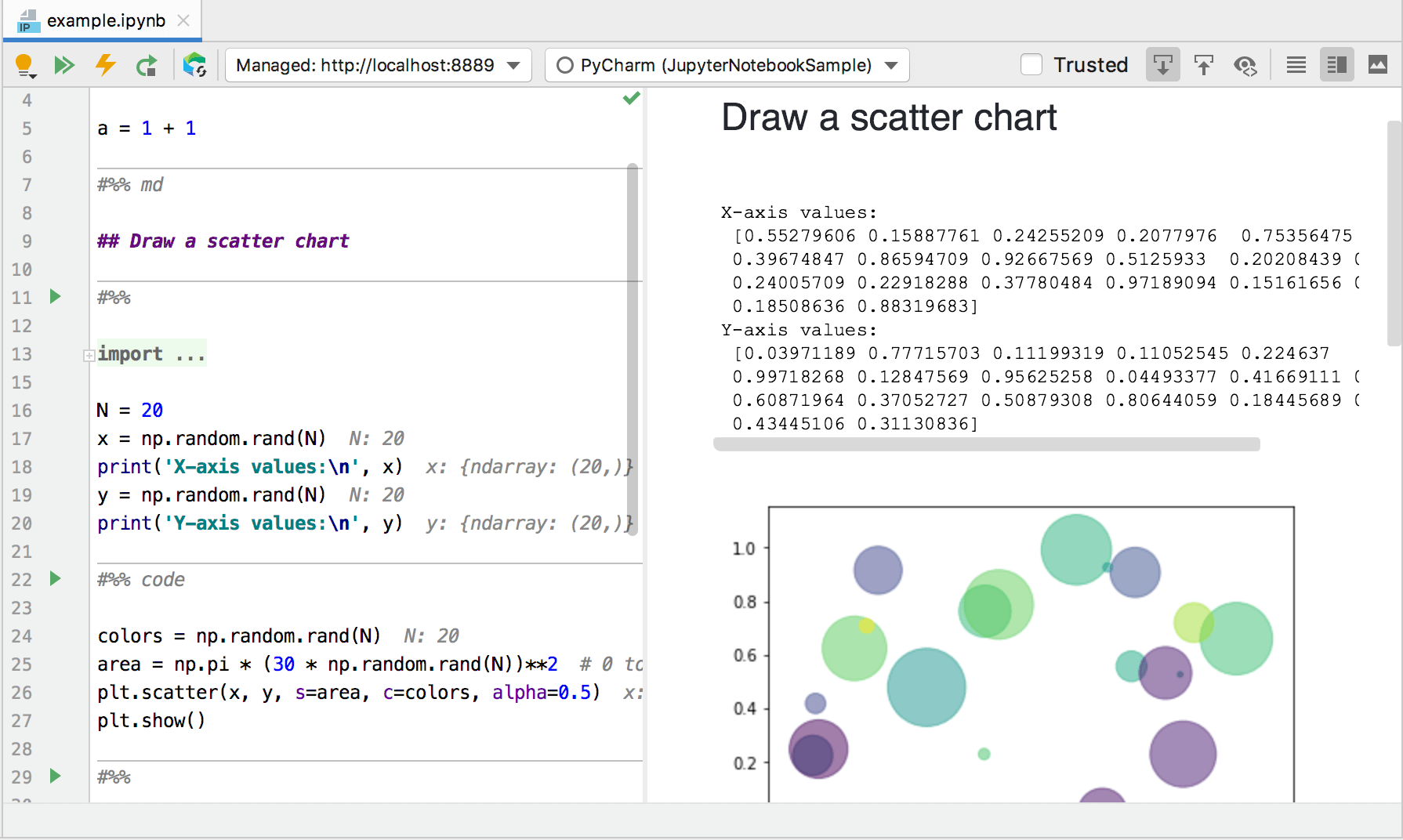
In this mode, you can preview markdown and raw cells as well as code cell execution results.
