TypeScript
PyCharm supports developing, running, and debugging TypeScript source code. PyCharm recognizes .ts and .tsx files and provides full range of coding assistance for editing them without any additional steps from your side. TypeScript files are marked with the ![]() icon.
icon.
TypeScript-aware coding assistance includes completion for keywords, labels, variables, parameters, and functions, error and syntax highlighting, formatting, numerous code inspections and quick-fixes, as well as common and TypeScript-specific refactoring. PyCharm also verifies TypeScript code on the fly and shows errors in a dedicated Problems tool window.
Compilation errors are reported in the TypeScript tool window. Learn more from Compiling TypeScript into JavaScript.
Before you start
Make sure the JavaScript and TypeScript plugin is enabled in the settings. Press Control+Alt+S to open the IDE settings and then select . Click the Installed tab. In the search field, type JavaScript and TypeScript. For more information about plugins, refer to Managing plugins.
Create a new application
Click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. The New Project dialog opens.
In the left-hand pane, choose any project type that is aimed for application development, for example, Angular CLI, React App, React Native, and so on.
In the right-hand pane, specify The path to the folder where the project-related files will be stored.
Expand More settings and specify other required project options.
Start with an existing TypeScript application
If you are going to continue developing an existing TypeScript application, just open it in PyCharm. Optionally download the required npm dependencies.
Open the application sources that are already on your machine
Click Open on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu. In the dialog that opens, select the folder where your sources are stored.
Check out the application sources from your version control
Click Get from VCS on the Welcome screen.
Alternatively, select or from the main menu.
Instead of Git in the main menu, you may see any other Version Control System that is associated with your project. For example, Mercurial or Perforce.
In the dialog that opens, select your version control system from the list and specify the repository to check out the application sources from. For more information, refer to Check out a project (clone).
Project security
When you open a project that was created outside PyCharm and was imported into it, PyCharm displays a dialog where you can decide how to handle this project with unfamiliar source code.
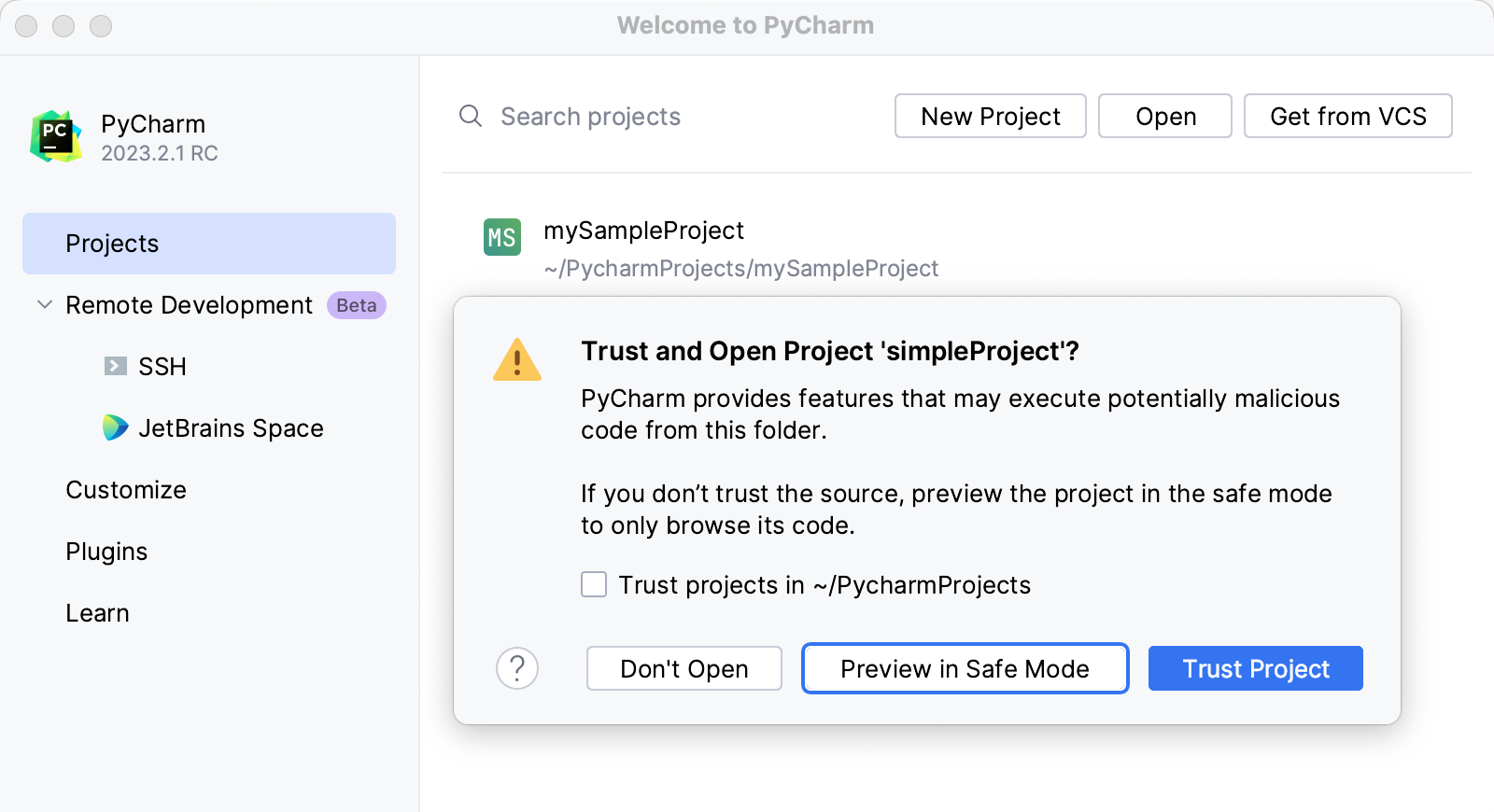
Select one of the following options:
Preview in Safe Mode: in this case, PyCharm opens the project in a preview mode. It means that you can browse the project's sources but you cannot run tasks and script or run/debug your project.
PyCharm displays a notification on top of the editor area, and you can click the Trust project… link and load your project at any time.
Trust Project: in this case, PyCharm opens and loads a project. That means the project is initialized, project's plugins are resolved, dependencies are added, and all PyCharm features are available.
Don't Open: in this case, PyCharm doesn't open the project.
Learn more from Project security.
Verify TypeScript
PyCharm verifies TypeScript code mainly based on the data from the TypeScript Language Service which also compiles TypeScript into JavaScript.
Descriptions of the errors detected in the current file and quick-fixes for them are available from the editor and from the File tab of the Problems tool window.
Errors across the entire project and quick-fixes for them are shown in the Project Errors tab of the Problems tool window. To open the tool window, click the Inspection widget in the upper-right corner of the editor:
![]()
For more information, refer to View problems and apply quick-fixes in the editor and Problems tool window.
Verify TypeScript in the current file
In the editor, hover over the highlighted problem. PyCharm shows a tooltip with a description of the problem.
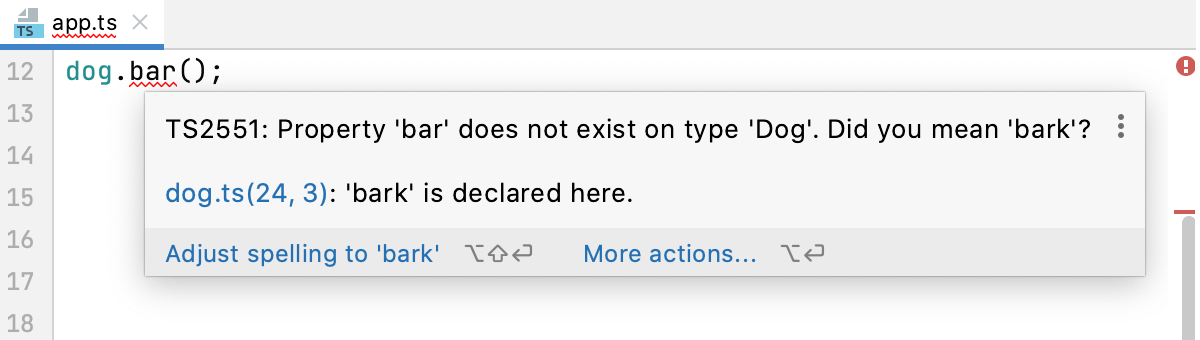
Apply the suggested quick-fix or click More actions and select the relevant one from the list.
