CamelHumps
CamelHumps is a feature that identifies parts of compound names composed according to CamelCase, where each part starts with a capital letter, or when parts of a compound name are separated by underscores. You can type only initial letters of these parts, and JetBrains Rider will find items with matching names automatically.
CamelHumps in search commands
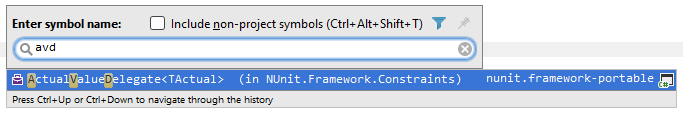
CamelHumps always works in all Search by name commands, namely Search Everywhere, Go To File, Go to File Member, and Go to Symbol. It is very convenient to type initial letters of name parts and get the list of matching items: 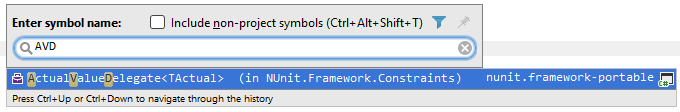
CamelHumps in editor assistance actions
CamelHumps can also work for Extend/Shrink Selection and other typing assistance commands:
Caret Move Ctrl+Right/ Ctrl+Left
Caret Move with Selection (Ctrl+Shift+Right/ Ctrl+Shift+Left)
Select Word at Caret Ctrl+W
Delete to Word Start/End (Ctrl+Backspace and Ctrl+Delete respectively)
Double-clicking (if Honor "CamelHumps" word settings when selecting using double click is enabled).
Enable CamelHumps in typing assistance actions
Press Ctrl+Alt+S or choose (Windows and Linux) or (macOS) from the menu.
Go to the page of JetBrains Rider settings.
With the Use CamelHumps checkbox, toggle CamelHumps support in typing assistance features.
Click Save in the Settings dialog to apply the modifications and let JetBrains Rider choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see Layer-based settings.
If the CamelHumps is enabled, the Extend/Shrink Selection commands take into account parts of compound names. Suppose you have placed the caret in the middle of a compound name with several parts that begin with uppercase letters: 
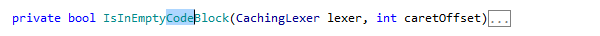
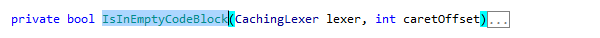
JetBrains Rider also provides similar actions that work in a mode opposite to the one selected in the Use CamelHumps setting:
Move Caret to Previous Word in Different "CamelHumps" mode
Move Caret to Previous Word with Selection in Different "CamelHumps" mode
Move Caret to Next Word in Different "CamelHumps" mode
Move Caret to Next Word with Selection in Different "CamelHumps" mode
Delete to Word End in Different "CamelHumps" mode
Delete to Word Start in Different "CamelHumps" mode
For example, If Use CamelHumps is enabled, the action Move Caret to Next Word in Different "CamelHumps" mode moves the caret to the end of word regardless of uppercase characters in this word; if Use CamelHumps is disabled, then the caret moves to the next CamelHump within this word.
These actions have no default keyboard shortcuts, and are not included in the menus but you can invoke them from Go to Action Go to Action Ctrl+Shift+A:
You can bind them with the shortcuts of your choice as described in the section Customize keyboard shortcuts.
CamelHumps in code completion
By default, CamelHumps support is also enabled for Code Completion features, that is, you can start typing a CamelCase abbreviation of a symbol (also in lowercase) and the completion popup will display matched items. If necessary, you can configure this behavior.
Change the way code completion filtering works with CamelHumps
Press Ctrl+Alt+S or choose (Windows and Linux) or (macOS) from the menu, then choose on the left.
Select the Match case checkbox. If First letter only is chosen, you will need to type the first letter of a CamelCased identifier in the upper case, and then you can type middle letters that you want to match in the upper or lower case. If All letters is chosen, you will need to type all dividing letters of a CamelCased identifier in the upper case to match it.
Click Save in the Settings dialog to apply the modifications and let JetBrains Rider choose where to save them, or save the modifications to a specific settings layer using the Save To list. For more information, see Layer-based settings.