React Native
With React Native you can develop native mobile applications for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React. It is created by Facebook and used for such well-known apps as Instagram, Airbnb, and now JetBrains’ own YouTrack mobile application. Learn more from the React Native official website.
PyCharm helps you create, edit, lint, run, debug, and maintain your React Native applications. PyCharm also provides code completion for React and Flow symbols.
Before you start
Make sure you have Node.js on your computer.
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript plugin is enabled on the Settings/Preferences | Plugins page, tab Installed, see Managing plugins for details.
Creating a new React Native application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the left-hand pane, choose React Native.
In the right-hand pane:
Specify the path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
In the Node Interpreter field, specify the Node.js interpreter to use. Select a configured interpreter from the list or choose Add to configure a new one.
From the React Native list, select npx --package react-native-cli react-native.
Alternatively, for npm version 5.1 and earlier, install the
react-native-clipackage yourself by runningnpm install -g react-native-cliin the Terminal Alt+F12. When creating an application, select the folder where thereact-native-clipackage is stored.
When you click Create, PyCharm generates a React Native-specific project with all the required configuration files, downloads the dependencies, and creates a run/debug configuration of the type React Native with default settings..
Starting with an existing React Native application
To continue developing an existing React Native application, open it in PyCharm and download the required dependencies.
Open the application sources that are already on your machine
Click Open on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. In the dialog that opens, select the folder where your sources are stored.
Check out the application sources from your version control
Click Get from VCS on the Welcome screen. Alternatively, select or from the main menu.
<Your_VCS> stands for the Version Control System with which your currently opened project is associated.
In the dialog that opens, select your version control system from the list and specify the repository to check out the application sources from. See Check out a project (clone) for details.
Download the dependencies
Click Run 'npm install' or Run 'yarn install' in the popup:

You can use npm, Yarn 1, or Yarn 2, see npm and Yarn for details.
Install other tools to get started with React Native, for example, an iOS simulator. The list of these tools depends on your operating system and the mobile platform you are going to target your application at. See React Native Getting Started guide for detailed installation instructions.
Project security
A webpack configuration file from external sources may contain some potentially malicious code that can cause problems when PyCharm executes the configuration on opening a JavaScript file with import statements. For the sake of security, when you open a React Native project with webpack, PyCharm analyzes it, resolves the located data, and displays a warning that lets you decide whether the project is trustworthy or not.
If you click Skip, PyCharm disables analysis of the webpack configuration in the current project. As a result, PyCharm might not resolve some of the imports in the project or add imports that don't use resolution rules configured in the webpack configuration.
Learn more from Webpack and Project security.
Coding assistance
PyCharm provides code completion for React APIs and JSX in JavaScript code. Code completion works for React methods, React-specific attributes, HTML tags and component names, React events, component properties, and so on. See React: Completing Code for more information.
Running and debugging a React Native application
You can run and debug your application on a physical device or on a simulator. Before you launch your application, make sure that the simulator is already running or, if you are using a physical device, it is already connected to your computer.
