Populate projects
Populate your project by creating new elements of various types ( directories , packages and files). PyCharm suggests the following alternative ways of accessing the corresponding functionality:
from the main menu.
The context menu command.
The keyboard shortcut Alt+Insert.
As a result, the New menu is shown in which you select the type of an element to be created.
For generating PyCharm-specific elements, refer to Django support section.
Create new files
Do one of the following:
In the Project tool window (Alt+1), select the directory or package in which you want to create a new file, and then choose from the main menu.
Right-click the directory or package and select New from the context menu.
Select the directory and press Alt+Insert.
Select the desired file type. Generally, all the options except File, Package and Directory correspond to using a file template.

An existing file template may be missing from the list if this is a custom template whose filename extension (template extension) does not match the registered patterns of any of the recognized file types. In such a case, you may want to register the corresponding pattern for an existing recognized file type or add a new file type and register the corresponding pattern for this new type. For more information, refer to File type associations.
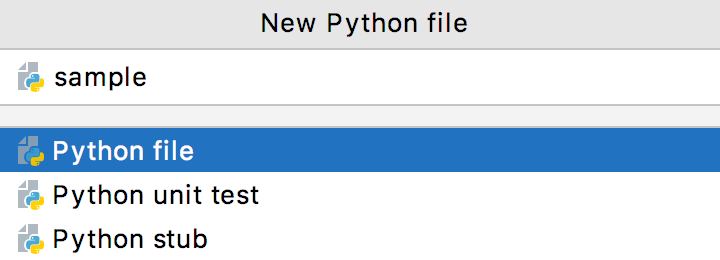
In the dialog that opens, type the name of the file in the corresponding field. Note that you should not type the filename extension.
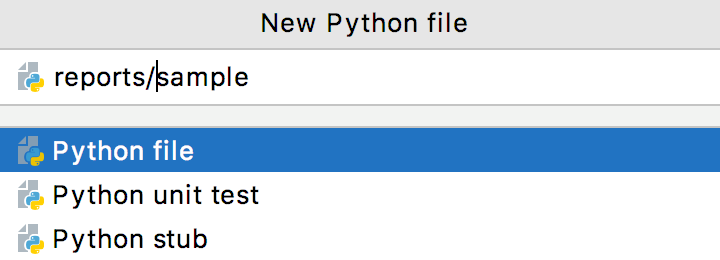
You can specify the whole directory structure prepending the new filename. If the nested directories do not yet exist, they will be created.
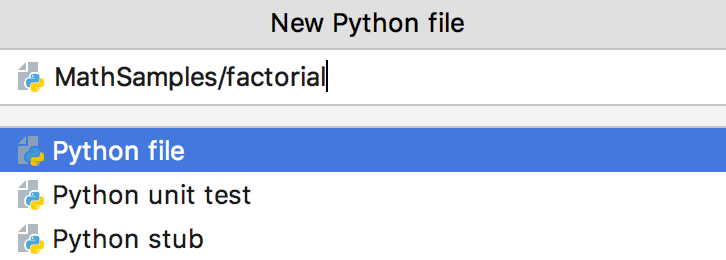
If required, specify the kind of the new template-based file, its extension, and other parameters. For example, if you select to create an HTML file, you'll be able to create HTML, HTML4, or XHTML file. In other words, use one of the corresponding related file templates.
Specify other information as required. For example, you may be asked to define the values of custom variables if the corresponding file template contains such variables and their values are not currently set.
Click OK. The new file that corresponds to the selected file template will be created under the target location.
If the names of non-existent sub-directories were specified before the new filename, the whole structure will be created under the target directory :
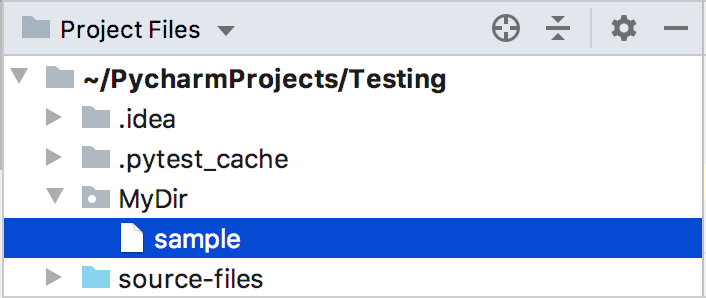
Sometimes, you may want to change the auto-generated filename extension. To do that, use the Rename refactoring ().
Create directories
Open the Project tool window (for example ).
Select the destination directory.
Do one of the following:
Select .
Select from the context menu.
Press Alt+Insert and select Directory.
In the dialog that opens, specify the directory name. If you want to create a number of nested directories, specify the directory names separated with slashes.
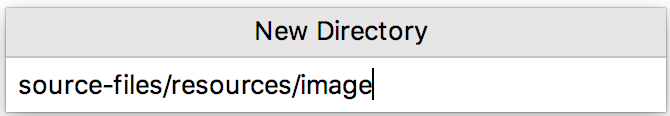
Press Enter to complete the task.
PyCharm makes it possible to create Python packages recursively, thus creating the whole package structure.
