Features
You can start with watching this 3-minute video where Matt Ellis gives a short overview of JetBrains Rider features for Unity Development.
Unity Explorer
By default, when working with a Unity project in Rider, the Explorer window switches to the Unity view showing you all the assets that constitute the project.
Primarily, the Packages node in the Unity view shows you the contents of the Packages folder in the root of your project. This might well only contain a manifest.json file which you can edit in Rider and when saved, Unity will update your project to include the packages you've added. More importantly, the Packages node will also show all the packages referenced in your project. Unity supports a number of different package types, and Rider will show them all. For more details on how Rider works with Unity packages, refer to the blog post.
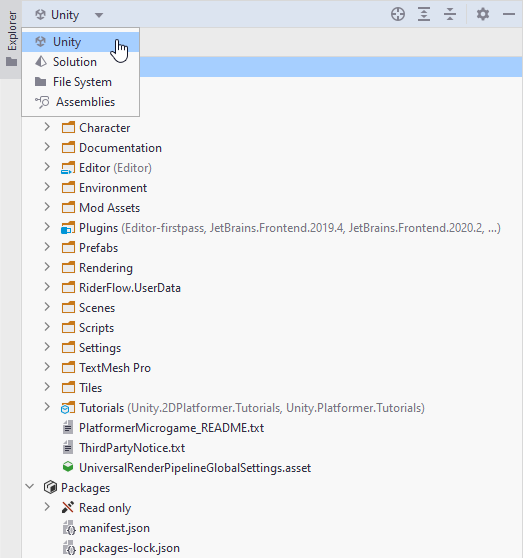
If you switch to the Solution view, you will see only the Scripts part of the project.
Control over Unity editor
To reduce the time you spend context switching between Rider and the Unity editor, some of the Unity editor's functionality is exposed directly in Rider on the Unity toolbar located in the top right corner.
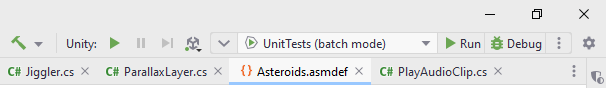
The toolbar allows:
Controlling play mode: The Play, Pause, and Step buttons correspond to the same buttons in the Unity editor and work in the exact same way.
Accessing important Unity-related actions using the
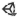 Unity-related Actions list:
Unity-related Actions list:Start Unity: start Unity Editor and open the Unity project that corresponds to the solution opened in Rider.
Start Unity with Coverage: start Unity Editor with enabled code coverage support and open the Unity project that corresponds to the solution opened in Rider.
Attach to Unity Process...: attach to the running Unity instance, for example for debugging or unit testing purposes.
Unity Settings...: quickly open the Rider's Unity Engine settings page.
Unity Log Window...: open the log viewer.
Show Non-Unity Applicable UI: switch between the full Rider UI and the minimized one (all UI elements that are not related to Unity are hidden).
Editor helpers
If Code Vision is disabled, JetBrains Rider shows the Unity gutter icon for classes, methods, and fields that are implicitly used by Unity:
Colors defined via UnityEngine.Color, UnityEngine.Color32, and Color.HSVToRGB are highlighted in the editor. You can also press Alt+Enter on a color usage and choose Pick color from palette to open the color editor and modify the color visually.

Find Usages
In Unity projects, the Find Usages Alt+F7 feature is extended with data pulled from Unity scenes, assets and prefabs. If you search for a class or a method used as an event handler, Rider will show where it is used in Unity files, grouped by type, component name, and parent game objects.
Moreover, there is a separate Find Unity Usages action that shows only the usages made from the Unity Editor. Another way to run this action is to run Ctrl+Shift+G and choose .
