Code Style Assistance in C++
JetBrains Rider provides a lot of features for keeping your code neat and clean. Being tightly interwoven with the majority of other JetBrains Rider's features, they help you produce code and change existing codebases according to the specific code style. The code style, which includes naming standards, formatting rules, and many other tiny aspects can be configured to a very detailed level and shared across your team.
Similarly to other languages, all C++ code style preferences can be applied in the desired scope with a single command using either Fix in scope or Code cleanup.
Note that built-in code cleanup profiles do not include some C++ specific tasks, so you need to create a new custom profile to enable them.Managing and applying code formatting rules
An important aspect of code style is how to format the code, that is, how to use whitespaces, tabs, and line breaks to arrange code elements, whether and how to use tabs for indents, whether and how to wrap long lines, and so on.
The extensive set of JetBrains Rider code formatting rules has a default configuration that takes into account numerous best practices. You can configure every detail of formatting rules and enforce the rules in your code. These rules are applied when JetBrains Rider produces new code with code completion and code generation features, applies code templates and performs refactorings. The formatting rules can also be applied to the existing code in the current selection, current file, or in a larger scope up to the entire solution.
JetBrains Rider stores formatting preferences using the mechanism of shared settings. You can configure formatting rules in options pages under the group. You can also store and share formatting settings in the EditorConfig and Clang-Format files.
Naming style
JetBrains Rider helps you define, control, and apply naming style for symbols in your code. Naming style is implemented as a set of rules, each of which targets specific identifiers with the set of constraints . Each rule can have one or more associated styles that define suffixes, prefixes, capitalization of compound words, and so on.
These rules are taken into account when JetBrains Rider produces new code with code completion and code generation features, applies code templates and performs refactorings. JetBrains Rider also helps you detect and fix violations of naming rules. If necessary, the automatic checkup of naming rules can be configured or disabled.
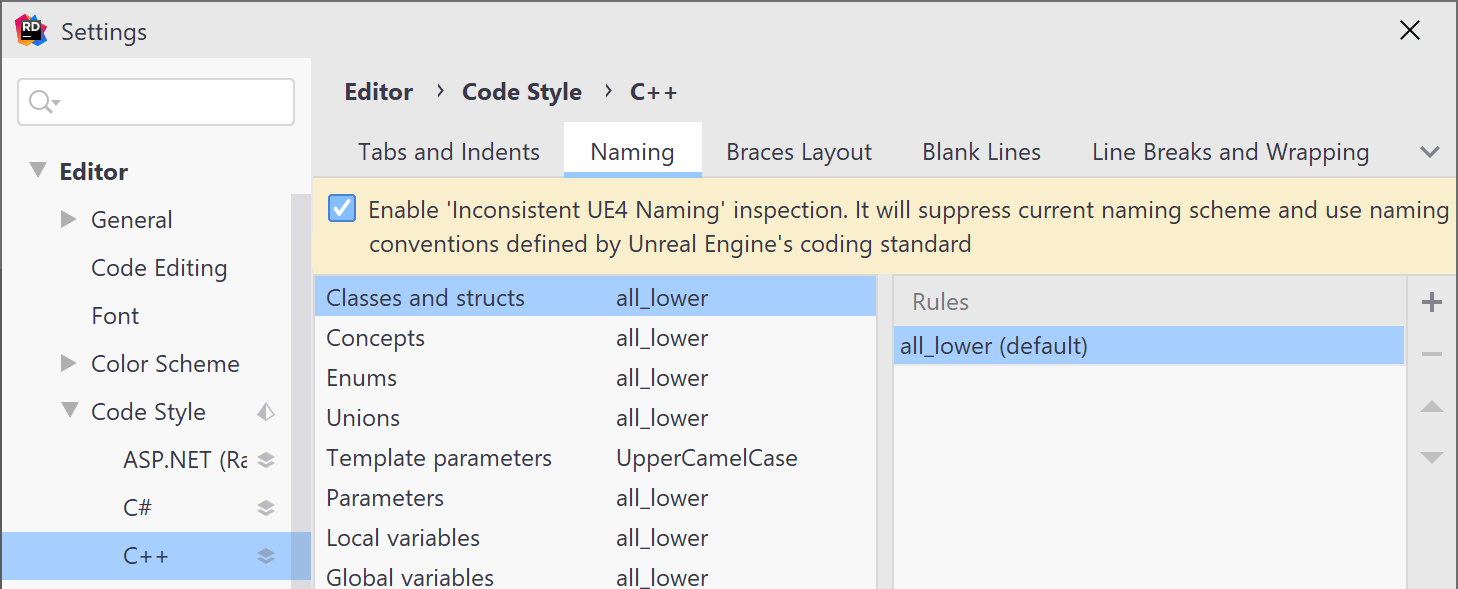
On the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S,
If you're working with a UE4 project, JetBrains Rider will automatically apply a naming ruleset corresponding to the Unreal Engine coding standard, which is not configurable. This means that the rules configured on the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S will be ignored when you're working on a UE4 project. If you still want to use your configured ruleset instead of the Unreal Engine coding standard, you can disable the corresponding inspection.