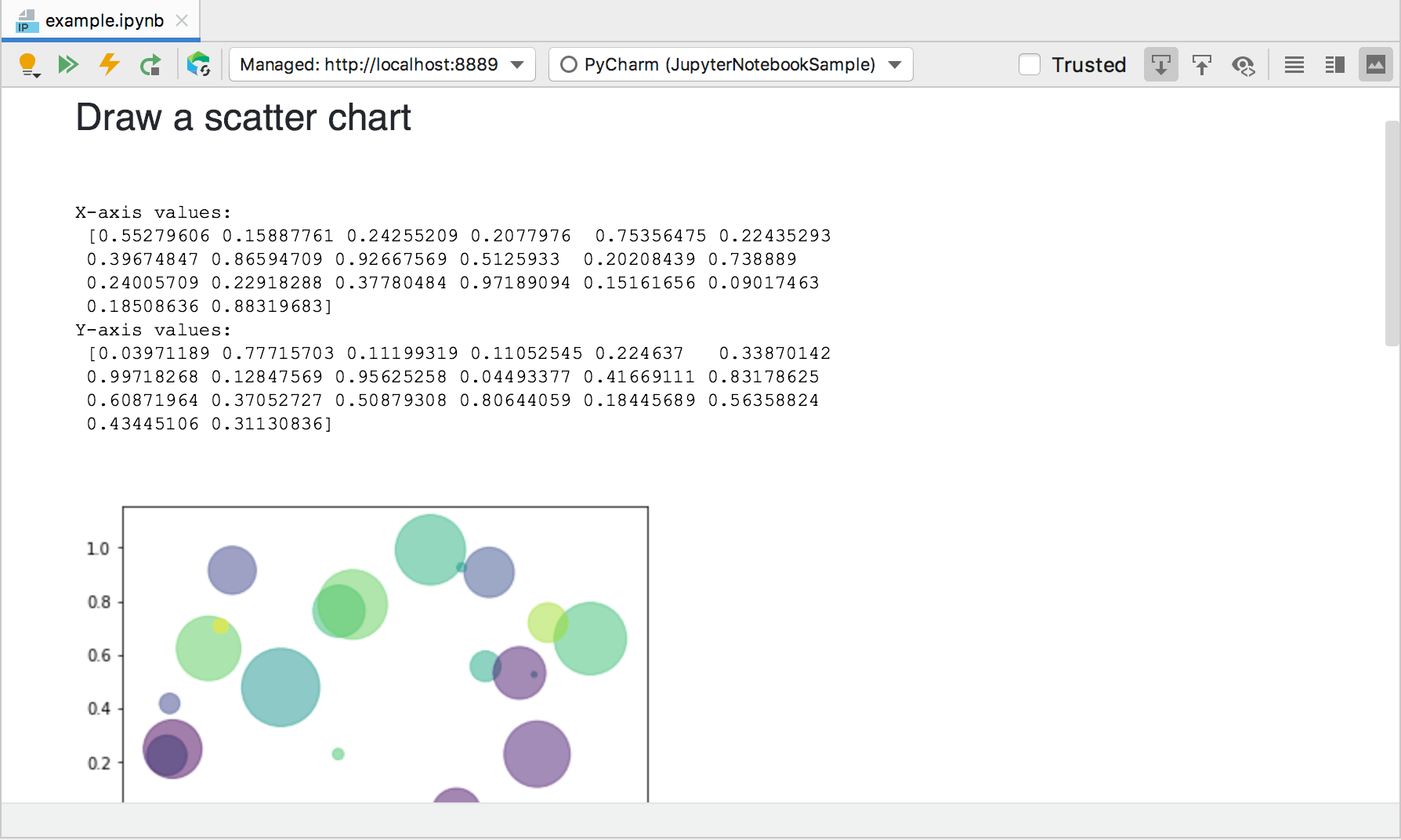
Editing and preview modes reflect the currently selected IntelliJ IDEA user interface appearance.