The Python package nodes are marked with the icon.
Create Python Packages
In the Project tool window, select the destination directory
.
From the context menu of the selection, choose , or press Alt+Insert to invoke the context menu:
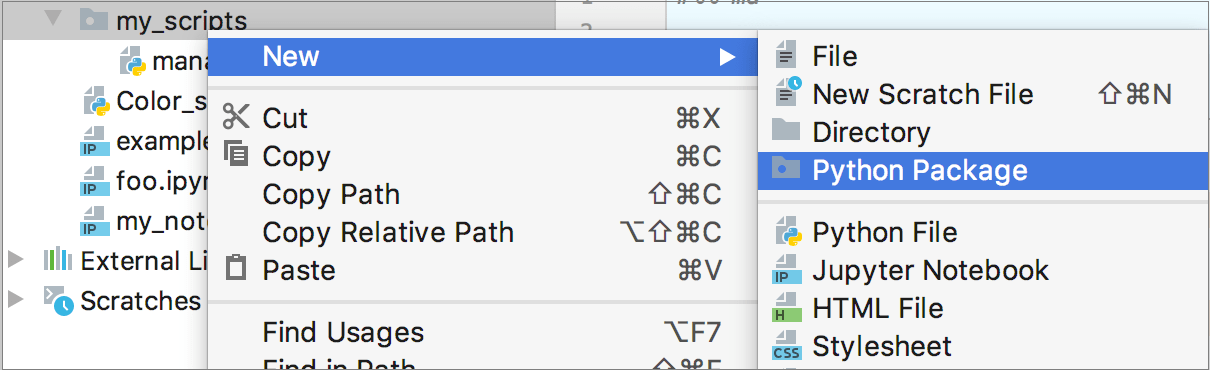
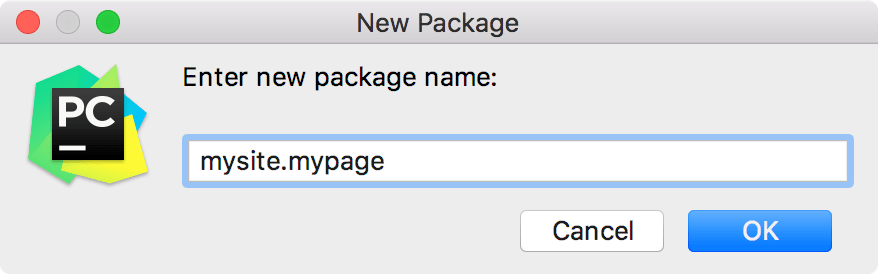
In the New Package dialog that opens, specify the package name.
You can also specify nested packages; in this case, the names should be delimited with dots:
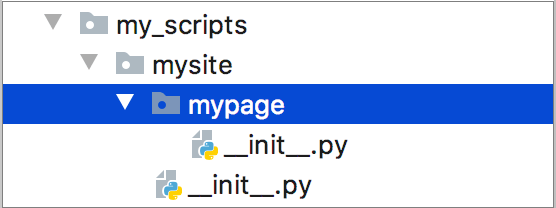
Click OK. PyCharm creates the new package or package structure:
Now that you created a package, you can do the following:
Import the package into the project files. Use code completion to discover it.
Commit and push the package into a VCS repository.