Arranging cv-qualifiers
JetBrains Rider helps you arrange cv-qualifiers in generated code. On the page of JetBrains Rider options, you can specify whether to put cv-qualifiers before or after the type specifier as well as the order of the const and volatile modifiers.
Include directive style
On the page of JetBrains Rider options, you can specify whether to use forward or backward slash as a path separator in include directives in generated code. You can also specify whether or not to generate forward declaration in the header file.
Sorting of includes
JetBrains Rider allows you to sort #include directives, rearrange the existing groups and create new ones separated by blank lines.
When the caret is on an #include directive, there are three context actions in the Sort #include directives submenu:
Sort #include directives | |
|---|---|
Sort and regroup #include directives | This action merges all 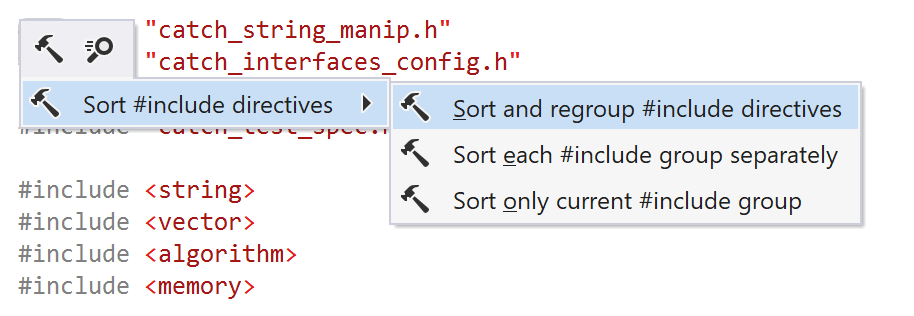 |
Sort each #include group separately | This action sorts 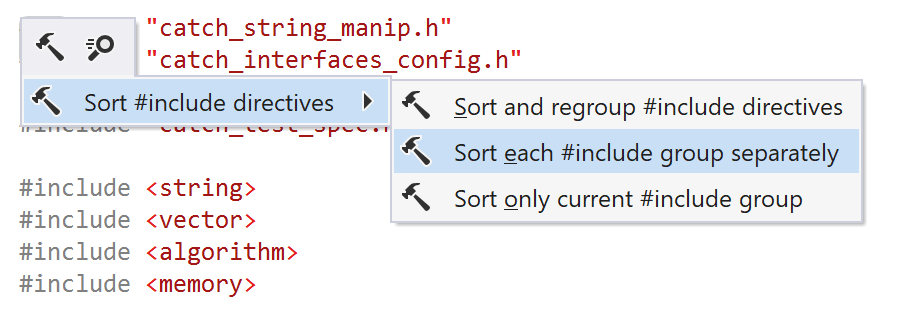 |
Sort only current #include group | This action sorts the group that the caret is on. |
You can configure the ordering rules on the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S.
Sorting of includes can also be applied with code cleanup.
Default pointer initializer style
You can specify 0, nullptr or NULL as the preferred initializer for pointer initializers, for example: const char *foo = nullptr. You can change your preference on the page of JetBrains Rider options.
File header style
Using file headers for copyright notices and other identifying messages is a common practice. JetBrains Rider allows you to configure the default header text and automatically insert it into code files of your solution.
You can configure file header either in JetBrains Rider settings or in .editorconfig files and then add it to new files created with file templates and insert it to existing files using code cleanup.