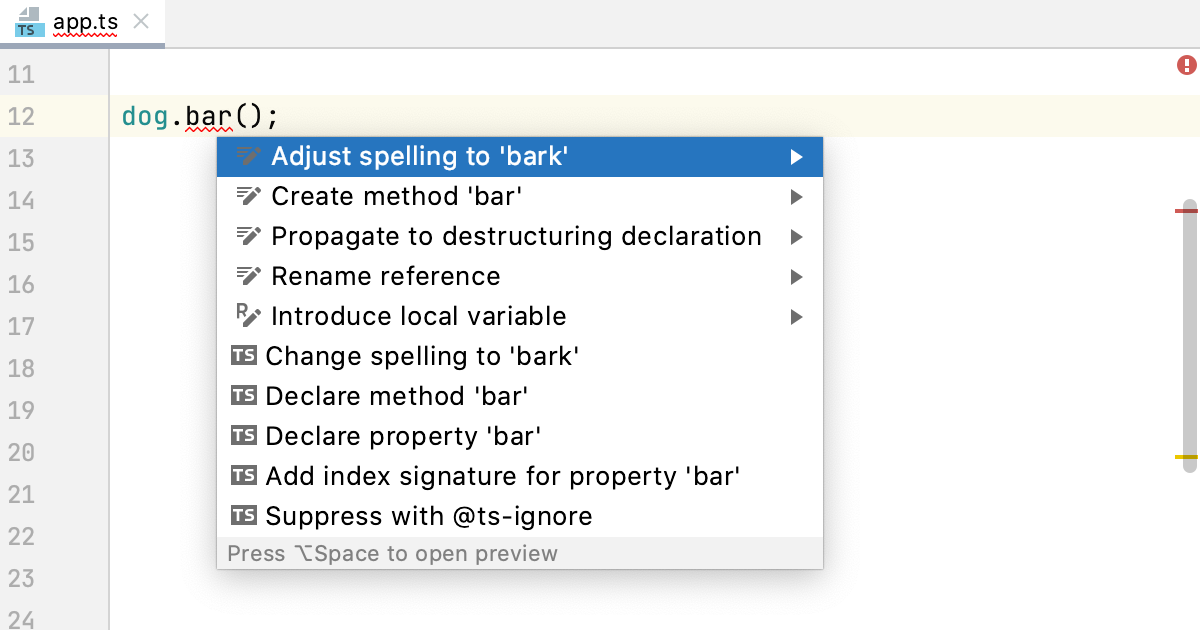
Alternatively open the File tab of the Problems tool window Alt+6, where you can view problem descriptions, apply quick-fixes, navigate to the fragments in the source code where errors occurred, as well as fix them in the Editor Preview pane without leaving the tool window. Learn more from Problems tool window.
Verify TypeScript in the entire project
To open the Problems tool window, click the Inspections widget in the upper-right corner of the editor.

Alternatively select from the main menu or press Alt+6.
Open the Project Errors tab, which shows the errors across the entire project, with error messages grouped by files in which they were detected.
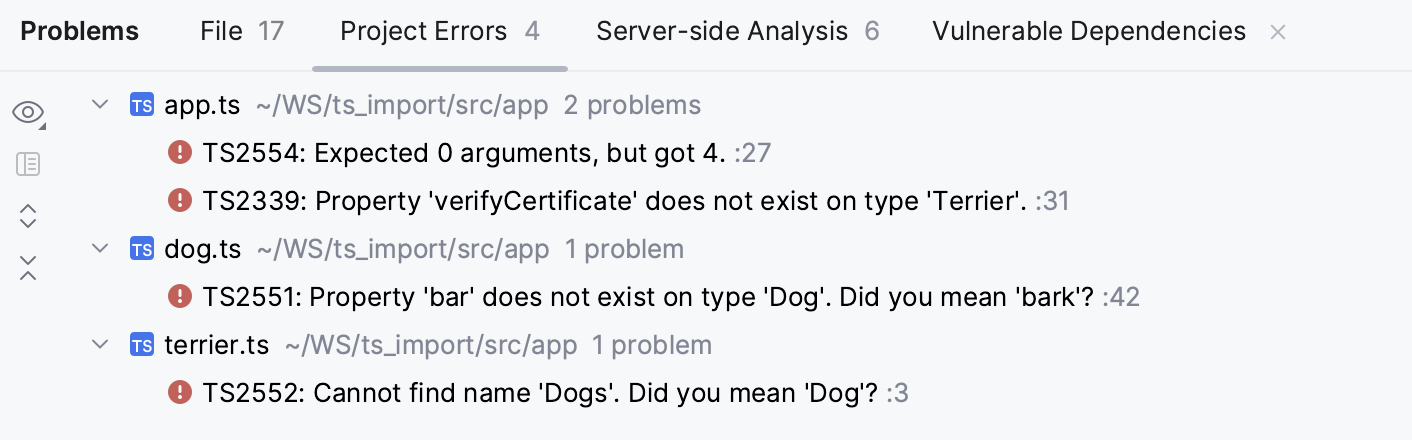
Here you can view problem descriptions, apply quick-fixes, navigate to the fragments in the source code where errors occurred, as well as fix them in the Editor Preview pane without leaving the tool window. Learn more from Problems tool window.
Configure integration with the TypeScript Language Service
In most cases, everything works out of the box and no manual configuration is required. However, if you want to use a custom typescript package or pass some command-line options to the TypeScript Language Service, you can customize the default settings.
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to .
Alternatively, click the TypeScript widget on the Status bar and select Configure TypeScript….
The TypeScript page opens.
Specify the Node.js interpreter to use.
If you choose the Project alias, PyCharm will automatically use the project default interpreter from the Node interpreter field on the Node.js page . In most cases, PyCharm detects the project default interpreter and fills in the field itself.
You can also choose another configured local or remote interpreter or click
and configure a new one.
In the TypeScript field, specify the version of the TypeScript to use (PyCharm displays the currently chosen version).
By default, the
typescriptpackage from the project's node_modules folder is used.Bundled: choose this option to use the
typescriptpackage that is shipped with PyCharm without attempting to find another one.Select: choose this option to use a custom
typescriptpackage instead of the one bundled with PyCharm. In the dialog that opens, choose the path to the relevant package.If your project package manager is Yarn 2, you have to use the
typescriptpackage installed via Yarn 2. In this case,yarn:package.json:typescriptis by default selected.Learn more about package managers from npm and Yarn.
Make sure the TypeScript Language Service checkbox is selected.
Use the controls below to configure the behaviour of the TypeScript Language Service.
In the Options field, specify the command-line options to be passed to the TypeScript Language Service when the tsconfig.json file is not found. See the list of acceptable options at TSC arguments. Note that the
-wor--watch(Watch input files) option is irrelevant.
Restart the TypeScript Language Service
Click the TypeScript widget on the Status bar and select Restart TypeScript Service from the list.
Localize error messages
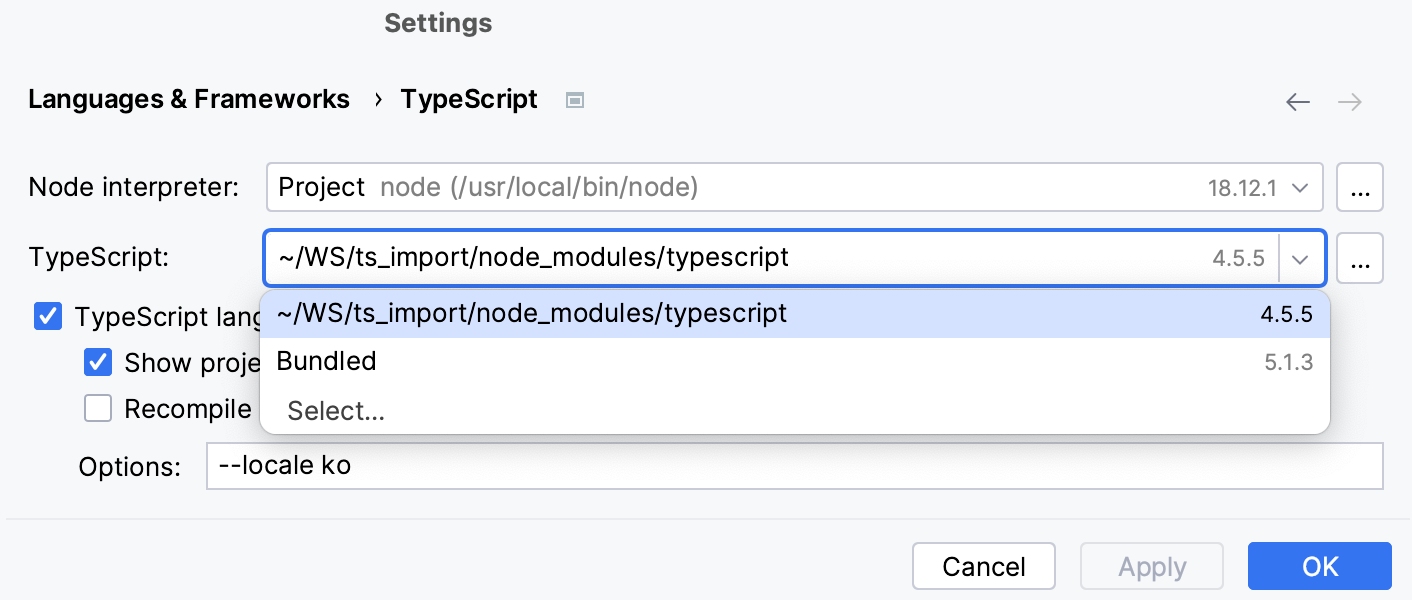
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to .
In the TypeScript field, specify a
typescriptpackage different from Bundled. This may be thetypescriptpackage from your projectnode_modulesfolder or from any other location.In the Options field, type
--locale <abbreviation of the language to use>. Currently, Korean (ko) and Japanese (ja) are supported.
Edit TypeScript code
PyCharm brings you smart coding assistance for TypeScript including context-aware code completion, auto-import for symbols, documentation look-up, parameter hints, navigation, TypeScript-aware syntax highlighting and linting, refactoring and more.
Auto import
PyCharm can generate import statements for modules, classes, components, and any other TypeScript symbols that are exported. By default, PyCharm adds import statements when you complete TypeScript symbols.
See Auto import to learn how to optimize import statements and configure their style.
When you type your code or paste a fragment with a symbol that is not yet imported, PyCharm can also generate an import statement for this symbol. If there is only one source to import the symbol from, PyCharm inserts an import statement silently. Otherwise, use an auto-import tooltip or a dedicated import quick-fix.
