Code Inspection: Use preferred style of 'new' expression when created type is evident
Starting with C# 9.0, you can create objects with the target-typed new operator without explicit type specification when the type can be inferred, that is List<string> _myList = new(); instead of List<string> _myList = new List<string>();.
Depending on the context, the optional type specification can either clutter your code with redundant information or, on the contrary, improve the readability.
This inspection controls code style preferences for object creation expressions when the created type is evident from usage, like in the following cases:
Initializers of fields/constants/properties/events
private Test field = new()Initializers of local variables when an explicit type is preferred
Test local = new()Return values of expression-bodied members
public List <Test> M() => new()Values within array initializer
new Test[] { new(), new() }Values within collection initializer
new List <Test> { new(), new() }Default parameter values
void M(TestStruct arg = new()) { }
By default, ReSharper highlights type specifications as redundant in evident cases and helps remove them:
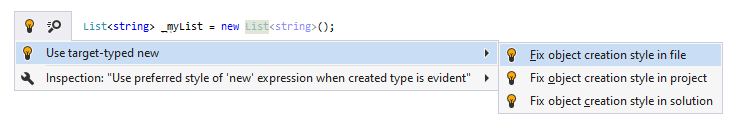
If you prefer another style for the new operator in your code, you can change the corresponding preferences.
For more information, see Code Syntax Style: Object Creation ('new()' vs 'new T()')