Change inspection severity
Inspection severity levels indicate how seriously the detected code problems affect your project. Every severity level has its own highlighting style. In PyCharm, there is a set of predefined severity levels:
Error: marks syntax errors.
 Warning: marks code fragments that might produce bugs or require enhancement.
Warning: marks code fragments that might produce bugs or require enhancement. Weak Warning: marks code fragments that can be improved or optimized (redundant code, duplicated code fragments, and so on).
Weak Warning: marks code fragments that can be improved or optimized (redundant code, duplicated code fragments, and so on). Server Problem: marks problems that come from an external build server, for example, from TeamCity.
Server Problem: marks problems that come from an external build server, for example, from TeamCity.Typo: marks spelling and grammar mistakes.
No highlighting, only fix: provides no code highlighting; the list of available fixes is invoked by pressing Alt+Enter.
Severity levels are designed to indicate problems, they don't have any impact on the code execution: if you change the severity for spelling mistakes from Typo to Error, this won't affect the execution of your application.
Change inspection severity in all scopes
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Editor | Inspections.
Select the profile that you want to modify and then choose an inspection from the list. Make sure that it is enabled.
From the Severity list, select a new severity level. You can also right-click the inspection and select the severity level from the context menu.
Apply the changes and close the dialog. The modified inspection will now have the new severity level in the selected profile.
If the list of available severity levels lacks the one that you need, you can create a new one.
Change inspection severity in specific scopes
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Editor | Inspections.
Select the profile that you want to modify and then choose an inspection from the list. Make sure that it is enabled.
From the In All Scopes list, select the scope for which you want to change the severity.
PyCharm shows severities for two scopes: the selected one and Everywhere else.
To add one more scope, click
. If you want to create a new scope, select Edit Scopes Order from the list of scopes and click
.
Select the necessary severity level from the list and apply the changes.
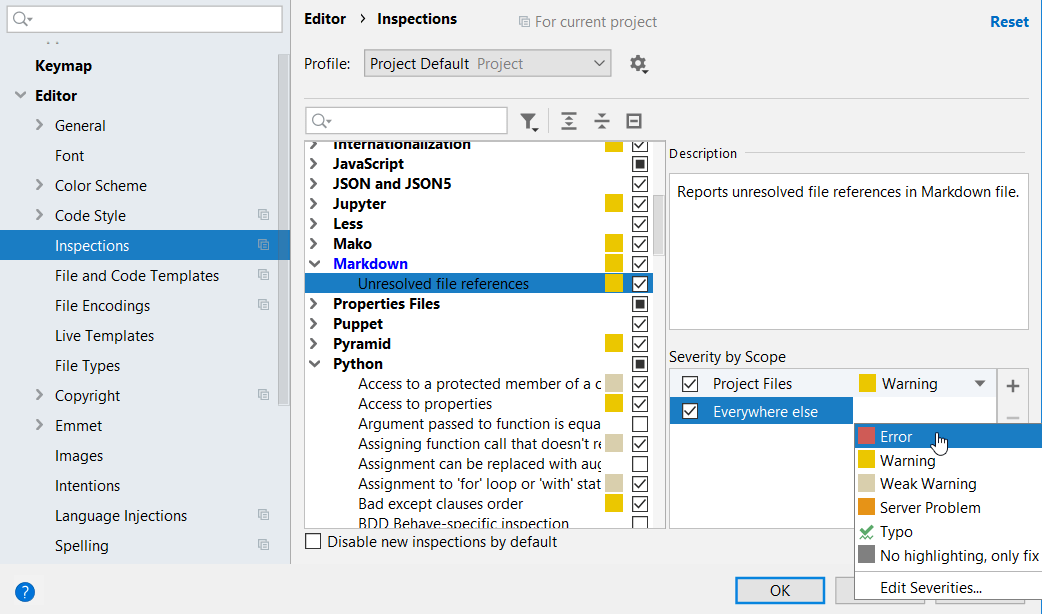
If you enable an inspection in multiple scopes, and files in these scopes match, the IDE will process these scopes according to their order in the list. For more information, refer to Change the order of scopes.
Configure error highlighting
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Editor | Inspections.
Select the profile that you want to modify.
From the list of severity levels, select Edit severities.
Select the severity for which you want to change the formatting and click Edit Settings | Colors & Fonts.
Configure the new highlighting rules. Use the preview section at the bottom of the dialog.

You can also modify highlighting in the settings under Editor | Color Scheme | General.
Create a new severity level
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Editor | Inspections.
Select the profile in which you want to create a new severity level.
Click any inspection and select Edit severities from the list of severity levels.
In the Severities Editor dialog, click
and name the new severity level.
Configure the formatting and set a priority using the
and
buttons — the higher you put the severity on the list, the higher its priority.
Click OK when finished.

Use scopes to manage Python version compatibility
You can use compatibility inspections to manage required Python versions for different projects that are opened in the same window.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Appearance & Behavior | Scopes.
Click
 and create a new scope for one of the projects. Then create yet another scope for another project opened in the same window.
and create a new scope for one of the projects. Then create yet another scope for another project opened in the same window. 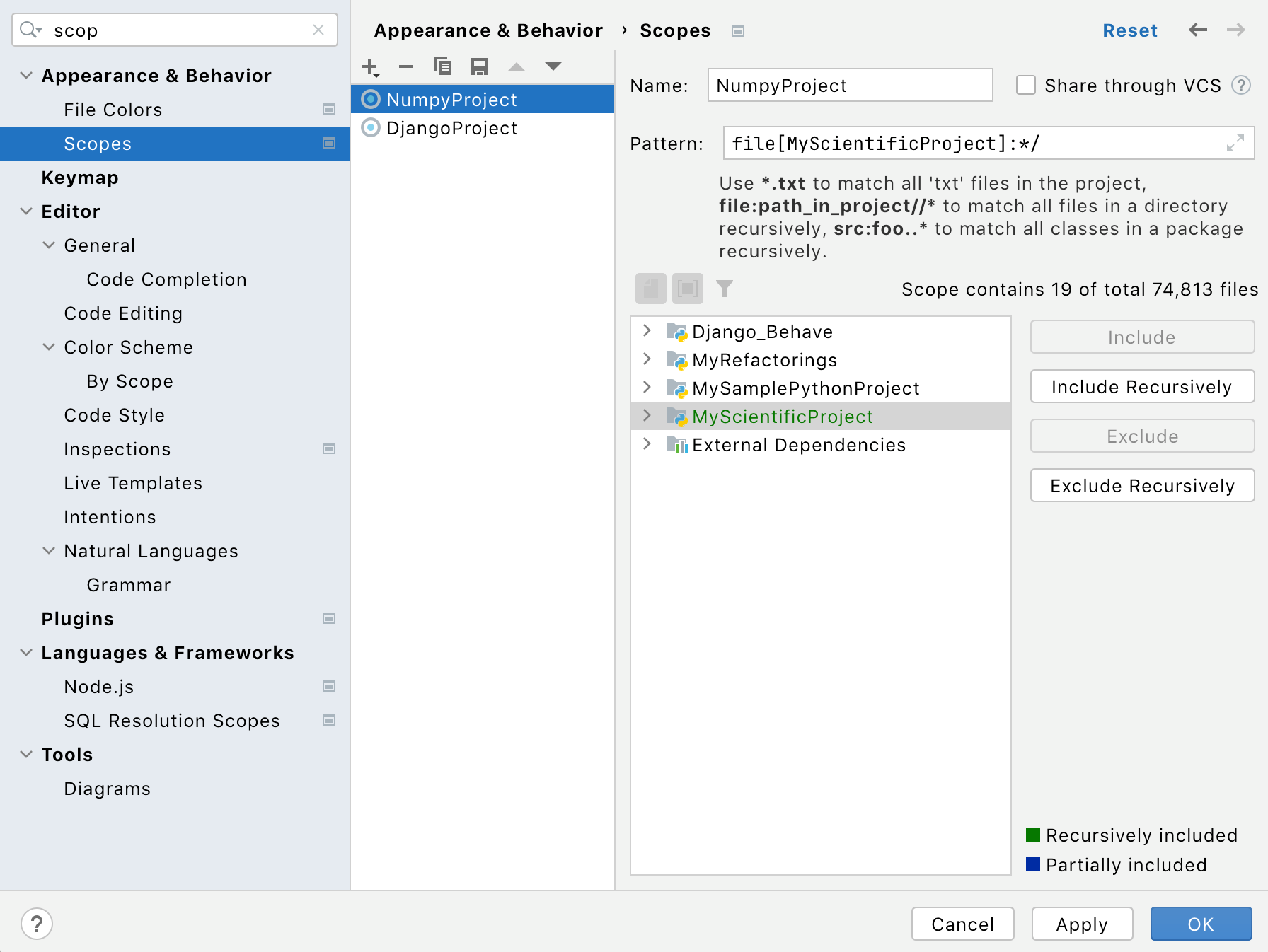
Click Apply to utilize newly created scopes.
Switch to the Editor | Inspections settings and start typing "incompatible" in the inspection search list. Select the Python compatibility inspection.
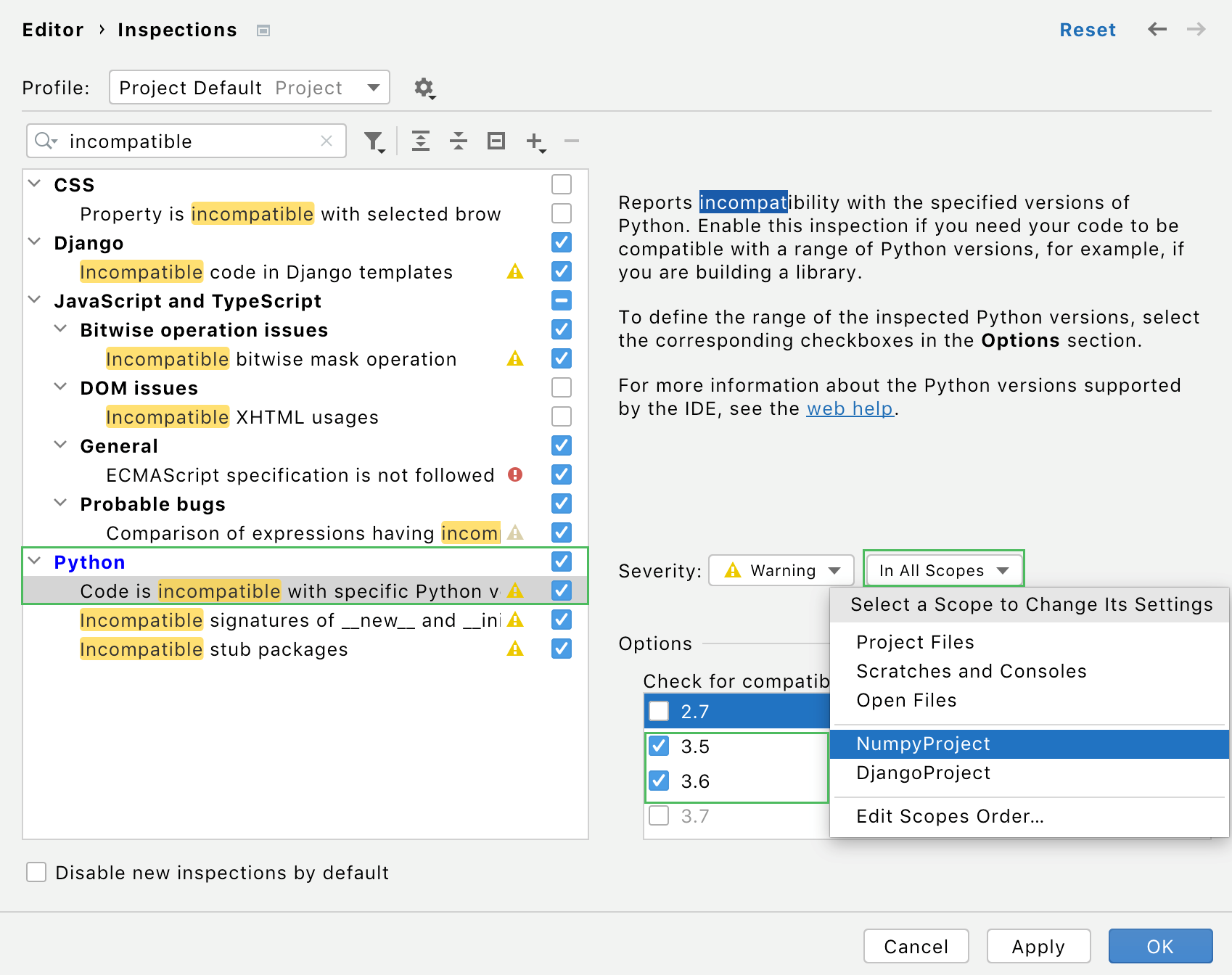
Select a newly created project-based scope from the list of scopes in the Severity settings. Check the required versions of Python for the selected scope. Click OK to save the changes.
Thanks for your feedback!