Add import statements on code completion
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to . The Auto Import page opens.
In the TypeScript/JavaScript area, make sure the Add TypeScript imports automatically and On code completion checkboxes are selected.
Add import statements on typing or pasting code
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to . The Auto Import page opens.
In the TypeScript/JavaScript area, make sure the Add TypeScript imports automatically and Unambiguous imports on the fly checkboxes are selected.
Use auto-import tooltips
If an import statement for a TypeScript symbol was not added on completion or editing, PyCharm shows you a popup that suggests importing the symbol. To accept the suggestion, press Alt+Enter:
If there's more than one possible source of import, PyCharm informs you about that:
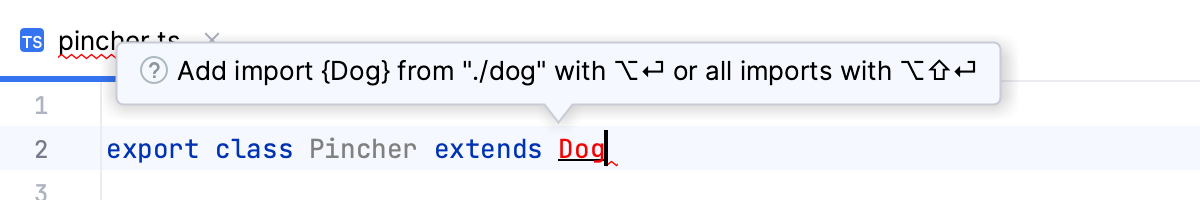
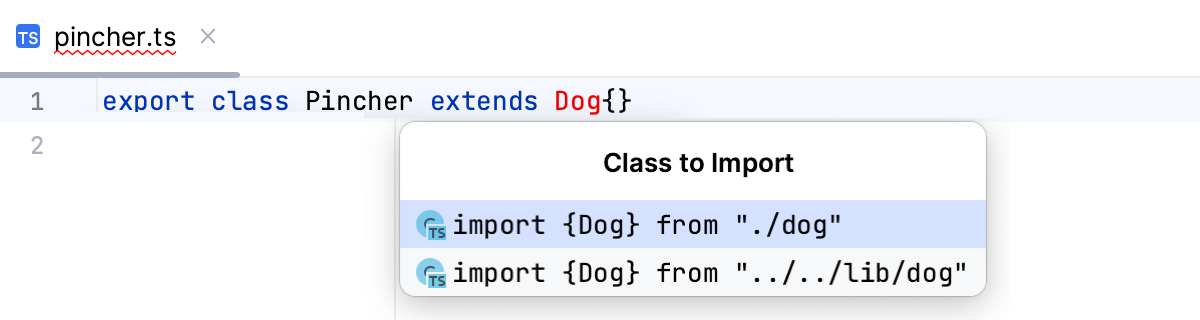
Pressing Alt+Enter in this case opens a list of suggestions:
To hide auto-import tooltips, open the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to , and clear the With auto-import tooltip checkbox.
Use import quick-fixes
If an auto-import tooltip doesn't show up, you can always press Alt+Enter and add an import statement via a quick-fix.
To generate an import, select Insert import from:
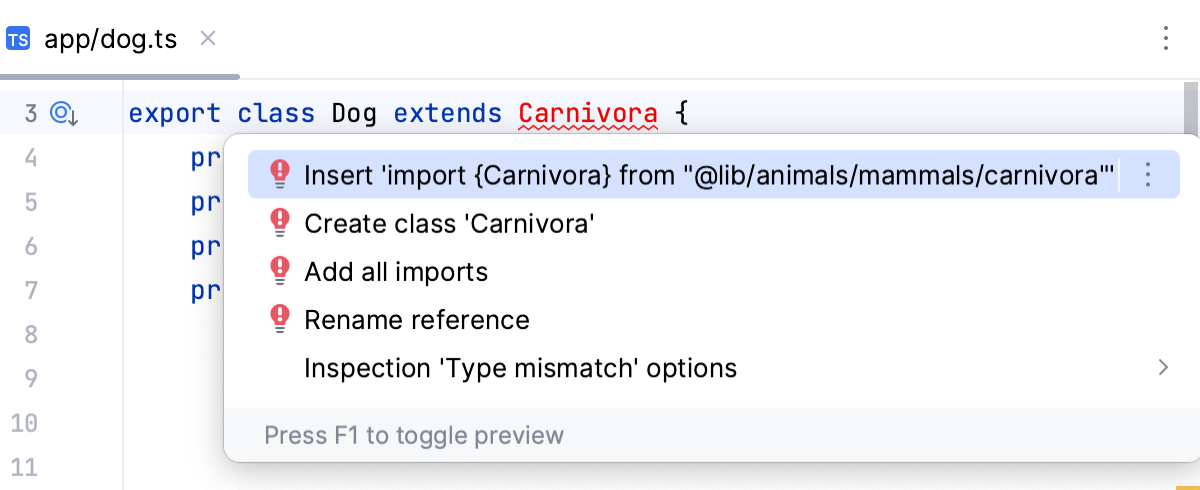
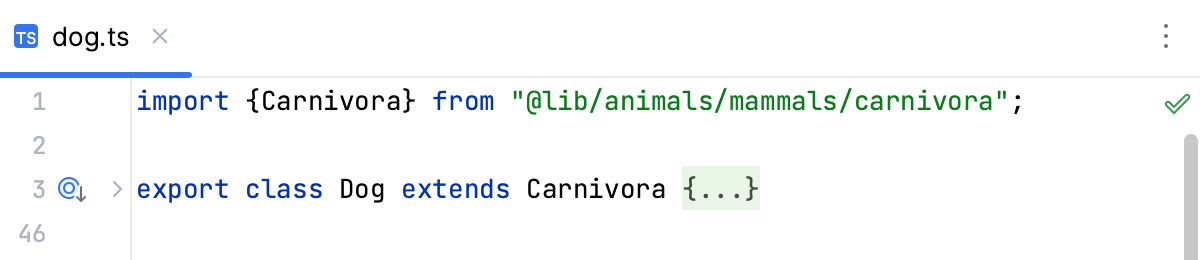
If there is only one source to import a symbol from, PyCharm generates an import statement:
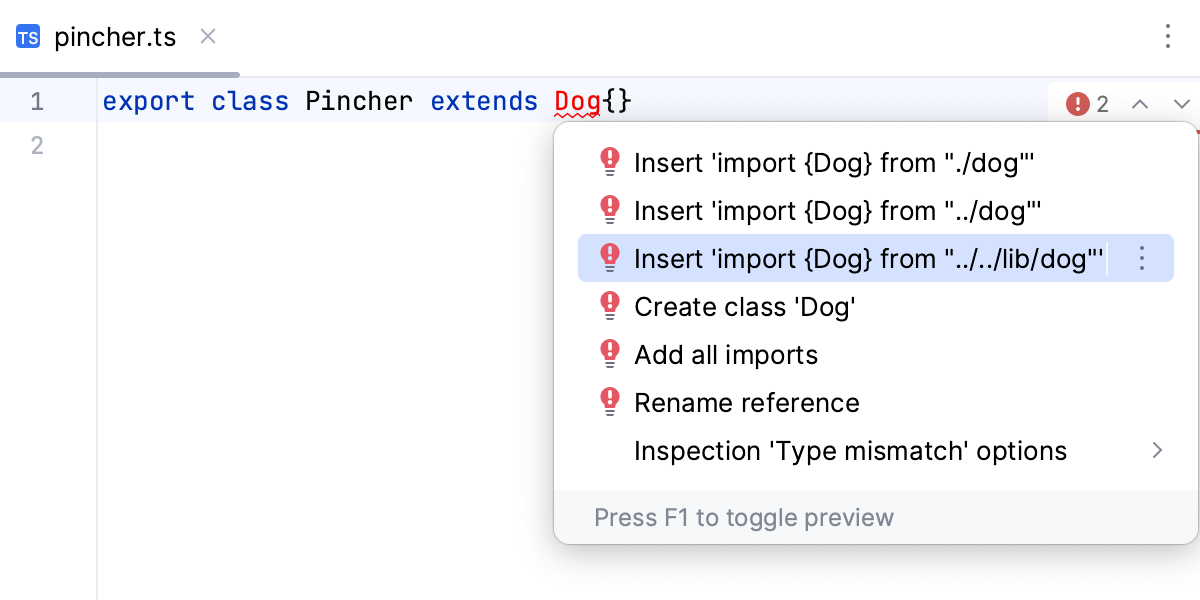
If there are several sources to import a symbol from, select the relevant one from the suggestion list:
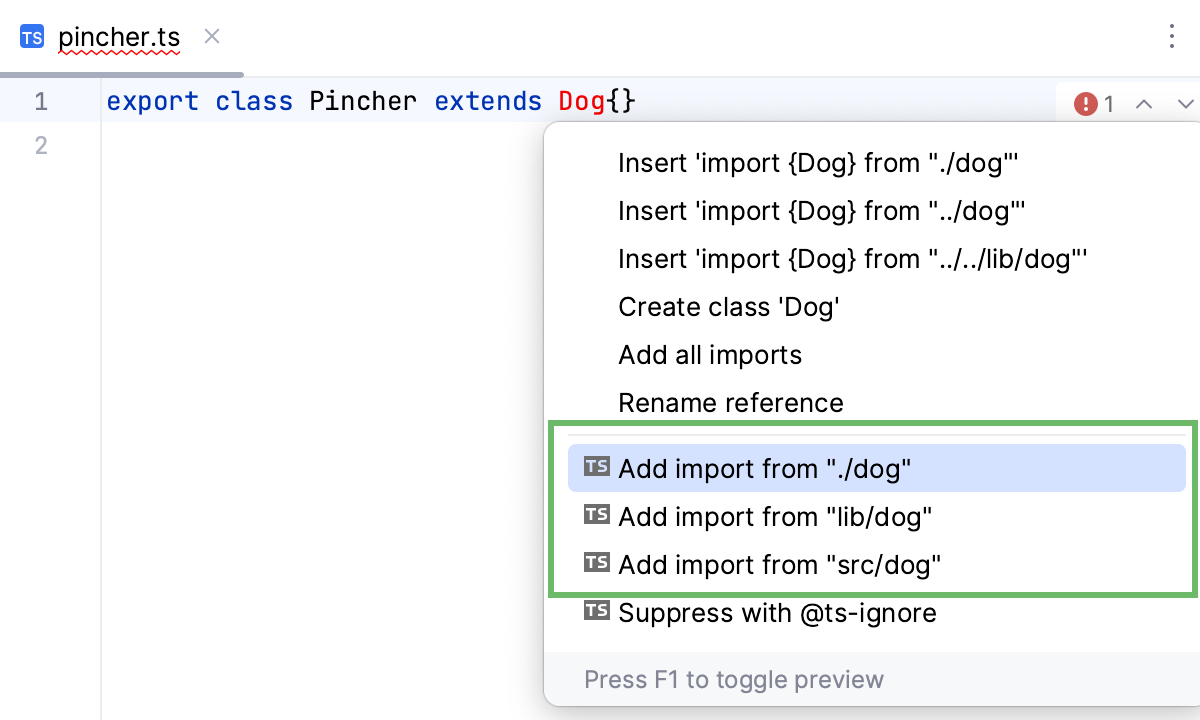
If the TypeScript Language Service is enabled in your project, you can also use its suggestion:
Enable type auto imports
Open your tsconfig.json file and set the importsNotUsedAsValues flag in
compilerOptionstoerror:"importsNotUsedAsValues": "error",
Learn more from the typeScript official website.
Configure the appearance of import statements
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to , and use the controls in the Imports tab.
Documentation look-up
PyCharm lets you get reference for symbols from your project and from its dependencies, for symbols defined in external libraries, and for standard JavaScript APIs because TypeScript implements all of them.
By default, documentation is shown in the Documentation popup but you can configure it to appear in the Documentation tool window.
Quick Documentation in a popup
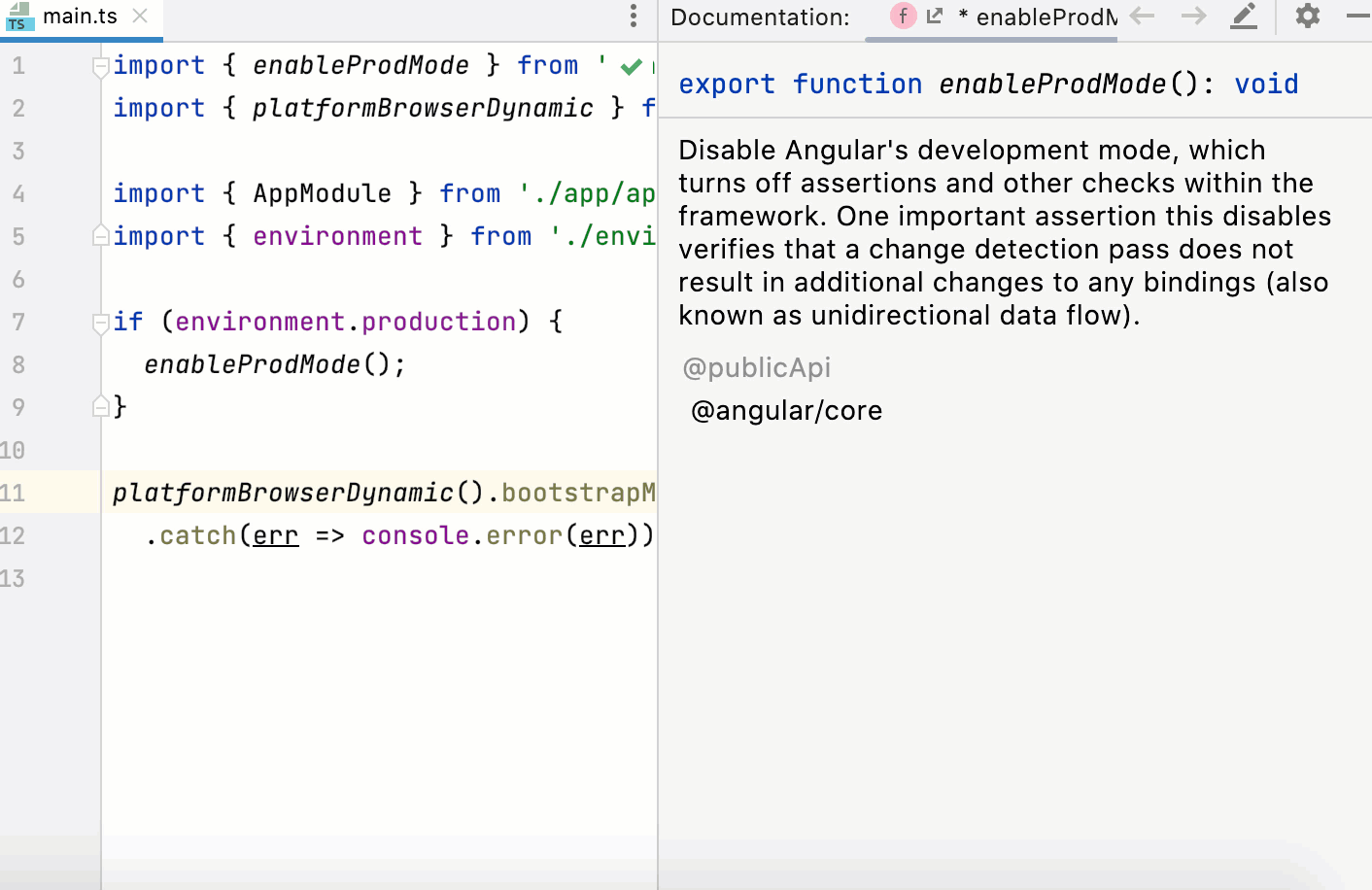
Hover over the necessary symbol in the editor.
Place the caret at the symbol and press Control+Q or select from the main menu.
For standard JavaScript methods available in TypeScript, PyCharm also shows a link to the corresponding MDN article.
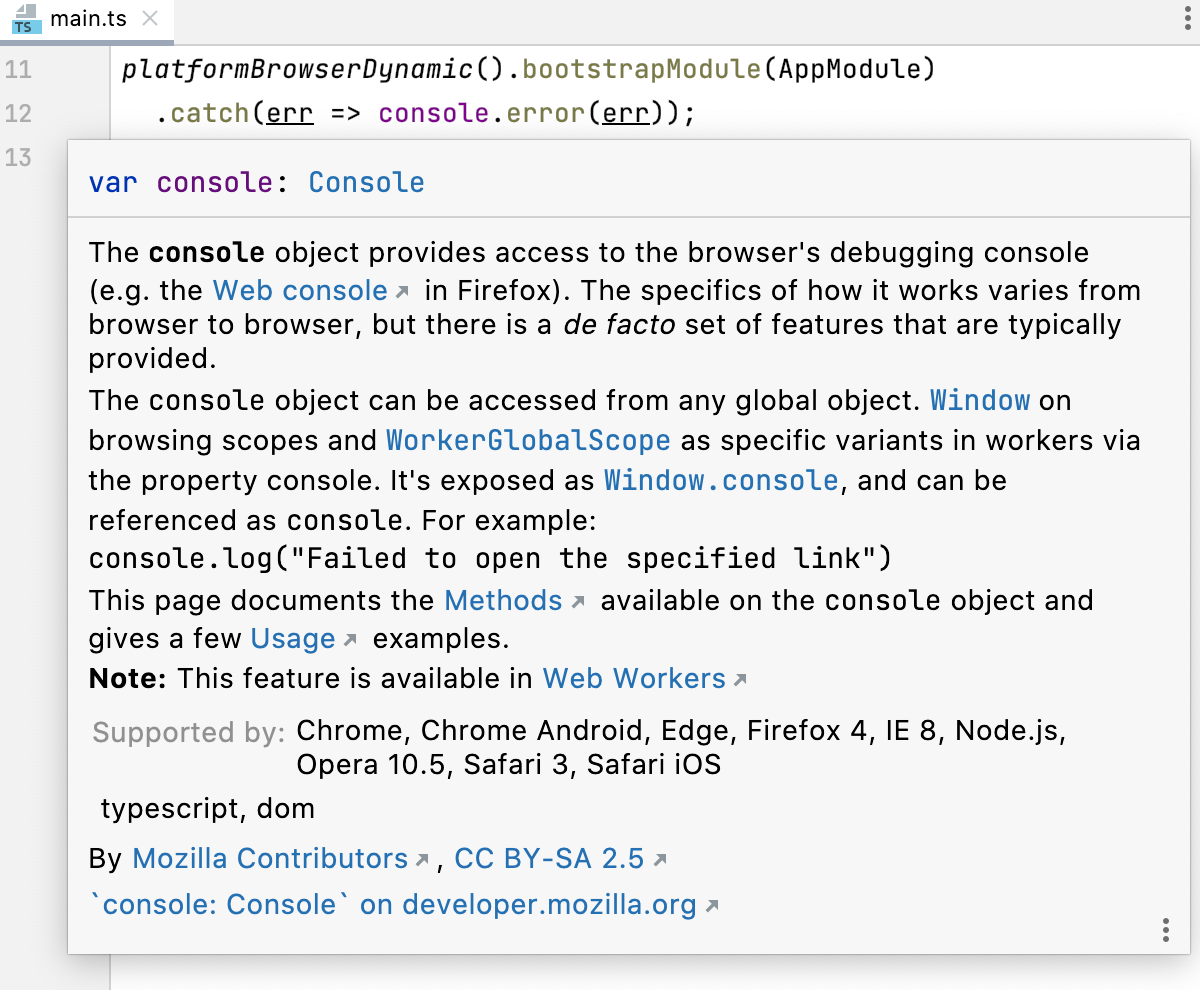
Press Control+Q again to open this documentation in the Documentation tool window.
Click
in the popup to change the font size, display the quick documentation toolbar, or go to the source code.
Click in the popup to change the font size, display the quick documentation toolbar, or go to the source code. For more information, refer to Quick Documentation in a popup.
Quick Documentation in the tool window
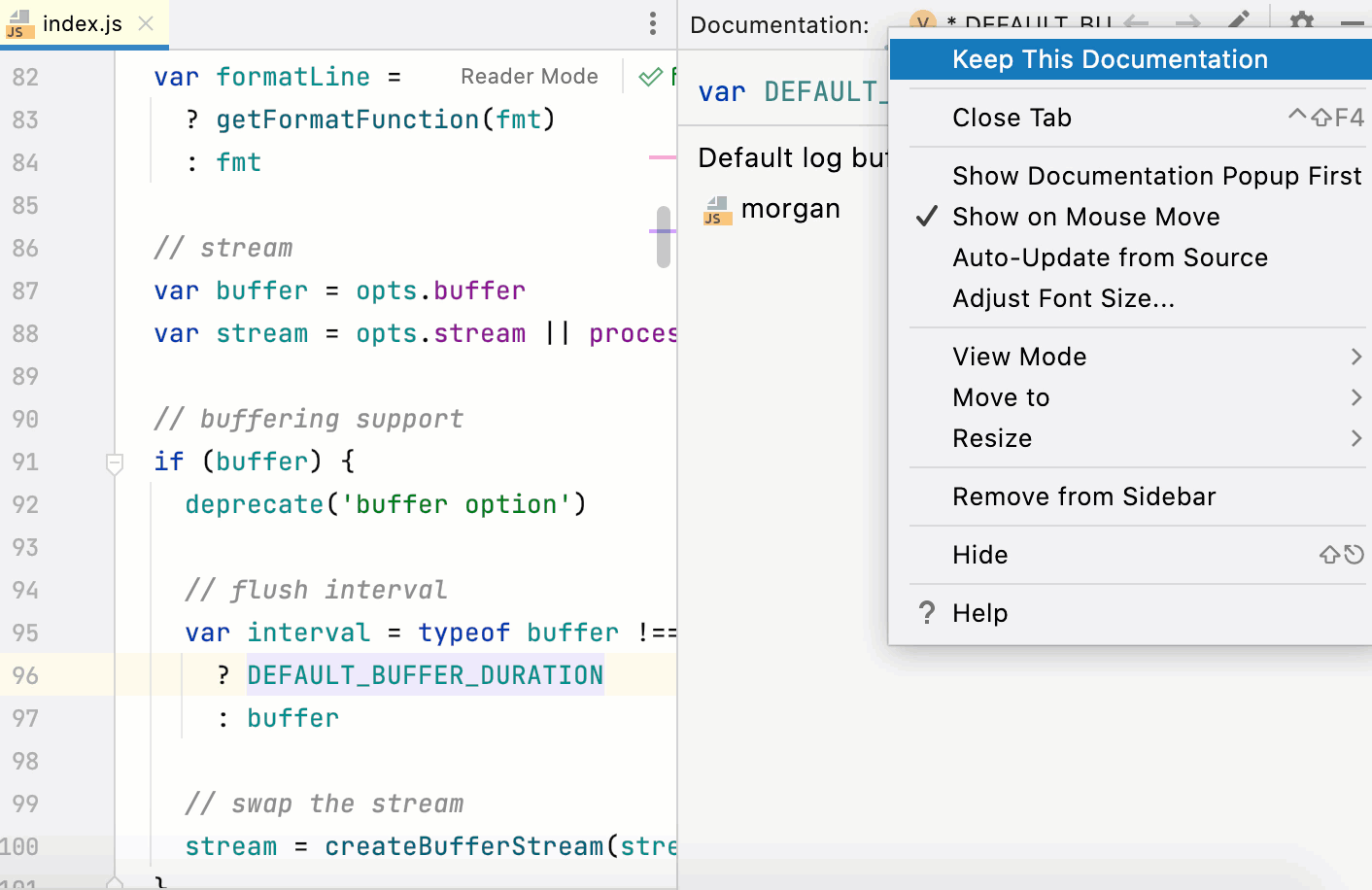
With the default settings, pressing Control+Q () opens quick documentation in a popup. You can change the settings to view documentation in the tool window.
In the quick documentation popup, click
and disable the Show Documentation Popup First option.
In the Documentation tool window, click the
icon on the tool window toolbar and disable the Show Documentation Popup First option.
You can open a piece of documentation for a specific code element in the tool window and keep viewing documentation for other elements in your current file as described in Keep documentation in the tool window.
In the tool window, code documentation is displayed on the unpinned tab (the tab marked with the asterisk symbol (*). You can view this documentation by hovering over a symbol or placing the caret at it.
View the MDN documentation for a symbol at caret
In the Documentation window Control+Q, click the MDN link.
Alternatively, press Shift+F1 or choose from the main menu.
PyCharm opens the MDN article in the default PyCharm browser.
View inlay hints
Inlay hints appear in the editor and provide you with additional information about your code to make it easier to read and navigate.
Parameter hints
Parameter hints show the names of parameters in methods and functions to make your code easier to read. By default, parameter hints are shown only for values that are literals or function expressions but not for named objects.
Configure parameter hints
Open the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S) and go to .
Expand TypeScript under Parameter names.
Specify the context in which you want parameter hints shown by selecting the corresponding checkboxes.
The preview shows how the changes you make in the settings affect the code appearance.
For some methods and functions, PyCharm does not show parameter hints in any context. Click Exclude list... to view these methods and functions, possibly enable parameter hints for them, or add new items to the list.
To hide parameter hints for any value type in any context, clear the TypeScript checkbox under Parameter names.
Return type hints
PyCharm can display function return types in function calls and call chains.
Function return type hints are inferred from a JSDoc comment or based on the static analysis of your code.
Return type hints in method chains are displayed if the method calls are split between multiple lines and return at least 2 different types.
Configure function return type hints
Open the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S) and go to .
Under Types, expand the TypeScript node, and then select the Function return types checkbox.
To show return type hints in method chains, expand the Method chains node and select the TypeScript checkbox.
The preview shows how the changes you make in the settings affect the code appearance.
Type hints
Type hints show the types of variables, fields, or parameters. The types of variables and fields are displayed next to their definition. Type hints for parameters are shown in function calls. Type hints are inferred from JSDoc comments or static analysis of your code.
Configure type hints
Open the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S) and go to .
Expand .
Expand the Type annotations node and specify the context where you want type hints to be shown.
The preview shows how the changes you make in the settings affect the code appearance.
To hide parameter type and return type hints for any value type in any context, clear the TypeScript checkbox under Types.
Numeric enum values
By default, PyCharm shows inferred values for numeric enums to make your code easier to read.
Hide numeric enum values
Open the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S) and go to .
Expand the Values node and select the TypeScript checkbox. PyCharm will hide the inferred values and show only the values of explicitly initialized constants. The preview shows how the changes you make in the settings affect the code appearance.
JavaScript libraries in TypeScript
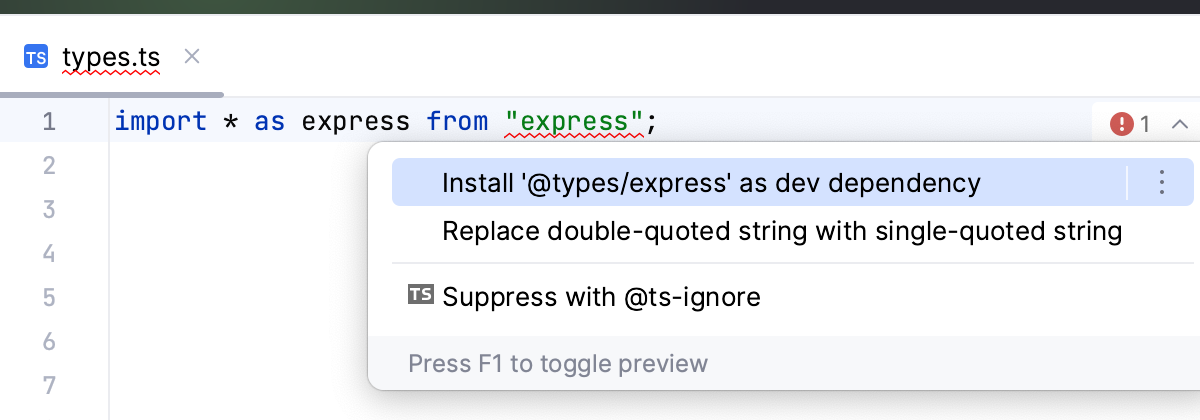
When working with JavaScript libraries in TypeScript, you need to install type declarations for them. PyCharm reminds you to install them via npm or yarn and updates your package.json file accordingly.
