Create and open projects and solutions
Create projects and solutions
You can create a new project in a new solution using or add a new project to the existing solution by right-clicking the solution or solution folder node in the Solution Explorer, and choosing .
When creating a new solution or project, Rider gives you a number of pre-installed templates, which are grouped by frameworks. There are templates to create an empty project, standard .NET class libraries and applications, as well as test projects. It will also create .NET projects, as console applications, testing and class libraries.
In every template, you can specify a number of options:
Solution/project name and folder
Language to use — many templates support C#, VB.NET and/or F#
Target framework for the project. Note that for a framework to be available from this list, it has to be installed on your system.
For Unity and Xamarin, several other options can be provided as well, for example the path to UnityEngine.dll, the target platform (Android or iOS), the type of app (blank, Android Wear, ...) Note that these options, too, depend on available frameworks on your system, such as the Mono/Android versions installed.
When you have specified the project options, just click Create. Once a project has been created, files can be added or removed by right-clicking on the project node in the Solution Explorer.
Open existing projects and solutions
When opening a .NET solution, Rider will automatically restore all NuGet packages in each project and will also detect the list of target .NET frameworks in each project. If there are multiple target frameworks, you will be able to change the active framework in editor breadcrumbs.
Open solution from welcome screen
When you start JetBrains Rider for the first time, a welcome screen appears where you can click Open and choose your solution.
On each subsequent start, JetBrains Rider automatically opens the solution you worked with in the previous session. If you want to change this behavior, clear the Reopen projects on startup checkbox on the Appearance & Behavior | System Settings page of the IDE settings Ctrl+Alt+S — this will enable the welcome screen to appear on each startup. When the welcome screen is enabled, all solutions that you worked with are listed in the right pane. You can search the list in case you have a lot of solutions — just start typing the solution name, and a search field will appear.
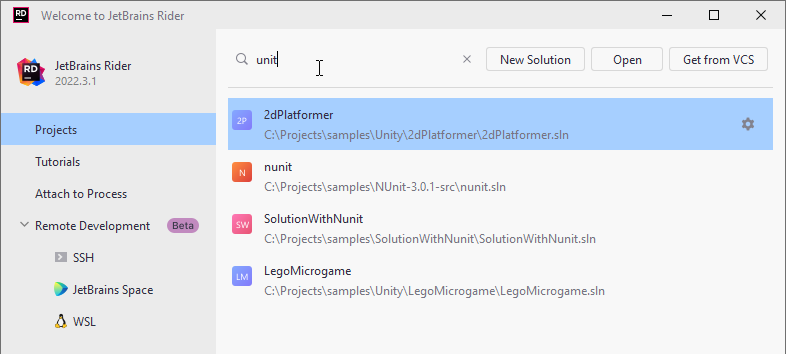
Switch to another solution
Press Ctrl+Shift+O or choose from the menu.
Choose any of the recently opened solutions from the list under .
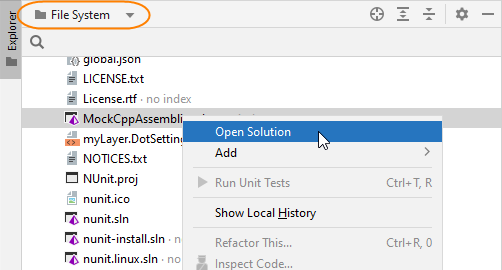
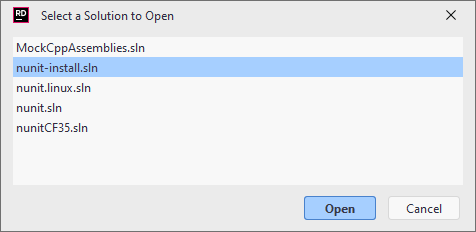
If you have several solutions in the same directory and one of them is open, you can switch to the File System view in the Explorer window to see all other .sln files in the directory. You can then right-click the desired .sln file and choose Open Solution:
Rider allows opening several solutions simultaneously in different windows. By default, each time you open a solution while another one is opened, it prompts you to choose whether to open the project in the same window or in a new window. If necessary, you can set the default way of opening projects on the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S.
On macOS, you can merge several opened solution windows into one window, where each solution will have its own tab. To do so, select from the main menu. To restore separate windows, drag tabs outside the application window frame.
Different ways to open solutions
When you click Open on the welcome page or choose from the menu, the Select Path dialog opens where you can choose the solution in different ways:
Choose either a solution file (.sln)
Choose a project file (for example, .csproj) — in this case Rider will generate an .sln file if necessary.
Choose a folder — in this case, you will be able to choose any of the solution files located in the selected folder or in any of its subfolders.
If your solution is directory-based, that is all its projects are arranged in subfolders without the .sln file, you can choose the root folder in the Select Path dialog to open all projects from subfolders, for example:
RootFolder ├── Project1 ├── Project1.csproj ├── [project contents] ├── Project2 ├── Project2.csproj ├── [project contents]Note that whenever you choose a folder in the Select Path dialog, you can always opt for opening it as a folder (as opposed to a .NET project). In this case you will be able to browse all files in this folder but code analysis and other features will not be available in .NET files (*.cs, *.vb, and so on).
Open project from a version control system
Rider also allows opening solutions from different version control systems. It can, for example, log in to GitHub, and clone a repo to the local file system. Once done, it will prompt you to choose a solution to open from those available in the repo.
