Explain code with AI
Use pre-written prompts to explain your code. JetBrains IDEs provide project-specific context, such as the languages and technologies used in your project.
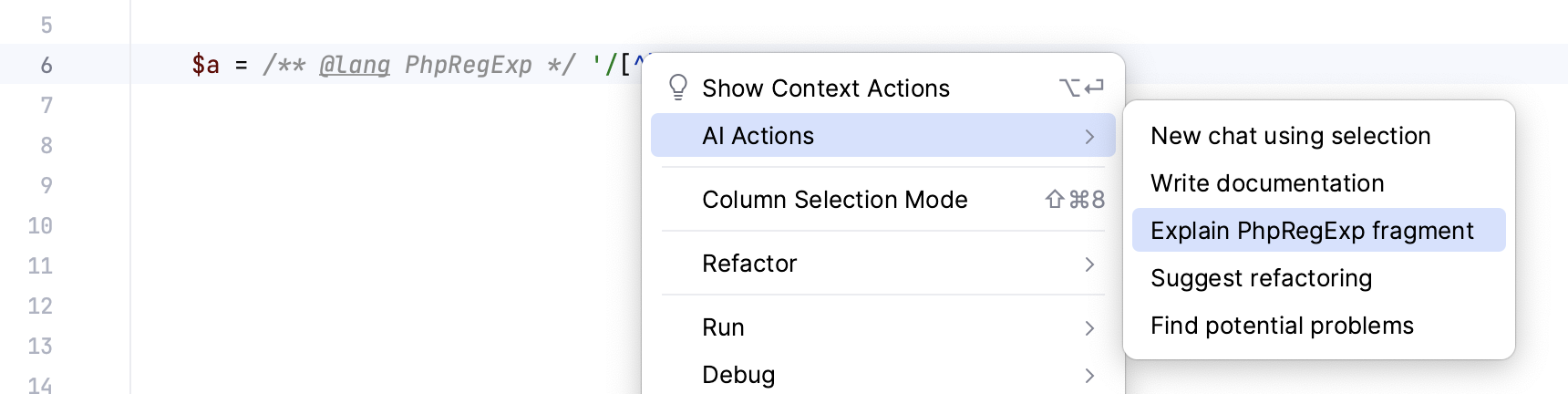
Select a code fragment and right-click it to open the context menu.
Alternatively, select a code fragment and press .
Select AI Actions and then Explain Code.
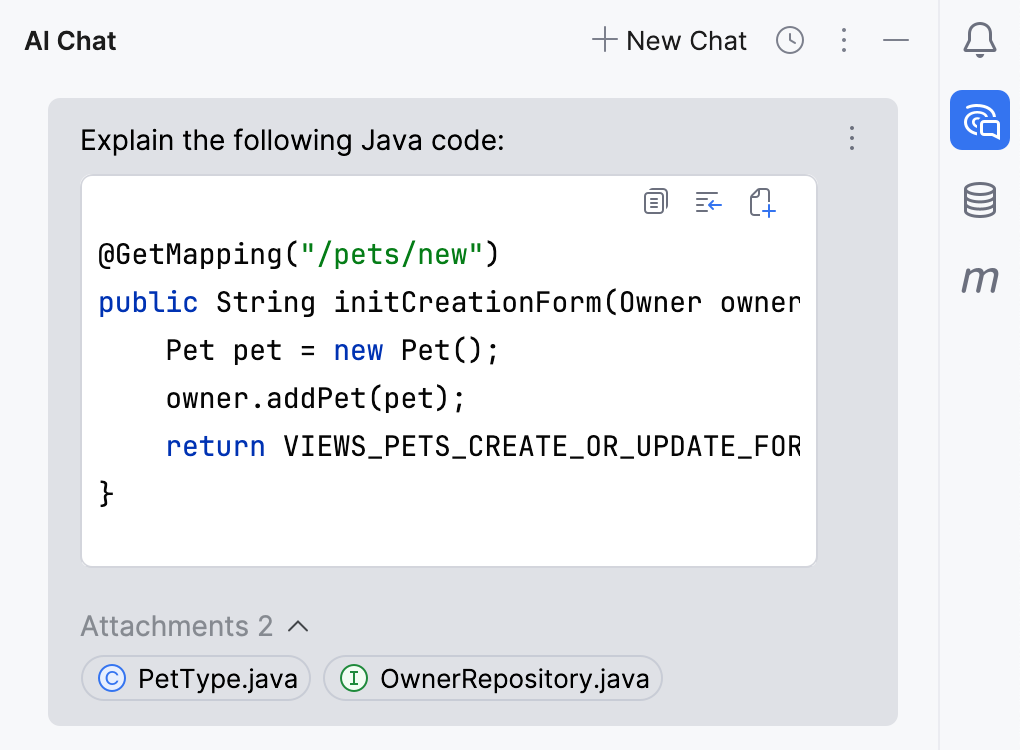
The AI Assistant tool window will open to provide you with an explanation.
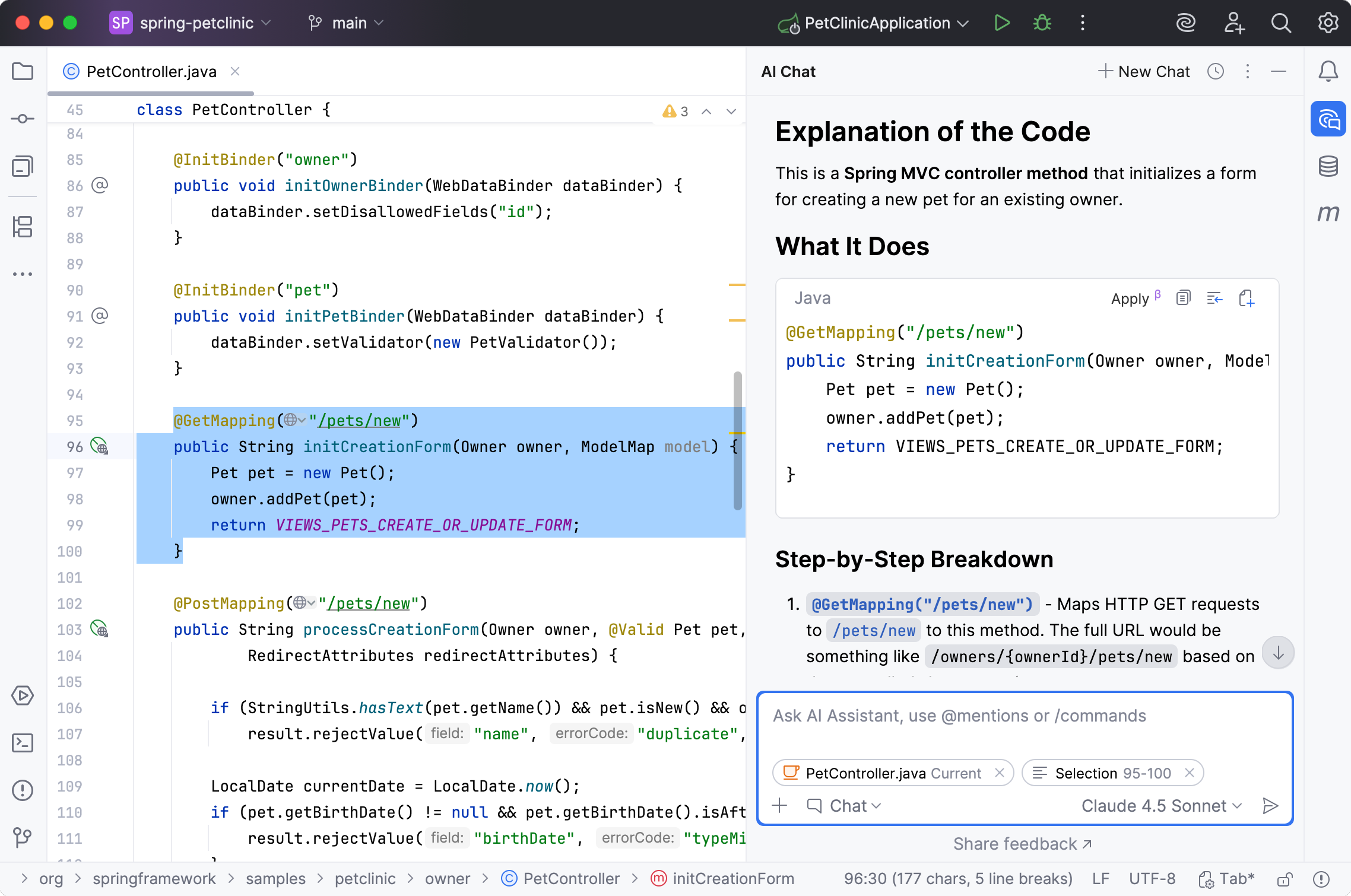
Click
Attached elements to see the list of files that provided the necessary context for generating the answer.
