Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB
Step 1. Check and create a LocalDB instance
To connect to your LocalDB instance with PyCharm, check if your LocalDB instance is ready for a connection. To do that, locate SqllocalDB.exe and run the following command in a command prompt:
You will see a list of available LocalDB instances on the server.
SqllocalDB.exe iNext, create a LocalDB instance. To create an instance, run the following command:
SqlLocalDB create "DEVELOPMENT" 15.0 -sThis command creates an instance of LocalDB named
DEVELOPMENTby using SQL Server 2017 binaries and starts the instance. If you omit15.0, the version number defaults to the version of the SqlLocalDB utility.To check an instance state, run this command.
SqllocalDB.exe i MSSQLLocalDBCurrently, the instance is running (see the
Statefield). If you have theStoppedstate, start the instance by running the following command in the terminal.SqllocalDB.exe s MSSQLLocalDB
Step 2. Create the LocalDB connection
In the Database tool window (), click the Data Source Properties icon
.
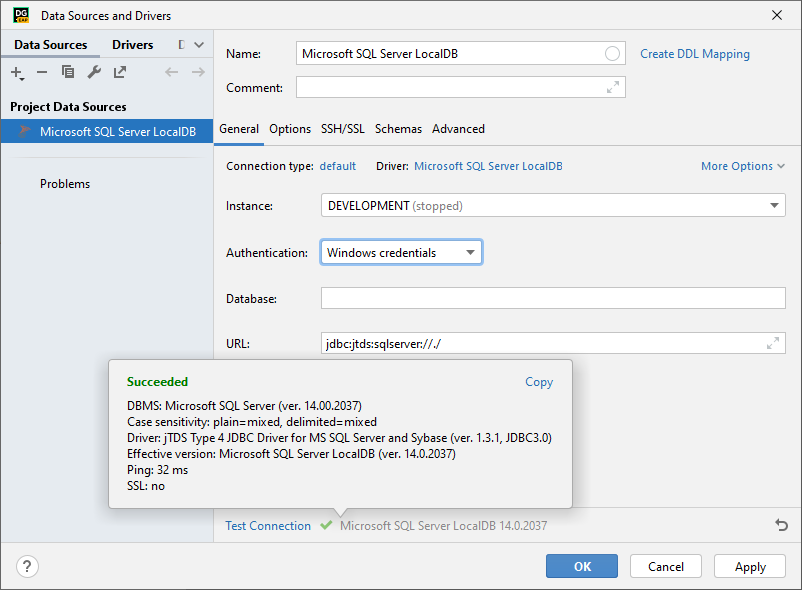
From the Driver list, select Microsoft SQL Server LocalDB.
Check if there is a Download missing driver files link at the bottom of the data source settings area. As you click this link, PyCharm downloads drivers that are required to interact with a database. The IDE does not include bundled drivers in order to have a smaller size of the installation package and to keep driver versions up-to-date for each IDE version.
You can specify your drivers for the data source if you do not want to download the provided drivers. For more information about creating a database connection with your driver, see Add a user driver to an existing connection.
From the Instance list, select the instance to connect to (for example,
DEVELOPMENT).From the Authentication list, select the authentication type:
User & Password: connect by using a username and a password.
Windows credentials: connect by using your Windows domain creadentials. Requires to run PyCharm on Windows in the same domain as the Microsoft SQL Server database. Works as the Single-Sign On (SSO).
Kerberos: connecting by using Kerberos authentication. Requires a Kerberos server and authentication with
kinit.No auth: connect without authentication.
Domain credentials: connect by using a domain, a username, and a password.
To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click the Test Connection link.