Create a Python project
Pure Python projects are intended for Python programming. A project helps you organize your source code, tests, libraries that you use, and your personal settings in a single unit.
In case you do not need a project, you can edit your file in LightEdit mode or create a Python file without setting up a project.
To create a project, do one of the following:
Go to .
On the Welcome screen, click New Project.
In the New Project dialog, specify the project location. The project name will be automatically derived from the folder name in the specified path.
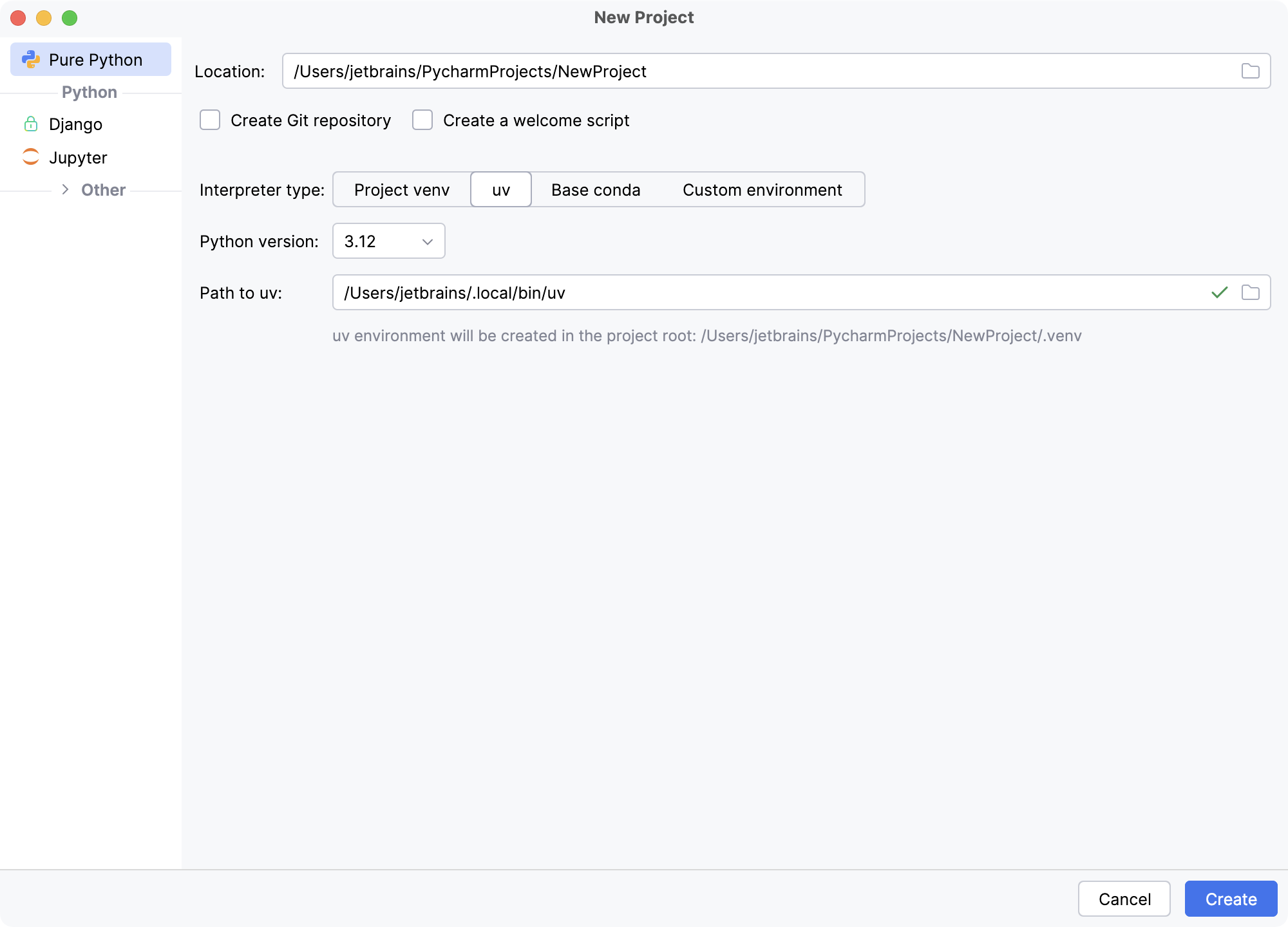
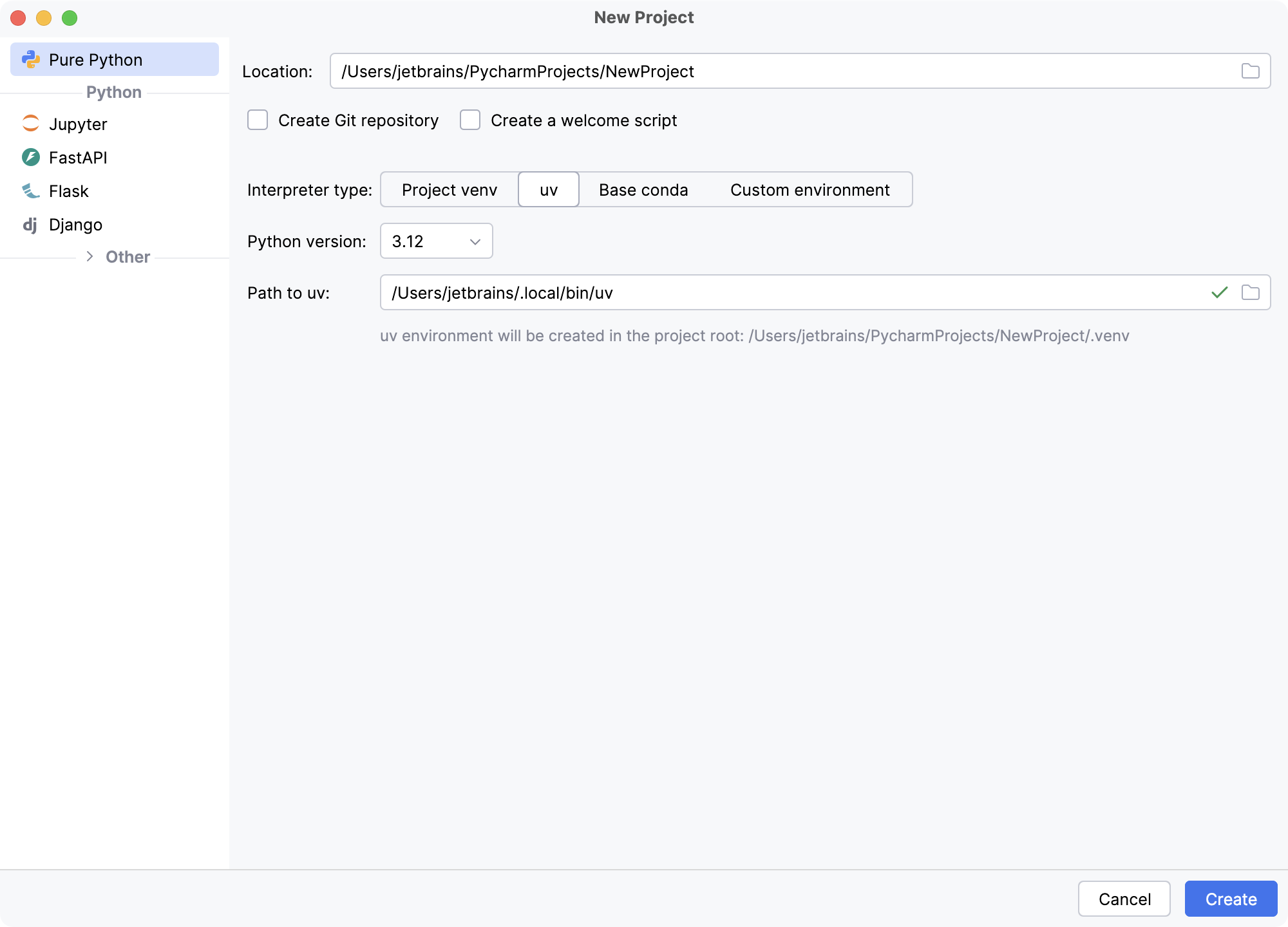
Select Create Git repository to put the project under Git version control.
Select Create a main.py welcome script if you want PyCharm to add the
main.pyfile to your project. This file contains a simple Python code sample and can be a starting point of your project.
If you want to proceed with the Project venv, uv or Base conda interpreter, select the corresponding option and click Create.
- Project venv
PyCharm creates a virtualenv environment based on the system Python in the project folder.
- uv
PyCharm configures a uv environment as the project interpreter.
- Base conda
PyCharm configures a conda base environment as the project interpreter.
To configure an interpreter of another type or to use an existing environment, select Custom environment.