AI Assistant can also detect and explain injected language fragments like regular expressions, SQL, or cron expressions. The detected fragment type is indicated in the context menu option (Explain RegExp fragment for regular expressions and so on).
Not available in: GoLand, Rider, RustRover
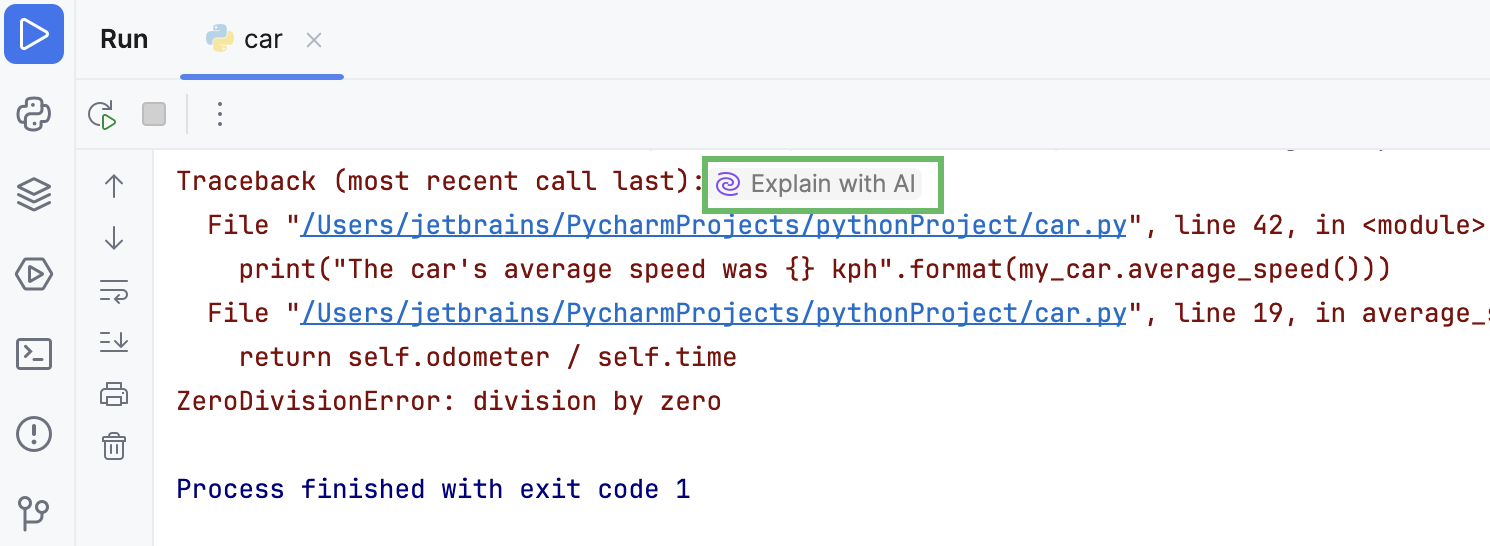
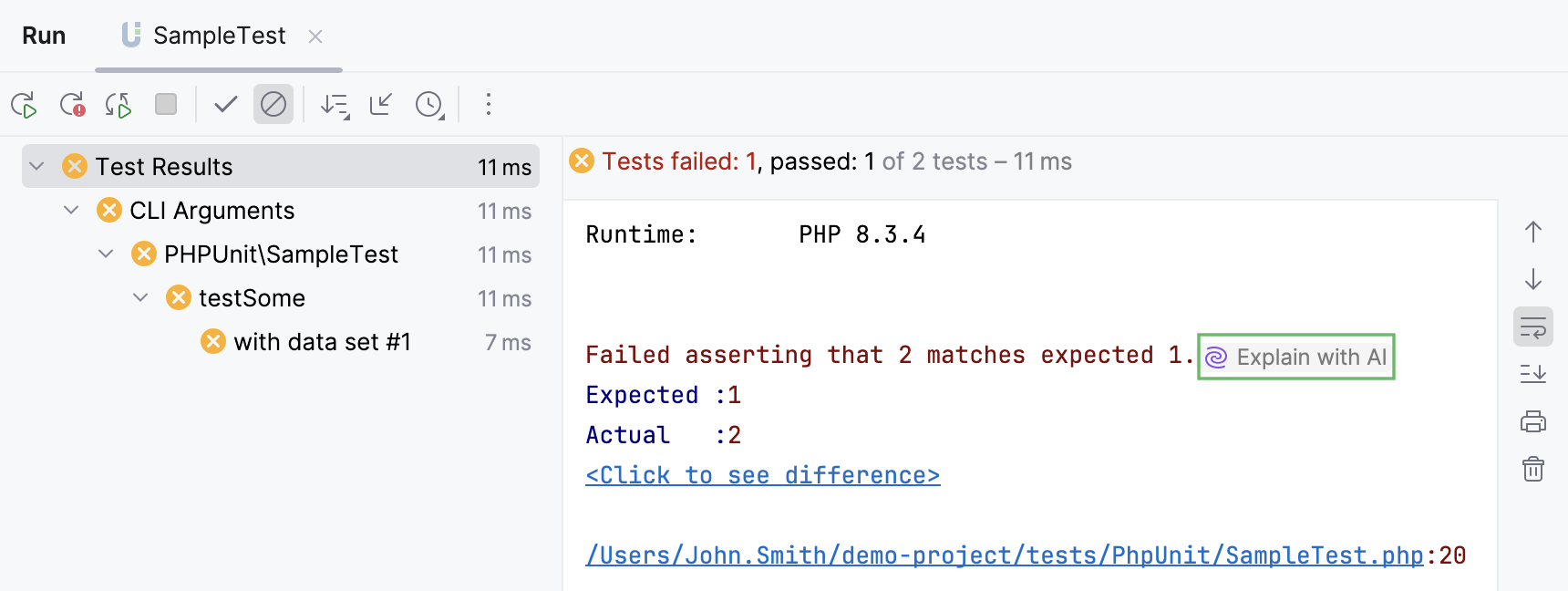
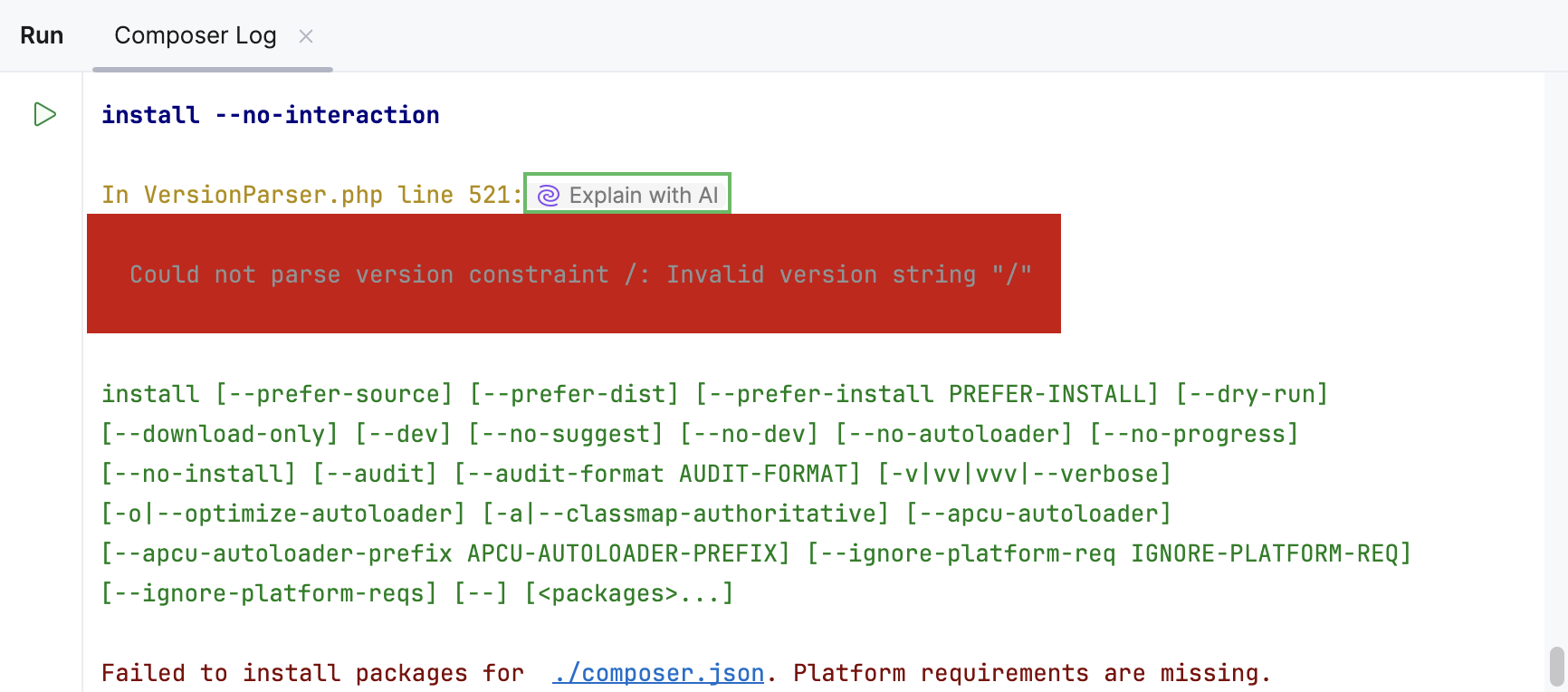
JetBrains IDEs provide you with AI explanations for errors that occur when running commands, queries, and files, Java and Python code, PHP scripts, and unit tests.