Install the type declarations
Place the caret at the warning and press Alt+Enter.
Select the suggestion and press Enter.
Syntax highlighting
You can configure TypeScript-aware syntax highlighting according to your preferences and habits.
In the Settings dialog (Control+Alt+S), go to .
Select the color scheme, accept the highlighting settings inherited from the defaults or customize them as described in Colors and fonts.
Code navigation
You can quickly navigate through your TypeScript project in the PyCharm editor using different actions and popups.
Go to declaration of a symbol
You can navigate from a variable, a field, a method, or any other symbol to its declaration or view the symbol definition in a popup without jumping anywhere from the code you are editing.
To jump to the declaration of a symbol, place the caret at a usage of the symbol and press Control+B or select from the main menu.
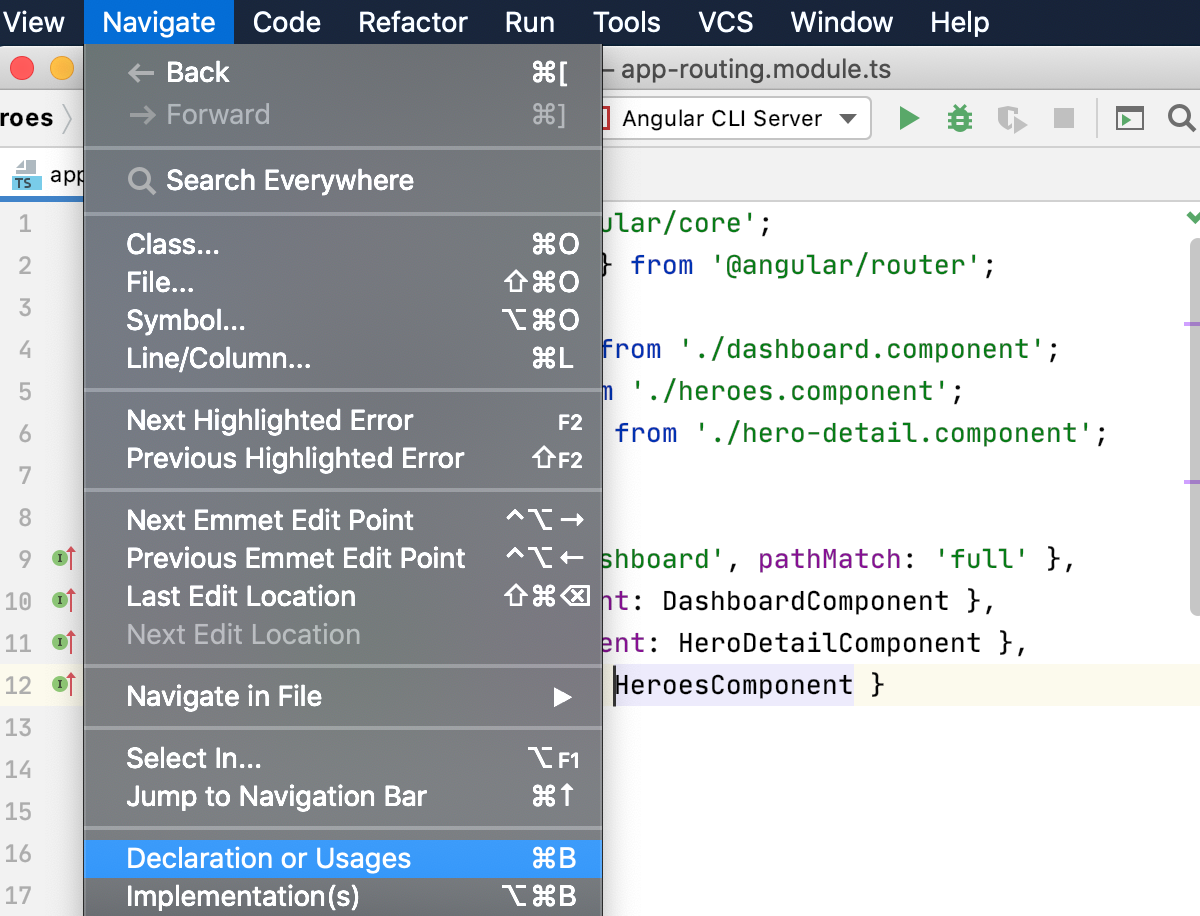
Alternatively, use Control+LeftClick: keeping Control pressed, hover over the symbol. When the symbol turns into a hyperlink, click the hyperlink without releasing Control.
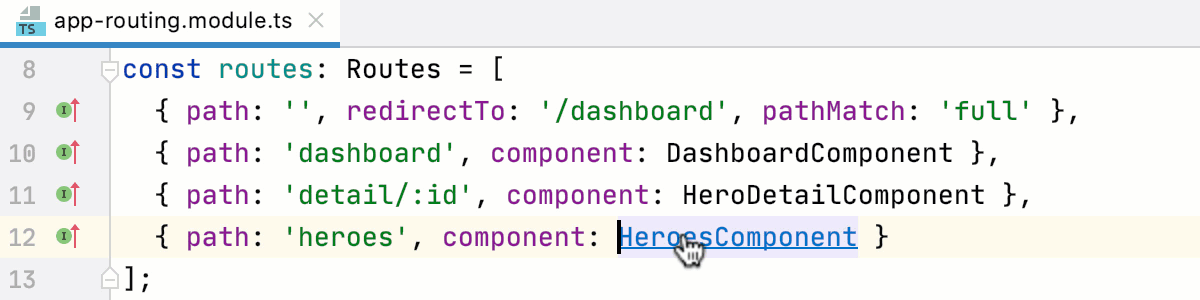
Go to usages of a symbol
You can view a list of usages of a symbol and select the one to jump to.
To get a list of usages of a symbol, place the caret at the declaration of the symbol and do one of the following:
Press Control+B or select from the main menu.
Press Control+Alt+F7 or select from the main menu.
From the list, select the usage of the symbol where you want to jump.
Go to type declaration of a symbol
You can navigate from a variable, a field, a method, or any other symbol to its type declaration. Alternatively, open the type definition in a popup without jumping to the type declaration.
PyCharm also shows the inferred type of an object. You can view the inferred type information in a tooltip or in the documentation popup.
Jump to type declaration
To jump from a symbol to the declaration of its type, place the caret at a usage of the symbol and press Control+Shift+B or select from the main menu.
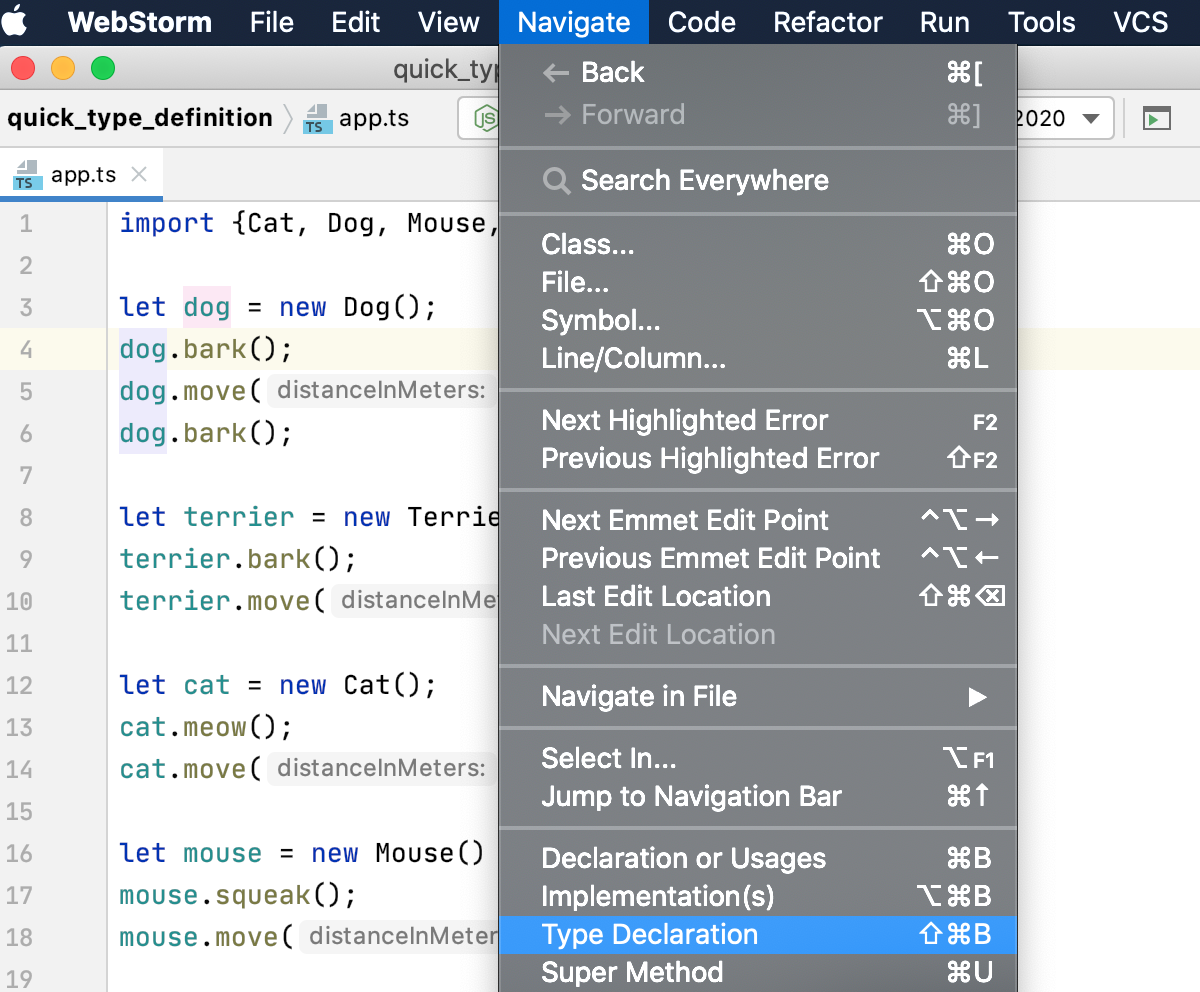
To view the type definition of a symbol in a popup, place the caret at the symbol for which you want to view the type definition and select .