To clone a repository, you can select from the menu or click Get from VCS on the welcome screen.
Trusted and untrusted solutions
Each MSBuild project in your solution contains an MSBuild script that is executed not only when you build the project, but also when you merely open the solution.
This happens because the IDE runs MSBuild on the project script to understand the structure of the project and its dependencies, and without this understanding the IDE would be nothing more than a basic text editor.
Malicious actors can use this design to base an attack on modified project scripts.
To address this security threat, JetBrains Rider relies on the concept of trusted solutions and trusted locations.
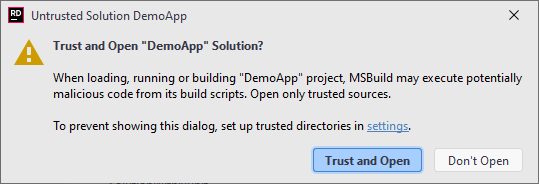
By default, each solution you open is considered untrusted and you will see a dialog where you can either make this solution trusted and open it or choose not open it. Once a solution was opened, it becomes trusted and you will not be asked for confirmation when you open it again.
You can also configure a list of directories where you keep your solutions to make all of them trusted. This list is configurable on the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S.
Install custom project templates
Rider supports the template system used by the .NET tooling dotnet new, which allows you to use project templates from the dotnet templates gallery as well as custom templates that you can create on your own.
There are two ways to install new project templates.
You can run
dotnet new --install [template package]in the command line, where[template package]is the template id from the dotnet templates gallery.In the New Project/New Solution dialog, click More Templates on the left, then click Install Template, and then choose a folder or a package file with the custom project template.
When the path to the template appears in the list, click Reload.
Create custom project template
Create a project with the desired structure. You can take any project as a starting point or create a new one using any of the existing templates.
To illustrate this, we take the simplest project that contains just one file.
ConsoleAppAsyncMain ├── bin ├── obj ├── MyProject.csproj ├── Program.csProgram.cs contains
async mainmethod as the default application entry point:using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyProject { class Program { static async Task Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } } }Copy the project folder to a location from which you will use it as a template.
Remove bin, obj, and any other directories and fies that are not related to the source code of the template.
In the copied project directory (which is now the template directory), add a folder named .template.config and a file named template.json inside it.
Now the template structure should look as follows:
MyTemplates ├── ConsoleAppAsyncMain ├── .template.config ├── template.json ├── MyProject.csproj ├── Program.csSpecify template properties in the template descriptor template.json
The minimal descriptor can look as shown below, but you can provide a much more detailed configuration if necessary. You can find more information and examples in this Microsoft .NET Blog article.
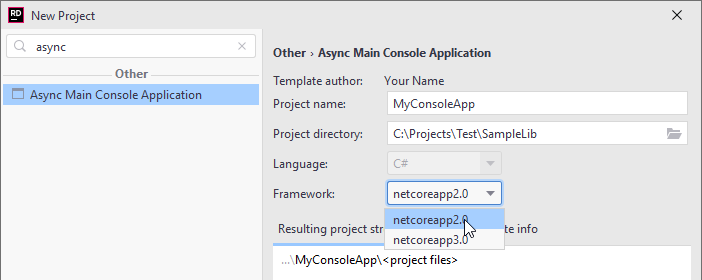
{ "author": "Your Name", "name": "Async Main Console Application", "description": "A project for creating a command-line application that can run on .NET on Windows, Linux and macOS, and has an async Main method.", "identity": "YourName.ConsoleApp.1.0", "shortName": "consoleasync", "tags": { "language": "C#", "type": "project" }, "sourceName": "MyProject", "symbols": { "Framework": { "type": "parameter", "description": "The target framework for the project.", "datatype": "choice", "choices": [ { "choice": "netcoreapp2.0" }, { "choice": "netcoreapp3.0" } ], "defaultValue": "netcoreapp2.0" } } }Properties in the above configuration are self-explanatory, except
"sourceName": "MyProject".When you create projects using this template, the value of this property will be replaced everywhere with the name you specify for the new project.
In our example, the new name will replace the project file name and the namespace in Program.cs.
Your new project template is ready, you can install it in the New Project/New Solution dialog — click More Templates on the left, then click Install Template, and then choose the ConsoleAppAsyncMain folder wherever you saved it.
When the path to the template appears in the list, click Reload.
As soon as the template is installed, you can find it in the list on the left and use it to create new projects:
Manage recent solutions
Each time you open a new solution, JetBrains Rider saves it in its history and lets you quickly reopen it from the menu.
To configure the list of recent solutions, choose from the main menu. In the popup that opens, you can click the ![]() icon next to a solution and choose one of the actions:
icon next to a solution and choose one of the actions:
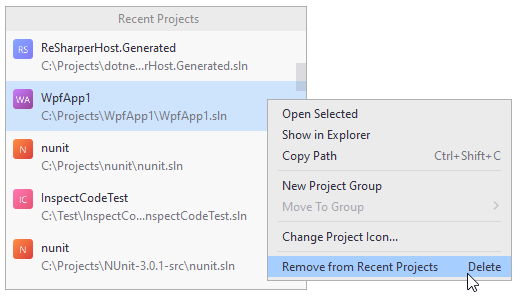
To remove a solution from the list of recent ones, you can also select it using the Up and Down keys, and then press Delete.