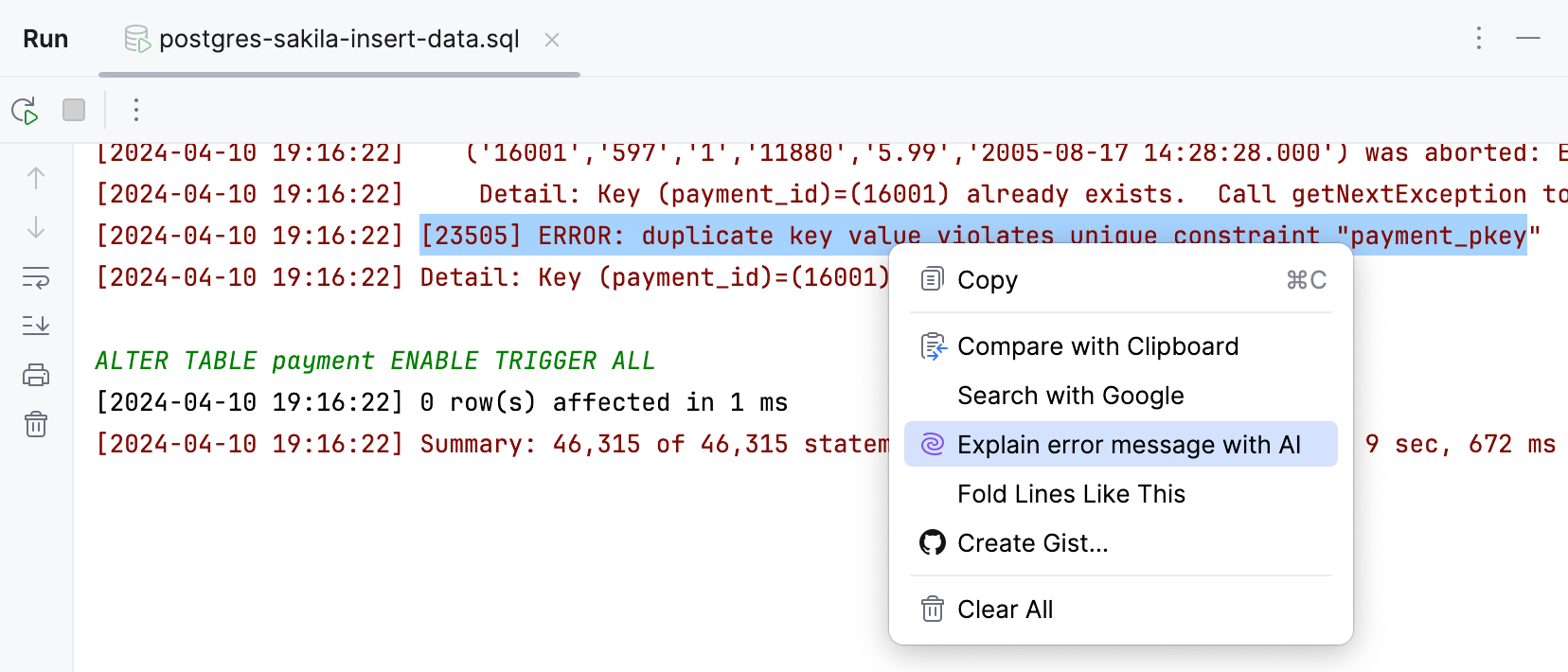
Click Explain with AI in the console.
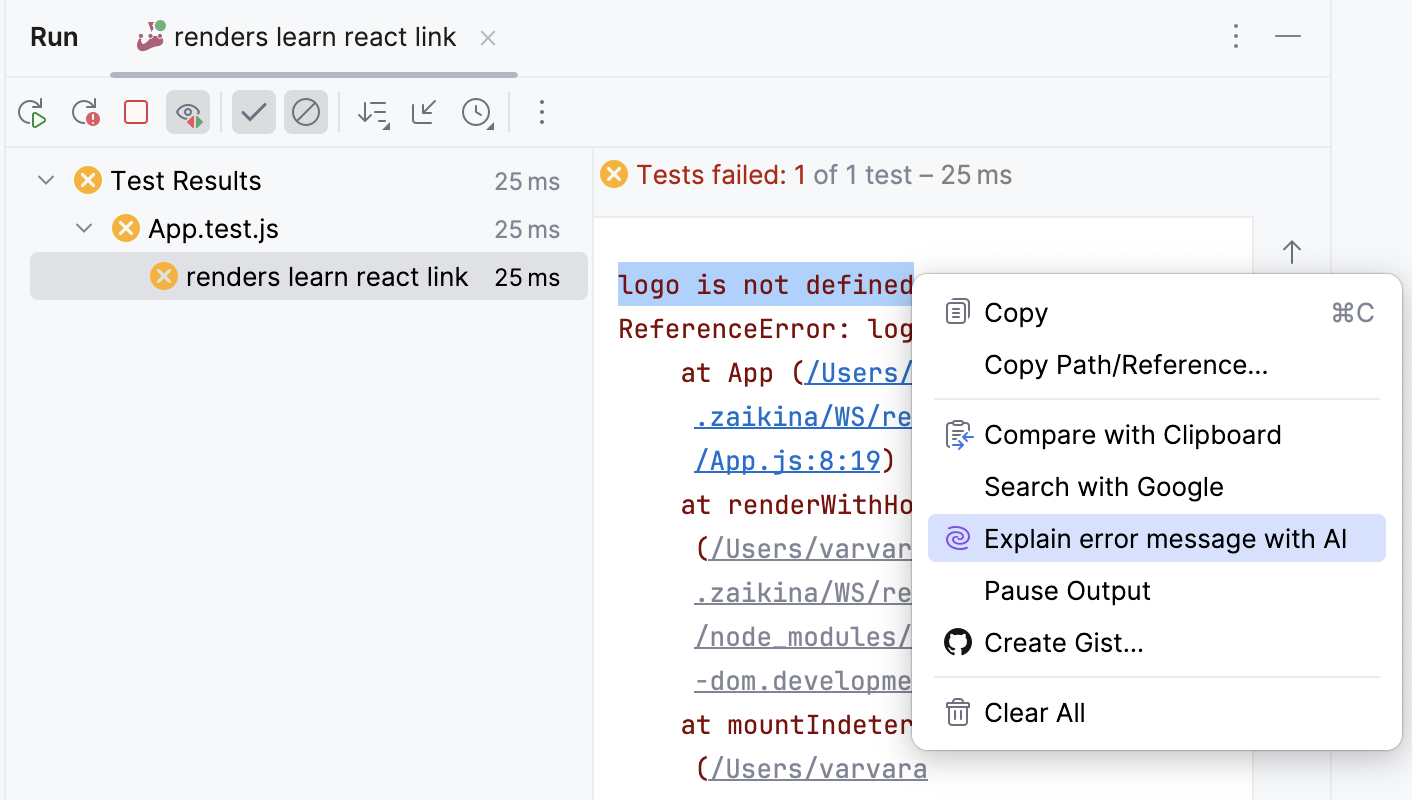
Alternatively, select the error message, right-click it, and then select Explain Error Message with AI from the context menu.
