Next.js
Available only in IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate: download to try or compare editions
Required plugins:
JavaScript and TypeScript, Next.js Support - The plugins are available only in IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate, where they are enabled by default.
IntelliJ IDEA integrates with the Next.js React framework.
Download and install Node.js.
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript and Next.js Support required plugins are enabled on the Settings | Plugins page, tab Installed. For more information, refer to Managing plugins.
The recommended way to start building a new Next.js application is the create-next-app package, which IntelliJ IDEA downloads and runs for you using npx. As a result, your development environment is preconfigured to use Next.js.
Of course, you can still download create-next-app yourself or create an empty IntelliJ IDEA project and install Next.js in it.
tip
Learn more about starting with Next.js from the Next.js official website.
Select File | New | Project from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select React in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand part of the wizard, specify the project name and the folder to create it in.
In the Project type area, select Next.js.
In the Node Interpreter field, specify the Node.js interpreter to use. Select a configured interpreter from the list or choose Add to configure a new one.
From the create-next-app list, select npx create-next-app.
Alternatively, for npm version 5.1 and earlier, install the
create-next-apppackage yourself by runningnpm install --save-dev next react react-domin the Terminal AltF12. When creating an application, select the folder where thecreate-next-apppackage is stored.Optionally:
To use TypeScript instead of JavaScript, select the Use TypeScript template checkbox. IntelliJ IDEA will generate .ts files for your application and a tsconfig.json configuration file.
When you click Create, IntelliJ IDEA generates a Next.js-specific project with all the required configuration files and downloads the required dependencies. IntelliJ IDEA also creates an npm start and JavaScript Debug configurations with default settings for running or debugging your application.
tip
Alternatively, open the built-in Terminal and type:
npx create-next-app <application-name>to create an application.
cd <application-name>to switch to the application folder.
npm startto start the Node.js server.
In this case, you will have to configure the build pipeline yourself. Learn more about adding Next.js to a project from the Next.js official website.
Select File | New | Project from the main menu or click the New Project button on the Welcome screen.
In the New Project dialog, select New Project in the left-hand pane.