The following steps depend on your choice:
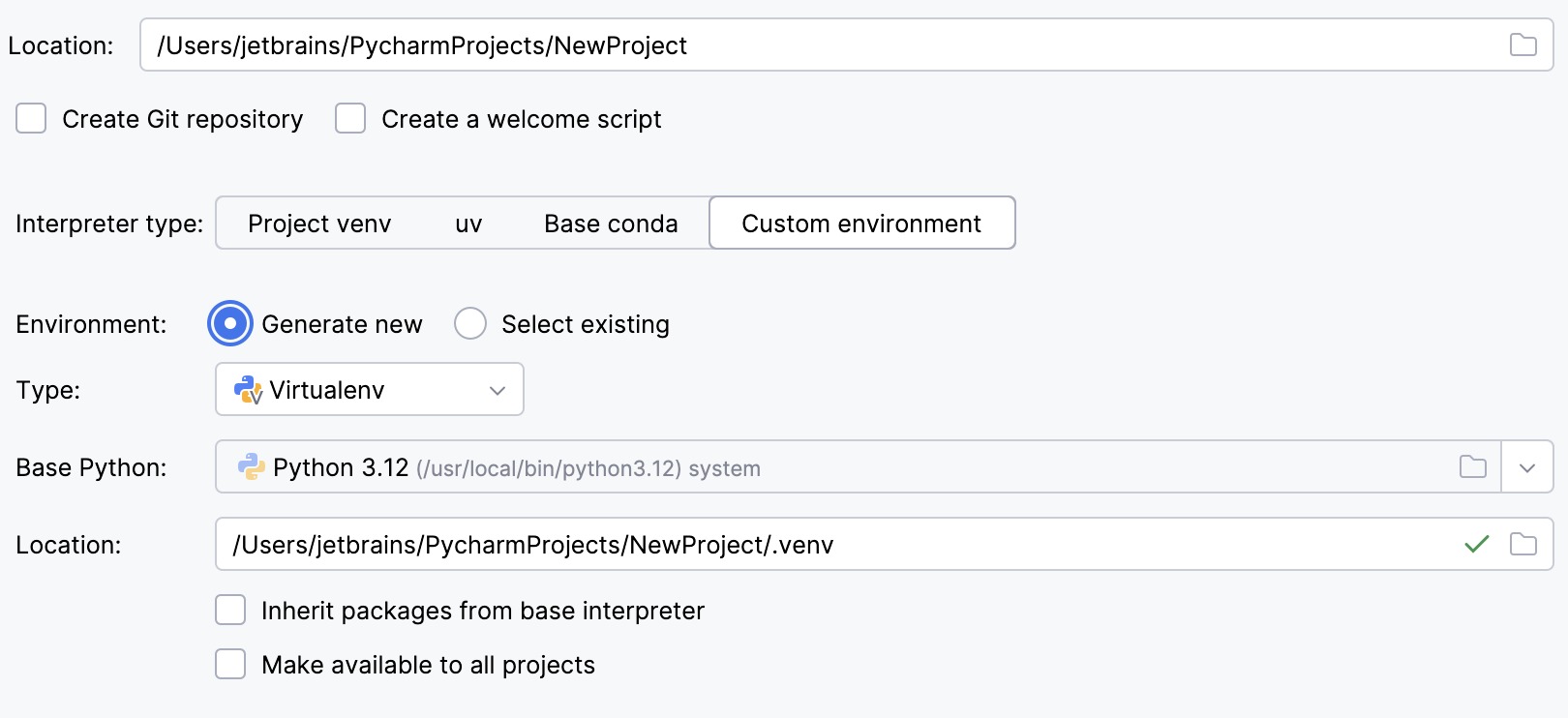
Select Virtualenv from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
Specify the location of the new virtual environment in the Location field, or click
and browse for the location in your file system. The directory for the new virtual environment should be empty.
Select the Inherit packages from base interpreter checkbox if you want all packages installed in the global Python on your machine to be added to the virtual environment you're going to create. This checkbox corresponds to the
--system-site-packagesoption of the virtualenv tool.Select the Make available to all projects checkbox if you want to reuse this environment when creating Python interpreters in PyCharm.