IntelliJ IDEAPyCharmDataSpellWebStormPhpStormDataGrip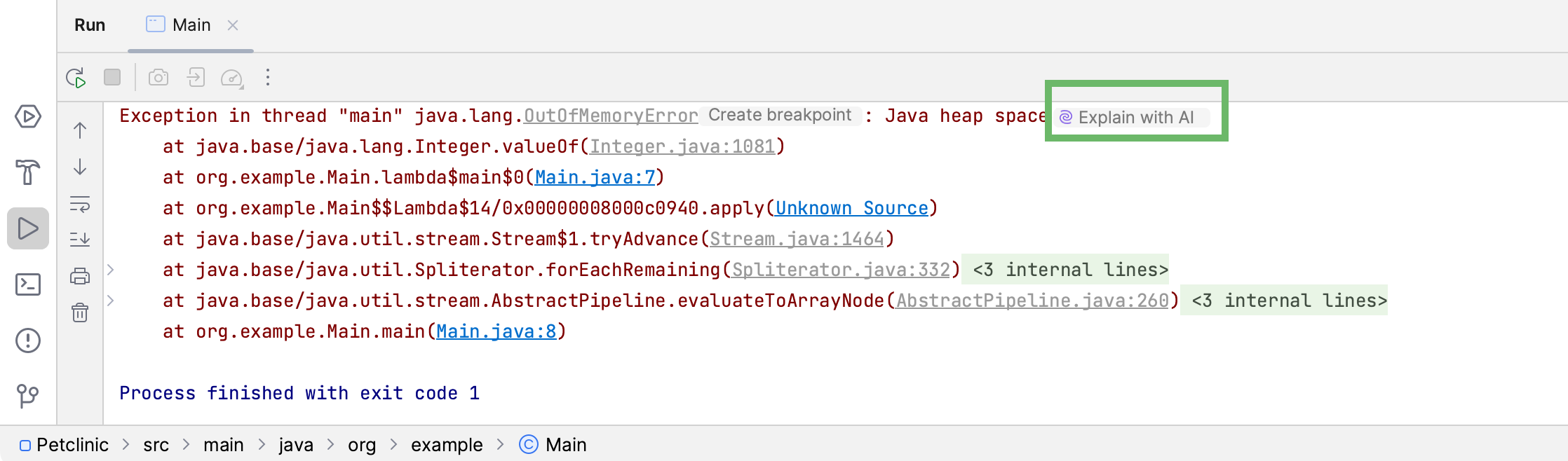

 PHP scriptsPHP unit testsComposer log consoleSymfony log console
PHP scriptsPHP unit testsComposer log consoleSymfony log console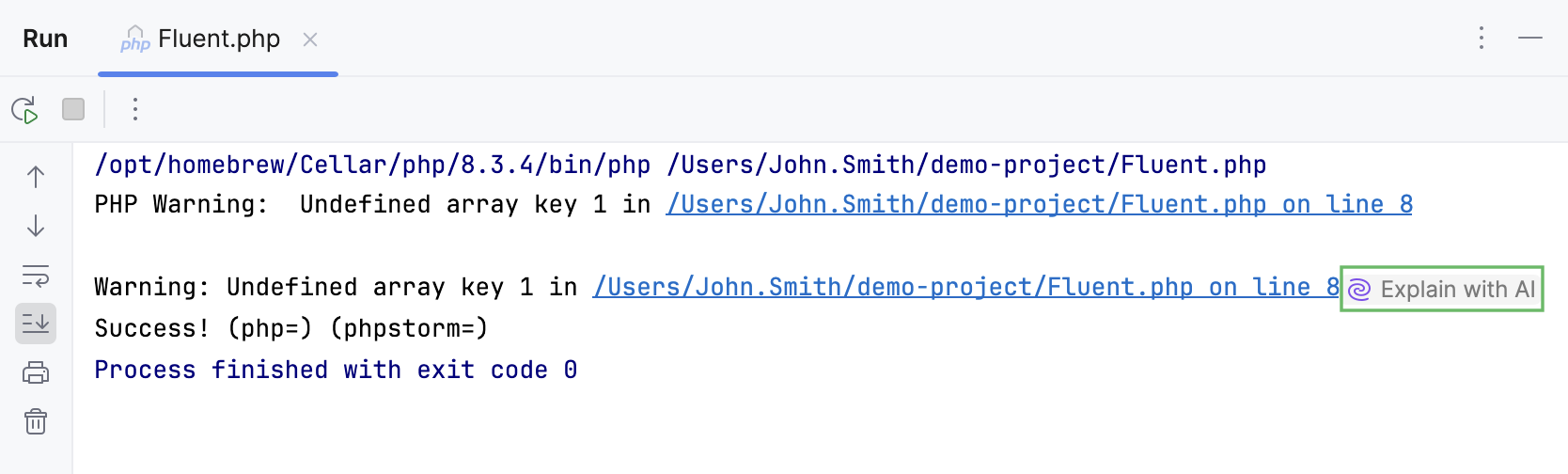
 SQL scriptSQL file
SQL scriptSQL file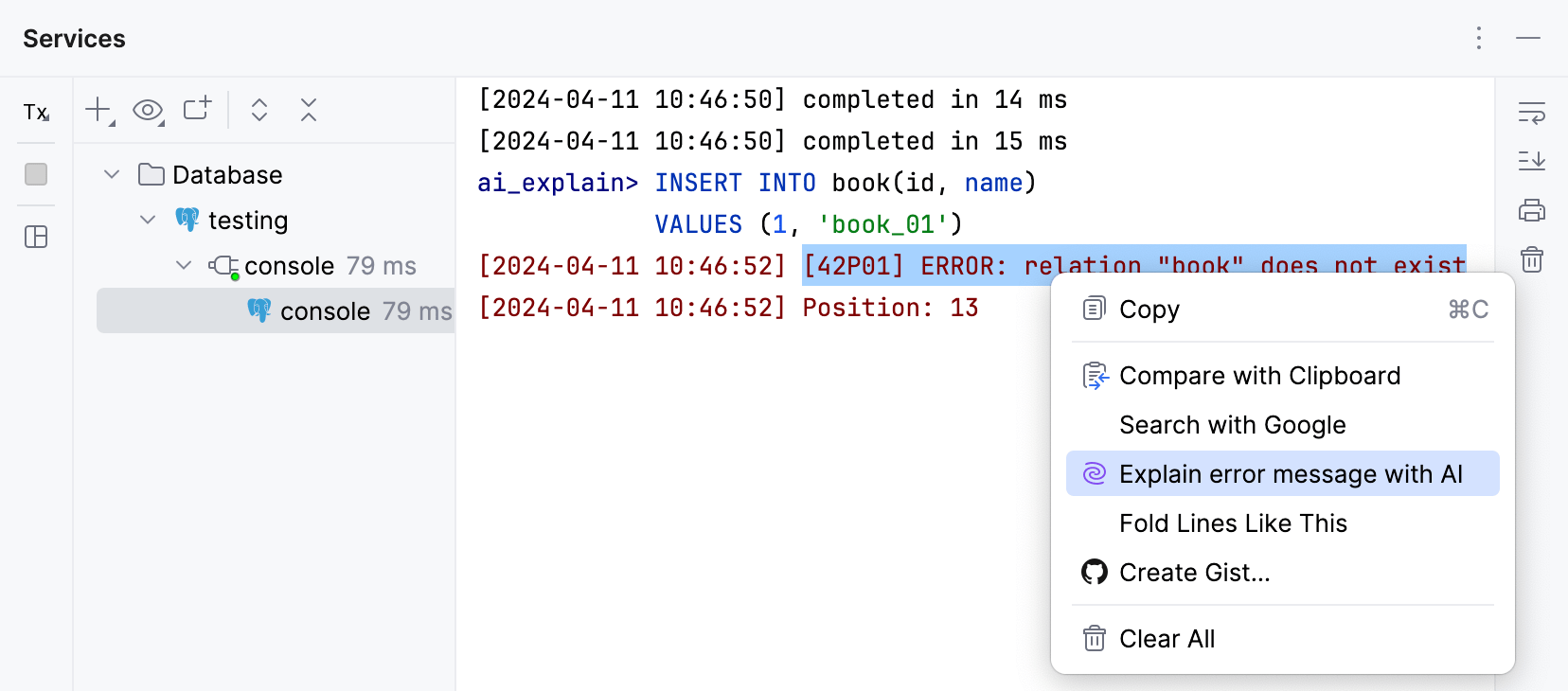
The AI Assistant tool window will open to give you an explanation of the error and suggest a fix.
