Vue.js
Vue.js is a framework for developing user interfaces and advanced single-page applications. IntelliJ IDEA provides support for the Vue.js building blocks of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with Vue.js-aware code completion for components, including components defined in separate files, attributes, properties, methods, slot names, and more.
With the built-in debugger, you can debug your Vue.js code right in IntelliJ IDEA, which can automatically generate the necessary run/debug configurations you need: an npm configuration that launches the development server and starts your application in the development mode and a JavaScript Debug configuration that launches a debugging session.
Before you start
Download and install Node.js.
Make sure a local Node.js interpreter is configured in your project: open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) and go to . The Node interpreter field shows the default project Node.js interpreter.
Learn more from Configuring a local Node.js interpreter.
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript, JavaScript Debugger, and Vue.js required plugins are enabled on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Installed. For more information, refer to Managing plugins.
Create a new Vue.js application
The recommended way to create a new Vue.js app is the create-vue official Vue project scaffolding tool, which IntelliJ IDEA downloads and runs for you using npx.
You can still use Vue CLI, if you choose this option IntelliJ IDEA also downloads and runs it with npx.
Of course, you can download any of these tools yourself or create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project and bootstrap it with Vue.js and other tools, such as Vite, babel, webpack, ESLint, etc.
Select from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select Vue.js in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, specify the project name and the folder to create it in. In the Node Interpreter field, specify the Node.js interpreter to use. Select a configured interpreter from the list or choose Add to configure a new one.
From the Vue CLI list, select npx --package @vue/cli vue.
Alternatively, for npm version 5.1 and earlier, install the
@vue/clipackage yourself by runningnpm install --g @vue/cliin the Terminal Alt+F12. When creating an application, select the folder where the@vue/clipackage is stored.To bootstrap your application with babel and ESLint, select the Use the default project setup checkbox.
When you click Create, IntelliJ IDEA generates a Vue.js-specific project with all the required configuration files and downloads the necessary dependencies. You can view the progress in the Run tool window.
Create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project
Select from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select JavaScript in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, choose JavaScript and click Next.
On the second page of the wizard, specify the project name and the folder to create it in.
When you click Create, IntelliJ IDEA creates and opens an empty project.
Install Vue.js in an empty project
Open the empty project where you will use Vue.js.
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install vue
Start with an existing Vue.js application
To continue developing an existing Vue.js application, open it in IntelliJ IDEA and download the required dependencies.
Open the application sources that are already on your machine
Click Open or Import on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. In the dialog that opens, select the folder where your sources are stored.
Check out the application sources from your version control
Click Get from VCS on the Welcome screen.
Alternatively, select or or from the main menu.
Instead of Git in the main menu, you may see any other Version Control System that is associated with your project. For example, Mercurial or Perforce.
In the dialog that opens, select your version control system from the list and specify the repository to check out the application sources from. For more information, refer to Check out a project (clone).
Download the dependencies
Click Run 'npm install' or Run 'yarn install' in the popup:

You can use npm, Yarn 1, or Yarn 2, refer to npm and Yarn for details.
Alternatively, select Run 'npm install' or Run 'yarn install' from the context menu of package.json in the editor or in the Project tool window.
Project security
When you open a project that was created outside IntelliJ IDEA and was imported into it, IntelliJ IDEA displays a dialog where you can decide how to handle this project with unfamiliar source code.

Select one of the following options:
Preview in Safe Mode: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens the project in a preview mode. It means that you can browse the project's sources but you cannot run tasks and script or run/debug your project.
IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification on top of the editor area, and you can click the Trust project link and load your project at any time.
Trust Project: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens and loads a project. That means the project is initialized, project's plugins are resolved, dependencies are added, and all IntelliJ IDEA features are available.
Don't Open: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA doesn't open the project.
Learn more from Project security.
Write and edit your code
In .vue files, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes script, style, and template blocks. You can use JavaScript and TypeScript inside script tags, Style Sheet languages inside style tags, and HTML and Pug inside template tags.
When you use TypeScript inside a script tag, IntelliJ IDEA invokes the TypeScript Language Service for type checking and shows detected errors in the Errors and Compile errors tabs of the TypeScript tool window. Alternatively, you can use TsLint as described in Linting TypeScript in Vue.js components using TSLint
Vue.js components
IntelliJ IDEA recognizes the .vue file type and provides a dedicated .vue file template for Vue.js components.
Create a Vue.js component
In the Project tool window, select the parent folder for the new component, and then choose Vue Component from the list.