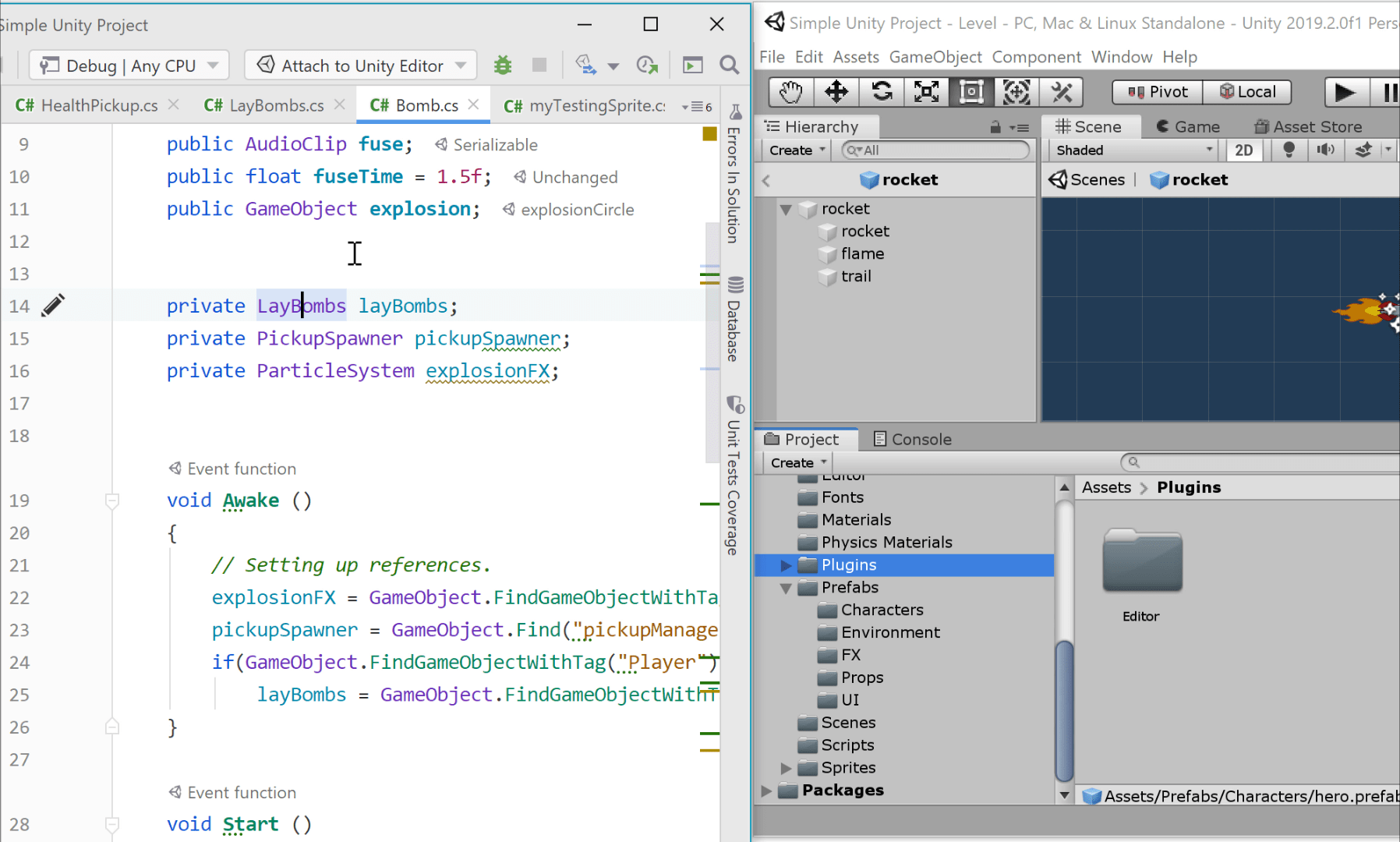
Code Vision
Code Vision also supports Unity. When it is enabled, you can see what classes, methods, fields (including field values set in Unity), and even assets are implicitly used. Code Vision provides navigation to the Unity Editor.