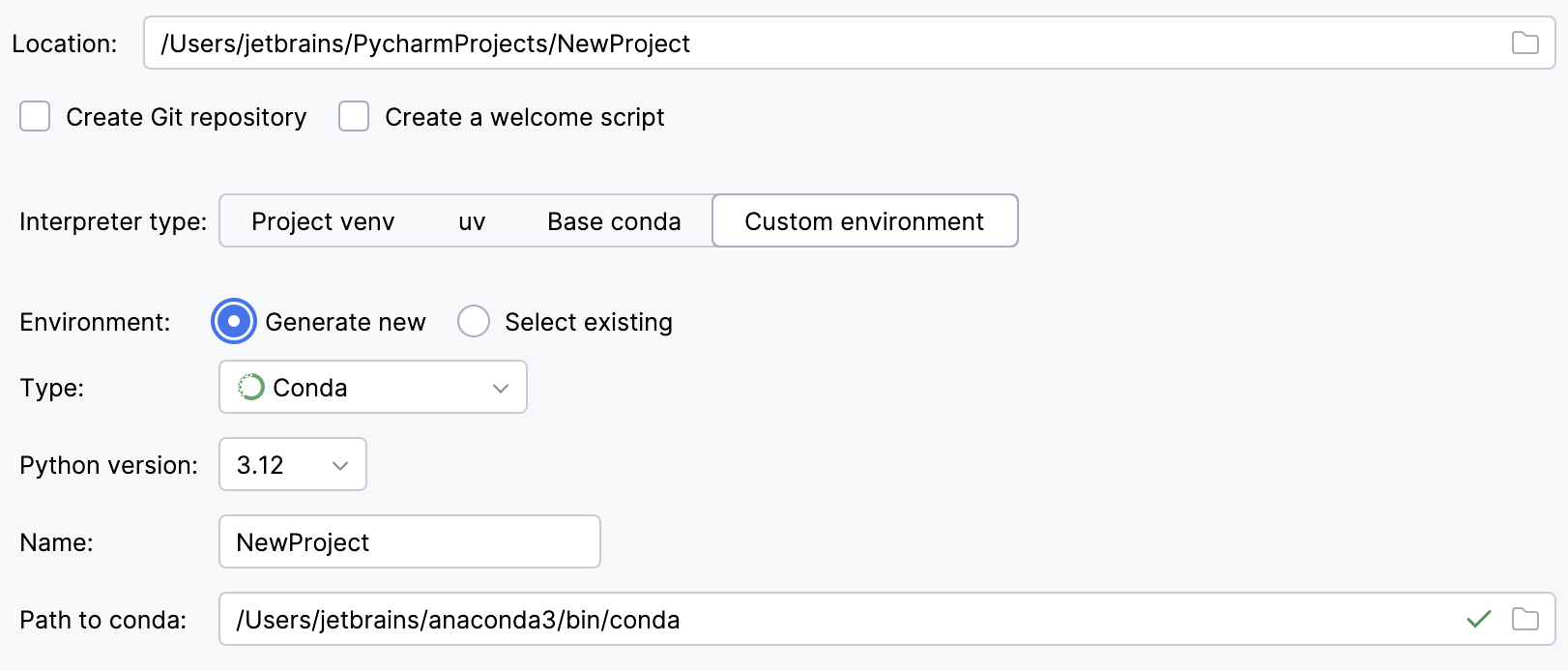
Select Conda from the list of environment types.
Select the Python version from the list.
Specify the environment name.
PyCharm will detect a conda installation.
If PyCharm did not detect the installation automatically, specify the location of the conda executable, or click
to browse for it.
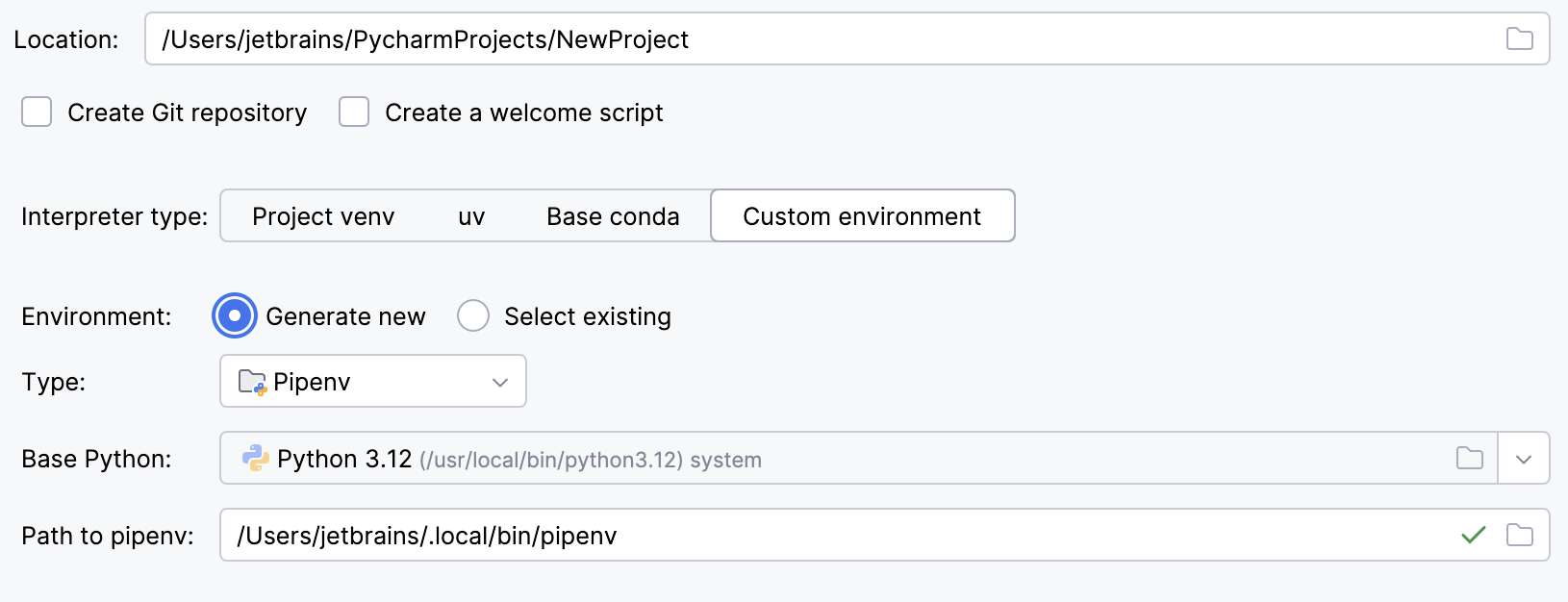
Select Pipenv from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
If you have added the base binary directory to your