You can also extract a new Vue.js component from an existing one without any copying and pasting but using a dedicated intention action or refactoring. All the data and methods used in the newly extracted template stay in the parent component. IntelliJ IDEA passes them to the new component with properties and copies the related styles.
Extract components
Select the template fragment to extract and invoke component extraction:
To use the intention action, press Alt+Enter, and then choose Extract Vue Component from the list.
To use the refactoring, choose from the main menu or from the context menu of the selection.
Type the name of the new component. If this name is already used or invalid, IntelliJ IDEA shows a warning. Otherwise, a new single-file component is created and imported into the parent component.

Code completion
Complete code inside script, style, and template blocks
By default, IntelliJ IDEA provides code completion for ECMAScript 6 inside
scriptblocks and for CSS insidestyleblocks.
Inside the
templatetag, code completion Ctrl+Space and navigation to the definition Ctrl+B for Vue.js components and attributes is available.
Complete Vue.js properties and methods
IntelliJ IDEA also suggests completion for Vue.js properties, properties in the
dataobject, computed properties, and methods.
Complete slot names
IntelliJ IDEA provides completion for the names of slots from library components and from components defined in your project.
If your project contains a component with named slots, IntelliJ IDEA shows suggestions for these names in the
v-slotdirective of atemplatetag.If you’re using Vuetify, Quasar, or BootstrapVue, code completion for slot names is also available.
Complete components defined in separate files
If a component is defined in several files, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes the links between the parts of the component and provides proper code completion for properties, data, and methods.
For example, if the parts of your component are defined in separate JavaScript and stylesheet files that are linked in the vue file through the
srcattribute, properties defined in JavaScript are properly completed in the template as methods do.Templates inside template literals in the
templateproperty of a component get completion just as if this code were inside atemplatetag.Completion is also available if a template is defined in a separate HTML file and then linked to the
templateproperty.
Complete code inside Vue.js injections
Within Vue.js injections inside HTML files, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes Vue.js syntax and highlights your code accordingly. You can also get completion for symbols from Vue.js libraries that are linked from a CDN in an HTML file without adding these libraries to your project dependencies.

Open the HTML file with a CDN link to an external Vue.js library. IntelliJ IDEA highlights the link.
To enable completion for the library, press Alt+Enter on the link and select from the list. Alternatively, hover over the link and click Download library.
The library is added to the list of JavaScript libraries on the page. For more information, refer to Configuring a library added via a CDN link.
Parameter hints
Parameter hints show the names of parameters in methods and functions to make your code easier to read. By default, parameter hints are shown only for values that are literals or function expressions but not for named objects.
Configure parameter hints
Open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) and go to .
Expand Vue under Parameter names.
Specify the context in which you want parameter hints shown by selecting the corresponding checkboxes.
The preview shows how the changes you make in the settings affect the code appearance.
For some methods and functions, IntelliJ IDEA does not show parameter hints in any context. Click Exclude list... to view these methods and functions, possibly enable parameter hints for them, or add new items to the list.
To hide parameter hints for any value type in any context, clear the Vue template checkbox under Parameter names.
Navigate with component usages
Use inlay hints to jump from a component to its usages. If a component is used more than once, IntelliJ IDEA shows a list of detected usages. Select the relevant usage to jump to it.

Show component usages hints are displayed by default. To turn them off, press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and select Editor | Inlay Hints. Then clear the Component usages checkbox under Code vision.
Alternatively, right-click a Show component usages hint in the editor and select Hide 'Code Vision: Component usages' Inlay Hints.

Vue.js live templates
With IntelliJ IDEA, you can use a collection of Live templates for Vue.js adapted from the collection created by Sarah Drasner.
Type the abbreviation of the template to use or press Ctrl+J and select it from the list of available templates.
To expand the template, press Tab.
To move from one variable to another inside the template, press Tab again.

Nuxt.js in Vue.js applications
With IntelliJ IDEA, you can use the Nuxt.js framework in your Vue.js applications. The recommended way to set up a Nuxt.js app in IntelliJ IDEA is use the create-nuxt-app command. Alternatively, you can install Nuxt.js in an existing project.
Create a project with create-nuxt-app
Create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project.
Select from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select Javascript in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, again choose JavaScript and click Next.
On the second page of the wizard, specify the project folder and name and click Finish.
Open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type:
npx create-nuxt-app <project name>or
yarn create nuxt-app <project name>The wizard asks you some questions. After you answer them, a Nuxt project is initialized in the current folder and is ready to use in IntelliJ IDEA.
Learn more from the Nuxt.js official website.
Install Nuxt.js in an existing project
Open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type:
npm install --save nuxt
Install the @nuxt/types package
With the @nuxt/types package, you can get better code completion.
If you’re using a Nuxt.js version from 2.9.0 onwards and don’t have the
@nuxt/typespackage installed, IntelliJ IDEA notifies you about it and suggests installing it as a development dependency. Click the Install @nuxt/types as dev dependency link in the notification popup.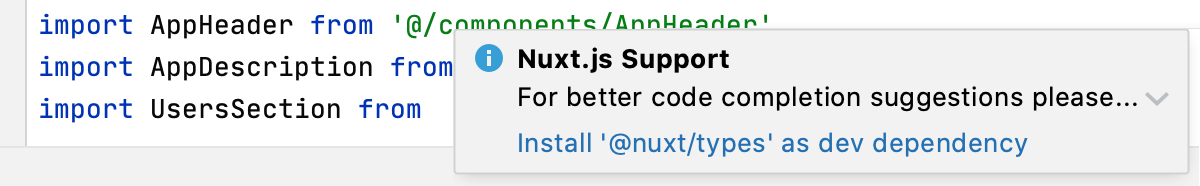
If you close the popup, you can still install
@nuxt/typesby clicking the Install @nuxt/types as dev dependency link in the Event Log tool window ().Alternatively, open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type:
npm install --save-dev @nuxt/types
Nuxt.js-aware coding assistance
IntelliJ IDEA suggests code completion and shows quick documentation for all core Nuxt.js components.

IntelliJ IDEA resolves references to the Vuex store and provides highlighting and completion for them.

IntelliJ IDEA resolves all references to assets stored in the static folder in the <img src='/logo.png/> format.
Edit nuxt.config.js
IntelliJ IDEA provides proper completion suggestions for the nuxt.config.js configuration file.

On hover, you’ll also see the Documentation popup showing the type information for the Nuxt options used in the file.

Module resolution
IntelliJ IDEA supports Nuxt.js-specific webpack setup. Starting with Nuxt.js 2.12.0, IntelliJ IDEA automatically finds the webpack.config.js configuration file and uses the module resolution rules from it for coding assistance.