PyCharm makes running and debugging React Native applications very flexible. For example, if you are starting your application for the first time, you can choose to run the React Native bundler, build the application, and open it on the simulator - all that as part of a running or debugging session. You can also skip launching the bundler if it is already running or refuse building the application if you have not made any changes to its native code since the previous run.
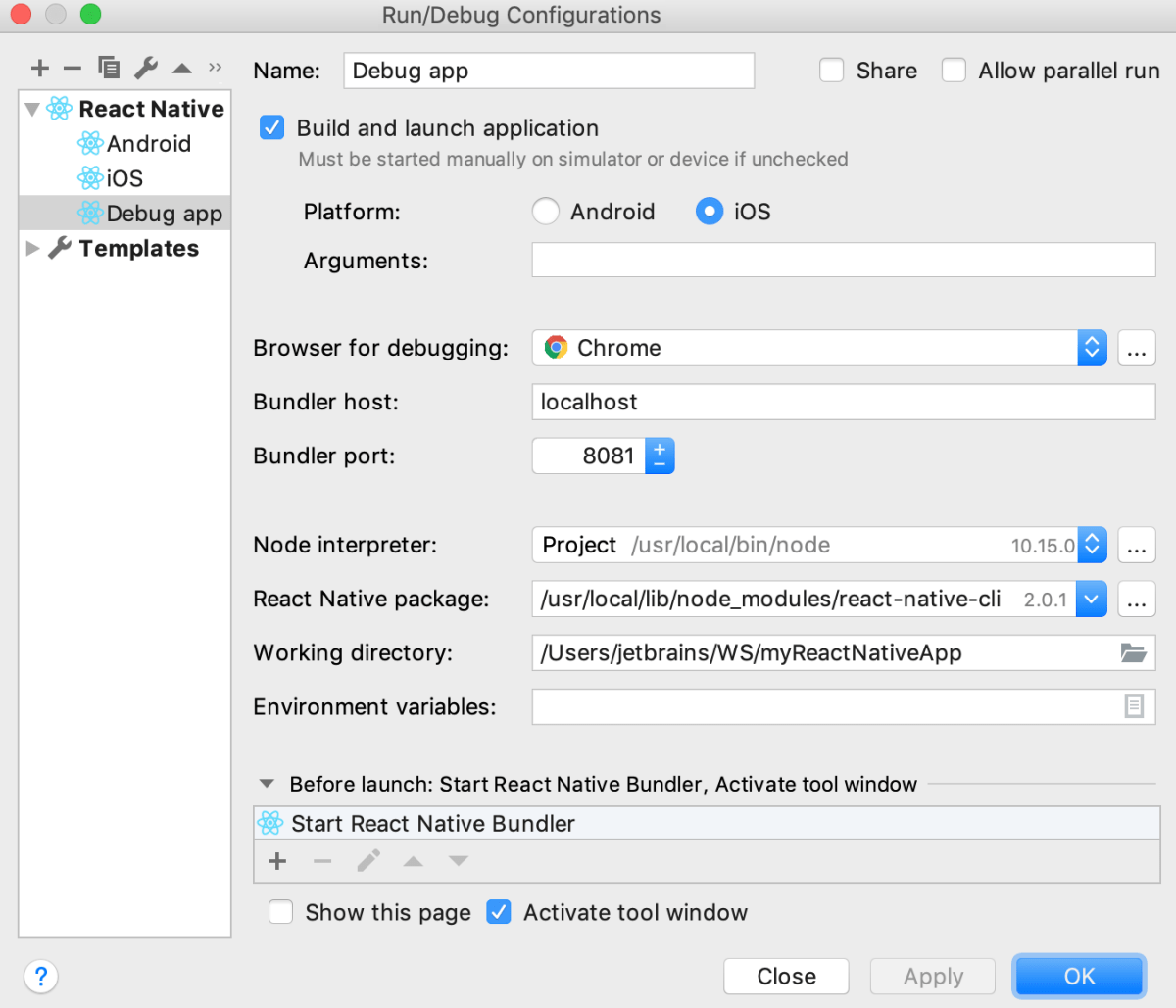
Create a React Native run/debug configuration
On the main menu, go to , click
and select React Native from the list.
Choose whether you want PyCharm to build and launch the application for you:
Select the Build and launch checkbox if you are launching your application for the first time or if you have updated its native code since the last run.
Clear this checkbox if you haven't made any changes to the native code of your application since the last build.
When you start debugging, PyCharm waits for you to open your application in the simulator with the Remote debug enabled as described on the React Native official website
If your application uses Expo, clear the checkbox because this bundler takes care of the process itself.
If you selected the Build and launch checkbox, choose the target platform, Android or iOS.
Depending on your choice, PyCharm will run the bundler with
react-native run-iosor withreact-native run-android.To emulate the Android platform, use an Android virtual device.
To emulate the iOS platform, you need to install the ios-sim command-line tool globally. You can do it through the Node Package Manager (npm), see npm, pnpm, and Yarn, or by running the
sudo npm install ios-sim -gcommand, depending on your operating system.
Learn more from the React Native official website.
Optionally, in the Arguments field, type the arguments to be passed to React Native, for example, specify the simulator type through the
‑‑simulatorflag:‑‑simulator="iPhone 4s".Specify the browser to use.
In debugging React Native applications, PyCharm relies on the Chrome runtime, which is used by React Native itself. You can also use DevTools together with PyCharm. When you initiate a debugging session, PyCharm starts a new Chrome instance and attaches to it.
In the Bundler host field, specify the host where the React Native bundler runs, the default value is localhost.
In the Bundler port field, specify the port on which the React Native bundler runs, by default 8081 is chosen, learn more from the React Native official website.
If your application uses Expo, you may need to change the port to 19000 or 19001, depending on the Expo configuration.
Choose the Node.js interpreter to use. This can be a local Node.js interpreter or a Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Specify the path to react-native-cli and the working directory of the application. Optionally, type the environment variables for
react-native run-androidorreact-native run-ios.By default, PyCharm starts the React Native bundler automatically when you invoke the run/debug configuration. If you have already started the bundler from outside PyCharm, for example, from the command line, you can re-use it without stopping and restarting. Select your bundler in the Before Launch area and click
.
For information on the settings that are common for all run/debug configurations, see Run/debug configurations.
Prepare a device or a simulator
If you are using an Android device, you need to prepare it every time you start working with an application.
An iOS simulator has to be installed only once, after that PyCharm starts it automatically with react-native run-ios.
To prepare an Android device, launch an Android virtual device or enable debugging over USB and connect to a physical Android device via USB.
Learn more from the React Native official website.
To prepare an iOS simulator, open the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) and type:
<nmp_path>\npm install --global ios-sim
Run an application
Choose the newly created React Native configuration in the Select run/debug configuration list on the toolbar and click
next to it. PyCharm opens the Run tool window and first starts the React Native bundler in a new React Native tab. After that, the
react-native run-iosorreact-native run-androidcommand is executed, depending on the selected target platform. If the build is successful, the simulator shows your application: