Code coverage
Manage suites: Run | Manage Coverage Reports
Coverage settings: Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Coverage
Code coverage in IntelliJ IDEA lets you analyze which lines of code were executed during a particular run. It helps determine the share of code covered by tests and identify areas that lack sufficient test coverage.
This functionality relies on the Code Coverage for Java plugin, which is bundled and enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press to open settings and then select Plugins.
Open the Installed tab, find the Code Coverage for Java plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
The entry points for running coverage analysis are the same as you would normally use to run an application:
For main method definitions, click
Run in the editor gutter, then select Run with Coverage

For run configurations, click
More Actions in the Run widget, then select Run with Coverage

For Gradle tasks, go to Gradle tool window, right-click the task, and select Run with Coverage

Coverage analysis executes the corresponding run configuration with the coverage agent attached. This agent instruments the bytecode to keep track of the execution line-by-line. After the execution completes, the results of the analysis appear in the IDE.
The collection of coverage data for a specific run is called a coverage suite.
IntelliJ IDEA can display the results for one or more coverage suites at once. If multiple suites are selected, the IDE displays merged results from these suites. This means that a line is considered covered if it was executed in at least one of the selected suites.
The corresponding suite files are located in the IntelliJ IDEA's system directory:
%LOCALAPPDATA%
~
~
In the main menu, go to Run | Manage Coverage Reports .
In the Choose Coverage Suite to Display menu:
Use the checkboxes to select active suites. Active suites define the coverage data that is currently displayed in the IDE.
Use
Add to import external suite file, for example, generated in the CI server or sent to you by someone else. You can use .ic (IntelliJ IDEA runner) or .exec/.xml (JaCoCo runner) files.
To view an imported suite collected with IntelliJ IDEA runner, you do not have to compile or run the project.
Use
Remove to remove a suite from the list but keep the file in the storage.
Use
Delete to remove a suite from the list and delete the file from the storage.
IntelliJ IDEA shows coverage results in:
Coverage tool window
Project tool window
Editor
note
Code coverage is only supported for the code that belongs to your current project.
Code coverage results are displayed in the Coverage tool window, in the Project tool window, and in the editor after you launch at least one run configuration with coverage.
The Project tool window displays:
the percentage of the covered classes and lines for directories
the percentage of the covered methods and lines for classes

The report breaks down the project by coverage percentage of classes, methods, lines, and branches.
note
If a class contains lambdas, anonymous, or inner classes, their coverage will be shown in the containing class coverage
Branch coverage shows the percentage of the executed branches in statements like if-else or switch. It is available for the JaCoCo runner and for the IntelliJ IDEA runner with the Branch Coverage option enabled.