TypeScript in Vue.js applications
If your Vue.js project is written in TypeScript, you need to choose the service to get coding assistance for .ts and .vue files from. That can be either IntelliJ IDEA integration with the TypeScript Language Service, or the Vue Language server (Volar), or the internal IntelliJ IDEA parser and code inspections.
For TypeScript 5.0.0 and later, the Vue Language Server (Volar) is used by default because the TypeScript Language Service is not supported for these versions.
For earlier versions, the default solution is integration with the TypeScript Language Service, but you can also use integration with the Vue Language Server (Volar).
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
Specify the service to use.
By default, the Automatically option is chosen. In this mode, IntelliJ IDEA detects the TypeScript version used in your project and enables integration with the appropriate service.
For TypeScript version 5.0.0 and later, IntelliJ IDEA downloads the
@vue/language-serverpackage and uses the Vue Language Server (Volar).For earlier versions of TypeScript, the TypeScript Language Service is used. Learn more from Configure integration with the TypeScript Language Service.
If you select Vue Language Server (Volar), IntelliJ IDEA will always provide coding assistance in .ts and .vue files through integration with the Vue Language Server, no matter which version of TypeScript you are using.
Note that the Vue Language Server coding assistance will be restricted to error highlighting only. Code completion and navigation will be provided by the IntelliJ IDEA internal support.
Select TypeScript to always use the TypeScript Language Service in .ts and .vue files.
Note that the TypeScript Language Service does not work with TypeScript version 5.0.0 and later. Therefore, if your project is using one of these versions, error highlighting will be provided through the IntelliJ IDEA internal code inspections.
Select Disabled to turn both the TypeScript Language Service and the Vue Language Server off and get coding assistance from the IntelliJ IDEA internal support.
In the Vue Language Server field, specify the Vue Language Server version to use.
Accept the suggested default version.
If you have another version of
@vue/language-serverpackage installed, this version appears on the list. You can select it or accept the default version.
Alternatively, click Select or
and specify the path to a custom
@vue/language-serverpackage.
Formatting in Vue.js applications
Configure indentation
By default, code within top-level tags is indented uniformly, in the Vue.js-specific style. You can configure this indentation to depend on the language used, for example, be HTML or Pug-specific.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , and open the Tabs and Indents tab.
By default, the contents of all top-level tags are indented uniformly, in the Vue.js-specific style. Accept the default indentation settings or customize them using the controls on the page. As you change the settings, the Preview in the right pane shows how the changes affect code formatting.
To have the code inside top-level tags indented with regard to its language, select Specific to the language in the block.
In the Indent children of top-level tag field, specify the top-level tags where the code should have initial indentation.
By default, only the code inside
templatetags has initial indentation. If necessary, add other tags using commas as separators. For example, if you specifyscriptin the field, the code inside allscripttags gets initial indentation as shown in the Preview pane.
Configure spaces
By default, IntelliJ IDEA automatically inserts spaces after the opening curly brace (
{) and before the closing one (}) in Vue.js text interpolations with Mustache syntax.To suppress inserting spaces automatically, open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , then open the Spaces tab and clear the Interpolations checkbox.
By default, when you enclose a code fragment in a block comment, the text starts right after the opening
/*characters without any spaces. Before the closing*/characters no space is inserted either.This default code style may conflict with some linters' rules, for example, ESLint. To improve the code style, configure enclosing block comments in leading and trailing spaces.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to or , open the Code Generation tab, and configure the spaces and formatting in the Comments area.
Configure wrapping and braces
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , and open the Wrapping and Braces tab.
If a JavaScript expression inside a Vue.js interpolation has line breaks, IntelliJ IDEA automatically starts this JavaScript expression from a new line and adds a new line after it.
Clear the New line after '{{' and the New line before '}}' checkboxes to change this default behavior.
Configure multiple right margins as described in Vue.js code style: Visual guides.
Configure wrapping in interpolations as described in Wrapping options.
Reformat Vue.js code with Prettier
You can configure Prettier to reformat specific files every time such file is changed and the changes are saved automatically or manually, refer to Run Prettier automatically on save.
Also, Prettier can be set as default formatter for specific files. It will run against such files every time you reformat your code with Ctrl+Alt+L.
For more information, refer to Reformat code with Prettier.
Reformat code with Prettier
In the editor, select the code fragment to reformat. To reformat a file or a folder, select it in the Project tool window. Then select Reformat with Prettier from the context menu.
To run Prettier automatically against specific files, open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , and use the On code reformatting and On save checkboxes to specify the actions that will trigger Prettier.
For more information, refer to Run Prettier automatically on save and Set Prettier as default formatter.
IntelliJ IDEA can apply the key code style rules from the Prettier's configuration to the IntelliJ IDEA Code Style settings so that generated code (for example, after refactoring or quick-fix) and the code that is already processed with Prettier are formatted consistently.
Apply Prettier code style rules
In the project where Prettier is enabled, open package.json and click Yes in the pane at the top of the tab.

