Configure an interpreter using Vagrant
Ensure that the following prerequisites are met (outside of PyCharm):
Oracle's VirtualBox is installed on your computer.
Vagrant is installed on your computer, and all the necessary infrastructure is created.
The parent folders of the following executable files are added to the system
PATHvariable:vagrant.bat or vagrant from your Vagrant installation. This should be done automatically by the installer.
VBoxManage.exe or VBoxManage from your Oracle's VirtualBox installation.
The required virtual boxes are created.
Configure a remote Python interpreter
Ensure that you have downloaded and installed Python on your computer.
Ensure that you have properly initiated and started Vagrant. Basically, you need to open the Terminal window and execute the following commands:
$ vagrant init ubuntu/trusty64and
$ vagrant upSee Vagrant documentation for more information.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and select Plugins.
Install the Vagrant plugin.
Do one of the following:
Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose .
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the project Settings/Preferences and go to . Then click the
icon and select Add.
In the left-hand pane of the Add Python Interpreter dialog, click Vagrant:

Click the browse button
next to the field Vagrant instance folder, and specify the desired Vagrant instance folder.
This results in showing the link to Vagrant host URL.
The Python interpreter path field displays the path to the desired Python executable. You can accept default, or specify a different one.
Click OK. The configured remote interpreter is added to the list.
Back in the Python Interpreter page, if necessary, configure the path mappings:
Click
:
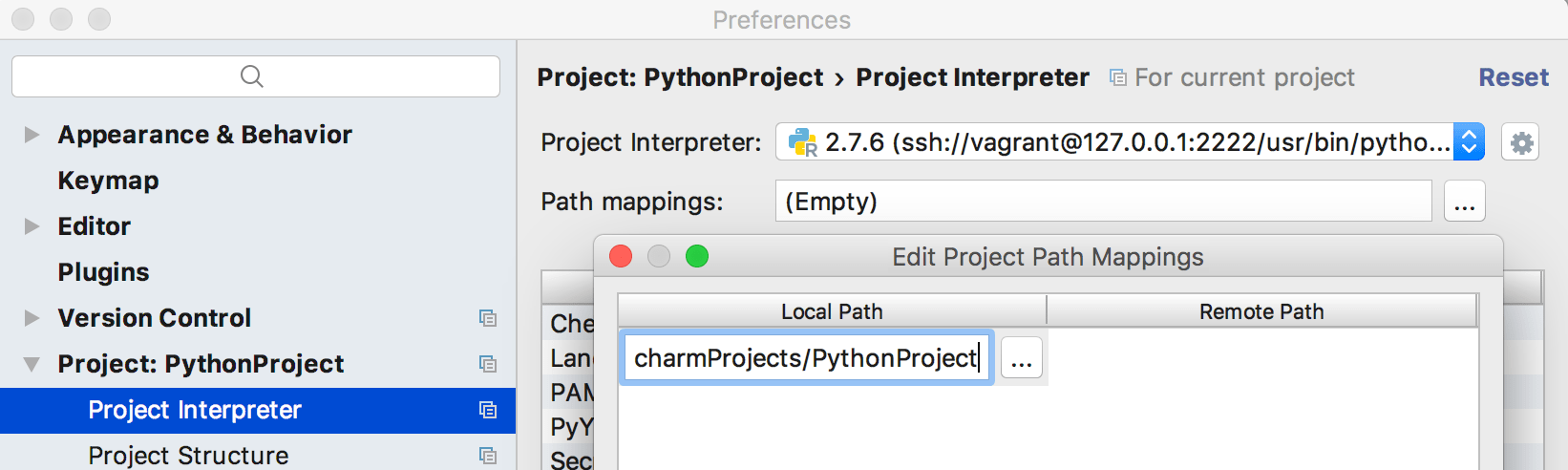
In the dialog that opens add
or delete
path mappings as desired.