Minifying CSS
Minification or compression means removing all unnecessary characters, such as spaces, new lines, comments, without changing the functionality of the source code. During development and debugging, these characters make code easier to read. At the production stage, they only increase the size of code to be transferred.
Most often compression is done as a step in your build process, with tools like webpack. If you're not using build tools, you can use stand-alone tools, such as CSSO or cssnano.
To minify your code automatically, you need to install a minification tool and configure a File Watcher which will track changes to your files and run the minification tool.
By default, minification starts as soon as a CSS file in the File Watcher's scope is changed and saved. You can specify other events that invoke the tool. Learn more from File Watchers.
The generated minified code is stored in a separate file with the name of the source CSS file and the extension min.css. The location of this generated file is defined in the Output paths to refresh field of the New Watcher dialog. However, in the Project Tree, the file with the minified code is shown under the source CSS file which is displayed as a node. To change this default presentation, configure file nesting in the Project tool window Alt+1.
The example below shows how you can use CSSO to minify your CSS code right from IntelliJ IDEA.
Example: Compressing CSS with CSSO
To minify your code automatically, you need to install CSSO and configure a CSSO File Watcher which will track changes to your files and run the tool.
By default, minification starts as soon as a CSS file in the File Watcher's scope is changed and saved. You can specify other events that invoke CSSO. Learn more from File Watchers.
The generated minified code is stored in a separate file with the name of the source CSS file and the extension min.css. The location of this generated file is defined in the Output paths to refresh field of the New Watcher dialog. However, in the Project Tree, the file with the minified code is shown under the source CSS file which is displayed as a node. To change this default presentation, configure file nesting in the Project tool window Alt+1.
Before you start
Make sure you have Node.js on your computer.
Make sure the CSS plugin are enabled in the settings. Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select . Click the Installed tab. In the search field, type CSS. For more information about plugins, refer to Managing plugins.
Install and enable the File Watchers plugin on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Marketplace, as described in Installing plugins from JetBrains Marketplace.
Install csso-cli globally
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install -g csso-cli
Create a CSSO File Watcher
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , click File Watchers under Tools. The File Watchers page that opens shows the list of already configured File Watchers.
Click
or press Alt+Insert and select the CSSO CSS Optimizer predefined template from the list.
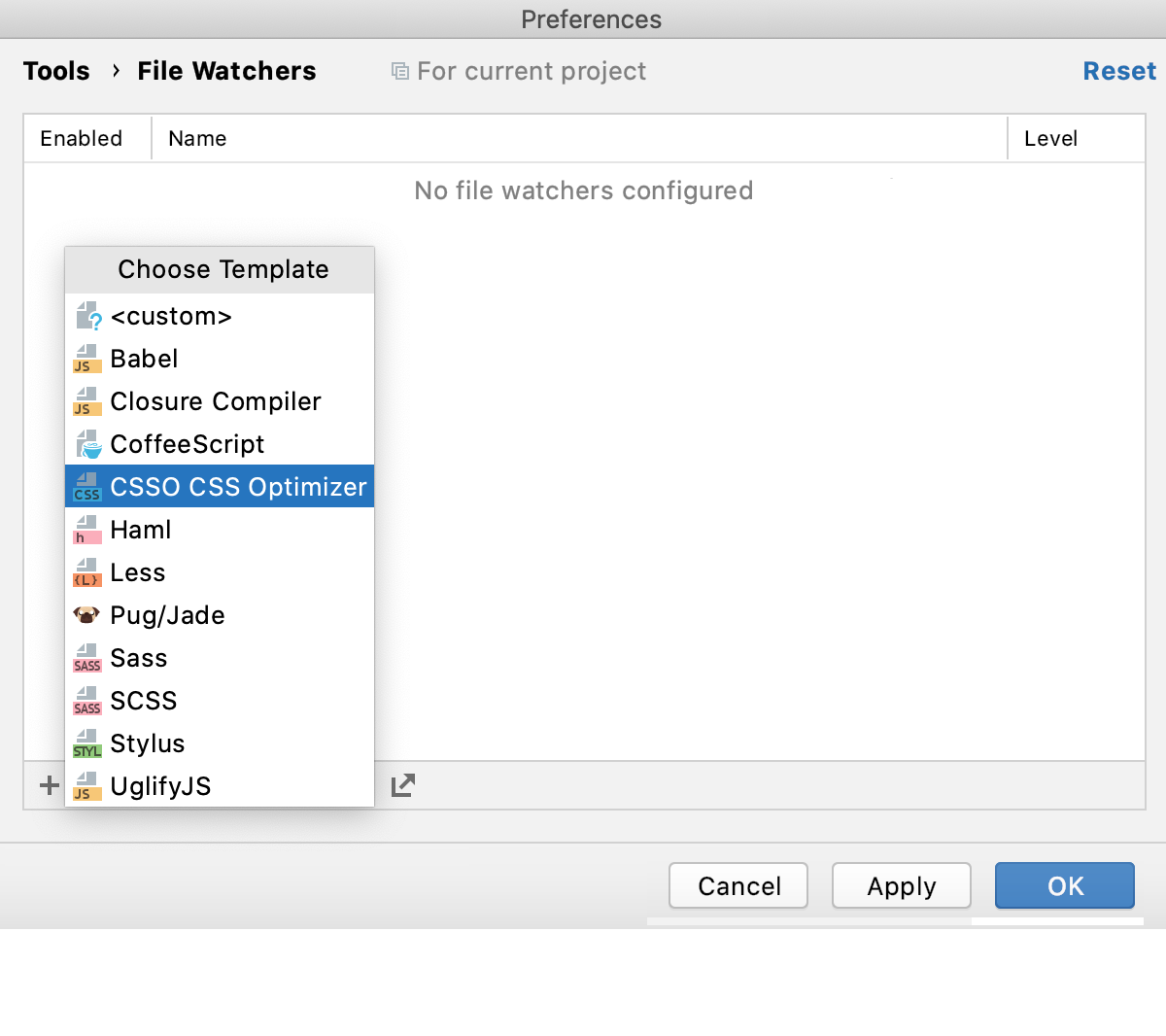
The New Watcher dialog opens.
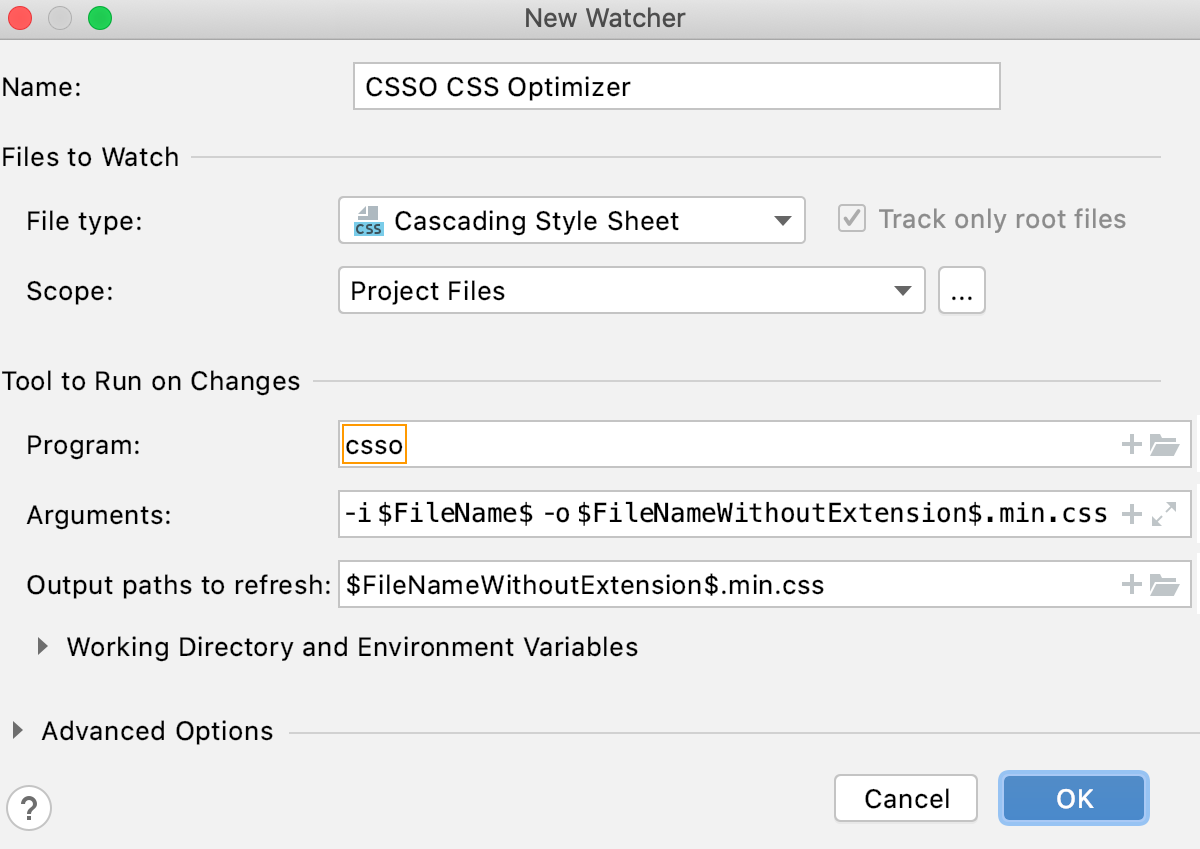
In the Program field, specify the location of the
cssoexecutable file.If you installed
csso-clithrough the Node Package Manager, IntelliJ IDEA locates the package itself and fills in the field automatically with thecssoalias Otherwise, type the path manually or clickand select the file location in the dialog that opens.
Accept the default File Watcher settings or reconfigure them, if necessary, as described in File Watchers.
In this example, the default values are as follows:
-i $FileName$ -o $FileNameWithoutExtension$.min.cssin the Arguments field.$FileNameWithoutExtension$.min.cssin the Output paths to refresh field.$FileDir$in the Working directory field.
Click OK to get back to the File Watchers page where the new File Watcher is added to the list:
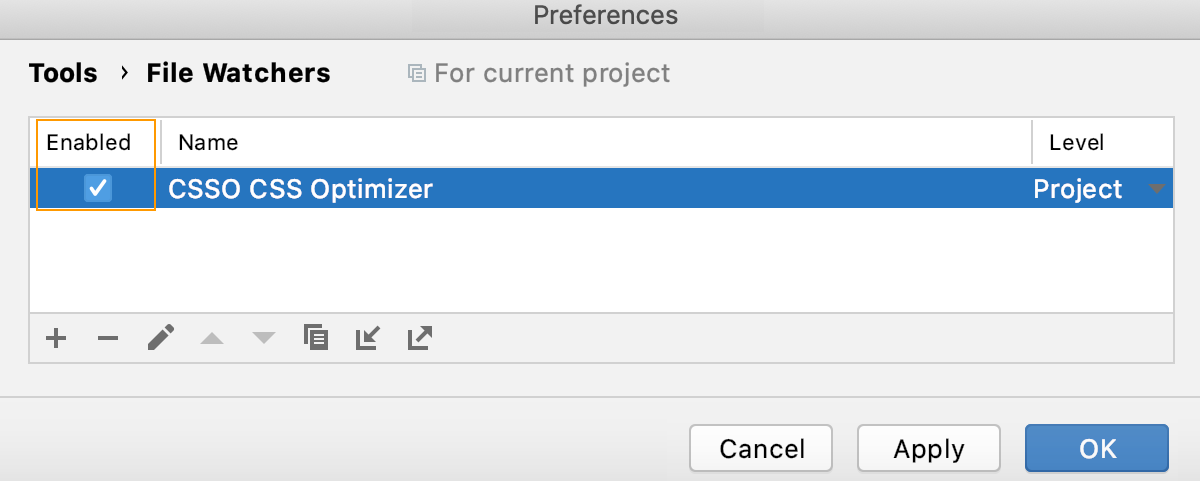
Make sure the Enabled checkbox is selected.
By default, the File Watcher will be available in the current project. To use it in other projects, select Global from the Level list.