Quick-fixes for code issues
ReSharper helps you instantly repair most code issues that it detects in design time. It is as simple as pressing Alt+Enter at a highlighted code issue and choosing the appropriate way to fix the problem or improve the suboptimal code.
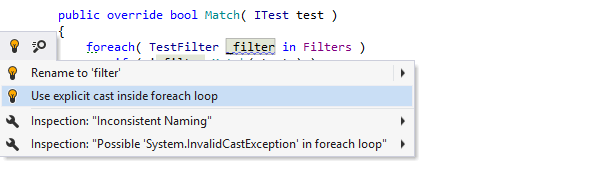
Apply quick-fixes
Quick-fixes are visually displayed as action indicators to the left of a highlighted code issue. These indicators appear when you set the caret at the code issue. The following indicators imply quick-fixes:
| Suggests a quick-fix for the detected code issue with the Error severity level. |
| Suggests to find an unresolved type or namespace in the NuGet package gallery, |
| Suggests an inplace refactoring or a refactoring that can fix the detected code issue. |
| Suggests a quick-fix for the detected code issue with Warning, Suggestion or Hint severity level. |
| Suggests a Visual Studio's code correction or refactoring action. |
| Suggests a quick-fix for redundant code that can be safely removed. |
View and apply quick-fixes
Use the issue highlighting in the editor and the marker bar to navigate to a specific code issue.
Set the caret at the highlighted issue.
Press Alt+Enter or click the action indicator to the left of the caret to open the action list.
Click the desired quick-fix or select it using arrow keys and then press Enter.
In most cases, a quick-fix is applied immediately. However, some quick-fixes (for example, Change All) require user interaction to choose how exactly they transform your code. In these cases, a Hot spot session is deployed in the editor, where you can select one of the suggested values or provide your own values in the active input positions:

To complete the hot spot session:
If ReSharper suggests some values for the current parameter, use Up and Down arrow keys to navigate through the list of suggested values, or just type in a desired value.
Press Tab or Enter to accept the value and move to the input position of the next parameter. If this is the last parameter, the hot spot session completes and the caret moves to the end position defined for the session.
Press Shift+Tab to move the input focus to the input position of the previous parameter.
Press Esc to exit the hot spot session. In this case, all session parameters will be initialized with default values.
Some quick fixes can be applied not only in the current caret position, but in a larger scope. For more information, see Fix in scope.
Quick-fixes from Visual Studio
Starting from version 2015, Visual Studio comes with its own code analysis engine (Roslyn) and provides its own light bulbs feature to perform quick actions including refactoring and fixing errors.
Visual Studio's quick actions often perform the same fixes as ReSharper's quick-fixes, context action, or refactorings. Therefore, for some errors you may have two similar suggestions from Visual Studio and from ReSharper. In the illustration below, you can see two bulbs both suggesting to remove redundant using directives:
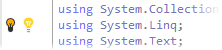
To avoid this, ReSharper provides the Hide Visual Studio light bulb option on the page of ReSharper options. This option is enabled by default, so you will not see the duplicated bulbs unless you disable it.
If Visual Studio Light Bulb is suppressed, Visual Studio actions can be integrated into ReSharper's action list by selecting the Merge Visual Studio light bulb actions into ReSharper action indicator checkbox. If it is selected, ReSharper does the following for each Visual Studio's quick action:
If there is a similar ReSharper's quick-fix or context action, the Visual Studio's quick action is not displayed.
If there are no similar ReSharper's action, the Visual Studio's action becomes available in ReSharper's action list. You can recognize Visual Studio's quick actions by the special icon
.png) .
.
This feature is supported in the following languages and technologies:
The instructions and examples given here address the use of the feature in C#. For details specific to other languages, see corresponding topics in the ReSharper by language section.