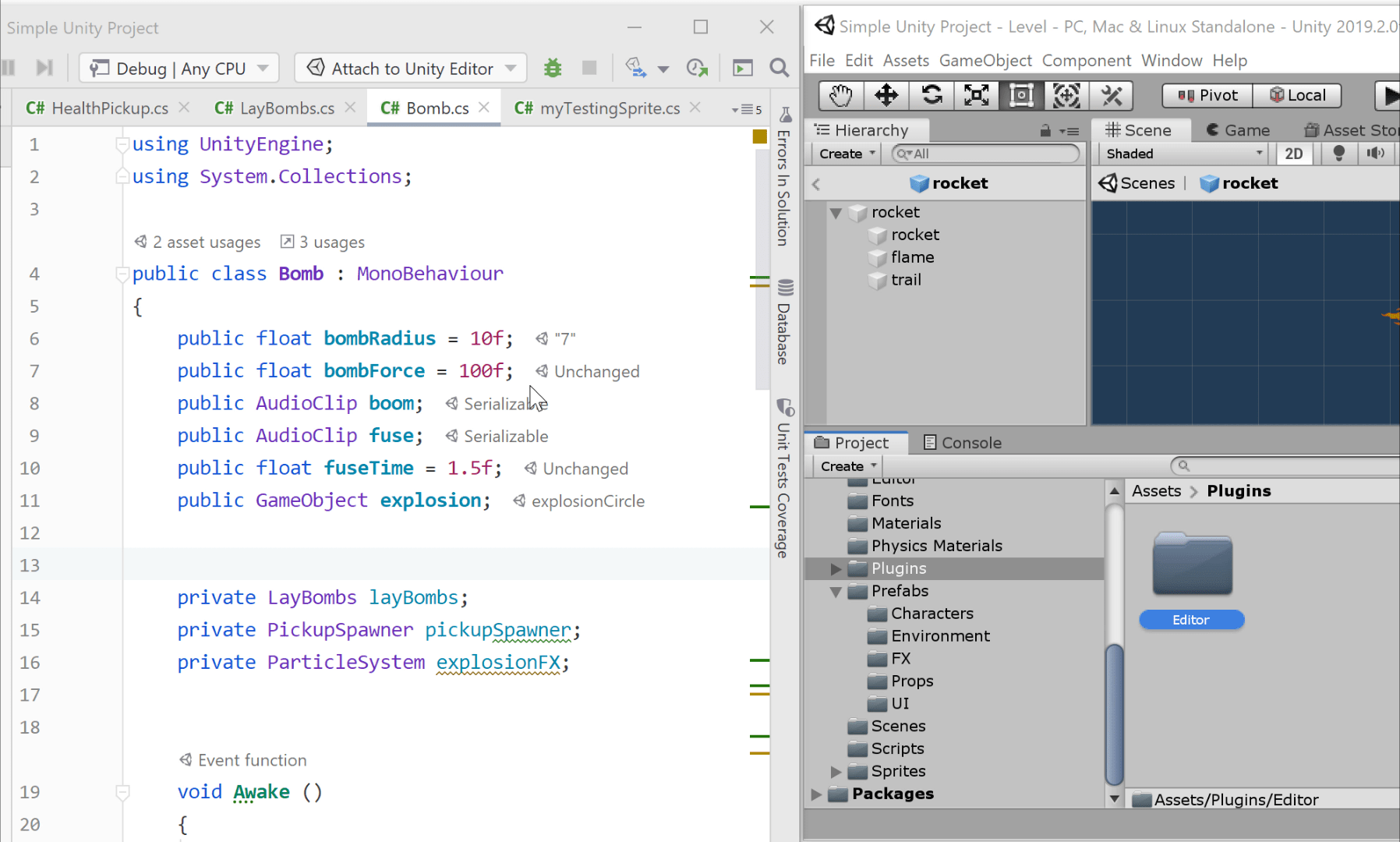
Performance indicators
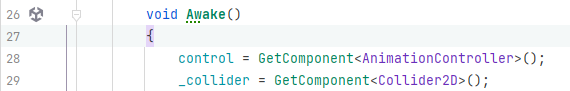
JetBrains Rider shows you performance sensitive areas: event functions that are called each frame, such as Update, FixedUpdate and LateUpdate, as well as coroutine methods. Inside these frequently called methods, performance indicators will also draw your attention to known expensive operations, like calls to GetComponent, Find or SendMessage, with context actions to move the initialization to Start or Awake.
When Code Vision is disabled, performance indicators are shown on the gutter:

If it is enabled, the indicators are shown as Code Vision metrics:
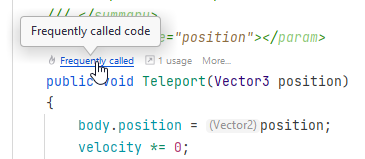
You can enable and configure performance indicators on the page of JetBrains Rider settings Ctrl+Alt+S, under Enable performance analysis in frequently called code.
