Breakpoints
Breakpoints are special markers that suspend program execution at a specific point. This lets you examine the program state and behavior. Breakpoints can be simple (for example, suspending the program on reaching some line of code) or involve more complex logic (checking against additional conditions, writing log messages, and so on).
Once set, a breakpoint remains in your project until you remove it explicitly, except for temporary breakpoints).
tip
If a file with breakpoints was modified externally, for example, updated through a VCS or changed in an external editor, and the line numbers have changed, breakpoints will be moved accordingly. Note that PhpStorm must be running when such changes are made, otherwise they will pass unnoticed.
Types of breakpoints
The following types of breakpoints are available in PhpStorm:
Line breakpoints: suspend the program upon reaching the line of code where the breakpoint was set. This type of breakpoints can be set on any executable line of code.
Method breakpoints: suspend the program upon entering or exiting the specified method or one of its implementations, allowing you to check the method's entry/exit conditions.
Exception breakpoints: suspend the program when
Exceptionor its subclasses are thrown. They apply globally to the exception condition and do not require a particular source code reference.
Set breakpoints
Set line breakpoints
Click the gutter at the executable line of code where you want to set the breakpoint. Alternatively, place the caret at the line and press Ctrl+F8.
Set method breakpoints
Click the gutter at the line where the method is declared. Alternatively, place the caret at the line and press Ctrl+F8.

Alternatively, do the following:
Press Ctrl+Shift+F8 or select Run | View Breakpoints from the main menu.
In the Breakpoints dialog that opens, press Alt+Insert or click
, and select PHP Method Breakpoints.
In the Add Method Breakpoint dialog, specify the class and the method, or the plain function to add a breakpoint for.
Set exception breakpoints
Click View Breakpoints
in the left part of the Debug tool window or press Ctrl+Shift+F8.
In the Breakpoints dialog, press Alt+Insert or click
, and select PHP Exception Breakpoints or JavaScript Exception Breakpoint.

In the Add Exception Breakpoint dialog, specify an exception class from a library or from your project.
See Debug with PHP exception breakpoints for details.
Resolved breakpoints
When using Xdebug, PhpStorm can employ its breakpoints resolving mechanism. Under this mechanism, the debugger evaluates whether PHP can generate internal executable bytecode for the current line. If no such code is generated for a line, the corresponding breakpoint cannot be hit. Xdebug will scan up to 5 subsequent lines, and stop at the line where executable code is located. Resolving breakpoints is supported in Xdebug 2.8 and later.
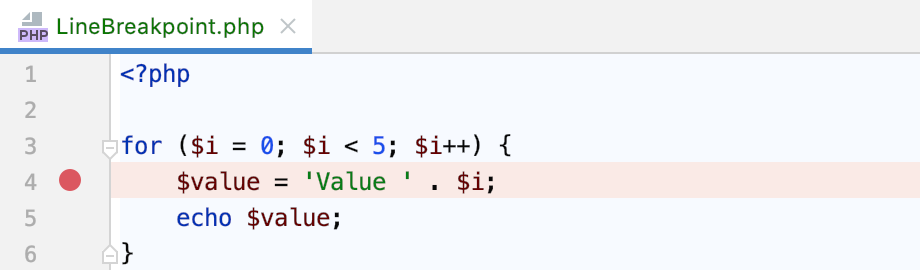
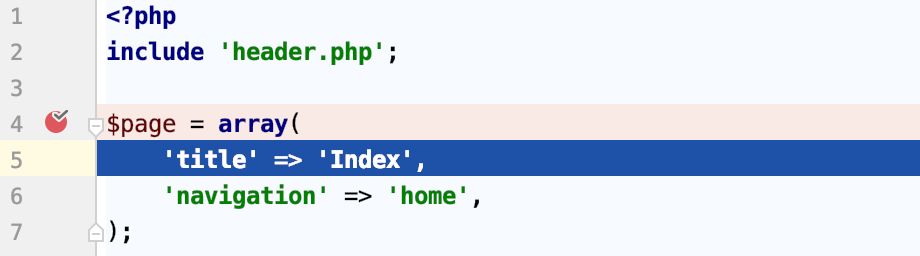
In the following example, no executable code can be located on line 4. The breakpoint is resolved to line 5, and the debugging session is suspended accordingly.
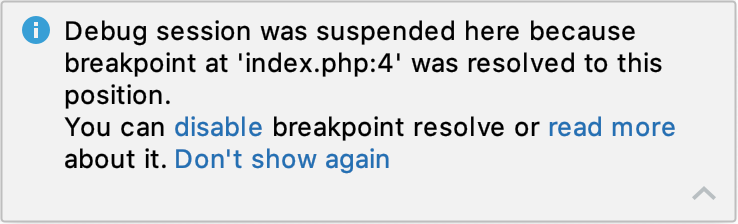
When a breakpoint is resolved, PhpStorm displays the corresponding notification.
If necessary, you can configure breakpoints resolving support in PhpStorm on the PHP | Debug page of the Settings/Preferences dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S):
In the Xdebug area, use the Resolve breakpoint if it's not available on the current line (Xdebug 2.8+) checkbox to toggle breakpoint resolving. Note that if resolving is disabled, the breakpoints set on the code lines without executable code will always be ignored.
In the Advanced settings area, use the Notify if breakpoint was resolved to a different line (Xdebug 2.8+) checkbox to choose whether PhpStorm should display a notification message when a breakpoint is resolved.
tip
To get an in-depth technical overview of how breakpoints resolving works, refer to this article and DBGP documentation.
Manage breakpoints
Remove breakpoints
For non-exception breakpoints: click the breakpoint in the gutter.
For all breakpoints: from the main menu, select Run | View Breakpoints Ctrl+Shift+F8, select the breakpoint, and click Remove Delete.
To avoid accidentally removing a breakpoint and losing its parameters, you can choose to remove breakpoints by dragging them to the editor or clicking the middle mouse button. To do this, go to Settings/Preferences | Build, Execution, Deployment | Debugger and select Drag to the editor or click with middle mouse button. Clicking a breakpoint will then enable or disable it.
Mute breakpoints
If you don't need to stop at your breakpoints for some time, you can mute them. This allows you to resume normal program operation without leaving the debugger session. After that, you can unmute breakpoints and continue debugging.
Click the Mute Breakpoints button
in the toolbar of the Debug tool window.
Enable/disable breakpoints
When you remove a breakpoint, its internal configuration is lost. To temporarily turn an individual breakpoint off without losing its parameters, you can disable it:
For non-exception breakpoints: right-click it and set the Enabled option as required. You can also toggle them with the middle mouse button if removing breakpoints is not assigned to it.
For all breakpoints: click View Breakpoints Ctrl+Shift+F8 and check/uncheck the breakpoint on the list.
Move/copy breakpoints
To move a breakpoint, drag it to another line.
To copy a breakpoint, hold Ctrl and drag a breakpoint to another line. This creates a breakpoint with the same parameters at the destination.
Configure breakpoints' properties
Depending on the breakpoint type, you can configure additional properties which allow you to tailor its operation for specific needs. The most used options are available via intentions.
To access breakpoint intentions, place the caret at the line with the breakpoint and press Alt+Enter. Use this option when you need to quickly configure basic breakpoint properties.
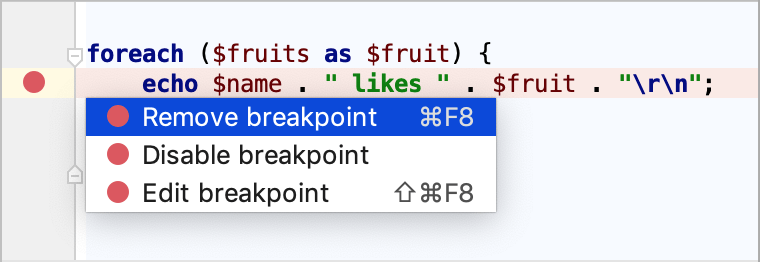
To access the full list of properties, right-click the breakpoint and click More or press Ctrl+Shift+F8. Use this option for a bird's eye view of all breakpoints and full control over their configuration.
Intentions reference
Intention | Description |
|---|---|
Remove breakpoint | Removes the breakpoint at the selected line. |
Disable breakpoint | Disables the breakpoint at the selected line. |
Edit breakpoint | Opens a dialog with the most used breakpoint properties. For more properties, click More or press Ctrl+Shift+F8. |
Breakpoints' properties
Breakpoint statuses
Breakpoints can have the following statuses:
Status | Description |
|---|---|
Verified | After you have started a debugger session, the debugger checks whether it is technically possible to suspend the program at the breakpoint. If yes, the debugger marks the breakpoint as verified. |
Warning | If it is technically possible to suspend the program at the breakpoint, however there are issues related to it, the debugger gives you a warning. This may happen, for example, when it is impossible to suspend the program at one of the method's implementations. |
Invalid | If it is technically impossible to suspend the program at the breakpoint, the debugger marks it as invalid. The most common cause for this is that there is no executable code on the line. |
Inactive/dependent | A breakpoint is marked as inactive/dependent when it is configured to be disabled until another breakpoint is hit, and this has not happened yet. |
Muted | All breakpoints are temporarily inactive because they have been muted. |
Disabled | This breakpoint is temporarily inactive because it has been disabled. |
Non-suspending | The suspend policy is set for this breakpoint so that it does not suspend the execution when hit. |
Breakpoint icons
Depending on their type and status, breakpoints are marked with the following icons:
Line | Method | Exception | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Regular | ||||
Disabled | ||||
Verified | ||||
Muted | ||||
Inactive/dependent | ||||
Muted disabled | ||||
Non-suspending | ||||
Verified non-suspending | ||||
Invalid | ||||
Productivity tips
- Use breakpoints for debug printing
Use non-suspending logging breakpoints (sometimes referred to as watchpoints in other debuggers) instead of inserting print statements in your code. This provides a more flexible and centralized way of handling debug log messages.
- Set logging breakpoints more quickly
To set a non-suspending logging breakpoint, hold Shift and click the gutter. This will not suspend the program execution and instead log a message like
Breakpoint reached: LineBreakpoint.php:10. If you want to log some expression that is in front of you in the editor, select it before holding Shift and clicking the gutter.- Add breakpoint descriptions
If you have many breakpoints in your project, you can add descriptions to breakpoints for ease of search. To do this, right-click a breakpoint in the Breakpoints dialog Ctrl+Shift+F8 and select Edit description from the menu. Now when you start typing the breakpoint name, it gets the focus.
- Group breakpoints
You can organize breakpoints into groups, for example, if you need to mark out breakpoints for a specific problem. To do this, in the Breakpoints dialog Ctrl+Shift+F8, select a breakpoint you want to place in a group and select Move to group from the menu.
- Jump to source
To jump from the Breakpoints dialog to the line of code where the selected breakpoint is set, press F4.
Thanks for your feedback!