PATHenvironmental variable, you do not need to set any additional options: the path to the pipenv executable will be autodetected.If PyCharm does not detect the pipenv executable, click Install pipenv via pip to allow PyCharm to install it for you automatically.
Alternatively, follow the pipenv installation procedure to discover the executable path and then specify it in the dialog.
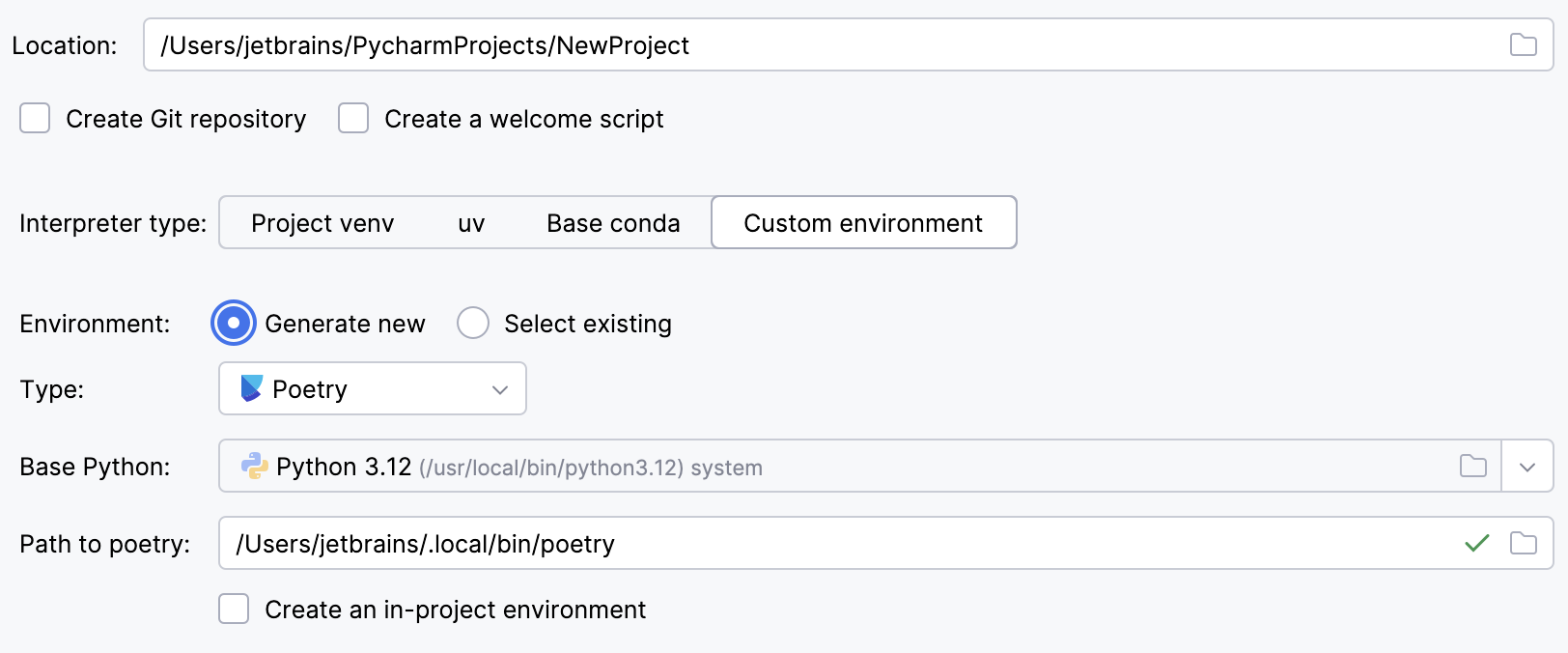
Select Poetry from the list of environment types.