In the right-hand pane, select JavaScript in the Language area.
Name the new project and change its location if necessary, then click Create.
Open the empty project where you will use Next.js.
In the embedded Terminal (AltF12) , type:
npm install --save-dev next react react-dom
To continue developing an existing Next.js application, open it in IntelliJ IDEA and download the required dependencies.
Click Open or Import on the Welcome screen or select File | Open from the main menu. In the dialog that opens, select the folder where your sources are stored.
Click Clone Repository on the Welcome screen.
Alternatively, select File | New | Project from Version Control or Git | Clone or VCS | Get from Version Control from the main menu.
Instead of Git in the main menu, you may see any other Version Control System that is associated with your project. For example, Mercurial or Perforce.
In the dialog that opens, select your version control system from the list and specify the repository to check out the application sources from. For more information, refer to Check out a project (clone).
Click Run 'npm install' or Run 'yarn install' in the popup:
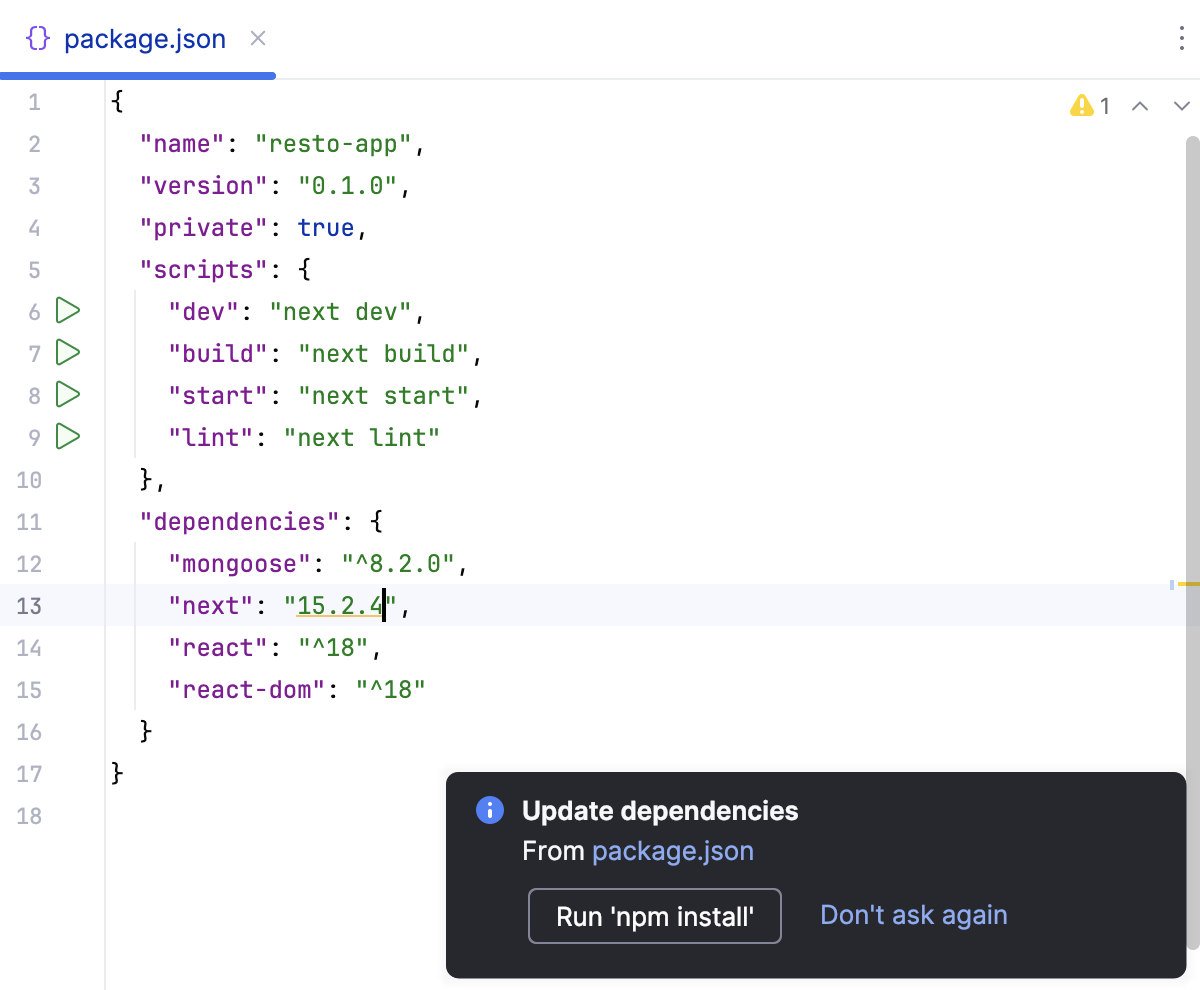
You can use npm, Yarn 1, or Yarn 2, refer to npm and Yarn for details.
Alternatively, select Run 'npm install' or Run 'yarn install' from the context menu of package.json in the editor or in the Project tool window Alt01.
When you open a project that was created outside IntelliJ IDEA and was imported into it, IntelliJ IDEA displays a dialog where you can decide how to handle this project with unfamiliar source code.
Select one of the following options:
Preview in Safe Mode: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens the project in a preview mode. It means that you can browse the project's sources but you cannot run tasks and script or run/debug your project.
IntelliJ IDEA displays a notification on top of the editor area, and you can click the Trust project link and load your project at any time.
Trust Project: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA opens and loads a project. That means the project is initialized, project's plugins are resolved, dependencies are added, and all IntelliJ IDEA features are available.
Don't Open: in this case, IntelliJ IDEA doesn't open the project.
Learn more from Project security.
tip
Projects created from the Welcome screen or via File | New | Project as described in are automatically considered trusted.
With IntelliJ IDEA, you can run your application and start debugging sessions in two ways:
From the editor - run the
next devcommand as a script from package.json or in the Terminal. Then start a debugging session by clicking the application URL in the Run tool window or in the Terminal.