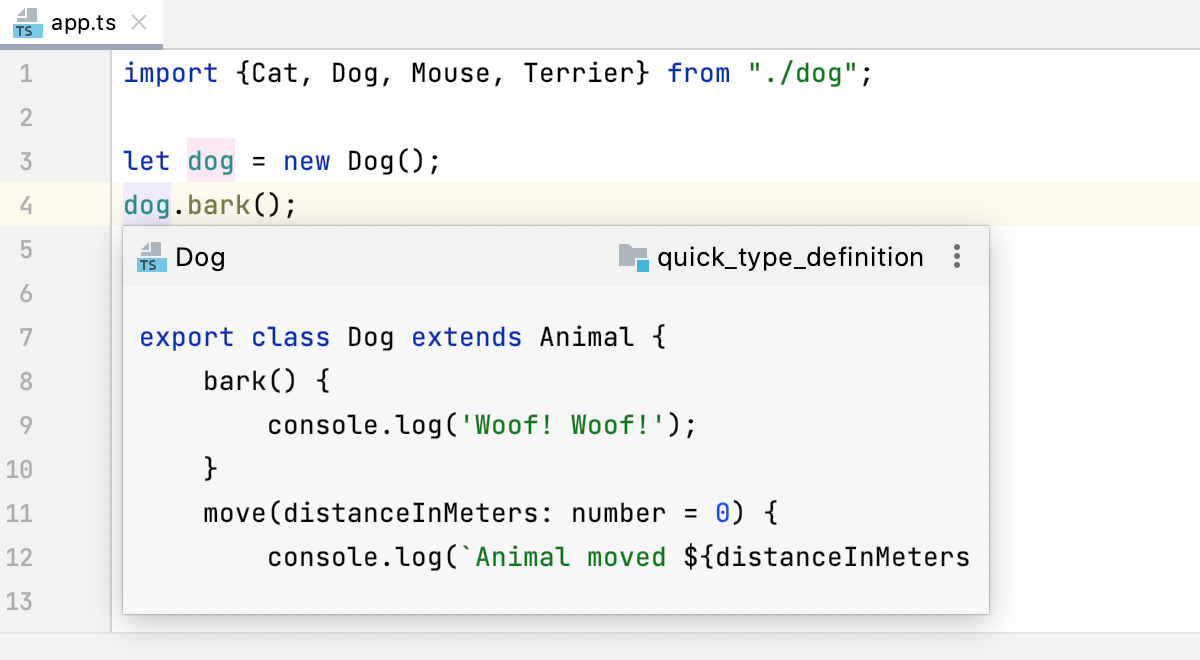
For an instance of a class, this will reveal the class itself instead of where this instance is defined.
View inferred type information of a symbol
Hold Control and hover over the symbol.
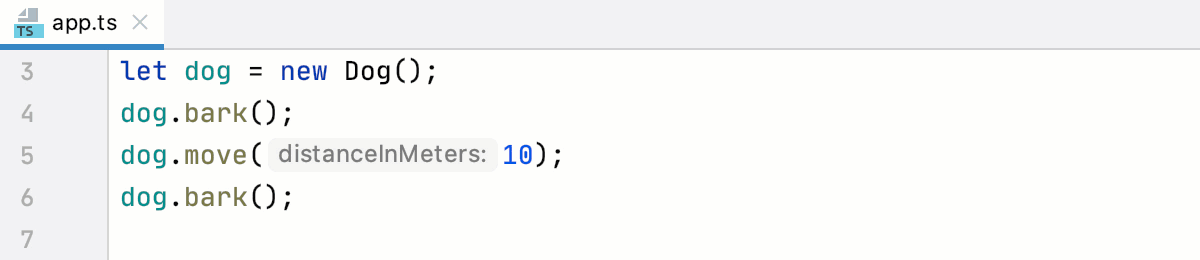
Alternatively, hover over a symbol. PyCharm immediately displays the reference for it in the Documentation popup.
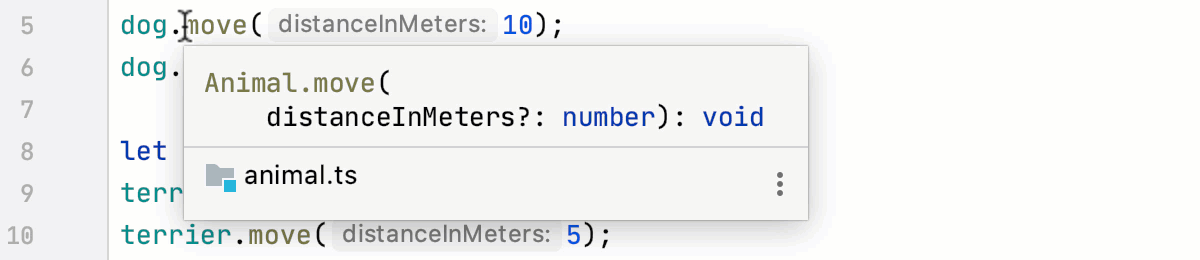
Learn more from Documentation look-up above.
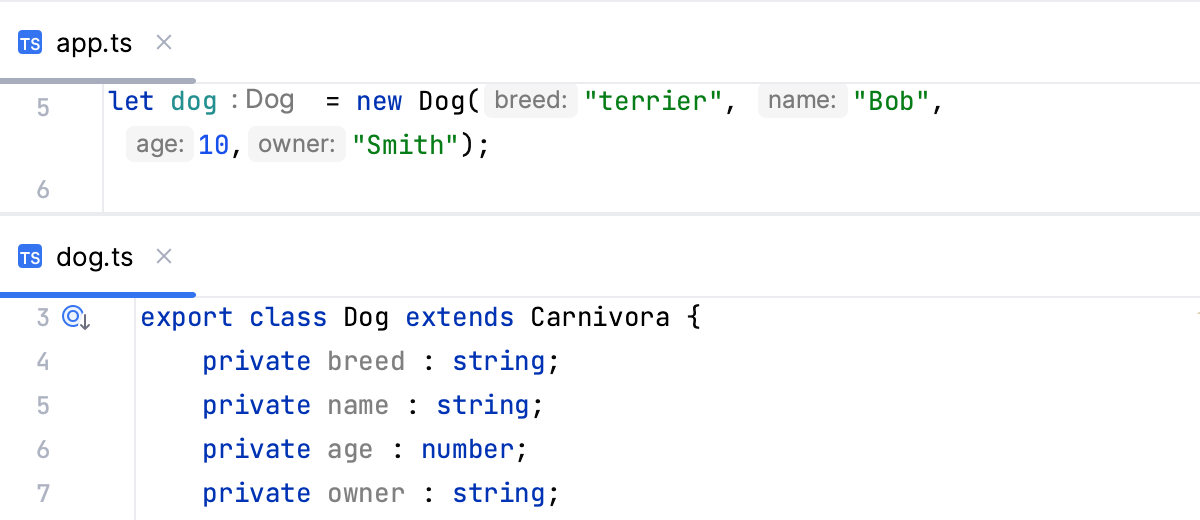
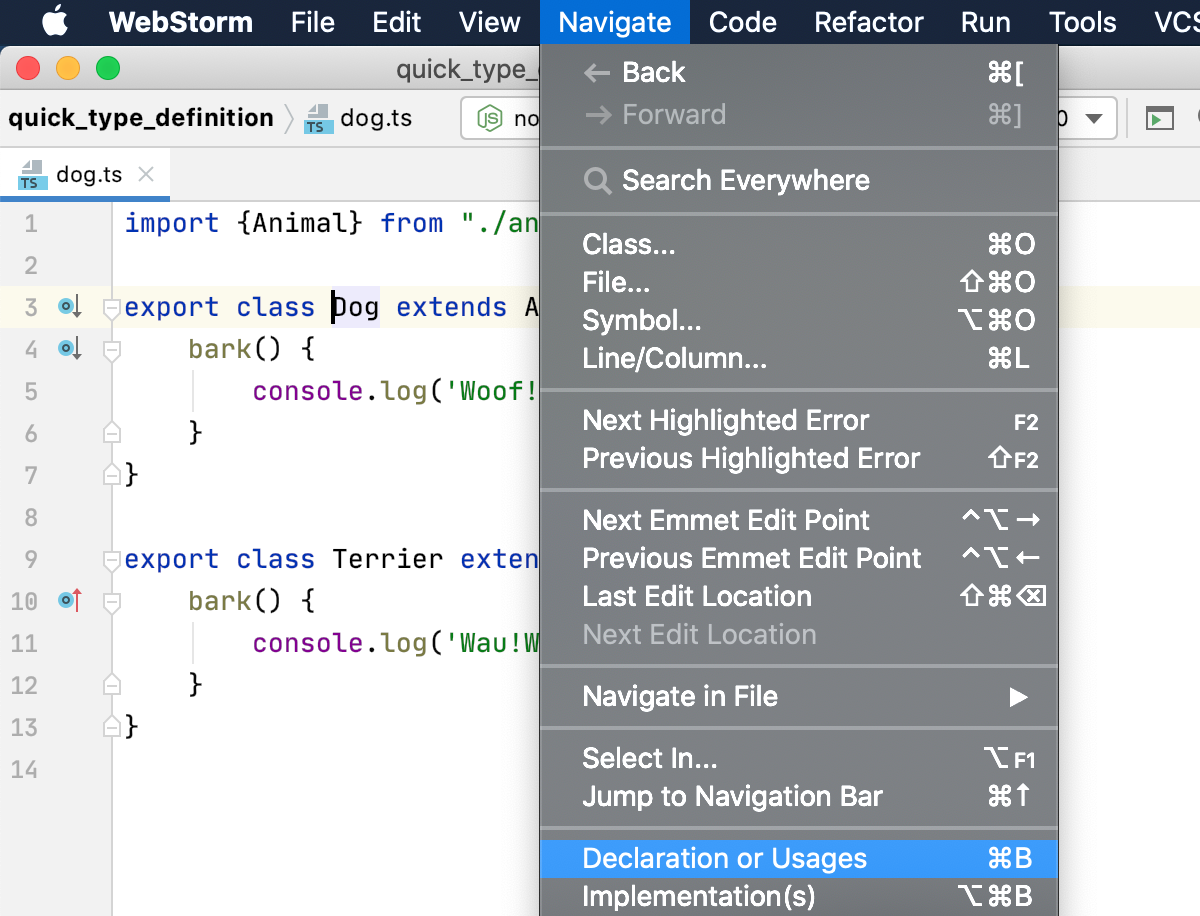
Note the difference between and . Suppose you have a file app.ts with the following code:
dog in dog.bark(), then brings you to the declaration of the variable in let dog = new Dog (), while brings you to the declaration of the class Dog.Navigate between subclasses, superclasses, overrides, and implementations
You can keep track of class implementations and overriding methods either using the gutter icons in the editor or pressing the appropriate shortcuts.
Go to a subclass
Press Control+Alt+B or click
in the gutter and then select the relevant class from the list.
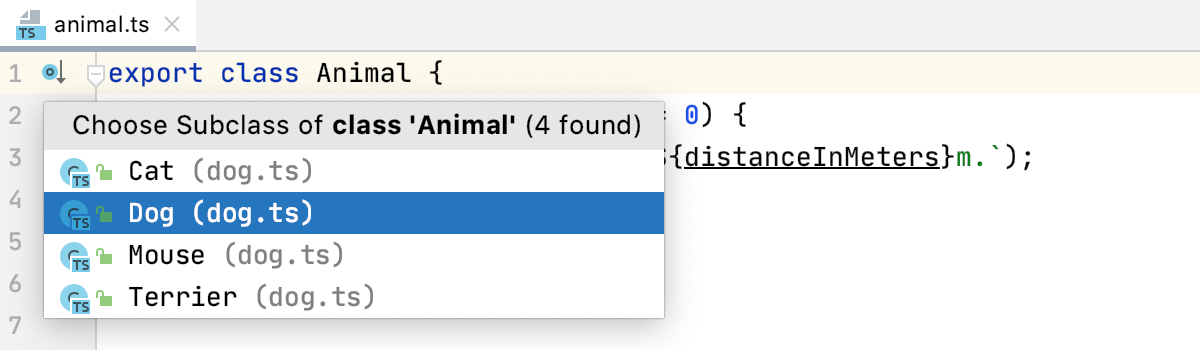
Alternatively, select from the main menu or from the context menu and then select the relevant class from the list.
Go to a superclass or overridden method
Place the caret at a subclass and press Control+U. PyCharm brings you to the declaration of the superclass and places the caret at its name.
Click
in the gutter next to an overriding method. PyCharm brings you to the superclass with the caret at the overridden method.
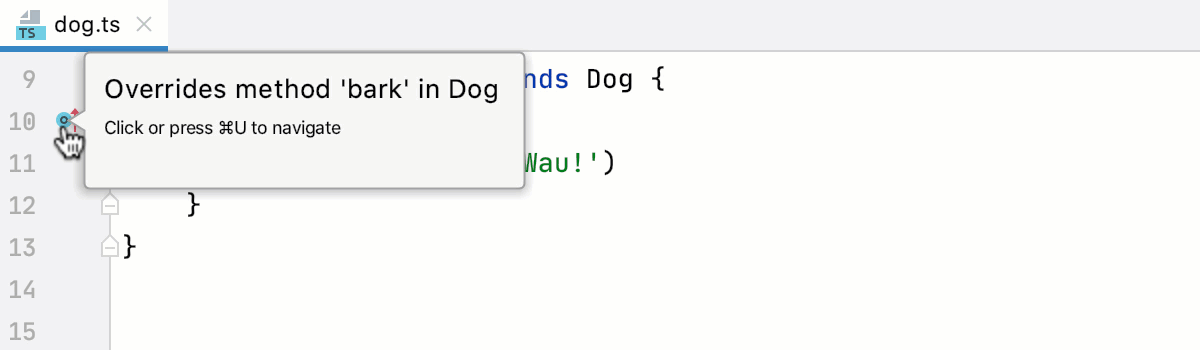
Alternatively, place the caret at the overriding method and press Control+U or select from the main menu or from the context menu.
Go to an interface or implemented method
Place the caret at an implementation of an interface, press Control+U, and select the interface to go to.
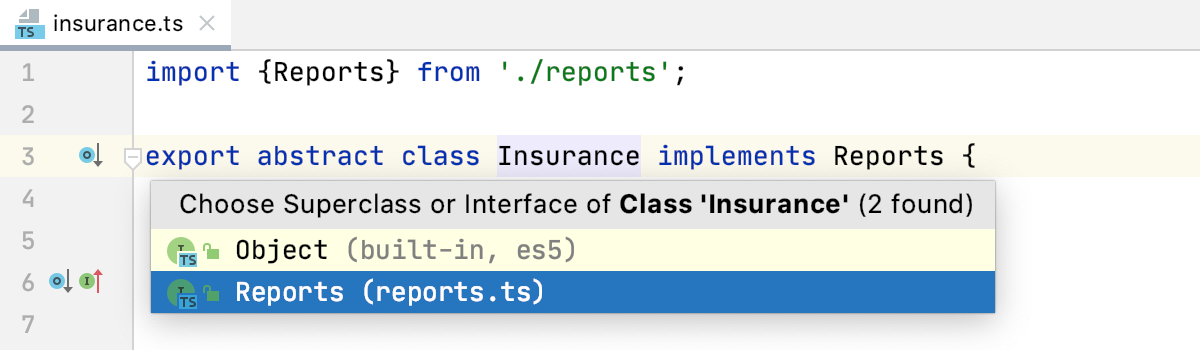
PyCharm brings you to the declaration of the interface and places the caret at its name.
Click
in the gutter next to the implementing method. PyCharm brings you to the corresponding interface with the caret at the implemented method.
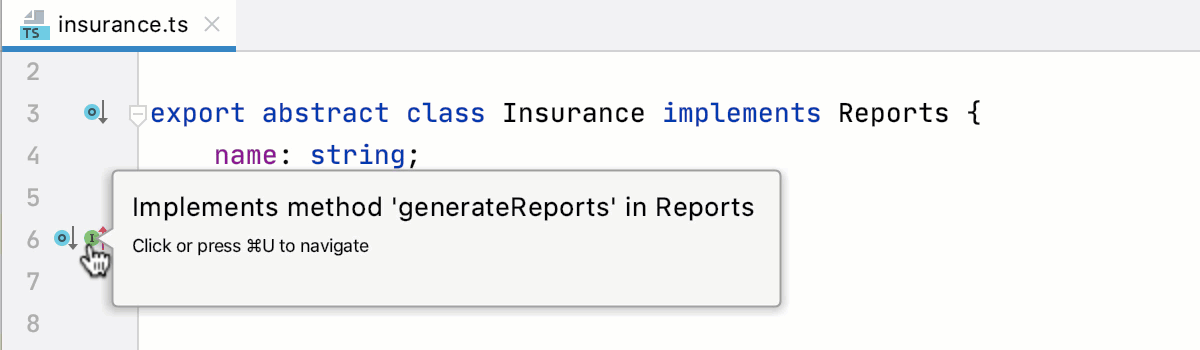
Alternatively, place the caret at the implementing method and press Control+U or select from the main menu or from the context menu.
Refactoring in TypeScript
PyCharm provides both common refactoring procedures, such as rename/move, and so on, and TypeScript-specific refactoring procedures, such as change signature, introduce parameter, introduce variable. For more information, refer to Rename refactorings and Copy and Move Refactorings.
Run and debug your application
With PyCharm, you can run and debug client-side TypeScript code and TypeScript code running in Node.js. Learn more from Running and debugging TypeScript.