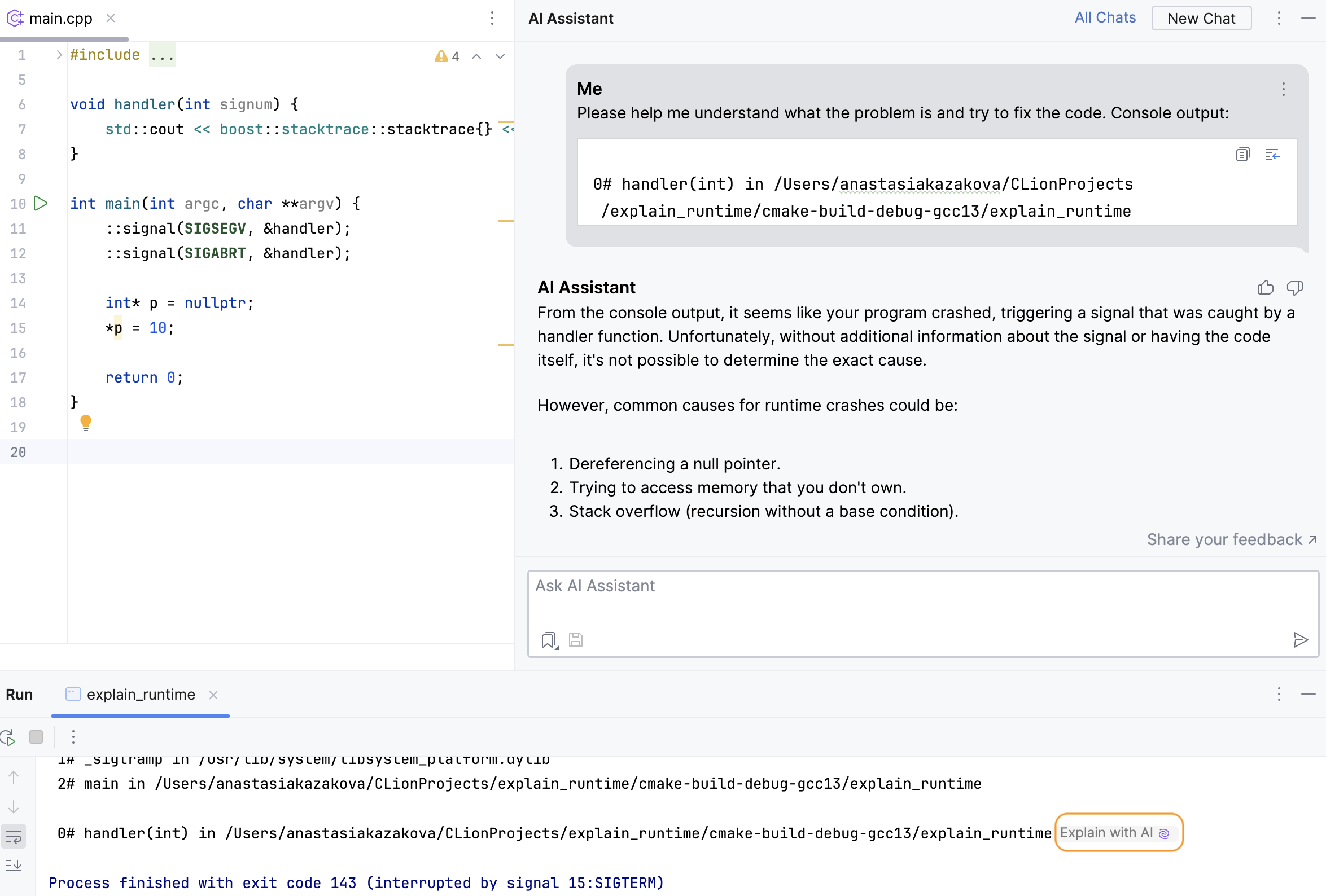
If you want to use the suggested fix, click
in the field with the refactored code to put the AI-generated code into the editor.
Only available in: PhpStorm
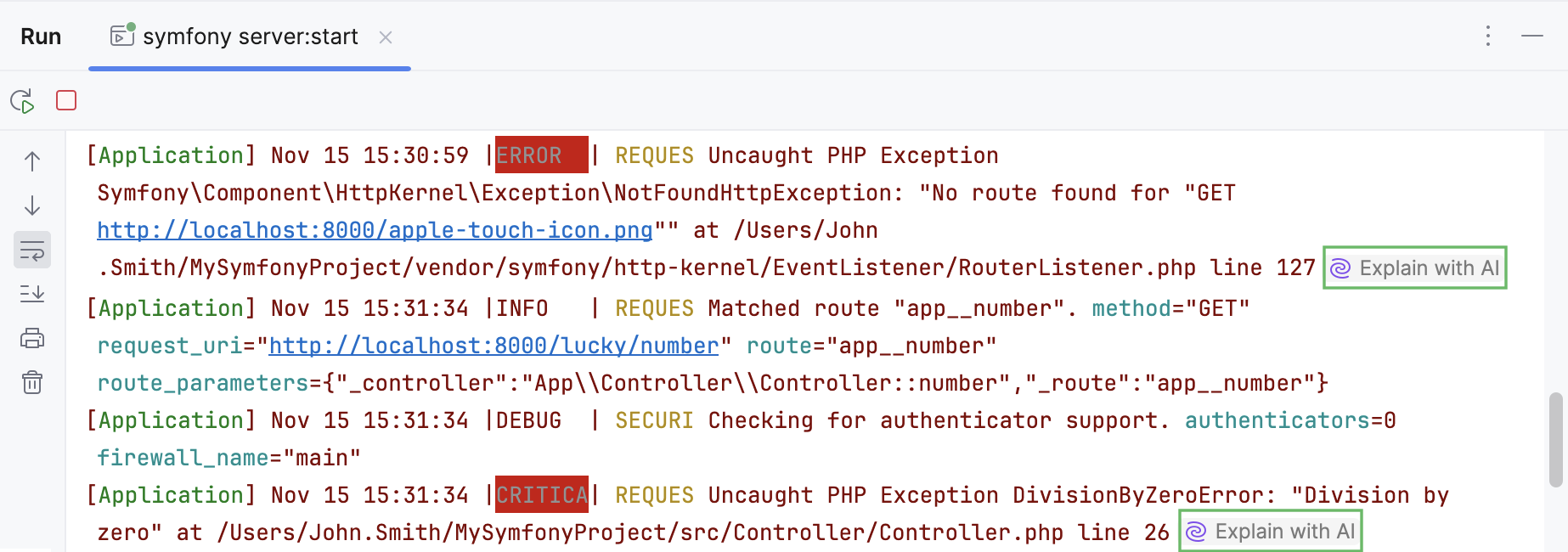
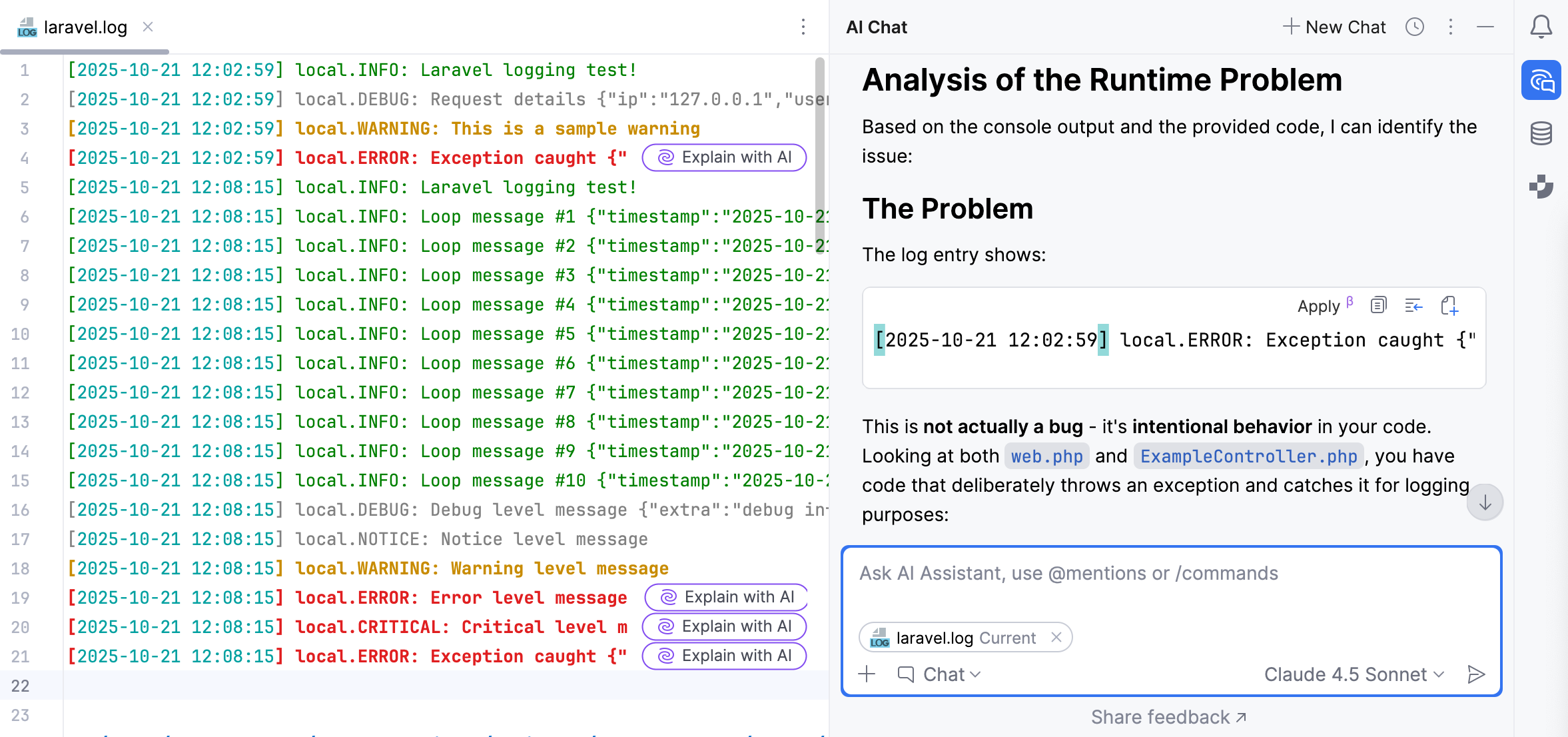
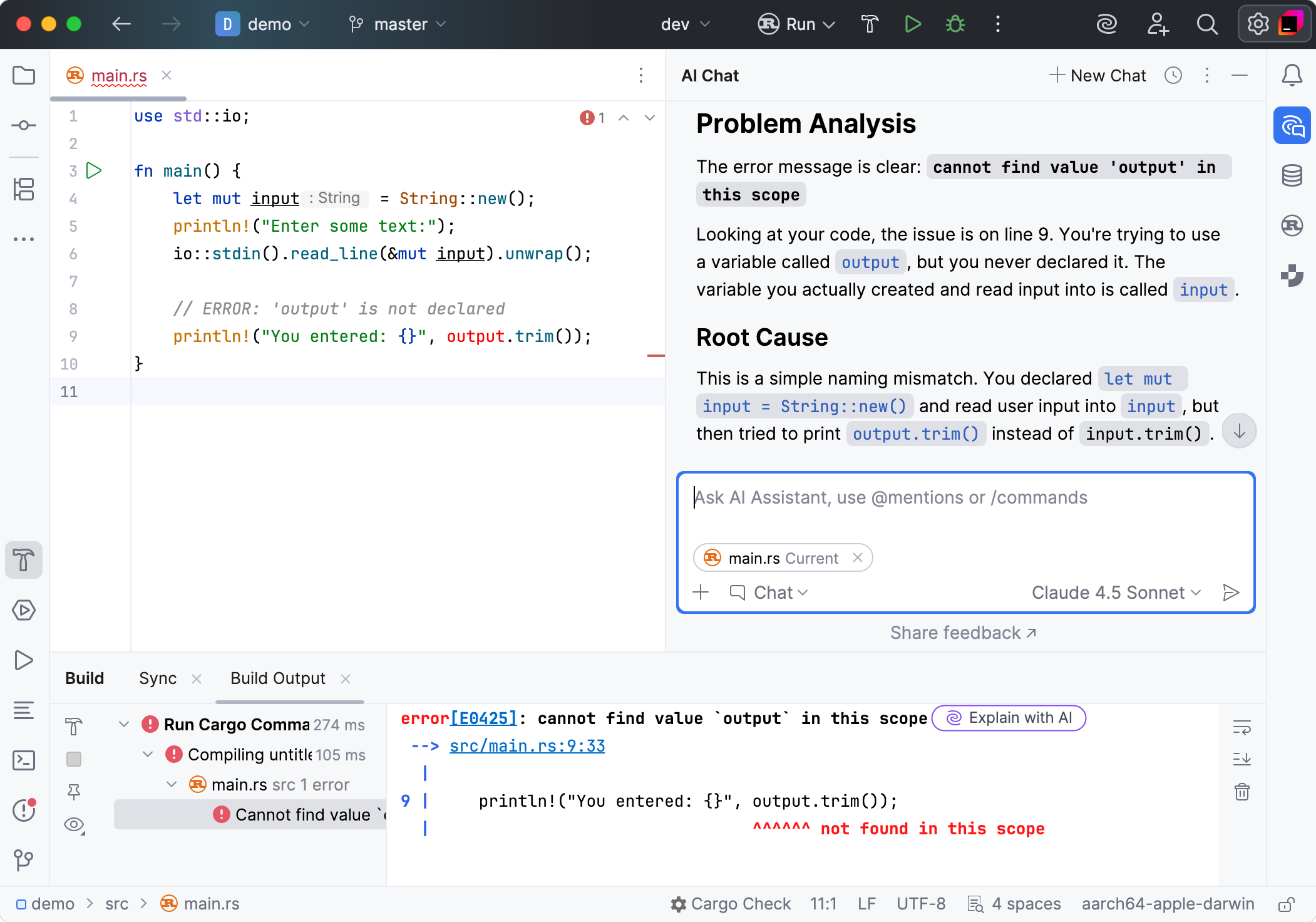
