Baseline
Baseline is a snapshot of the codebase problems taken at a specific Qodana run and contained in the qodana.sarif.json file.
Using the baseline feature, you can compare your current code with its baseline state and see new, unchanged, and resolved problems.
This feature is supported by all linters available under Community, Ultimate, and Ultimate Plus licenses and their trial versions.
How it works
If you run Qodana without a baseline, you will be able to see the problems detected at a current run.

In this case, you can only see the number of problems and their description, without classification to new and existing problems.
To improve the situation, you can add problems to a baseline and save them to the qodana.sarif.json file in your project directory as explained in the Baseline section of the Qodana report description. Once done, this file becomes a basis for comparing with subsequent code states. You can run Qodana with the baseline enabled using Qodana CLI, Docker images of Qodana, or JetBrains IDEs:
Here, the -v <path_to_baseline>:/data/base/ line mounts the directory containing the SARIF-formatted baseline file to the /data/base directory of the Qodana Docker image. The QODANA_TOKEN variable refers to the project token required by the Ultimate and Ultimate Plus linters.
In this snippet, the -v <path_to_baseline>:/data/base/ line mounts the directory containing the SARIF-formatted baseline file to the /data/base directory of the Qodana Docker image. The --baseline option specifies the path to the baseline file from the Docker filesystem. The QODANA_TOKEN variable refers to the project token required by the Ultimate and Ultimate Plus linters.
The list of the JetBrains IDEs containing this feature is available in the JetBrains IDEs section.
This animation shows how you can analyze your code using baseline.
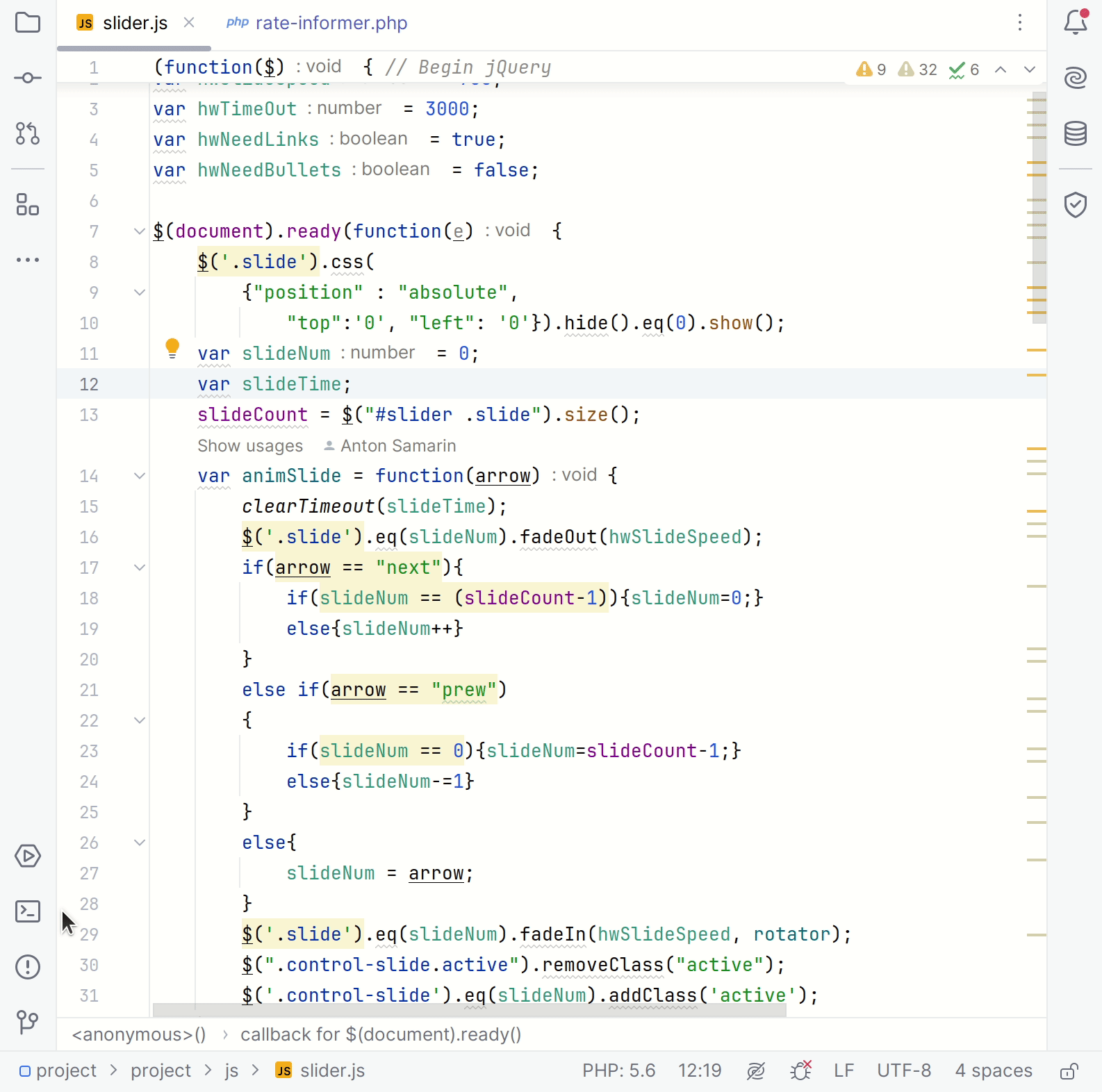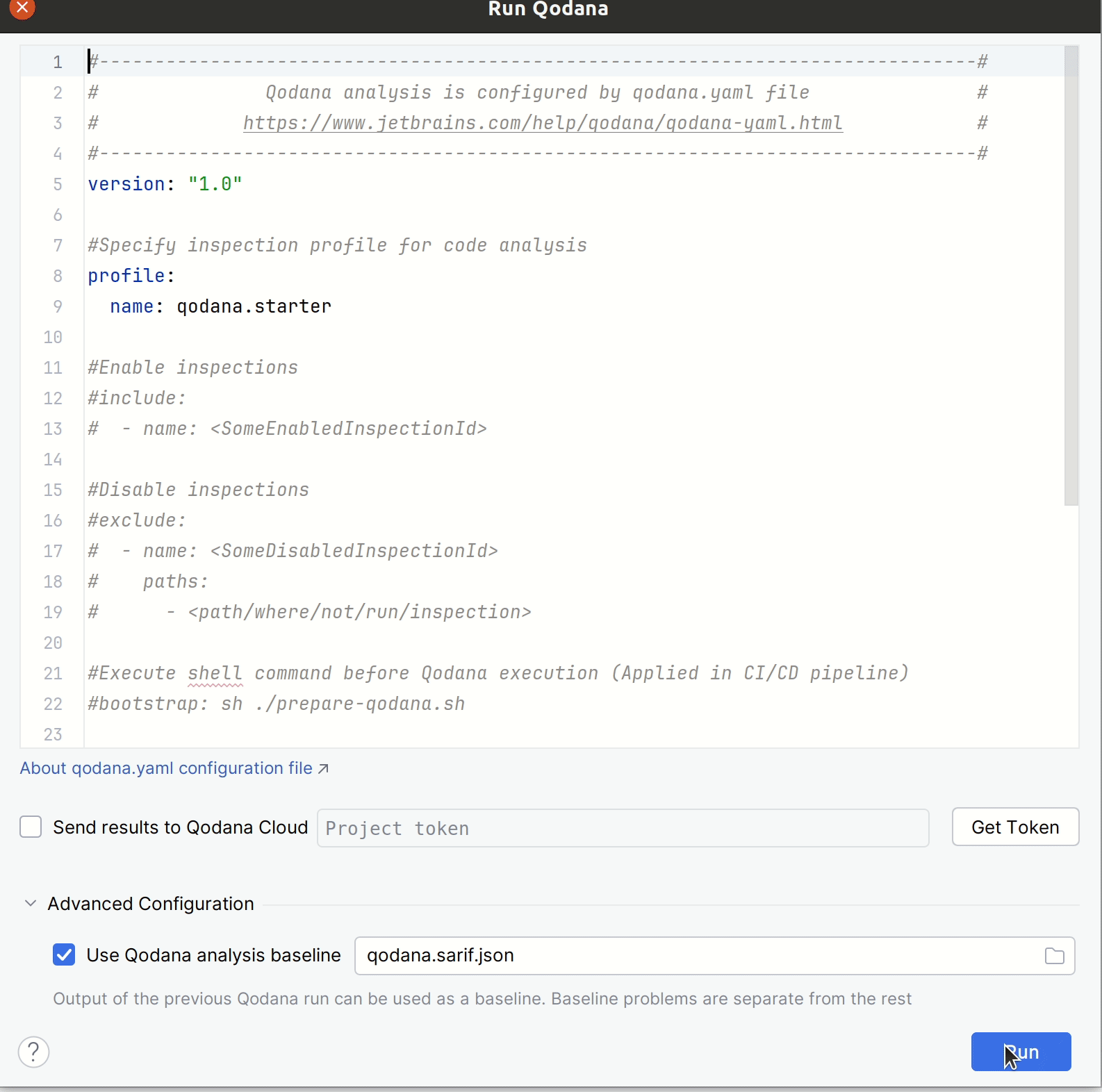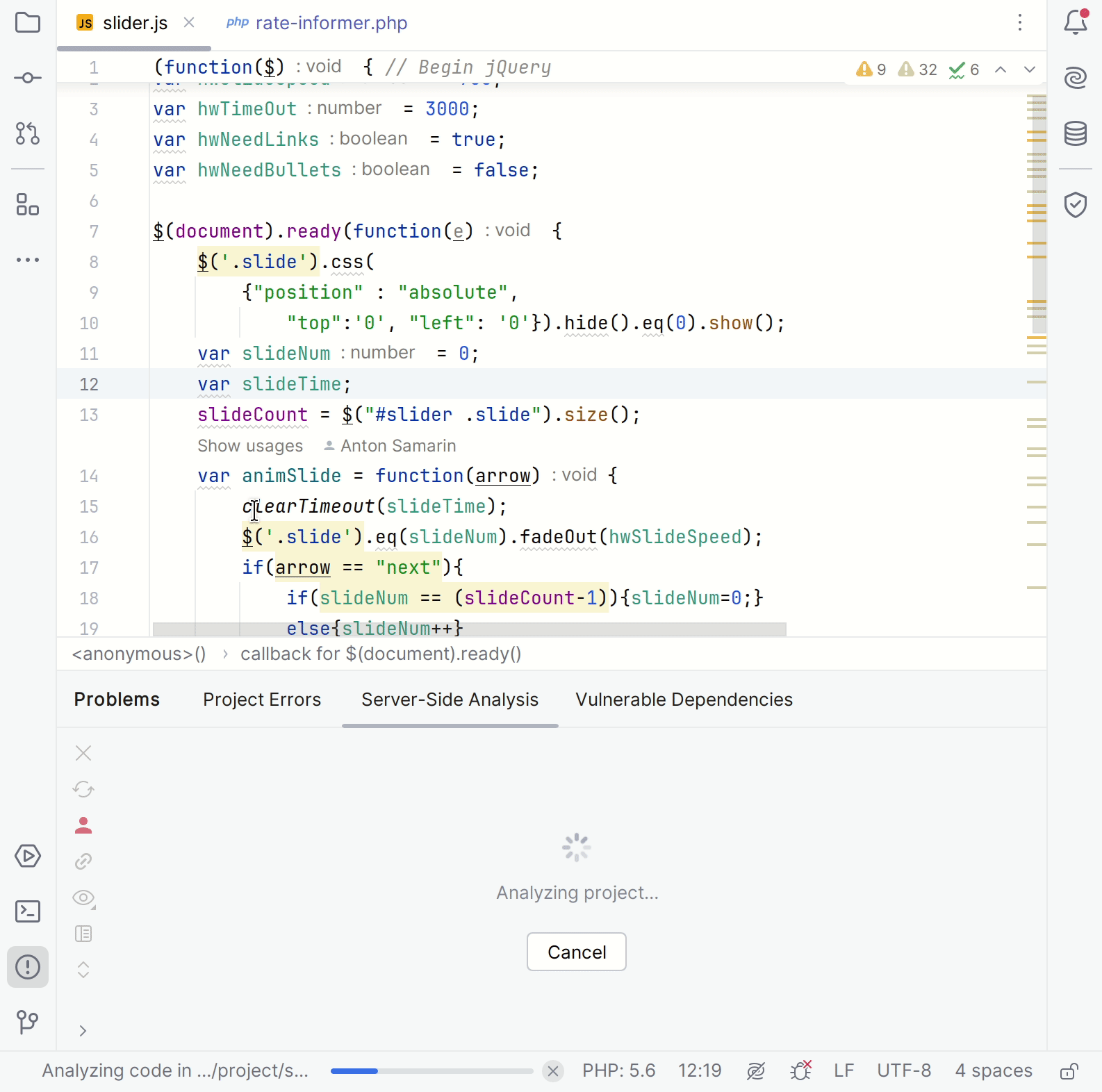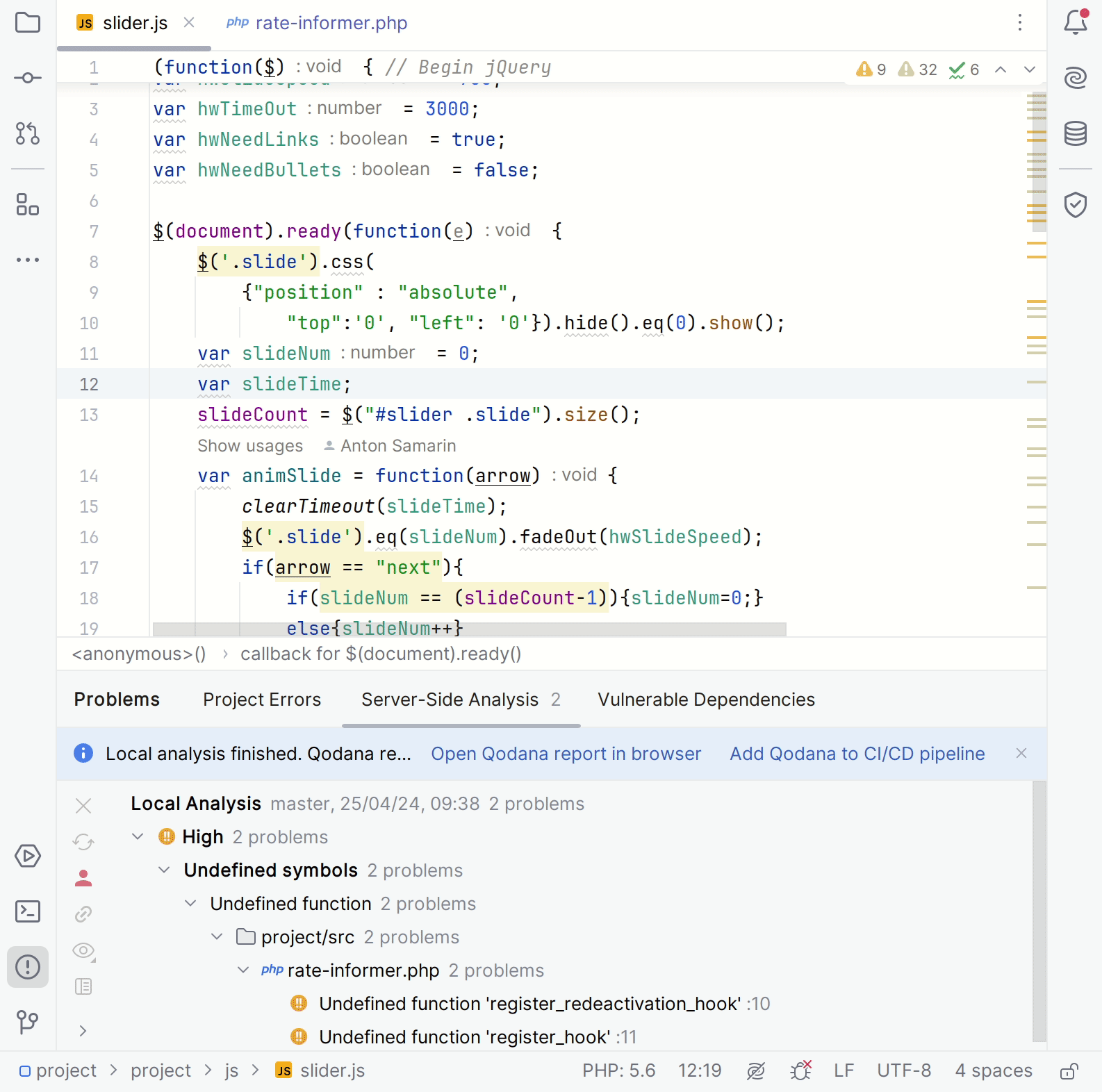
Here is the description of each step from the animation:
In your IDE, navigate to the tool window.
In the tool window, click the tab.