Notebook toolbar
The Jupyter notebook toolbar provides quick access to all basic operations with notebooks:
Opens the Jupyter Quick List for easy access to the basic notebook operations:
| |
|---|---|
| Executes all cells in the notebook. | |
| Click this icon if you want to interrupt any cell execution. | |
| Click this icon to restart the currently running kernel | |
| Upload to Datalore/Update uploaded notebook. Enables sharing the selected Jupyter notebook using Datalore, an intelligent web application for data analysis. Click this button to start sharing the current notebook file. Once you modify the notebook file, this button enables updating the shared notebook in Datalore. | |
| The Jupyter Server widget that shows the currently used Jupyter server. Click the widget and select to setup another local or remote Jupyter server. | |
| List of the available Jupyter kernels. | |
| Select this checkbox to allow executing JavaScript in your Jupyter notebook. | |
| This actions moves the current cell up. | |
| This actions moves the current cell down. | |
| You can preview the notebook in a browser. | |
| Enables auto scrolling from the source cell in the Editor to the corresponding output in the Preview pane. | |
| Enables auto scrolling from the cell output in the Preview pane to the corresponding source cell in the Editor. | |
| Click this icon to show source code fragments in the Preview pane. | |
| Click this icon to switch into the editor only viewing mode. | |
| Click this icon to show both Editor and the Preview pane. | |
| Click this icon to switch into the preview only mode. |
Tool windows
The Server Log tab of the Jupyter tool window appears when you have any of the Jupyter server launched. The Server log tab of this window shows the current state of the Jupyter server and the link to the notebook in a browser.
It also provides controls to stop the running server () and launch the stopped server (
).
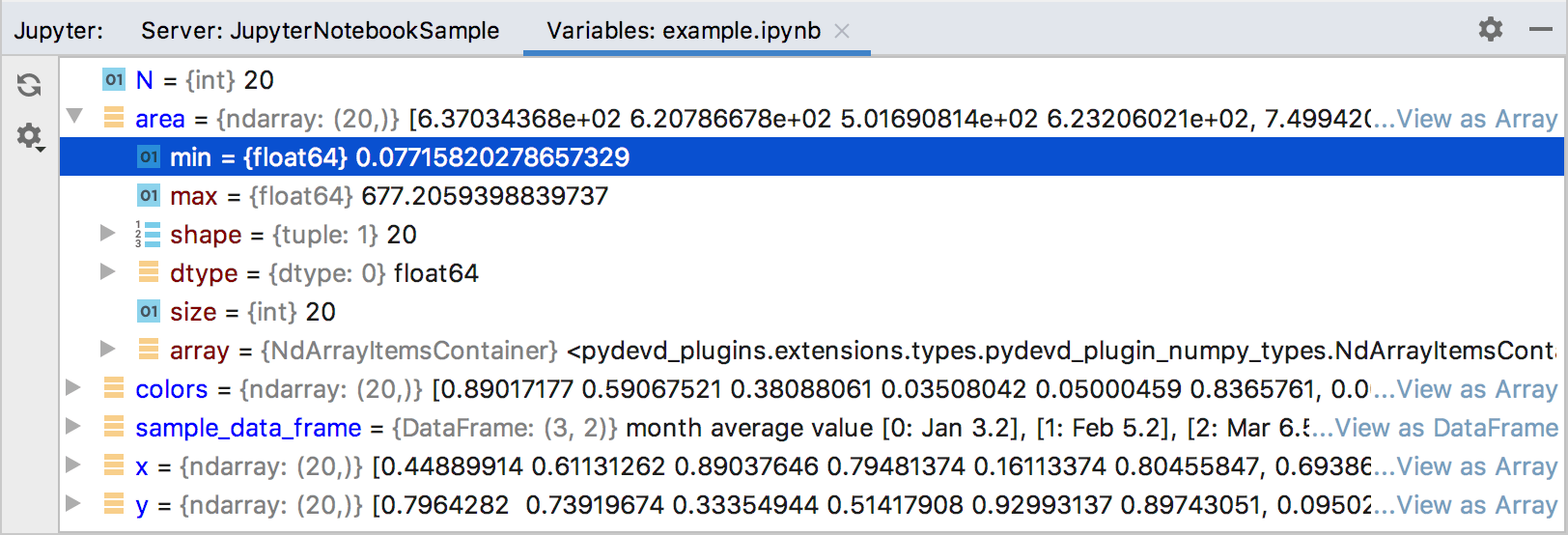
The Variables tab provides the detailed report about variable values of the executed cell.