Select the base interpreter from the list or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
If PyCharm does not detect the Poetry installation, click Install poetry via pip to allow PyCharm to install Poetry for you automatically.
Alternatively, specify the location of the Poetry executable, or click
to browse for it.
To create a virtual environment within the project directory, select the Create an in-project environment checkbox.
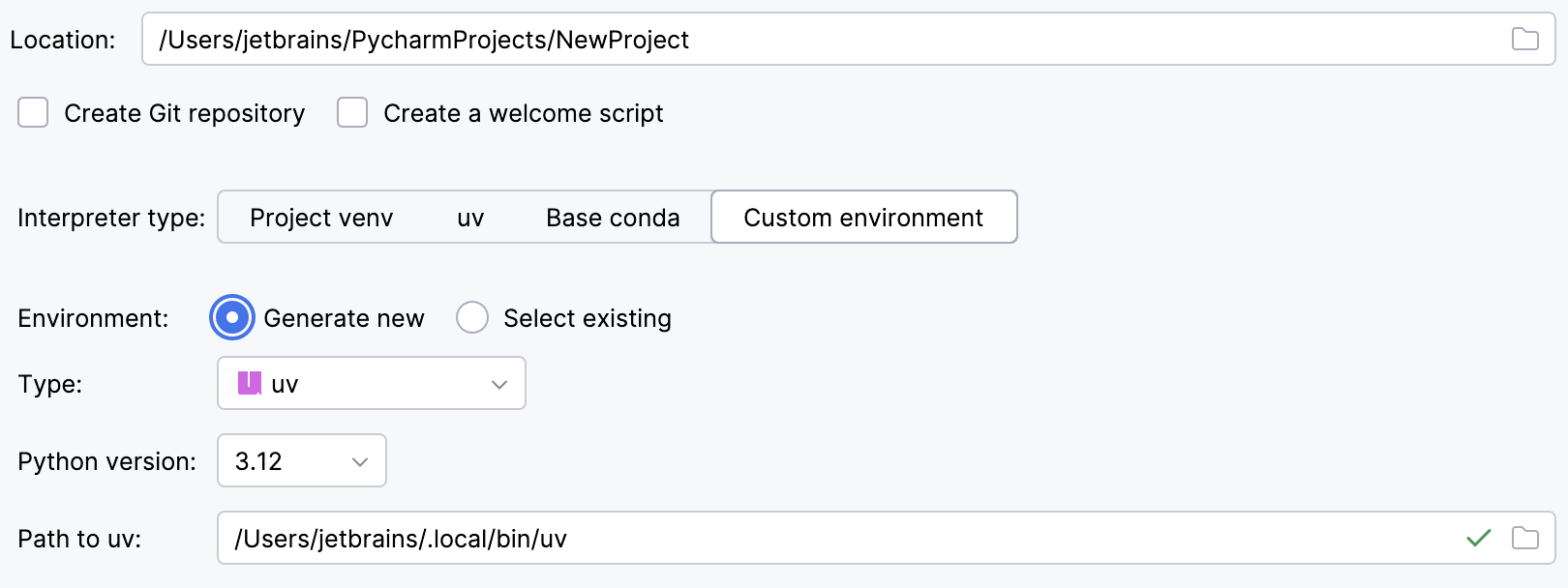
Select uv from the list of environment types.
Select the Python version from the list.
PyCharm will detect a uv installation.
Otherwise, specify the location of the uv executable, or click
to browse for it.
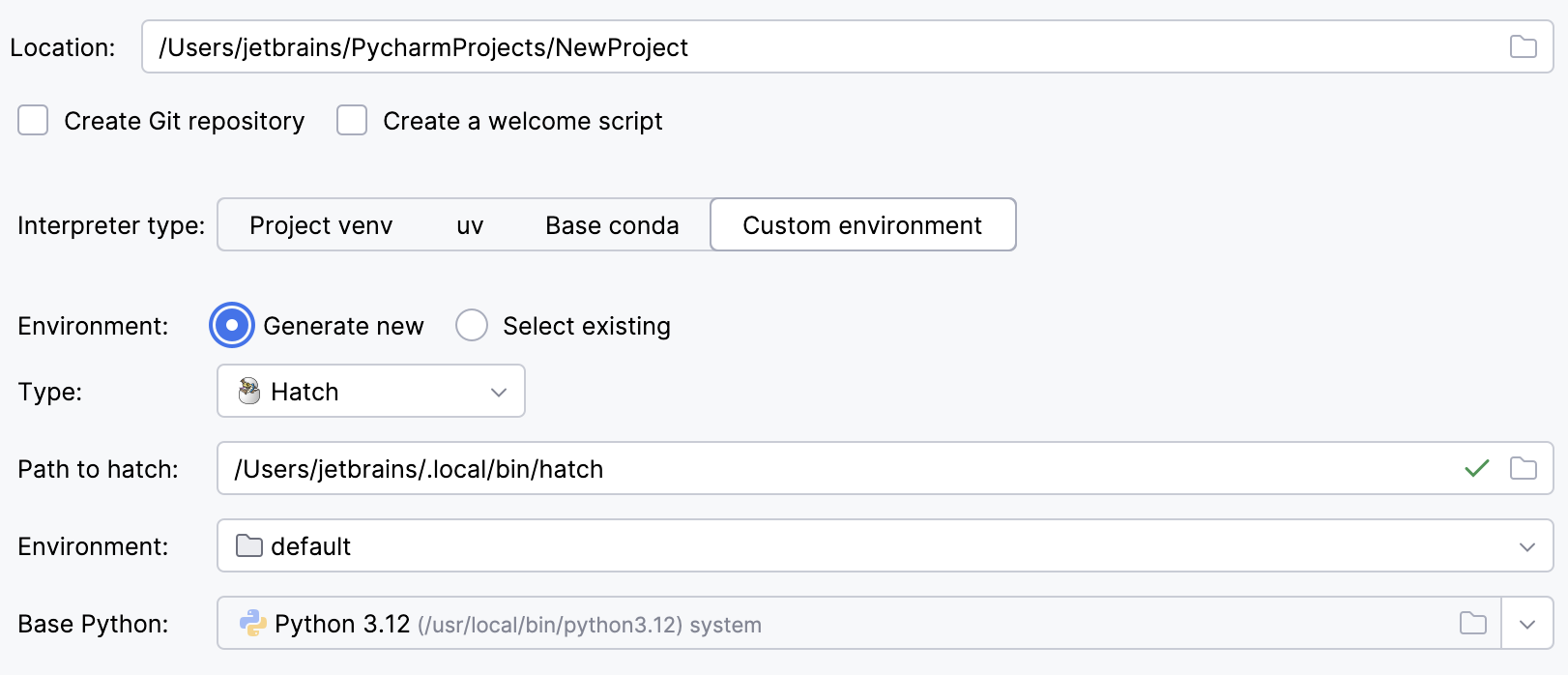
Select Hatch from the list of environment types.
PyCharm will detect a Hatch installation.
Otherwise, specify the location of the Hatch executable, or click
to browse for it.
Select an environment.
Hatch environments are workspaces designed for various project-specific tasks. If no environment is explicitly selected, Hatch will use the default environment.
Select the base interpreter from the list, or click
and find the Python executable in your file system.
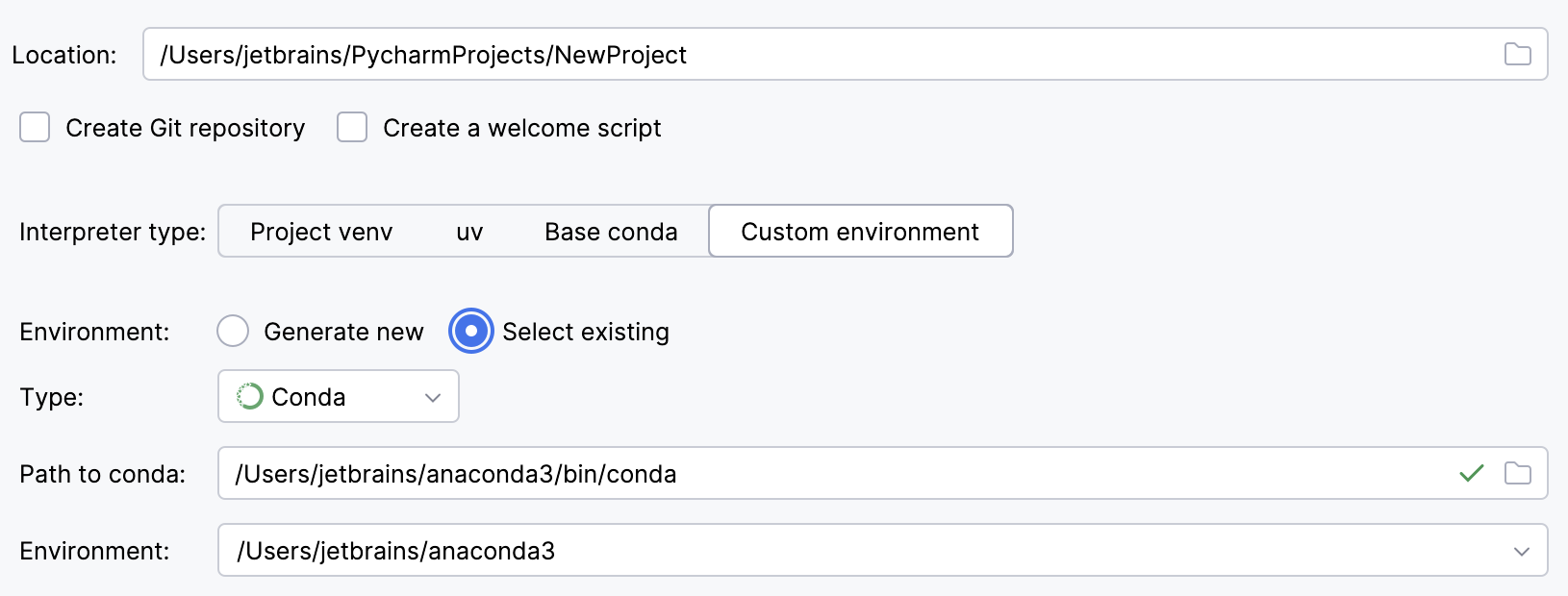
To reuse an existing conda environment:
Switch Type to Conda.