Сlick
in the gutter next to the
devscript in package.json, or execute thenext devcommand in the Terminal AltF12, or double-click thedevtask in the npm tool window (View | Tool Windows | npm).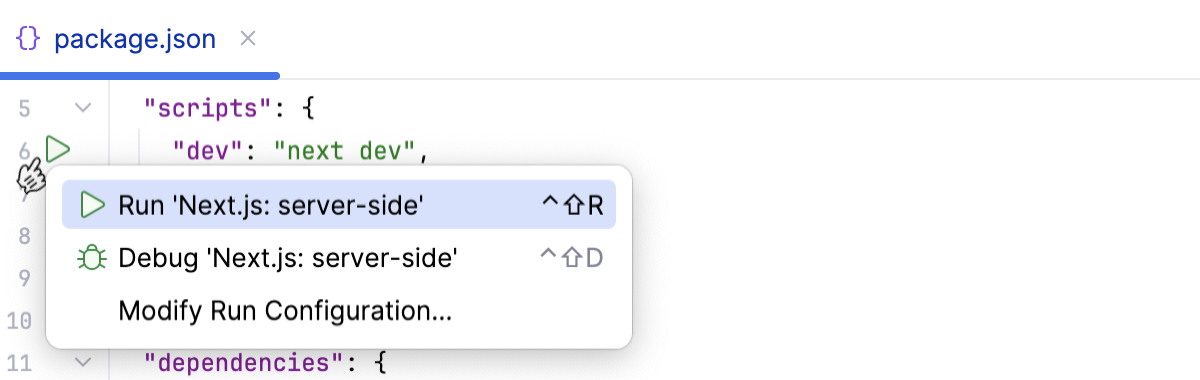
Wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running, the default URL is http://localhost:3000.
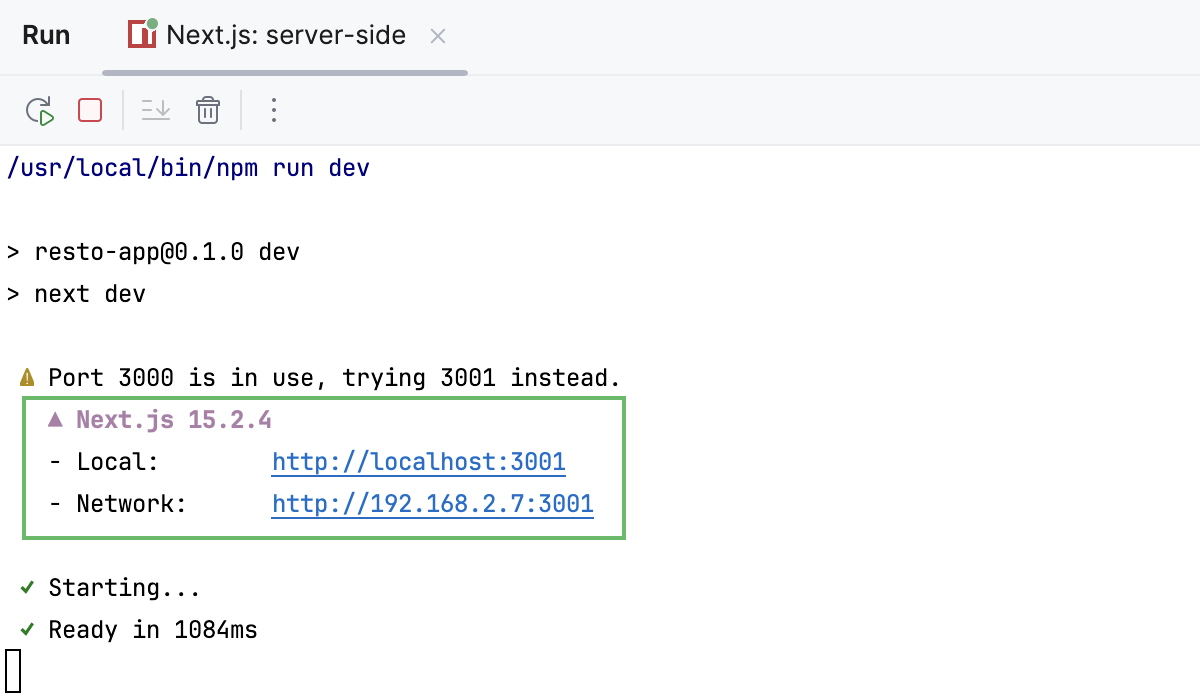
Click this link to view the application in the browser.
Set breakpoints where necessary.
Сlick
in the gutter next to the
devscript in package.json, or execute thenext devcommand in the Terminal AltF12, or double-click thedevtask in the npm tool window (View | Tool Windows | npm).Wait till the application is compiled and the development server is ready.
The Run tool window or the Terminal shows the URL at which your application is running, the default URL is http://localhost:3000.

Hold CtrlShift and click the link.
When the application opens in the browser, perform the actions that trigger the program execution, for example, click a link. The focus switches to IntelliJ IDEA with the Debug tool window open.
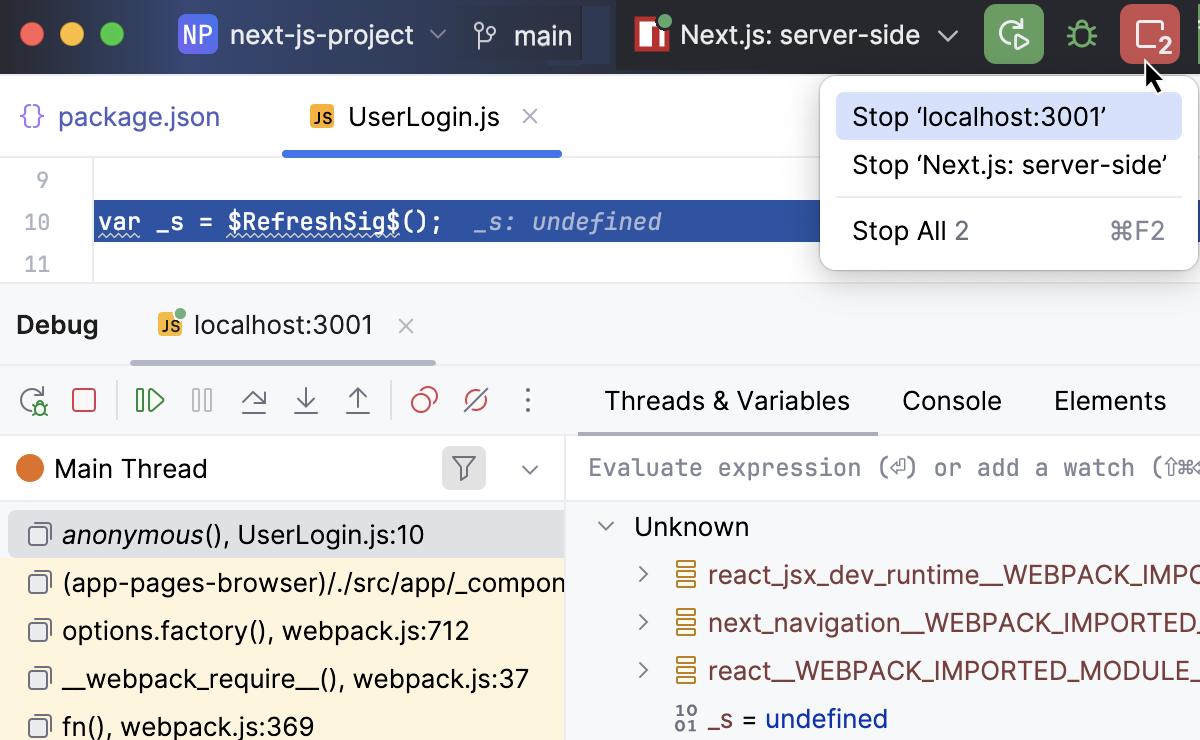
Proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume program execution, examine it when suspended, explore the call stack and variables, set watches, evaluate variables, view actual HTML DOM, and so on.
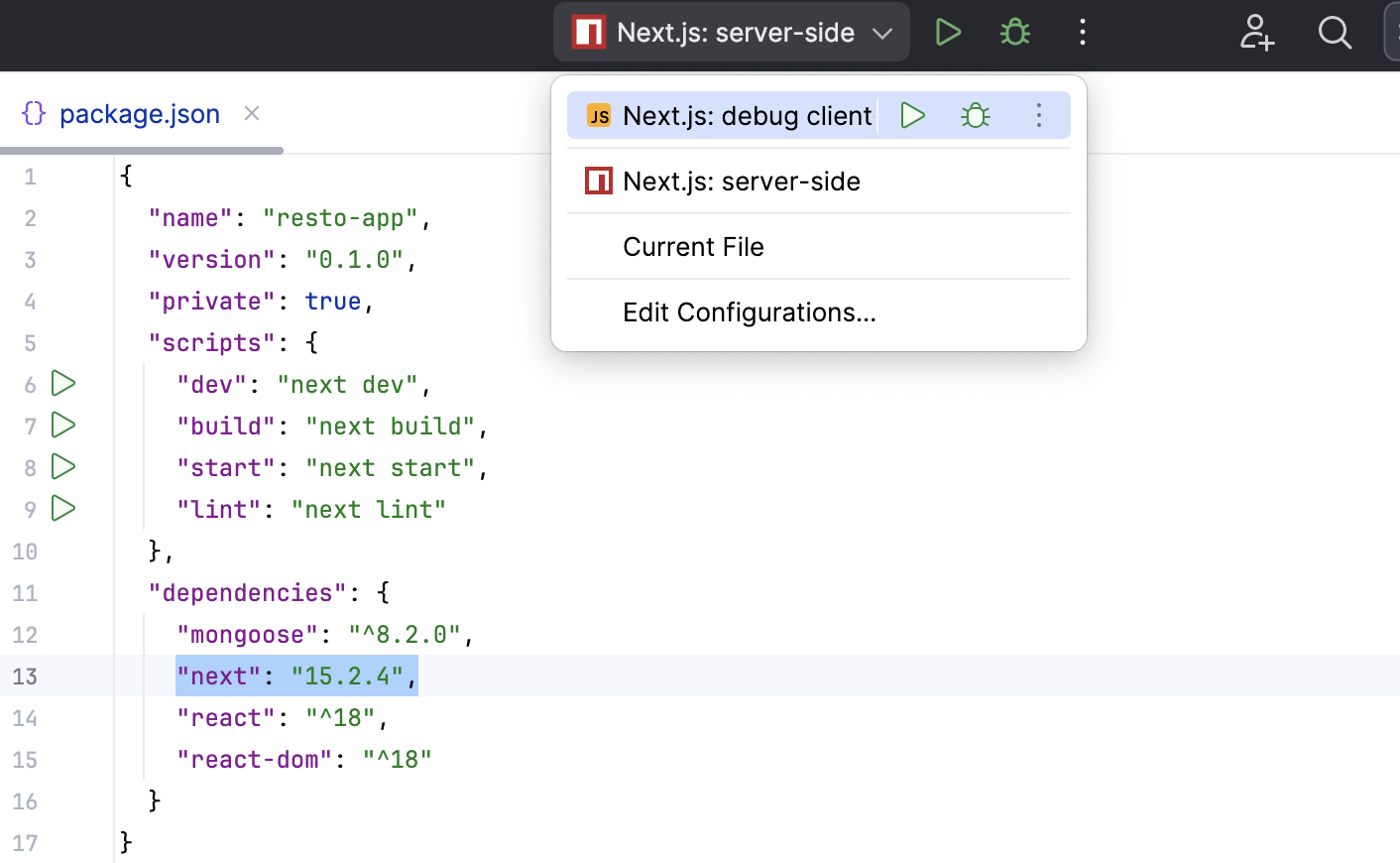
When you open a single-repo project with the next package listed as dependency in the root package.json, IntelliJ IDEA automatically generates two run/debug configurations:
Next.js: server-side of the type npm. The configuration executes the
next devcommand that starts the development server and runs your application in the development mode.Next.js: debug client-side of the type JavaScript Debug to debug your application in the browser.
note
For mono-repo projects, you have to create these run/debug configurations manually.
For projects generated via the New Project wizard, the run/debug configurations are generated on reopening a project.
If you remove an auto-generated run/debug configuration, it is not created anew automatically.
Go to Run | Edit Configurations. Alternatively, select Edit Configurations from the Run widget on the toolbar.

In the Edit Configurations dialog that opens, click the Add button (
) on the toolbar and select npm from the list.
In the Configuration tab of the Run/Debug Configurations: npm dialog that opens, specify the location of the package.json, the Node.js interpreter, and the package manager to use.