To re-apply the Prettier code style (after you've clicked No in the pane or modified the code style), press Ctrl+Shift+A and select Apply Prettier Code Style Rules from the Find Action list.
Linting TypeScript in Vue.js components using TSLint
You can lint TypeScript code in your Vue.js single file components using typescript-tslint-plugin.
Because typescript-tslint-plugin works only with TypeScript that is installed in the current project, make sure the typescript package from your project node_modules folder is selected in the TypeScript field on the TypeScript page of the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) .
Install and configure typescript-tslint-plugin
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install --save-dev typescript-tslint-pluginIn the
pluginsproperty of your tsconfig.json file, type:{ "compilerOptions": { "plugins": [{"name": "typescript-tslint-plugin"}] } }When you are using
typescript-tslint-plugin, TSLint is running via the TypeScript Language Service so you can disable the TSLint integration with IntelliJ IDEA to avoid duplicate error reporting.To do that, open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , and select Disable TSLint.
Run a Vue.js application
Сlick
in the gutter next to the
devscript in package.json, or runnpm run devin the Terminal Alt+F12, or double-click thedevtask in the npm tool window ().Wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running. If your application was generated with create-vue, the default URL is http://localhost:5173/. Click this link to view the application.

Run a Vue.js application via a run/debug configuration
For applications created with create-vue in the IntelliJ IDEA New Project wizard as described above, IntelliJ IDEA generates an npm configuration with the default name dev. This configuration runs the vite command that launches the development server and starts your application in the development mode.
In other cases, you need to create a run/debug configuration with the actual settings, such as, host, port, etc., manually.
Create an npm run/debug configuration
Go to . Alternatively, select Edit Configurations from the list on the toolbar.

In the Edit Configurations dialog that opens, click the Add button (
) on the toolbar and select npm from the list.
In the Configuration tab of the Run/Debug Configurations: npm dialog that opens, specify the location of the package.json, the Node.js interpreter, and the package manager to use.
In the Command field, select run from the list and then select the script to run from the Scripts list. Most likely it will be the default
devscript but you can configure another one in your package.json, for example, to run the application on a custom port.
Optionally:
To open the application in the browser, update the configuration as follows: in the Browser / Live Edit tab, select the After launch checkbox, select the browser to open the application in, and specify the URL address at which the application wil run.
If you are going to debug the application, select Google Chrome or another Chromium-based browser.

Run an application
From the list in the Run widget on the toolbar, select a run configuration of the type npm. This can be the autogenerated dev configuration or a custom one that you created yourself as described above.

Wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running. If your application was generated with create-vue, the default URL is http://localhost:5173/. Click this link to view the application.

Alternatively, enable IntelliJ IDEA to open the application on start as described above.
Debug a Vue.js application
You can start a debugging session either by launching a run/debug configuration or from the Run tool window that shows the URL at which your application is running in the development mode.
Start debugging via a run/debug configuration
To debug your Vue.js application you need two run/debug configurations:
An npm configuration to start your application in the development mode, as described above.
A JavaScript Debug configuration to attach the debugger to the application that is running in the development mode.
You can create a JavaScript Debug configuration within the npm configuration to launch them at once, as described in Run and debug a Vue application with an npm run/debug configuration.
Alternatively, launch an npm and a JavaScript Debug run/debug configurations separately, as described in Start debugging with a JavaScript Debug run/debug configuration.
Run and debug a Vue.js application with a single npm run/debug configuration
Set the breakpoints in your code.
Create an npm configuration as described above.
If you generated your application with
create-vue, IntelliJ IDEA has already created an npm configuration with the default name npm dev. The configuration is available from the Run widget and in the Run/Debug Configurations dialog.In the Configuration tab of the Run/Debug Configurations: npm dialog that opens, specify the location of the package.json, the Node.js interpreter, and the package manager to use.
In the Command field, select run from the list and then select the script to run from the Scripts list. Most likely it will be the default
devscript but you can configure another one in your package.json, for example, to run the application on a custom port.
In the Browser / Live Edit tab, select the After launch checkbox, select Google Chrome or another Chromium-based browser from the list, select the with JavaScript debugger checkbox, and then specify the URL at which your application will run.