Specify the environment name.
PyCharm will detect a conda installation.
If PyCharm did not detect the installation automatically, specify the location of the conda executable, or click
to browse for it.
Select the environment from the list. If you specified the path to conda manually, you may need to reload environments.
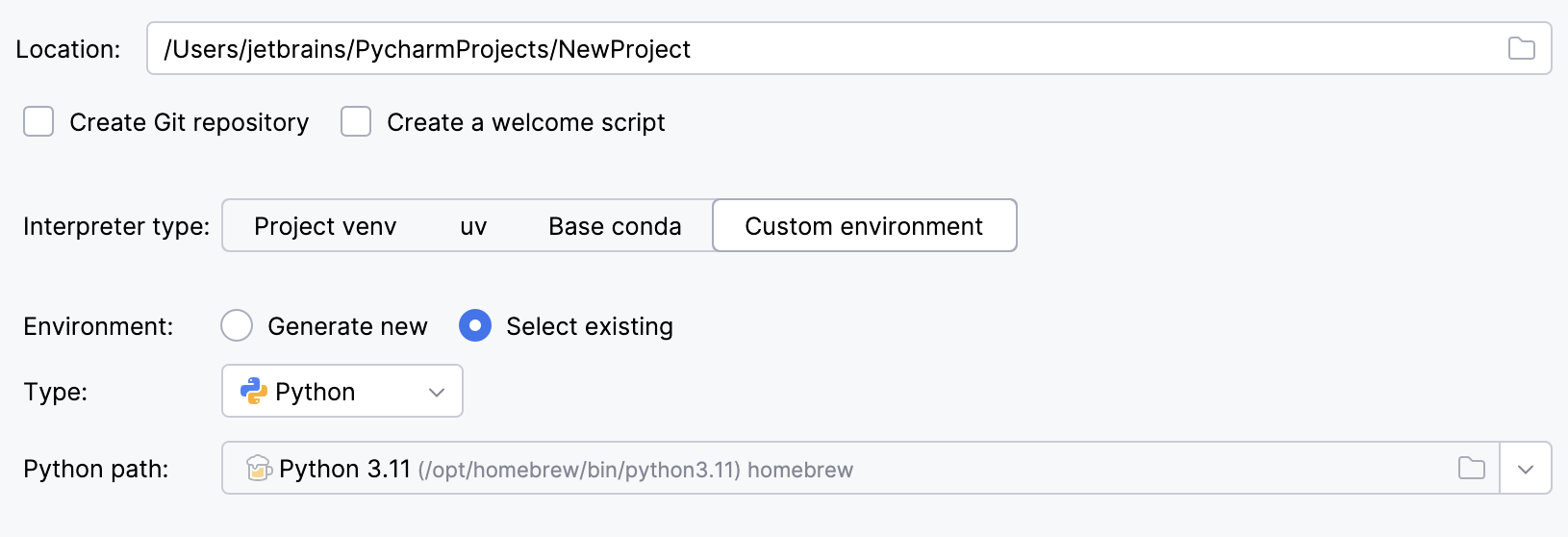
To reuse a different Python environment:
Switch Type to Python.
Select the Python executable from the list or click
to browse for it.
Once you have created a project, you can proceed with configuring the project structure.