On the tab, click the button.
On the dialog, expand the section, select the baseline file, and then click .
The baseline feature divides problems into these groups:
Unchanged are the problems added to a baseline and remaining unchanged since then.
New are the problems that arise in addition to the baseline problems.
Absent are the baseline problems that were resolved since the baseline was created.
This image explains how everything works.

The first Qodana run detected two problems in the codebase.
To create a baseline for your project, download the
qodana.sarif.jsonfile and save it to your project directory as shown in the Baseline section. Starting from this moment, these two problems are identified by Qodana as baseline problems.A subsequent Qodana run detected three problems. Fortunately, this time Qodana identifies one of them as new and marks it respectively. The other two are the baseline problems; they are already reflected in the baseline report and marked as unchanged.
After one baseline problem is resolved, you decided to run Qodana again. This time, the report will contain three problems. The new problem is the problem that was detected in the previous run and still remains new. There is also one unchanged problem that has not changed its status. Finally, the first baseline problem was resolved and now is marked as absent.
To include absent problems in the report, you need to run Qodana with the
--baseline-include-absentoption:qodana scan \ -v <path_to_baseline>:/data/base/ \ -e QODANA_TOKEN="<cloud-project-token>" \ --baseline /data/base/qodana.sarif.json \ --baseline-include-absentdocker run \ -v $(pwd):/data/project/ \ -v <path_to_baseline>:/data/base/ \ -e QODANA_TOKEN="<cloud-project-token>" \ jetbrains/qodana-<linter> \ --baseline /data/base/qodana.sarif.json \ --baseline-include-absent
As you can see, new problems do not change the status across Qodana runs. To transform them to unchanged, you need to update your baseline.

Save the updated version of the
qodana.sarif.jsonfile to your project directory.Run Qodana again to see the change in the problem status.