Django support
Available only in PyCharm Pro: download to start your free trial and explore the full set of Pro features.
This functionality relies on the Django plugin, which is bundled and enabled in PyCharm by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press to open settings and then select Plugins.
Open the Installed tab, find the Django plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
Django framework and the corresponding Python interpreter are properly installed on your machine.
PyCharm supports the latest Django versions. The corresponding Python versions depend on Django. See What Python version can I use with Django?
Django support in PyCharm includes:
Dedicated project type.
Ability to run the tasks of the manage.py utility.
Django templates support (syntax and error highlighting, code completion, navigation, completion for block names, resolve and completion for custom tags and filters, and quick documentation for tags and filters).
Ability to create templates from usage.
Ability to debug Django templates.
Live templates (snippets) for the quick development of Django templates.
Run/debug configuration for Django server.
Code insight support for Django ORM.
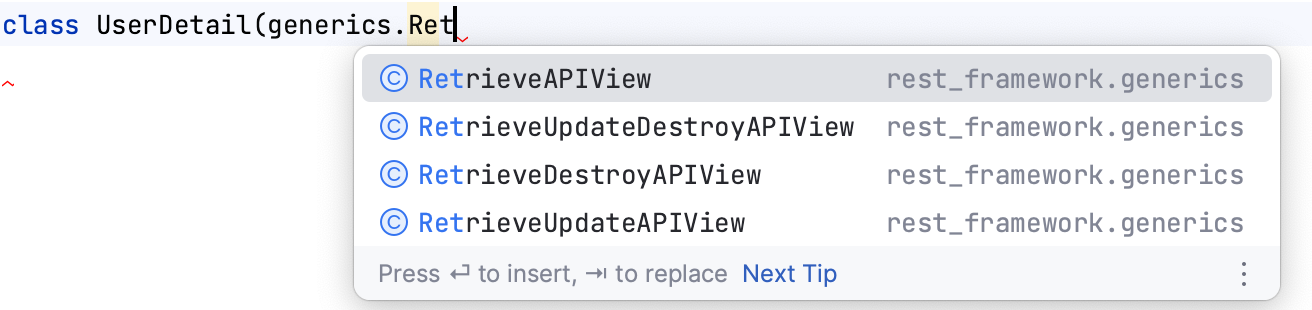
Code completion and resolve in
views.py and urls.py files:
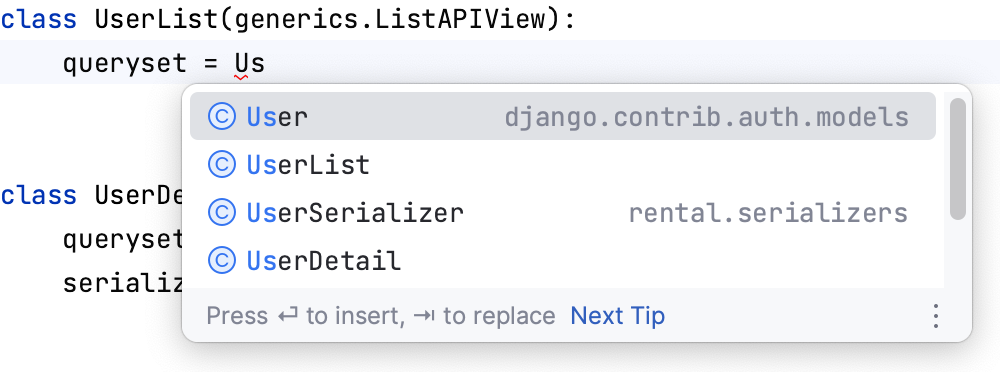
Models:
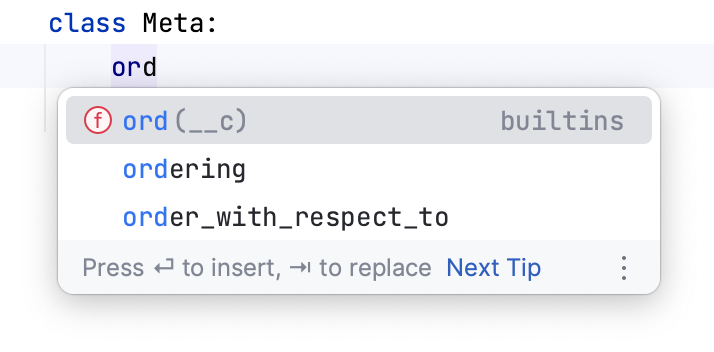
Meta model options:
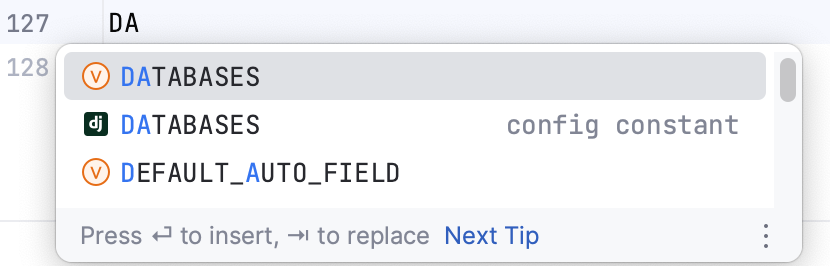
Configuration constants in the settings.py file
Class-based views. PyCharm provides Intention action to convert Django function-based generic views to class-based views.
Generating model dependency diagrams for Django models.
Django support for a Python project can be turned on or off by selecting/clearing the checkbox Enable Django support in the Django page.
Open the project Settings dialog () and navigate to the Languages & Frameworks | Django page.
Make sure that the checkbox Enable Django support is selected. You can also use the fields below to configure the required settings:
Item
Description
Enable Django support
The default state of this checkbox depends on the project type. For the empty projects, Django support is disabled. For the Django projects it is enabled by default; you can clear this checkbox if required. In this case, the other fields become unavailable.
Django project root
By default, this field shows the directory that contains all project files. If required, you can specify a different location.

Settings
Click the browse button to select the desired settings file.
Use one of the following approaches:
This can be any file with the name matching *settings*.py, located under the Django project root.
Point to any Python package and store settings in __init__.py.
This latter approach is useful when you want to split settings to several modules and import them.
By default, PyCharm shows the settings.py file, located in the Python package directory of your Django project.
Do not use Django test runner
By default, this checkbox is not selected. You can select it if you want to use any of the alternative test runners specified in the PyCharm Integrated Tools dialog window (File | Settings | Tools | Python Integrated Tools for Windows and Linux and PyCharm | Settings | Tools | Python Integrated Tools for macOS).
Manage.py tasks
Manage script
Specify here the desired manage.py file for the current project.
By default, PyCharm shows the manage.py file, located under the Django project root. Click
to select the desired manage file from the file system.
Environment variables
Specify here the environment variables to be passed to the script. Click
to open the Environmental Variables window. Press
to add a new variable and enter its name and value in the corresponding fields.
note
By default, Include system environment variables checkbox is enabled. Disable it if you only want to pass custom variables.
Folder pattern to track file
Specify here folder names separated with colons. If needed, you can use Glob-style wildcards. Django only pulls and adds to VCS files matched by this pattern.

Apply changes (if any) and close the dialog.