Event functions
You can generate event functions using Unity Event Functions the Generate Code menu Alt+Insert. This action is also available from Alt+Enter everywhere inside a Unity-based class.
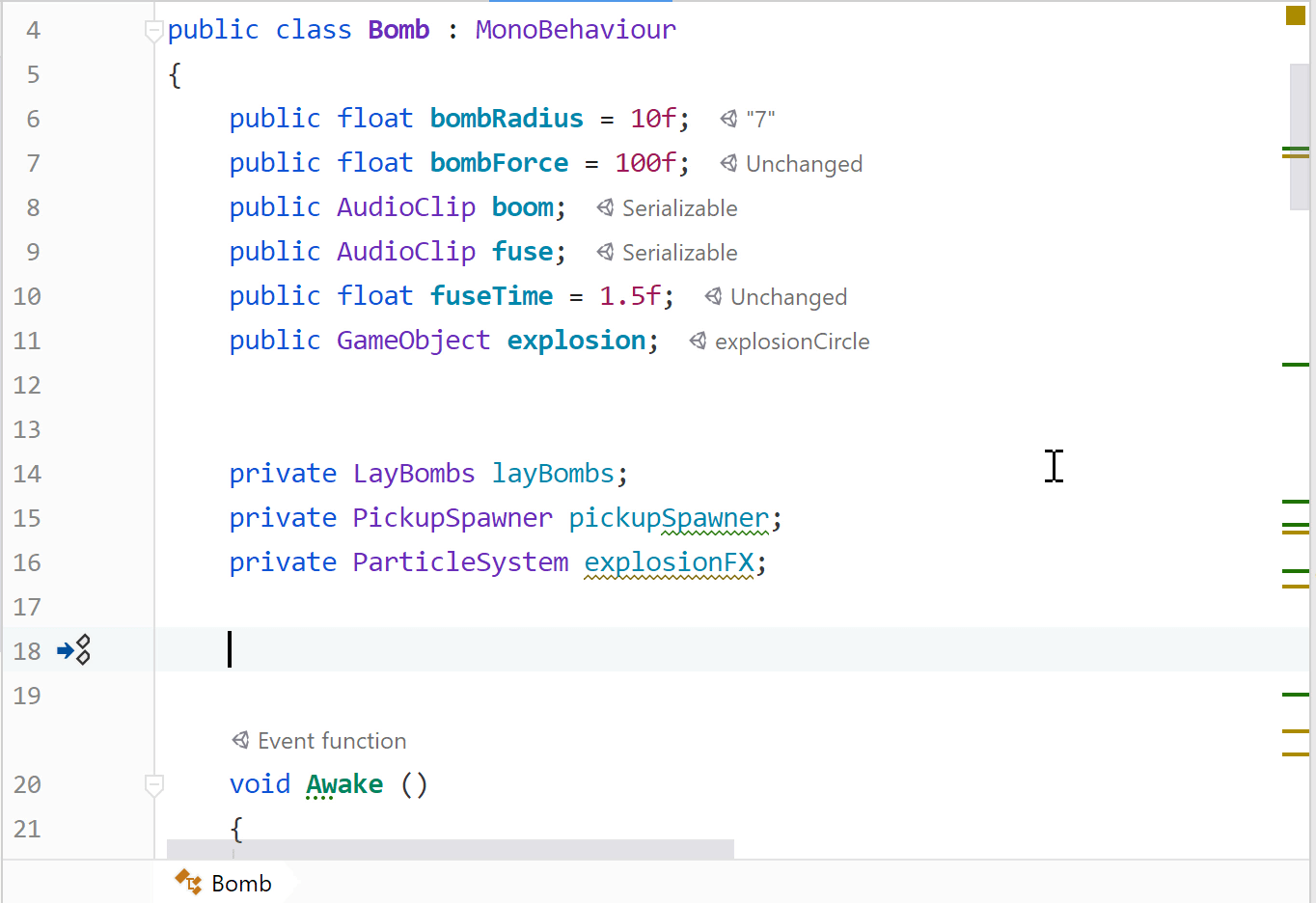
Auto-completion will suggest event function names when declaring methods in Unity-based classes, and expand to include method signature. Start typing an event function within a class deriving from a known Unity class, such as
MonoBehaviour.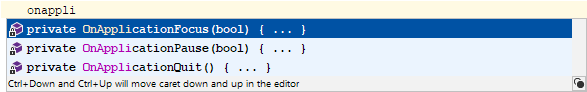
Descriptions for event functions and parameters in Unity based classes are shown in tooltips and Quick Documentation.