Click Run.
To re-run the configuration, select it from the list in the Run widget and click
next to it.
IntelliJ IDEA runs the application in the development mode and at the same time launches a debugging session.

When the first breakpoint is hit, switch to the Debug tool window and proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume program execution, examine it when suspended, explore the call stack and variables, set watches, evaluate variables, view actual HTML DOM, and so on.
Start debugging with a JavaScript Debug run/debug configuration
Set the breakpoints in your code.
Start the application in the development mode as described above and wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running. Copy this URL to specify it later in the JavaScript Debug configuration.

Create a JavaScript Debug configuration. To do that, go to in the main menu, click
, and select Javascript Debug from the list.
If you generated your application with
create-vue, IntelliJ IDEA has already created a JavaScript Debug run/debug configuration with the default name Debug Application and the default URLhttp://localhost:5173. Select this run/debug configuration from the list under the JavaScript Debug node.
In the Run/Debug Configurations: JavaScript Debug dialog that opens, specify the name of the configuration and the URL address at which the application is running in the development mode. You can copy this URL in the Run tool window or in the Terminal, as described above.

Click Debug.
To re-run the configuration, select it from the list in the Run widget and click
next to it.

When the first breakpoint is hit, switch to the Debug tool window and proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume program execution, examine it when suspended, explore the call stack and variables, set watches, evaluate variables, view actual HTML DOM, and so on.
Start debugging from the Run tool window or from the built-in Terminal
If your application is running in the development mode on localhost, in particular, if it was generated with create-vue, you can launch a debugging session right from the >Run tool window or from the built-in Terminal.
Set the breakpoints in your code.
Start the application in the development mode as described above and wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running. Hold Ctrl+Shift and click this URL link. IntelliJ IDEA starts a debugging session with an automatically generated Debug Application configuration of the type JavaScript Debug.

When the first breakpoint is hit, switch to the Debug tool window and proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume program execution, examine it when suspended, explore the call stack and variables, set watches, evaluate variables, view actual HTML DOM, and so on.
Troubleshooting for Node.js 17+
In you are using Nuxt.js in the application and your Node.js version 17 or later, during a debugging session you may face network connectivity issues. That may result in problems with attaching the debugger or with loading sourcemaps.
The workaround is to pass --host 127.0.0.1 to the server by updating the dev script in your package.json as follows:
Use several frameworks within a project
Sometimes you may need to use other frameworks within one Vue.js project.
To get context-aware coding assistance in each file, create a configuration file .ws-context and specify which framework should be used in each particular file or folder. The settings from this file will override the default configuration.
In the project root, select New | File from the context menu and specify
.ws-contextas the file name.In
.ws-context, use two types of properties:<context-name>with the context value stringA GLOB pattern with a context details object
Use the following context values:
framework:vue,angular,react,svelte,astroangular-template-syntax:V_2,V_17nextjs-project:nextjsastro-project:astrovue-store:vuex,piniavue-class-component-library:vue-class-component,vue -property-decorator,vue-facing-decoratorjsdoc-dialect:jsdoc-typescript,jsdoc-closure
Use path nesting for simplicity.
The last segment of a GLOB path is the file name pattern, it only supports the
*wildcard.If the last segment is a
**it matches all nested directories and files.Top level context properties should have the
/**pattern.
When several patterns match the same file name, the following rules are used for disambiguation:
Choose the pattern with maximum number of path segments, excluding
**segments.Choose the pattern that is a pure file name pattern, which means that it does not end in
**or/.Choose the pattern that was defined first.
Example
Suppose you have a project with a number of frameworks used in various folders.

To get context-aware assistance for each file in the project, add the following code to .ws-context: