RuboCop
Required plugin: Ruby
IntelliJ IDEA supports integration with RuboCop and enables you to fix its offenses right inside the IDE, for example, in the code editor.
You can also check the entire project and display all RuboCop warnings in a single report.
If necessary, you can enable the Standard wrapper and use it for analyzing project sources.
The RuboCop inspection is enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default and requires the 'rubocop' gem to be installed in the project’s SDK. If this gem is not installed, IntelliJ IDEA will suggest doing this.
If you want to use Standard to analyze your project, add the 'standard' gem to your Gemfile and install it.
To enable or disable RuboCop and Standard inspections, do the following:
Open the Settings dialog CtrlAlt0S.
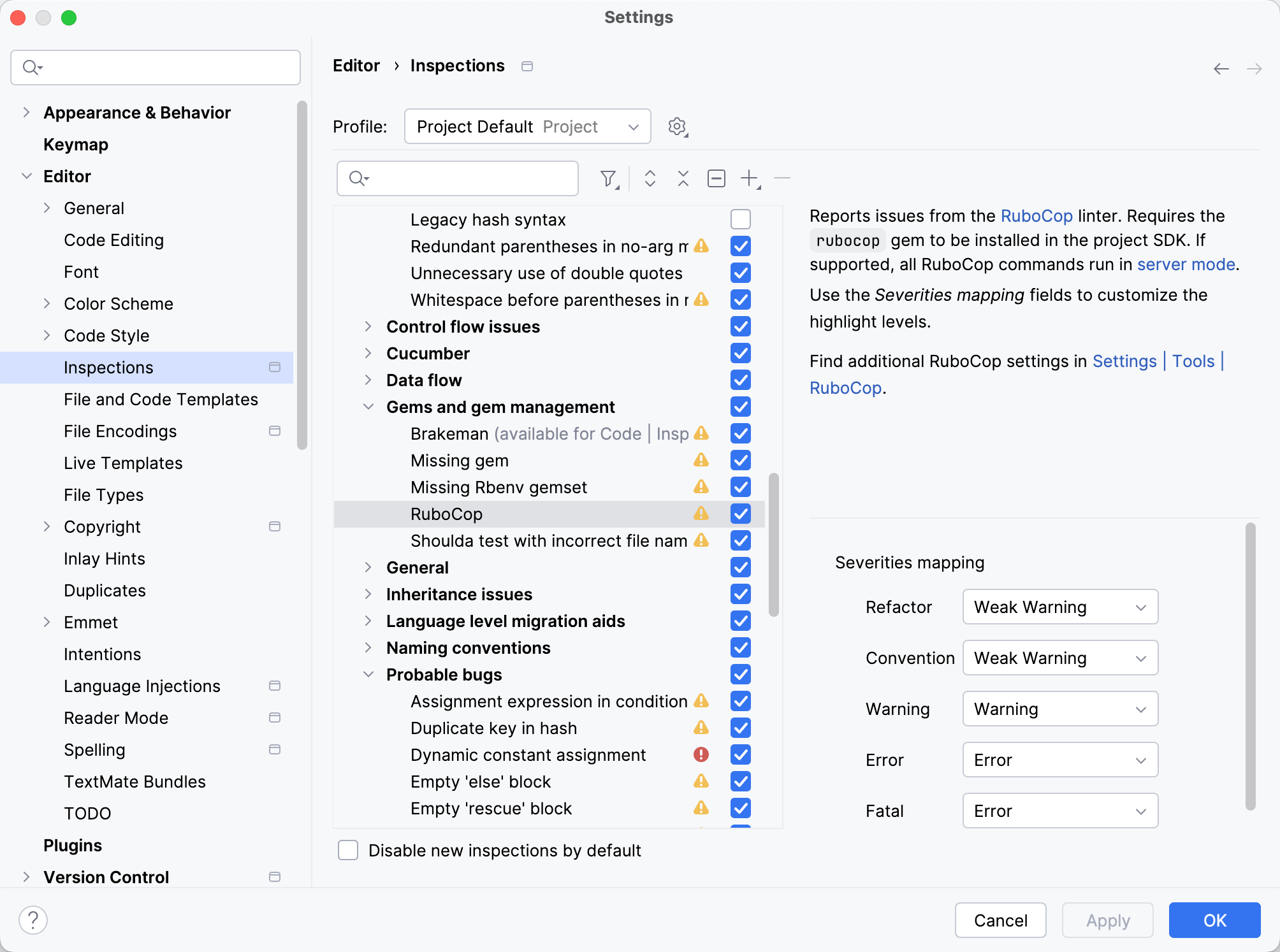
Go to the Editor | Inspections page and enable/disable the RuboCop inspection under Ruby | Gems and gem management.
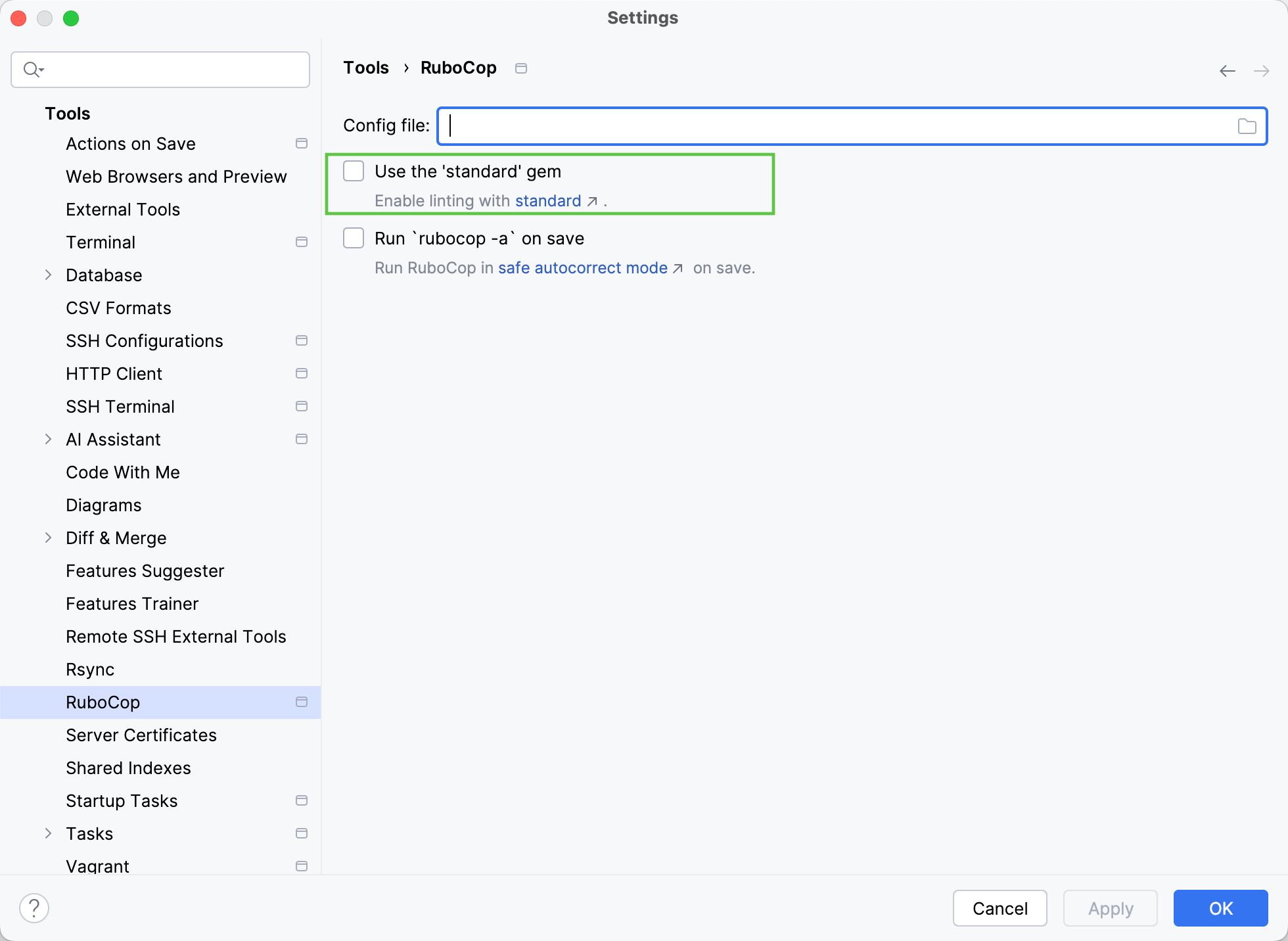
To use the Standard linter and formatter, go to the Tools | Rubocop page and enable the Use 'standard' gem option.
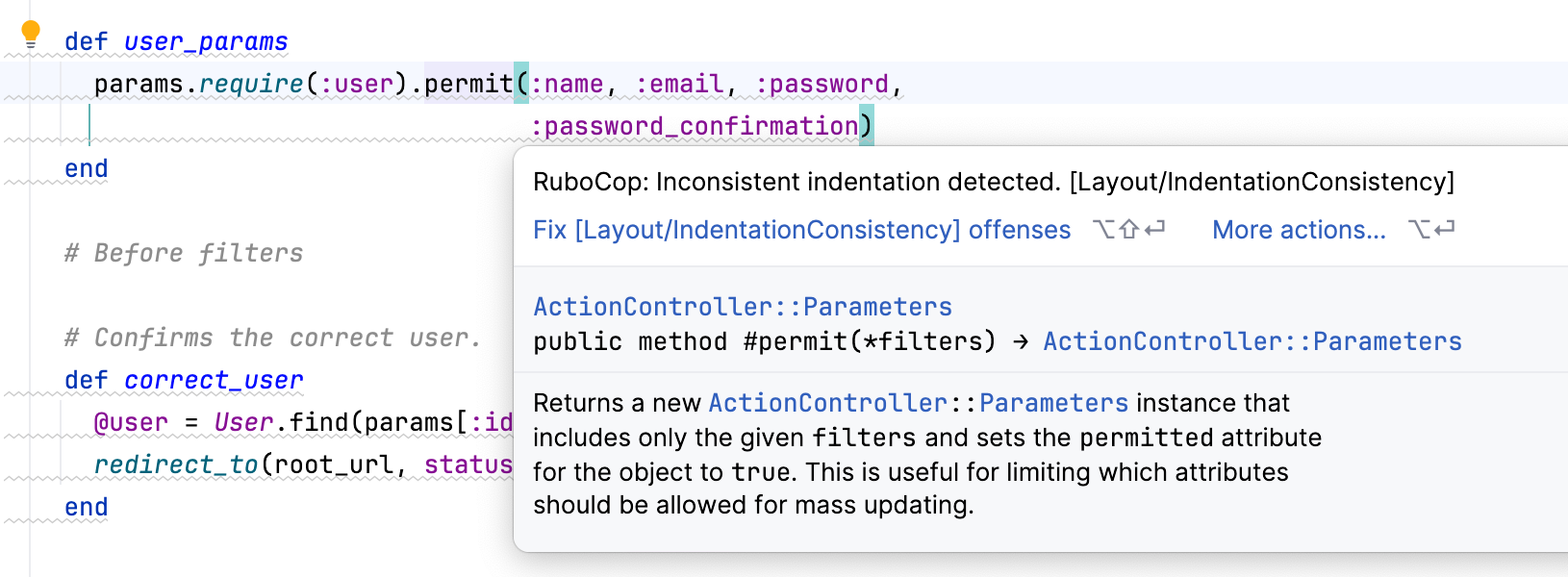
When RuboCop inspections are enabled, IntelliJ IDEA highlights its offenses in the code editor. To see the warning description and fix it, do the following:
Place the caret at the highlighted area and press CtrlF1.

To fix the offense, press AltEnter. You can fix all suggested offenses in a file, or you can apply only specific fixes by a class offense or cop department.
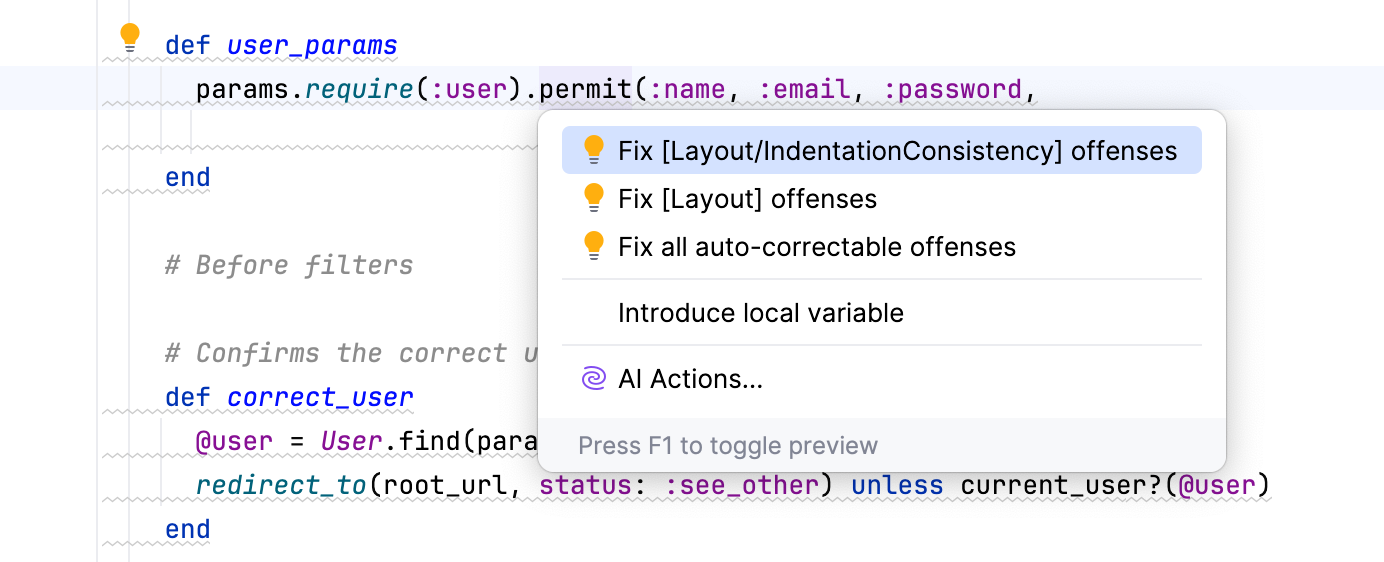
IntelliJ IDEA enables you to find RuboCop offenses for the entire project by running a corresponding inspection. To do this, follow the steps below:
Press CtrlAltShift0I or go to Code | Analyze Code | Run Inspection by Name in the main menu.
In the popup, find RuboCop and press Enter.
In the Run 'RuboCop' dialog, specify the scope of files that you want to analyze. If necessary, enable Use 'standard' gem. Click OK.
Wait until IntelliJ IDEA analyzes your project. In the Inspection Results tool window, you can explore RuboCop offenses and fix auto-correctable ones using the Fix all auto-correctable RuboCop offenses button.
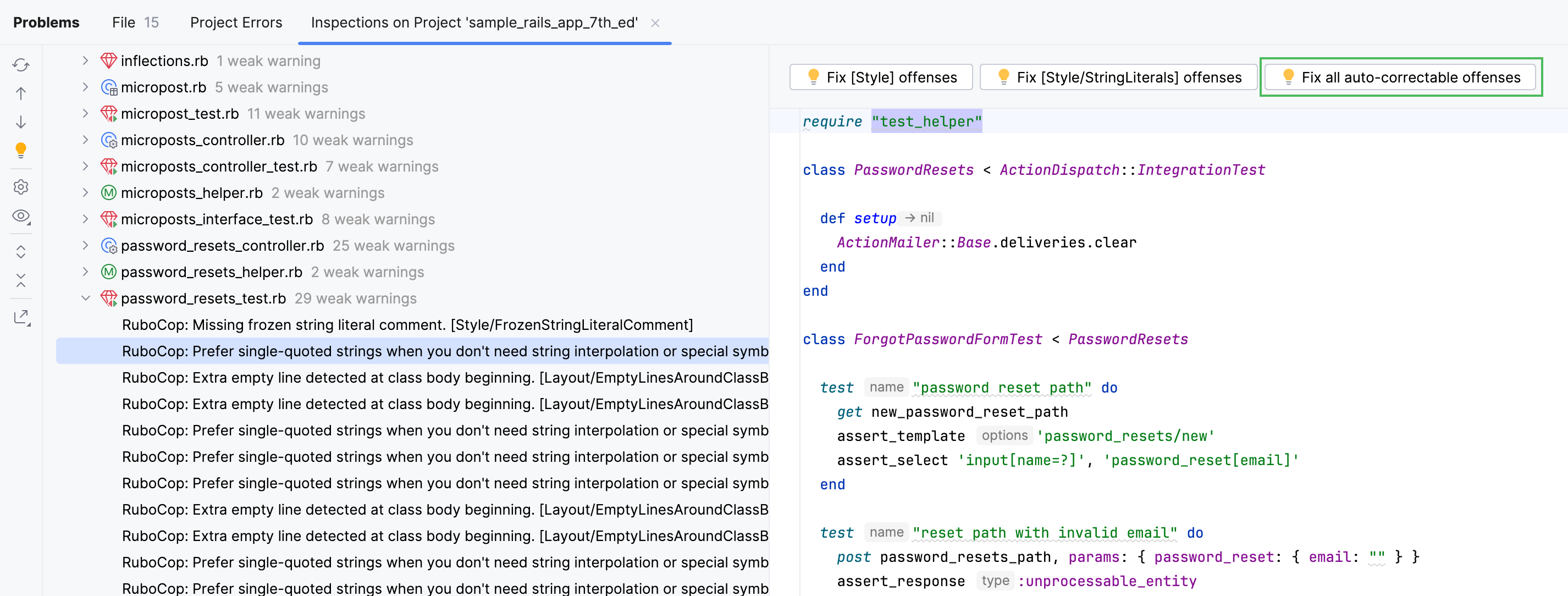
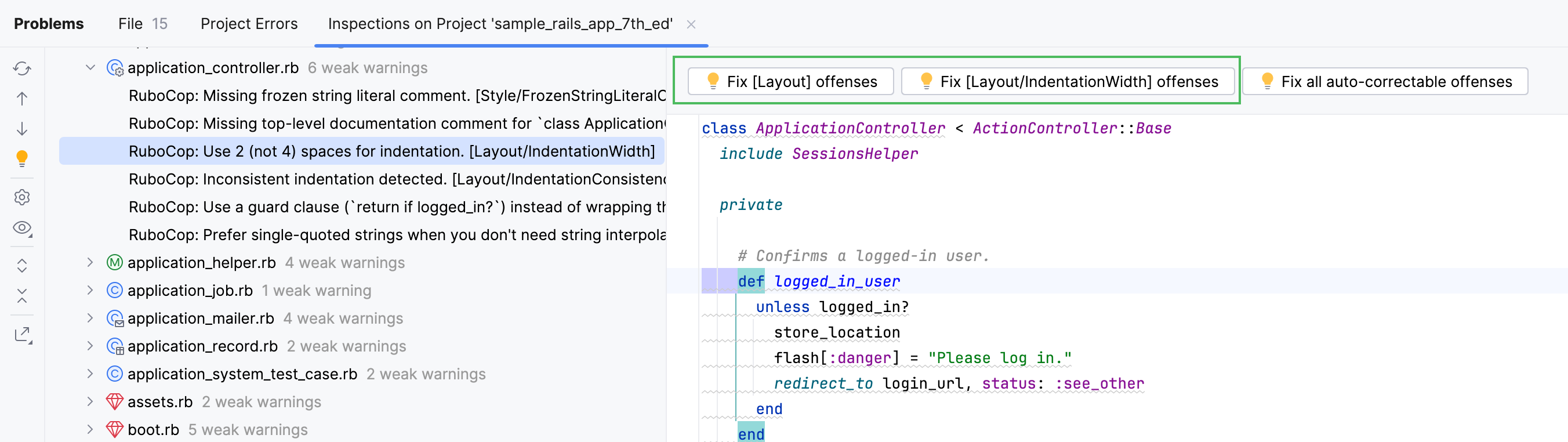
You can also explore individual files and apply specific fixes by a class offense or cop department.
You can configure IntelliJ IDEA to automatically launch RuboCop and autocorrect your code in safe mode every time you save your changes.
In the Settings dialog (CtrlAlt0S) , select Tools | Rubocop.
Select the Run `rubocop -a` on save option to enable RuboCop autocorrection on save.
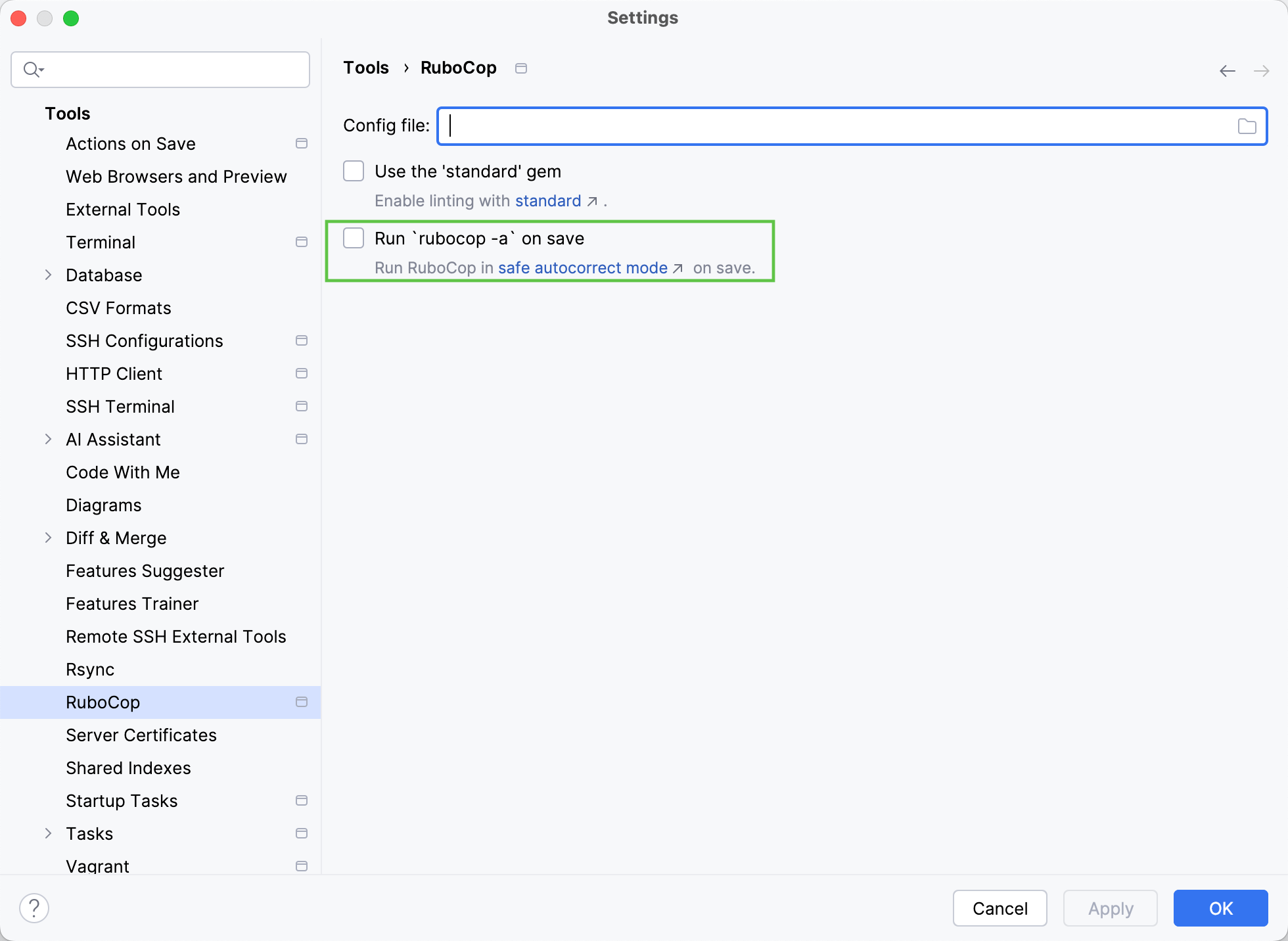
Click OK to apply the changes.
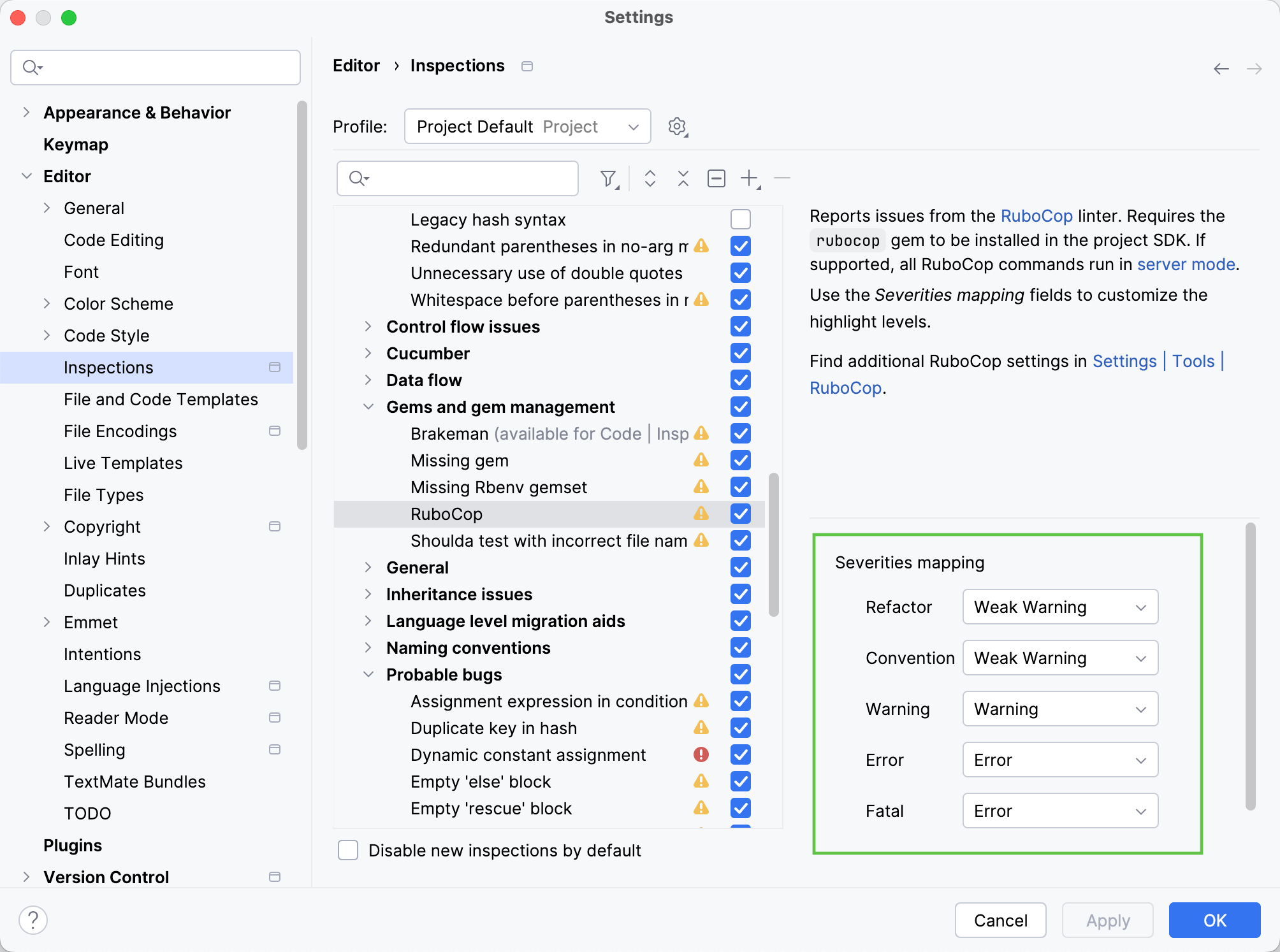
By default, IntelliJ IDEA maps RuboCop severities and inspection severities in the following way:
RuboCop severity | Inspection severity |
|---|---|
Refactor, Convention | Weak Warning |
Warning | Warning |
Error, Fatal | Error |
To change the default mapping, follow the steps below:
Open the Settings dialog CtrlAlt0S.
Go to the Editor | Inspections page and select the RuboCop inspection.
Configure how RuboCop severities map to inspection severities in the RuboCop Severities Mapping group.
RuboCop allows you to customize its behavior through configuration files. IntelliJ IDEA automatically detects .rubocop.yml file and uses it to run the inspection. Alternatively, you can specify a custom configuration file for the inspection.
IntelliJ IDEA takes into account all settings specified in the .rubocop.yml file. For example, if you disable some checks for a specified cop department, the editor will not show corresponding offenses. Moreover, these offenses won't be shown in the RuboCop inspection report.
note
Some RuboCop checks depend on the Ruby interpreter version. Make sure that the target Ruby version configured for the RuboCop is the same as the Ruby interpreter specified for a project.
To specify a custom RuboCop configuration file:
In the Settings dialog (CtrlAlt0S) , select Tools | Rubocop.
Specify the configuration file in the Config file field.
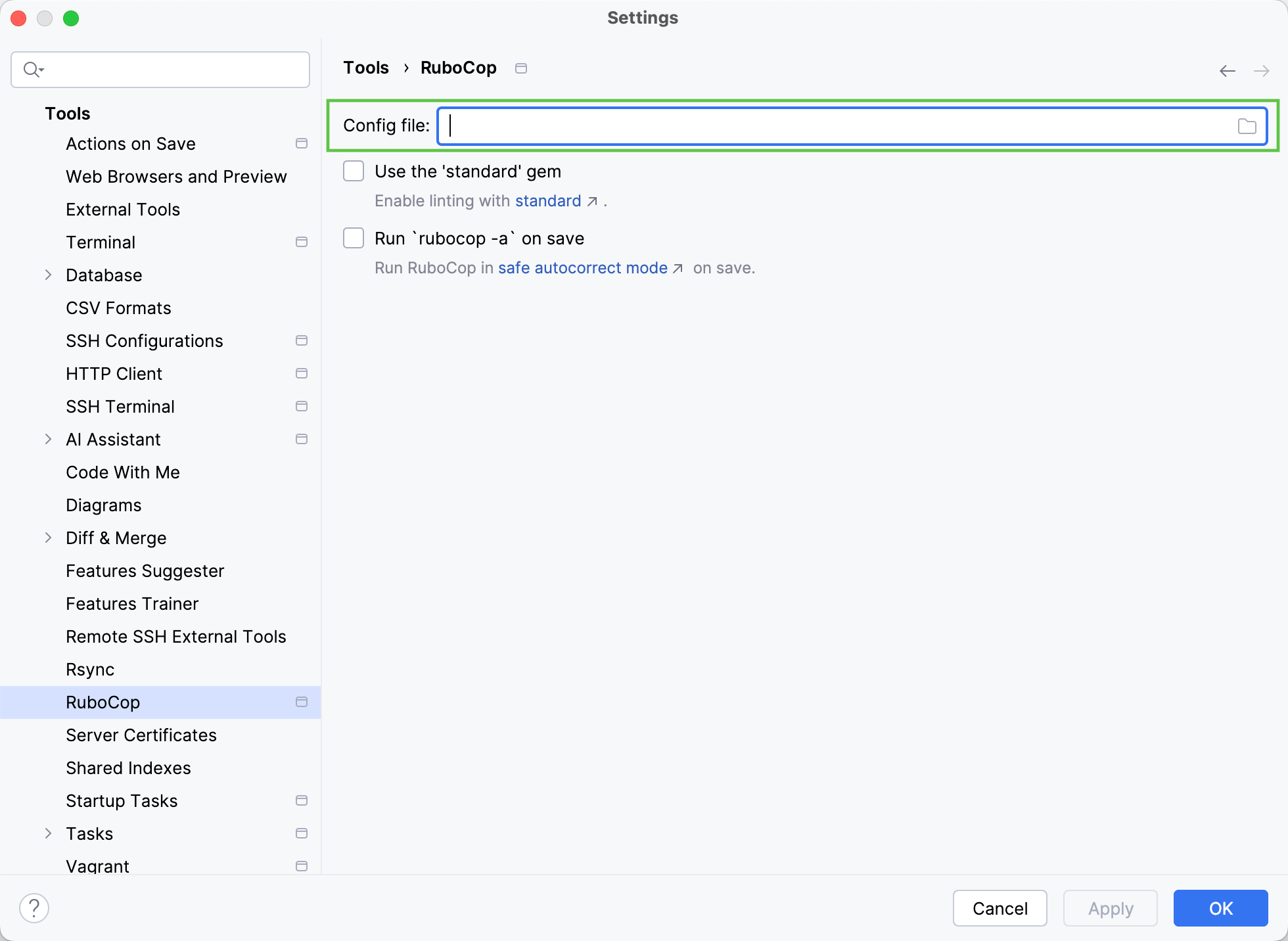
If no configuration file is selected, the inspection runs using .rubocop.yml if present in the project. Otherwise, IntelliJ IDEA uses the default settings.
Sometimes it is necessary to run RuboCop for the currently opened file with custom options. For example, this can be useful when RuboCop inspections are disabled, or you want to assign a shortcut for a specific RuboCop action.
In this example, we'll show how to use RuboCop as an external tool to correct layout offenses in the currently opened file.
In the Settings dialog (CtrlAlt0S) , select Tools | External Tools.
Click
and specify the following settings:
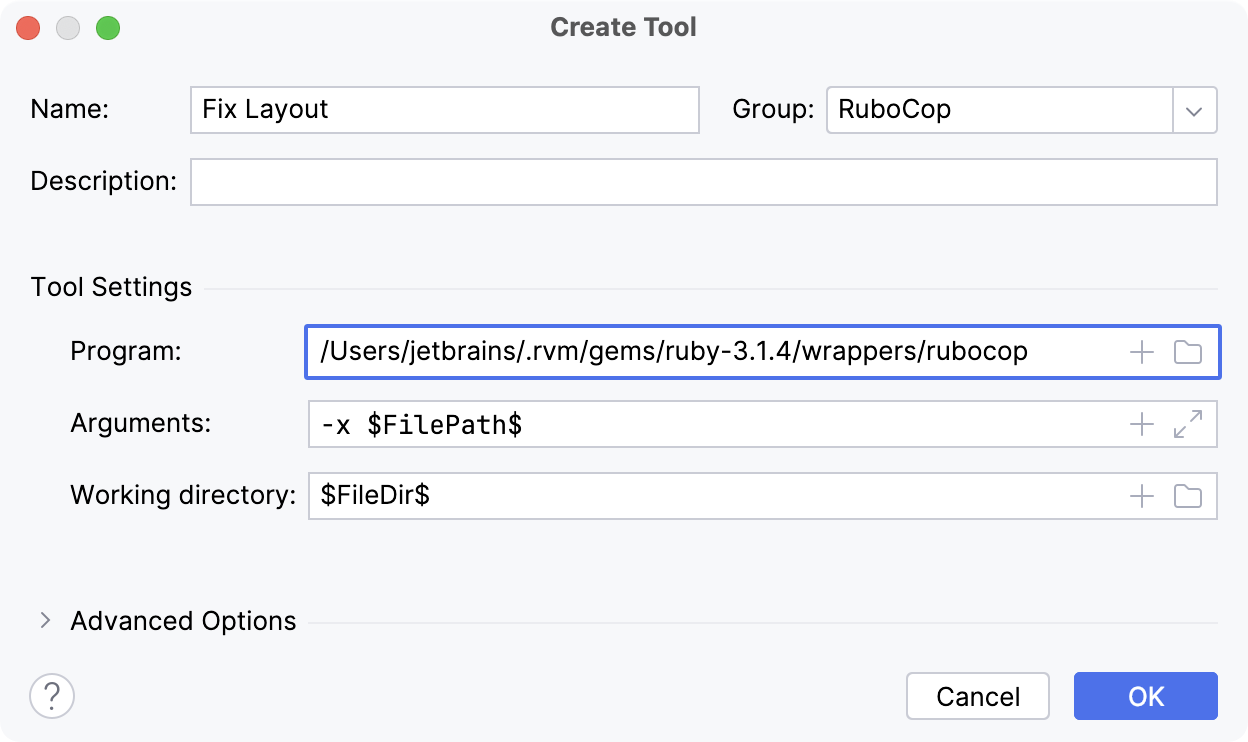
Name: The menu command that will be displayed in the IntelliJ IDEA interface (the Tools menu and context menus).
Group: The name of the group to which the command belongs. You can select an existing group or type the name of a new group.
Program: The name of the RuboCop executable.
Arguments: The arguments passed to the executable file, as you would specify them on the command line. Here we use
-xRuboCop option to run only layout cops for the current file.Working directory: The path to the current working directory from which the tool is executed.
Click OK to add the tool and then apply the changes.
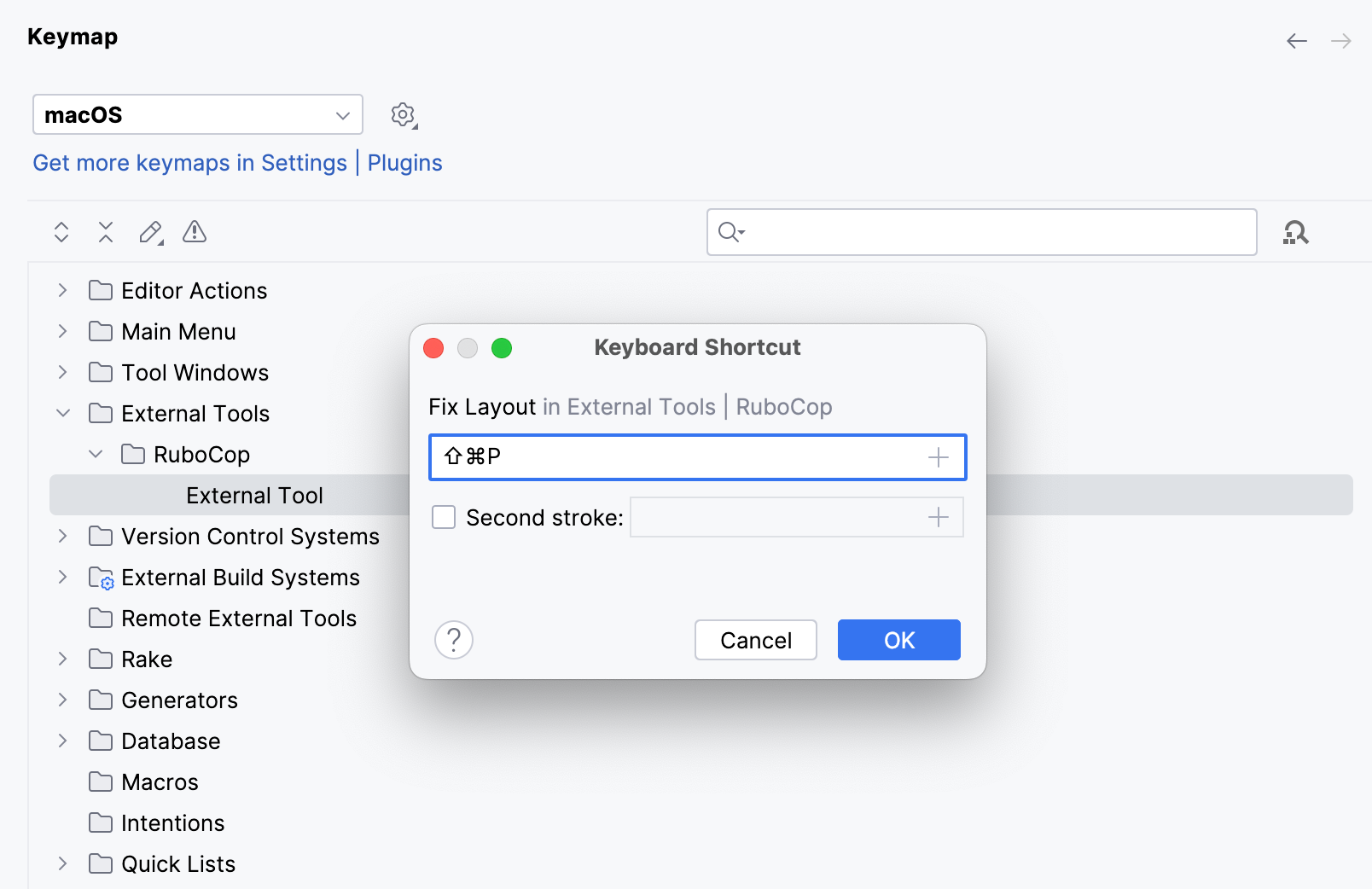
(Optional) Assign a shortcut for the created action. In the Settings dialog (CtrlAlt0S) , select Keymap, find the External Tool action under the RuboCop node and specify a shortcut.
To run the created RuboCop action, go to the Tools main menu or use the context menu of a file.
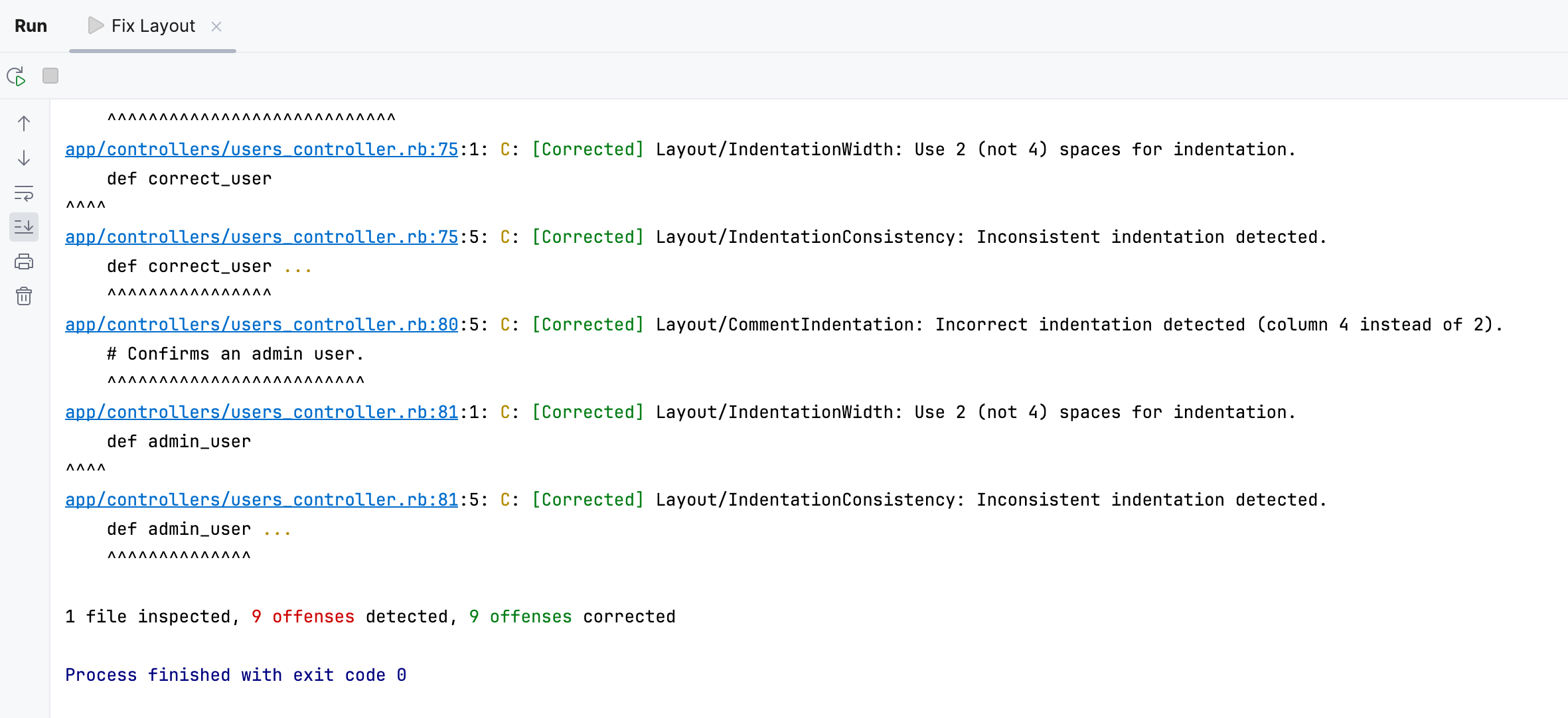
When the command runs, its output is displayed in the Run tool window.
Thanks for your feedback!