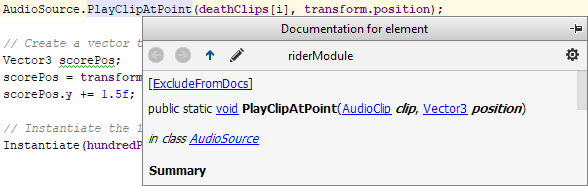
Inspections and quick-fixes
Rider shows warnings for unknown scenes, tags, and layers.

When the Solution-wide analysis is enabled, JetBrains Rider understands implicitly used fields and event functions and do not highlight them as not accessed.
Empty event functions are shown as dead code, with a quick-fix to remove them.
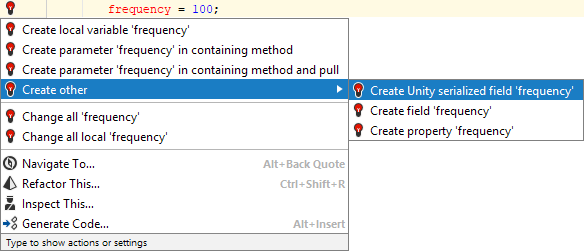
Using the
SyncVarAttributeinside any class other thanNetworkBehaviouris treated as an error.A quick-fix is suggested to create a serialized field from a usage of an unresolved symbol:
JetBrains Rider ensures that all of your event functions have correct signatures: it highlights incorrect signatures and offers a quick-fix to correct them:
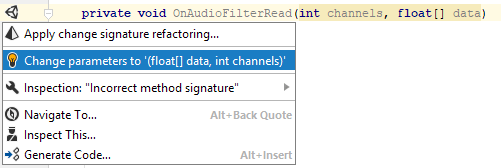
JetBrains Rider warns you against using an inefficient string literal comparison with the
tagproperty, and provides a quick-fix to rewrite this as a call toCompareTag.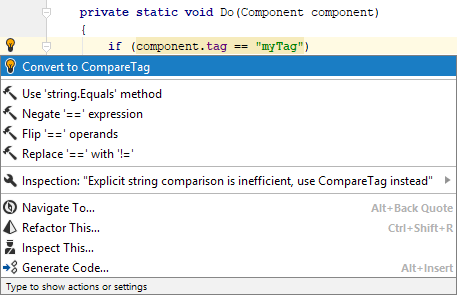
JetBrains Rider warns you if you try to use the
newkeyword to create a new instance of a class deriving fromMonoBehaviourorScriptableObject. A quick-fix is suggested to usegameObject.AddComponent<T>()orScriptableObject.CreateInstance<T>()instead.There are also inspections for the
[InitializeOnLoad]and[InitializeOnLoadMethod]attributes, ensuring that they have the correct method or constructor signatures, and JetBrains Rider will grey out a redundant[InitializeOnLoad]attribute if the class doesn't have a static constructor, with a quick-fix to either quickly remove the attribute, or create the constructor.
External annotations
A lot of Unity-specific assemblies are annotated with External annotations to improve code inspection when you make use of these assemblies.
Treating code marked with attributes from UnityEngine.dll, UnityEngine.Networking.dll and UnityEditor.dll as implicitly used.
Marking
Component.gameObjectandObject.nameas not-nullable.Debug.Assertmarked as assertion method to help null-value analysis (for example "value cannot be null" afterDebug.Assert(x != null)).Debug.AssertFormat,LogFormat, and so on gets string formatting helper functionality.Assertions.Assertmethods marked as assertion methods to help null-value analysis.EditorTestsWithLogParser.ExpectLogLineRegexgets regular expression helper functionality.Various attributes now require the class they are applied to derive from a specific base type. For example,
[CustomEditor]requires a base class ofEditor.Support for Unity 2017.2's modularised UnityEngine assemblies.
Support for .shader files
JetBrains Rider provides support for ShaderLab syntax in .shader files, with support for Cg/HLSL blocks.
Syntax and syntax error highlighting for ShaderLab syntax. Note that you can change the default color scheme in .