Install the package in a virtual environment locally or from VCS so that you can use it in your other projects with that environment.
If you want to ensure that imports from the same directory are resolved, mark that directory as a namespace package.
Mark a directory as a namespace package
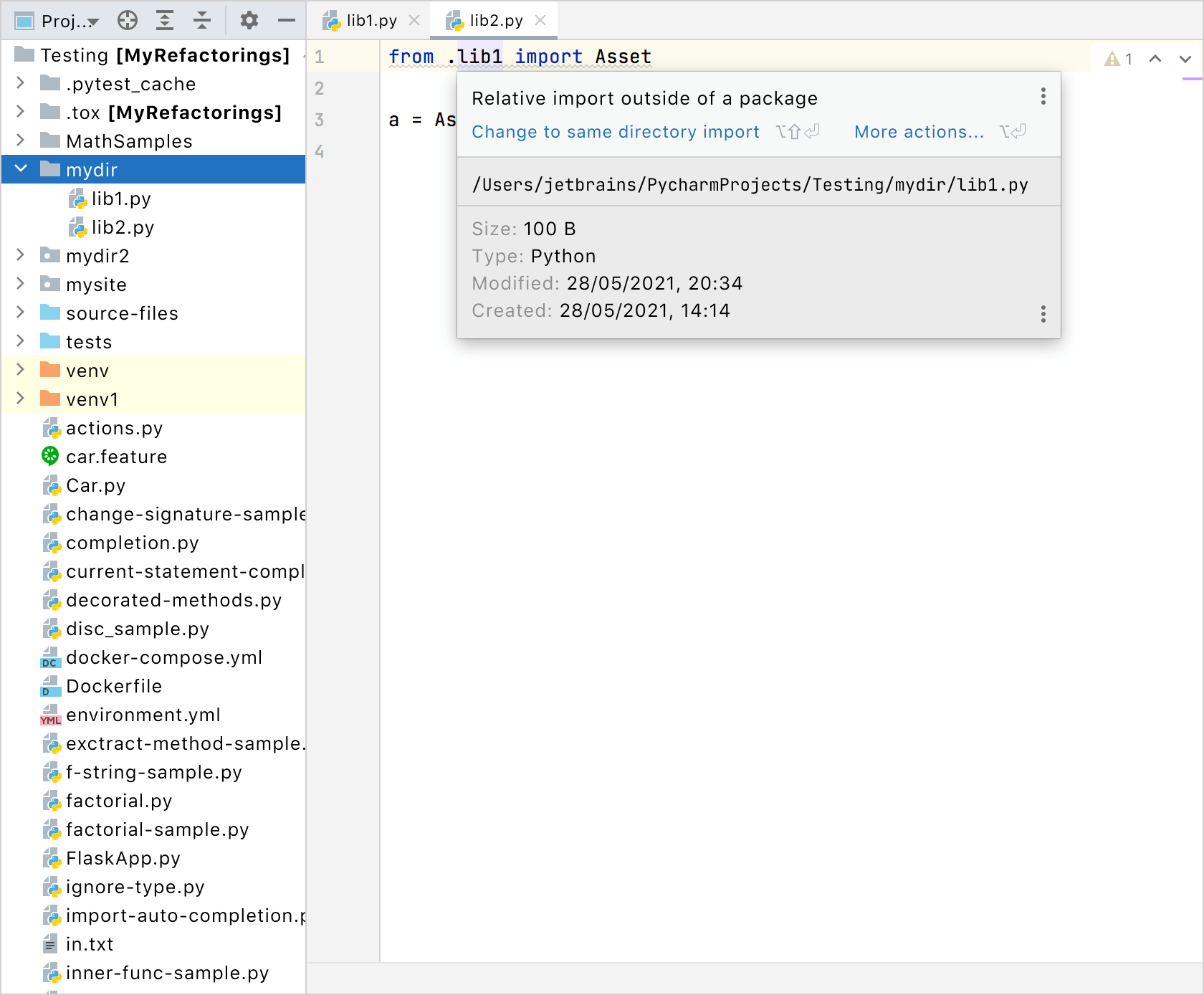
Consider two packages, lib1 and lib2 that reside in the same directory. Try to include a lib1 import statement into
lib2.py. PyCharm reports a relative import outside of the package.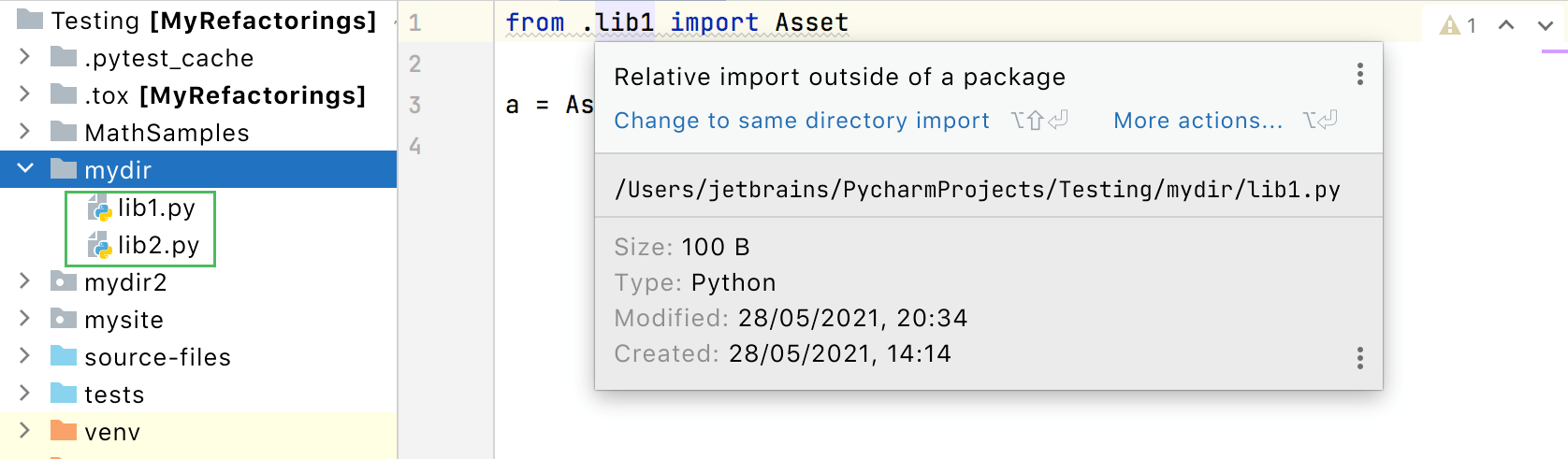
To resolve the import and avoid the warning, mark the mydir directory as a namespace package. You have the following options:
Place the caret at the import statement, press Alt+Enter (or click the yellow bulb), and apply the corresponding quick-fix.
Right-click the directory in the Project tool window and select .