In the Command field, select run from the list and then select the script to run from the Scripts list. Most likely it will be the default
devscript but you can configure another one in your package.json, for example, to run the application on a custom port.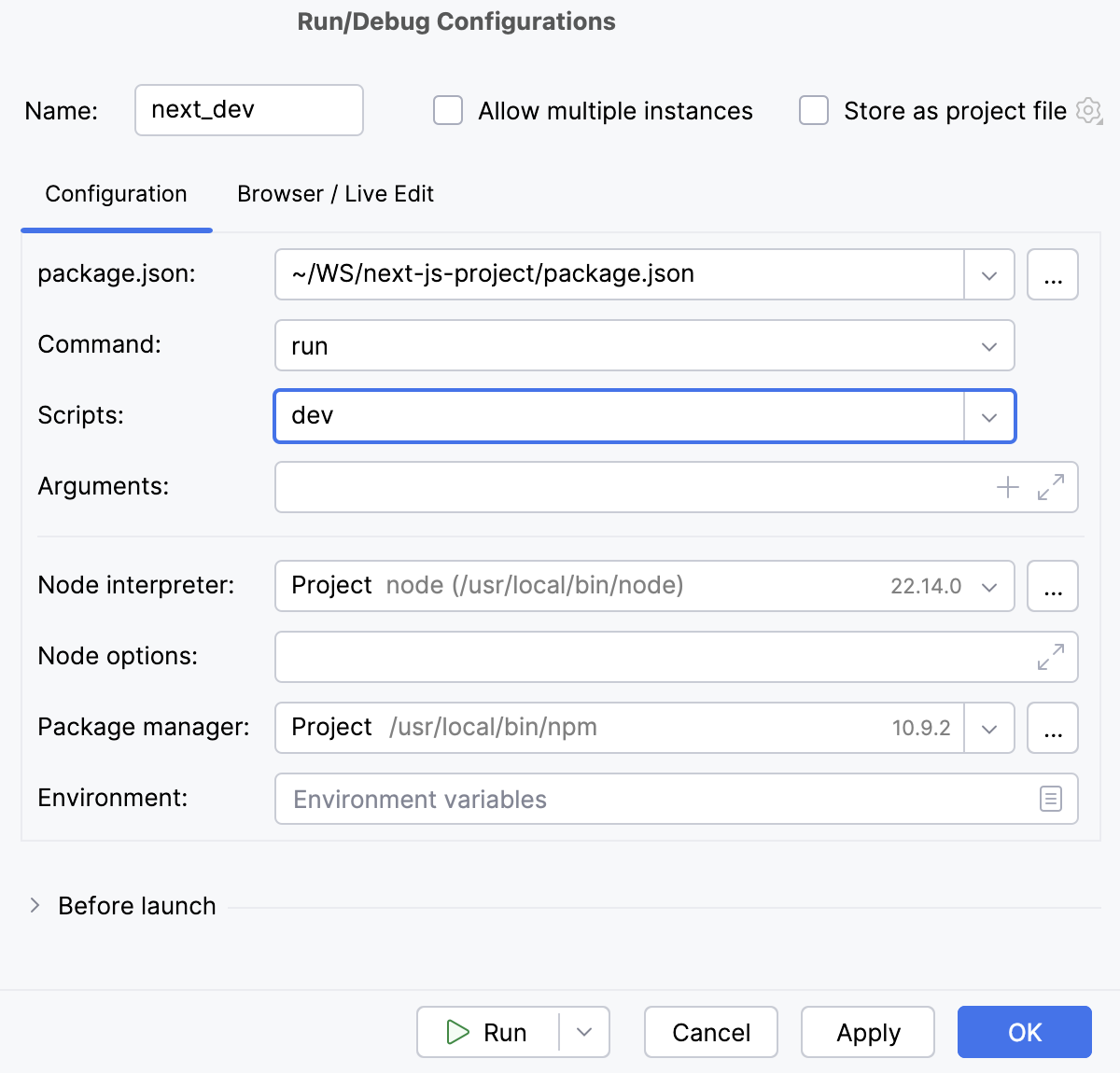
Optionally:
To open the application in the browser, update the configuration as follows: in the Browser / Live Edit tab, select the After launch checkbox, select the browser to open the application in, and specify the URL address at which the application wil run.

note
If you are going to debug the application, select Google Chrome or another Chromium-based browser.
From the list in the Run widget on the toolbar, select a run configuration of the type npm. This can be the autogenerated Next.js: server-side configuration or a custom one that you created yourself as described above.