The Coverage tool window has the following options:
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Select whether to show packages hierarchically or flatten the structure to show all of them on the same level. | |
If this option is on, IntelliJ IDEA automatically opens the selected item in the editor. Otherwise, you need to double-click items to open them. | |
If this option is on, IntelliJ IDEA automatically locates in the tool window the files that you open in the editor. | |
Generate a code coverage report and save it to the specified directory. For more information, refer to Generate coverage report. | |
Import a coverage suite from disk. | |
Filter coverage results. You can choose to view only the classes with uncommitted changes to focus on recent updates or hide the classes that are fully covered with tests. |
In the editor gutter, lines are highlighted according to their coverage status:
 Green – lines that have been executed
Green – lines that have been executed Red – lines that have not been executed
Red – lines that have not been executed Yellow – lines that were executed partially, like when only one branch of an
Yellow – lines that were executed partially, like when only one branch of an if-elsestatement is visited
To view statistics for a line of code, click the corresponding color indicator in the gutter. A popup that opens shows the number of hits and condition evaluation statistics (only for IntelliJ IDEA runner).
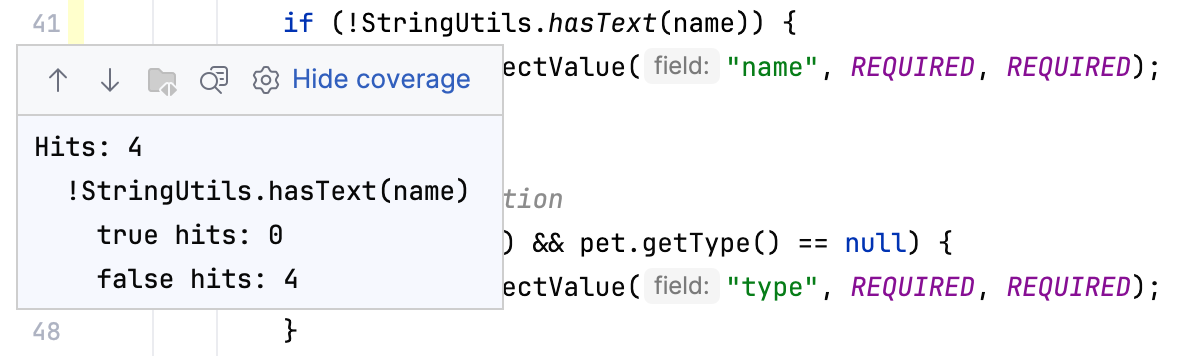
Additionally, the statistics popup has the following options:
For JUnit tests: open the test that covers a line in a separate dialog. To be able to use this feature, make sure you ran coverage analysis with the Branch Coverage and Track per test coverage options.
| |
Open the bytecode of the current class in a separate dialog | |
Change the colors of the coverage indicators in the gutter |
Do one of the following:
Close the tab with coverage statistics in the Coverage tool window (View | Tool Windows | Coverage).
Click coverage highlighting in the gutter and select Hide coverage.
Go to Run | Generate Coverage Report, or click
in the Coverage tool window.
note
This option only becomes available after you run the necessary tests with coverage.
In the Generate Coverage Report dialog, specify the directory to store the generated report and optionally select the Open generated HTML in browser checkbox.
In IntelliJ IDEA, there are coverage settings that apply to individual run configurations, and those applicable per-project.
For each run configuration, you can specify the scope of the coverage analysis.
Go to Run | Edit Configurations and click the run configuration on the left panel.
Click Modify options, then select the following options under Code Coverage:
Specify classes and packages: select this option to configure classes and packages for which you want to see the coverage information.
Exclude classes and packages: select this option to configure classes and packages that you want to exclude from coverage.
Coverage settings: Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Coverage
For projects, you can configure the following options:
Show options before applying coverage to the editor | Ask whether to make the recently collected coverage suite active every time you run coverage analysis. In this case a dialog will appear, where you can choose to only display the new results, to add them to the existing results, or save them to storage without viewing. |
Do not apply collected coverage | Only save the recently collected coverage suite to storage after you have run coverage analysis. In this case, new coverage data will not be shown unless you explicitly select the corresponding suite in Run | Manage Coverage Reports. |
Replace active suites with the new one | Hide the currently shown coverage suites and use the newly collected one after you have run coverage analysis. In this case, only the results from the most recent coverage run will be shown. |
Add to the active suites | Add the newly collected coverage suite to the list of active suites after you have run coverage analysis. This keeps the existing coverage results and adds the new results on top of it. |
Activate Coverage View | Open the Coverage tool window every time you run coverage analysis. |
Choose coverage runner | Select the coverage runner: IntelliJ IDEA or JaCoCo |
Branch coverage always on for JaCoCo | Collect granular coverage data for |
Track per test coverage only for JUnit tests; not supported for Gradle | Lets you trace back to specific tests, during which a line was executed. For details, refer to Per-test coverage. |
Collect coverage in test folders only for IntelliJ IDEA runner | Collect code coverage statistics for tests. By default, coverage data only shows which lines were covered in source roots. Use this option to enable coverage collection in test roots as well. |
Ignore implicitly declared default constructors only for IntelliJ IDEA runner | Exclude the implicit default constructors from coverage statistics. No-arg constructors that are declared explicitly will remain included. |
Exclude annotations only for IntelliJ IDEA runner | Exclude elements marked with the specified annotations from coverage results, for example, Lombok's |
Press to open settings and then select Editor | Color Scheme | General.
In the list of components, expand the Line Coverage node and select a type of coverage: for example, Full, Partial or Uncovered.
Click the Foreground field to open the Select Color dialog.
Select a color, apply the changes, and close the dialog.

When branch coverage is enabled, IntelliJ IDEA lets you track which lines of code are covered by each test and vice versa.
note
This feature is not supported for Gradle and test frameworks other than JUnit.
In Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Coverage, enable Branch coverage and Track per test coverage.
To navigate to tests covering a specific line:
Click the coverage highlighting in the editor gutter, then select
Show Tests Covering Line.

To only highlight the lines covered within a specific test:
In the Cover tool window, select a test and click Show Coverage per Test on the toolbar.

note
Show Coverage per Test disables branch coverage. Coverage will be highlighted as full/none.