Language injections
Language injections let you work with pieces of code in other languages embedded in your code. When you inject a language (such as HTML, CSS, XML, RegExp, and so on) into a string literal, you get comprehensive code assistance for editing that literal.
Temporarily inject a language
Position the caret inside the string literal, tag, or attribute, in which you want to inject a language and press Alt+Enter (or use the intention action icon
).
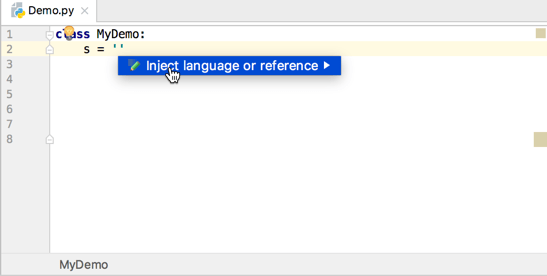
Select Inject language or reference and choose the language you want to inject.
Open a code fragment in the dedicated editor section
Position the caret within the injected code piece and press Alt+Enter (or use the intention action icon
).
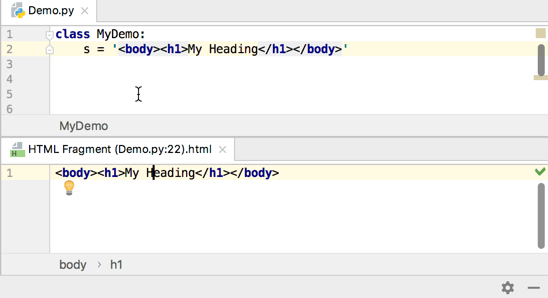
Select Edit <language ID> Fragment.
PyCharm will open a dedicated editor section for editing the code with the injected language. This editor provides full code assistance, including code completion, inspections, intentions and code style actions.
Use language injection comments
Add a blank line before the target string literal, and type the following comment:
// language=<language_ID>For comments, use the syntax of the language you want to inject. Language IDs are generally intuitive, for example, SQL, RegExp, XML, HTML.
A language fragment may be combined with a prefix and a suffix that act together as a wrapper, turning the fragment into a syntactically complete language unit. When editing your code, you can see prefixes and suffixes only in the fragment editor. They are not shown in the main editor.
The prefix and the suffix can be included in the injection comment as follows:
Cancel injections
Position the caret at the code fragment and press Alt+Enter (or use the intention action icon
).
Select Uninject language or reference.
To cancel a language injection, you can also delete the injection comment or annotation.
Configure injection rules
You can configure language injection rules on the Editor | Language Injections page of the IDE settings Ctrl+Alt+S.
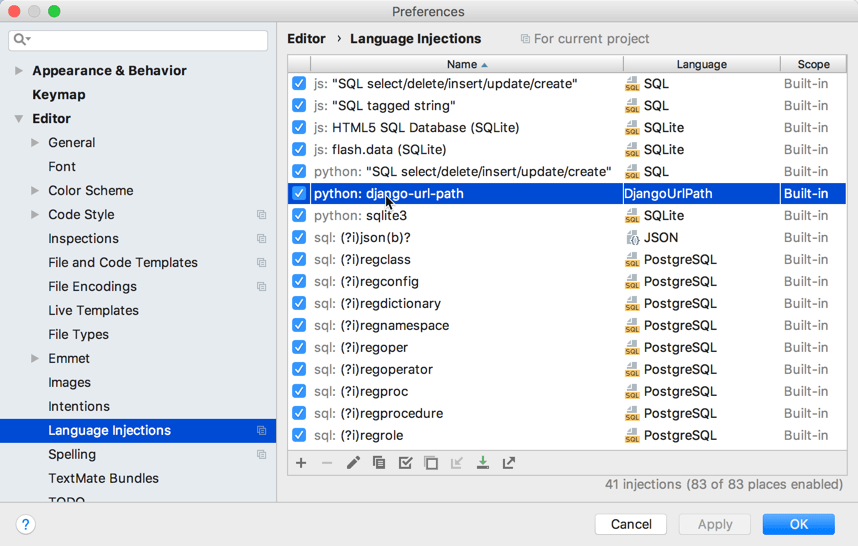
All pre-defined injection rules are configured for the Built-in scope. In other words, they are global (and therefore available in all PyCharm projects). Custom rules can be configured for the IDE or for one project only. To change the scope of custom injections, use the .
To configure custom injection rules, click to add a new rule, or copy a predefined rule and change its settings.