AI Assistant allows you to get AI explanations for the errors in log files when you open such files in the editor.
Click Explain with AI in the editor next to the log line with an error.
The AI Assistant tool window will open to give you an explanation of the error and suggest a fix.
Only available in: CLion
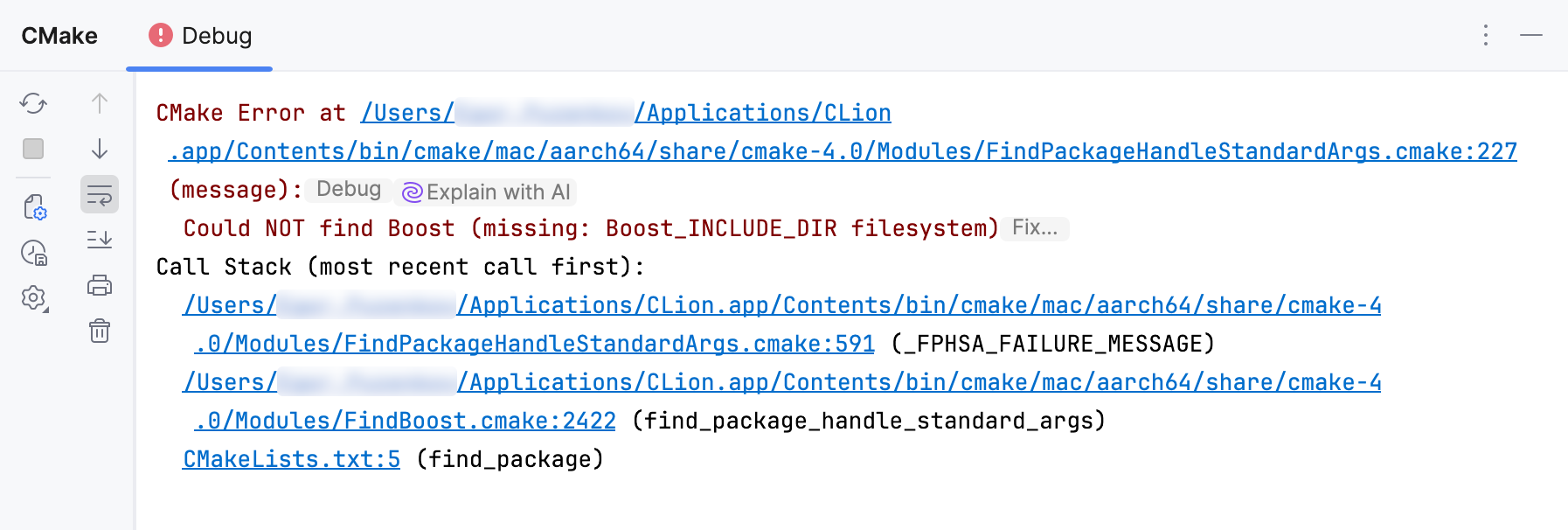
AI Assistant can help you investigate CMake execution problems.