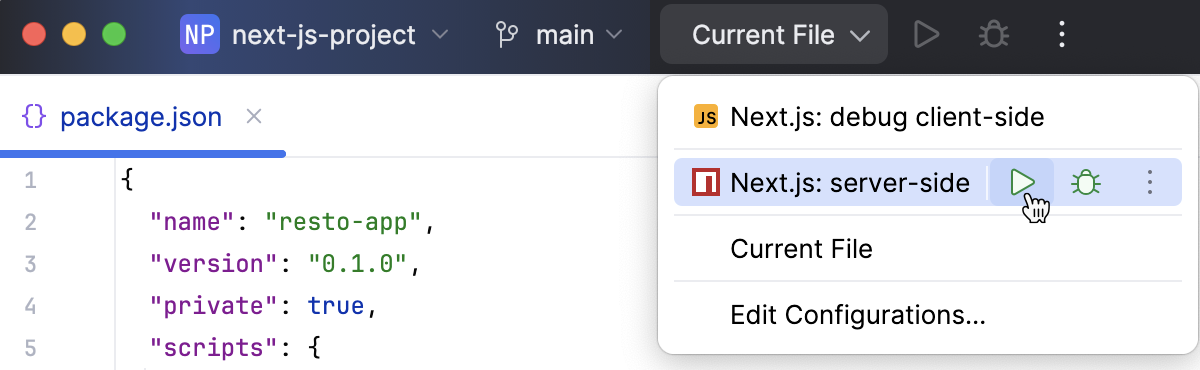
Click
.
When the application is compiled and the development server is ready, the Run tool window shows the URL at which your application is running. The default URL is http://localhost:3000, however if the default port
3000is already busy, the server tries starting on the closest free port.
Click this link to view the application.
Alternatively, enable IntelliJ IDEA to open the application on start as described above.
note
When the development server is running, your application is automatically reloaded as soon as you change any of the source files and save the updates.
Set breakpoints where necessary.
Run your application in the development mode with an npm run/debug configuration or with
next dev.When the application is compiled and the development server is ready, the Run tool window shows the URL at which your application is running. The default URL is http://localhost:3000, however if the default port
3000is already busy, the server tries starting on the closest free port.note
Make sure to specify the actual port in the JavaScript Debug configuration.
From the list in the Run widget on the toolbar, select a run configuration of the type JavaScript Debug. This can be the autogenerated Next.js: debug client configuration or a custom one that you created yourself as described above.
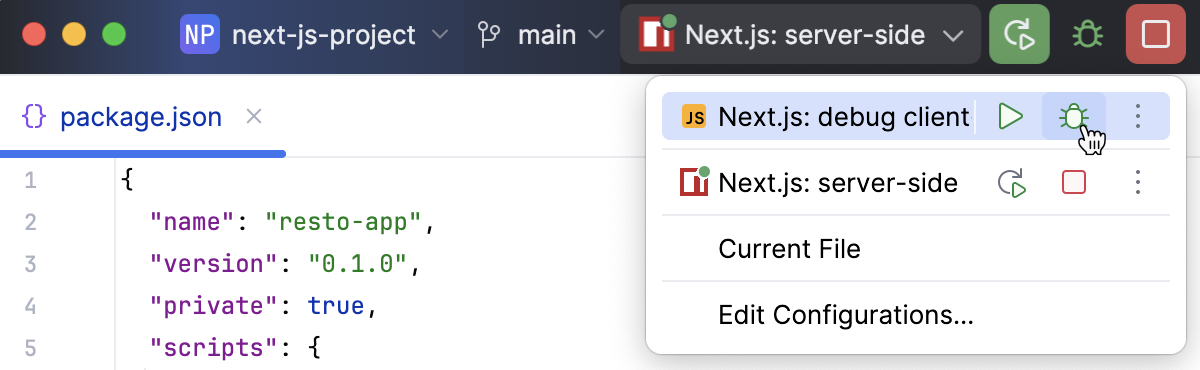
Click
.
When the application opens in the browser, perform the actions that trigger the program execution, for example, click a link. The focus switches to IntelliJ IDEA with the Debug tool window open.
Proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume program execution, examine it when suspended, explore the call stack and variables, set watches, evaluate variables, view actual HTML DOM, and so on.
Please, refer to Run a React application and Debug a React application.
Thanks for your feedback!