Click Explain with AI in the CMake tool window next to the error message:
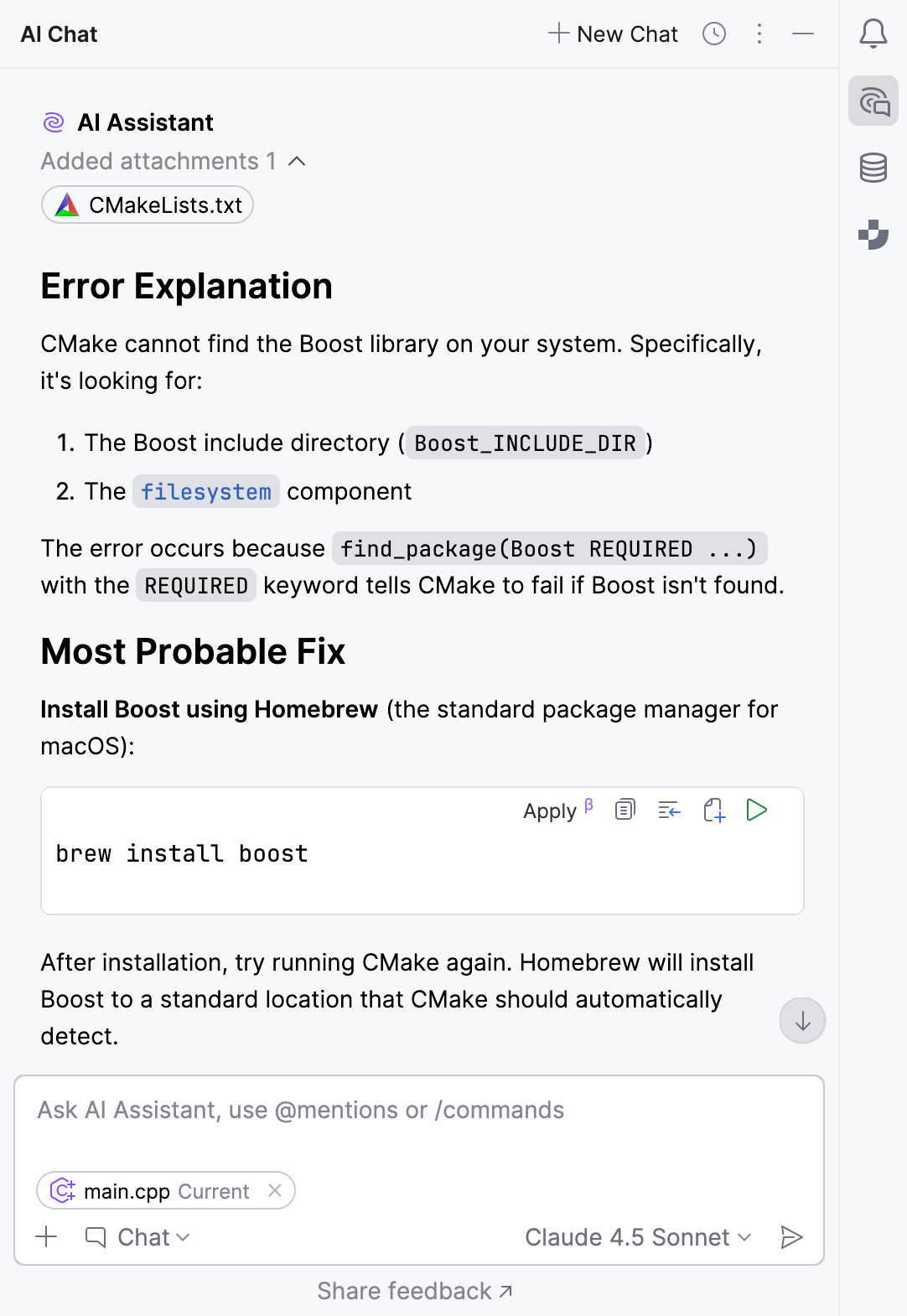
The AI Assistant will explain the error for you and suggest how to fix it:
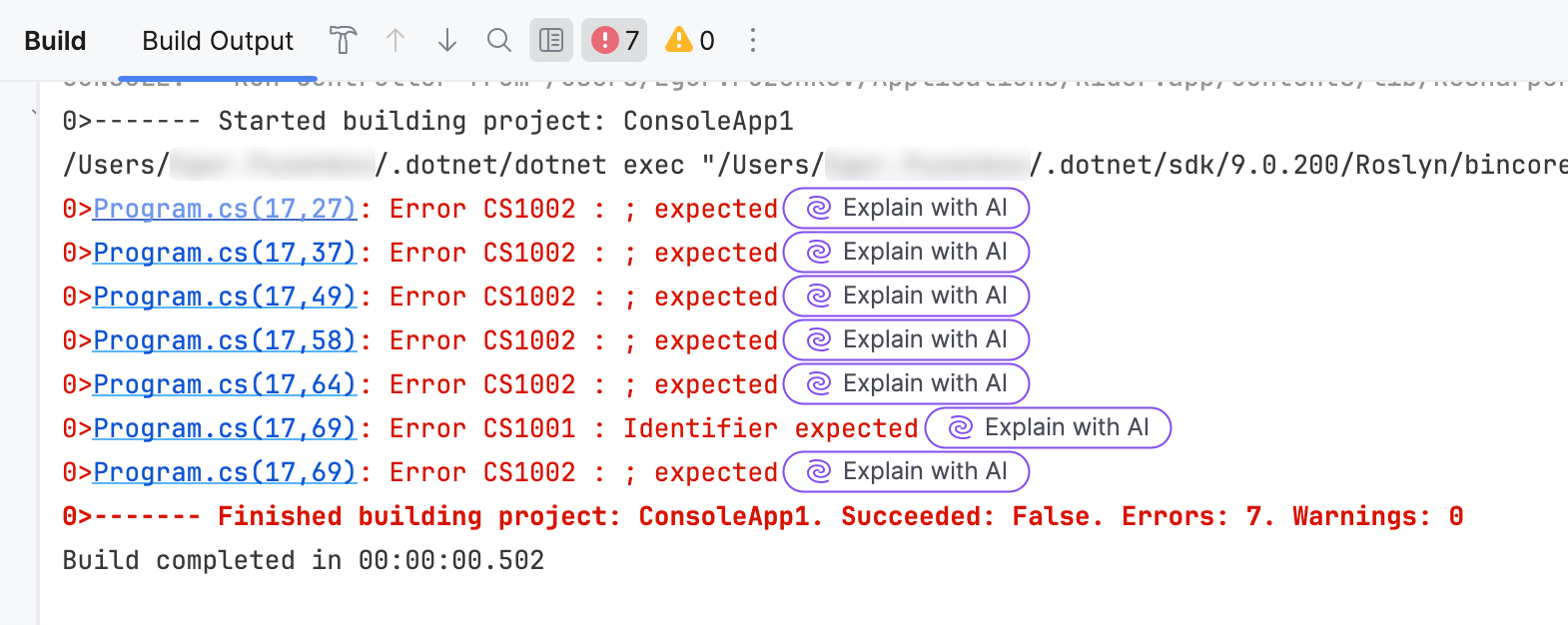
Only available in: Rider
If you have any warnings or errors in the Build tool window , you can select any message, right-click it and choose Explain error message with AI:
Only available in: RustRover
AI Assistant can also help you analyze build error messages.
In the console, locate the error message and click Explain with AI.

The AI Assistant tool window will open to provide you with an explanation.
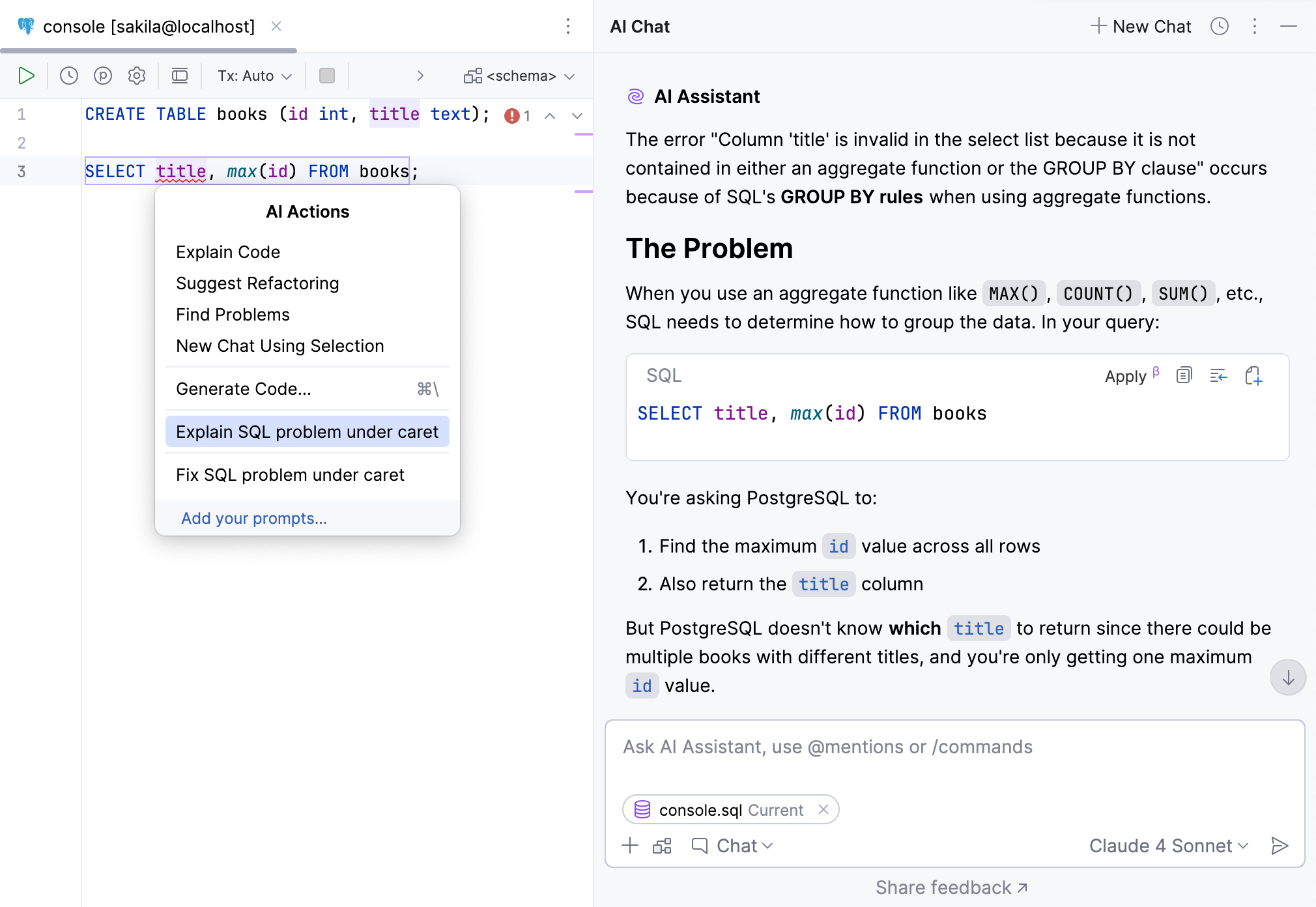
This feature can require attaching the database schema to suggest proper explanations.
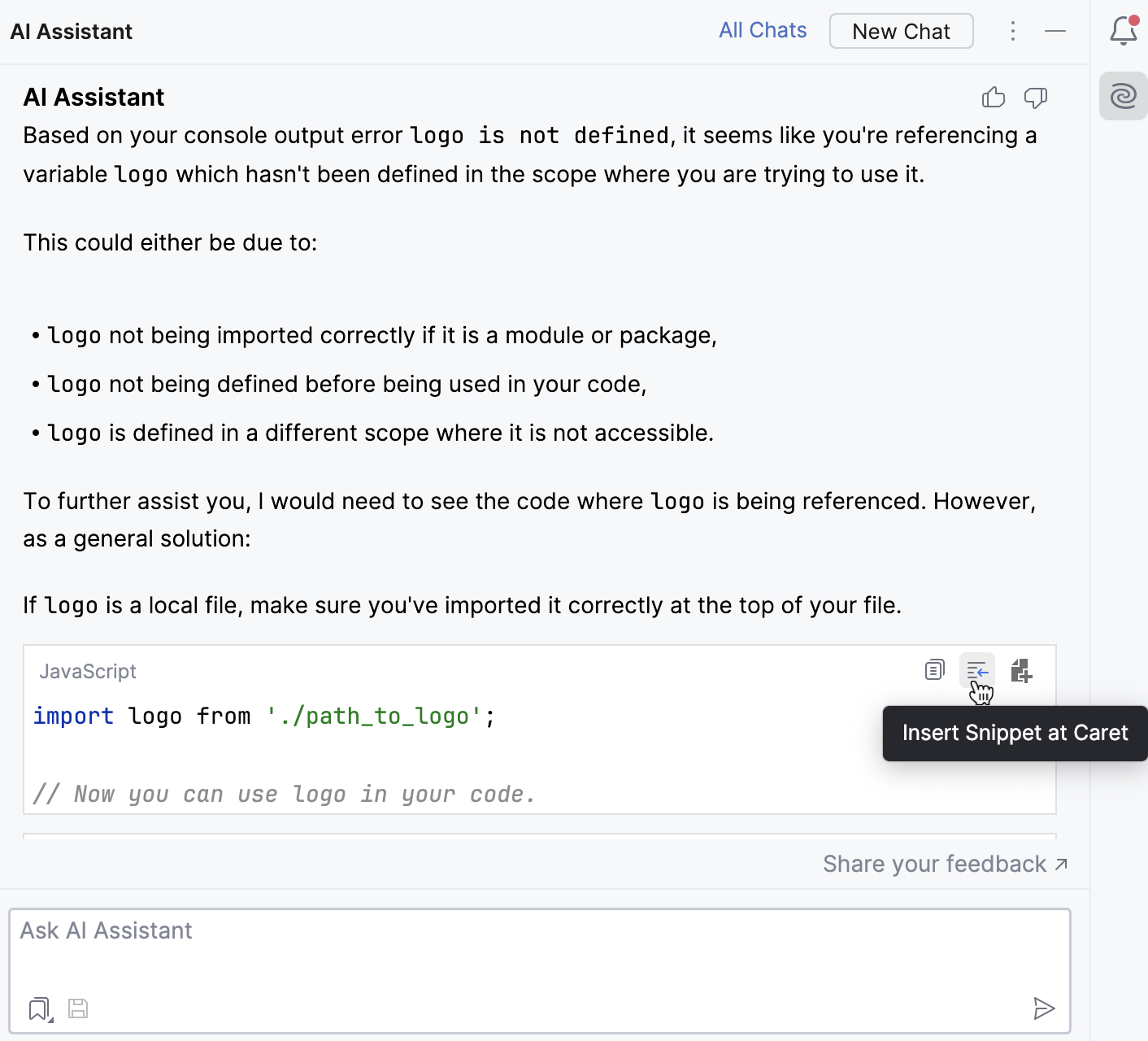
For any problems higher than weak warning, the assistant suggests an explanation. To use it, do the following:
In the editor, invoke the intention actions by placing the caret at the highlighted code and pressing , then select AI Actions.
In the AI Actions dialog, select Explain SQL problem under caret.
AI Assistant will provide its explanation in chat.