JetBrains Rider provides code completion.
Brace matching and highlighting, comment/uncomment Ctrl+/, and to-do explorer support.

[Cg/HLSL] Syntax highlighting for
CGPROGRAM/CGINCLUDEblocks and .cginc files.[Cg/HLSL] Code completion in Cg/HLSL blocks.
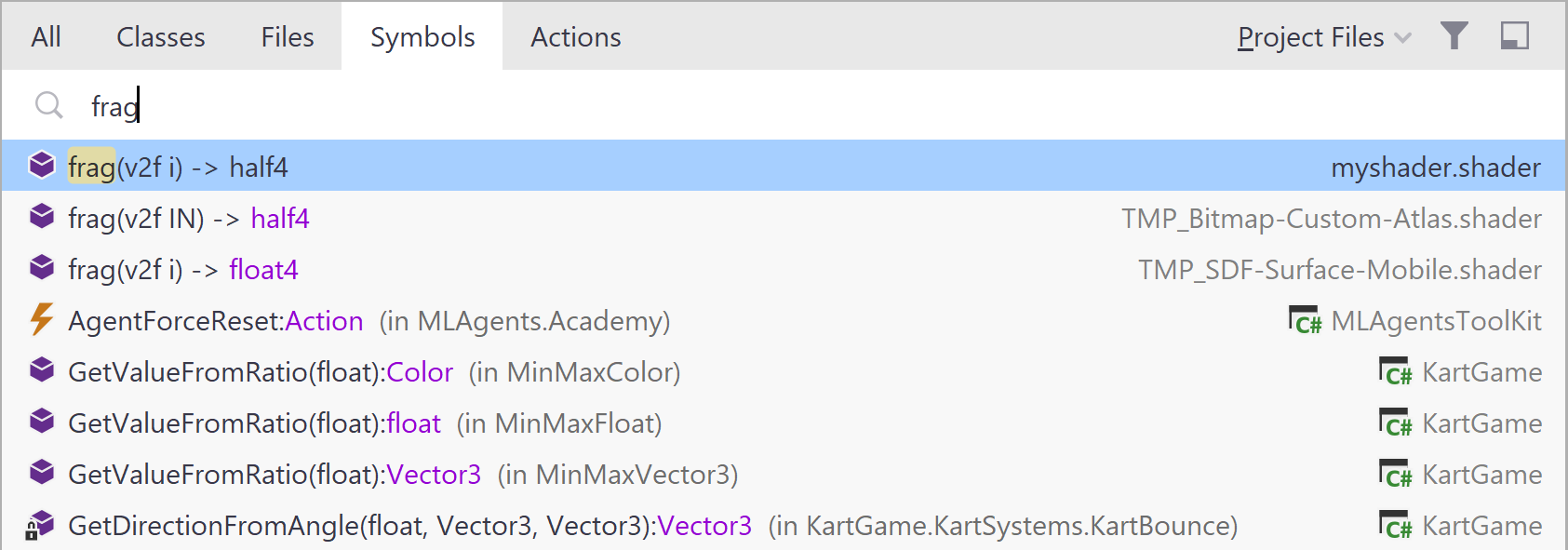
Search everywhere will help you to navigate to symbols inside shader files.
Support for assembly definition files
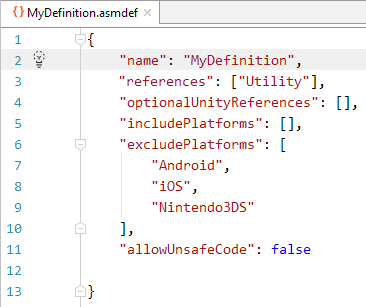
Assembly definition files (.asmdef) are used to separate project scripts into multiple assemblies in order to reduce compilation time. Unity will rebuild only required assemblies when you make changes in a script.
Rider provides support for .asmdef files: JSON schema validation, code completion, Find Usages, Rename refactoring, Navigation on references elements, and inspections/quick-fixes for self-reference and filename/assembly name mismatch. For more details on .asmdef files support, refer to the blog post.
Live templates
JetBrains Rider offers a couple of Unity-specific live templates:
sprop: a Unity property with a serialized backing field.
sfield: a Unity serialized field.
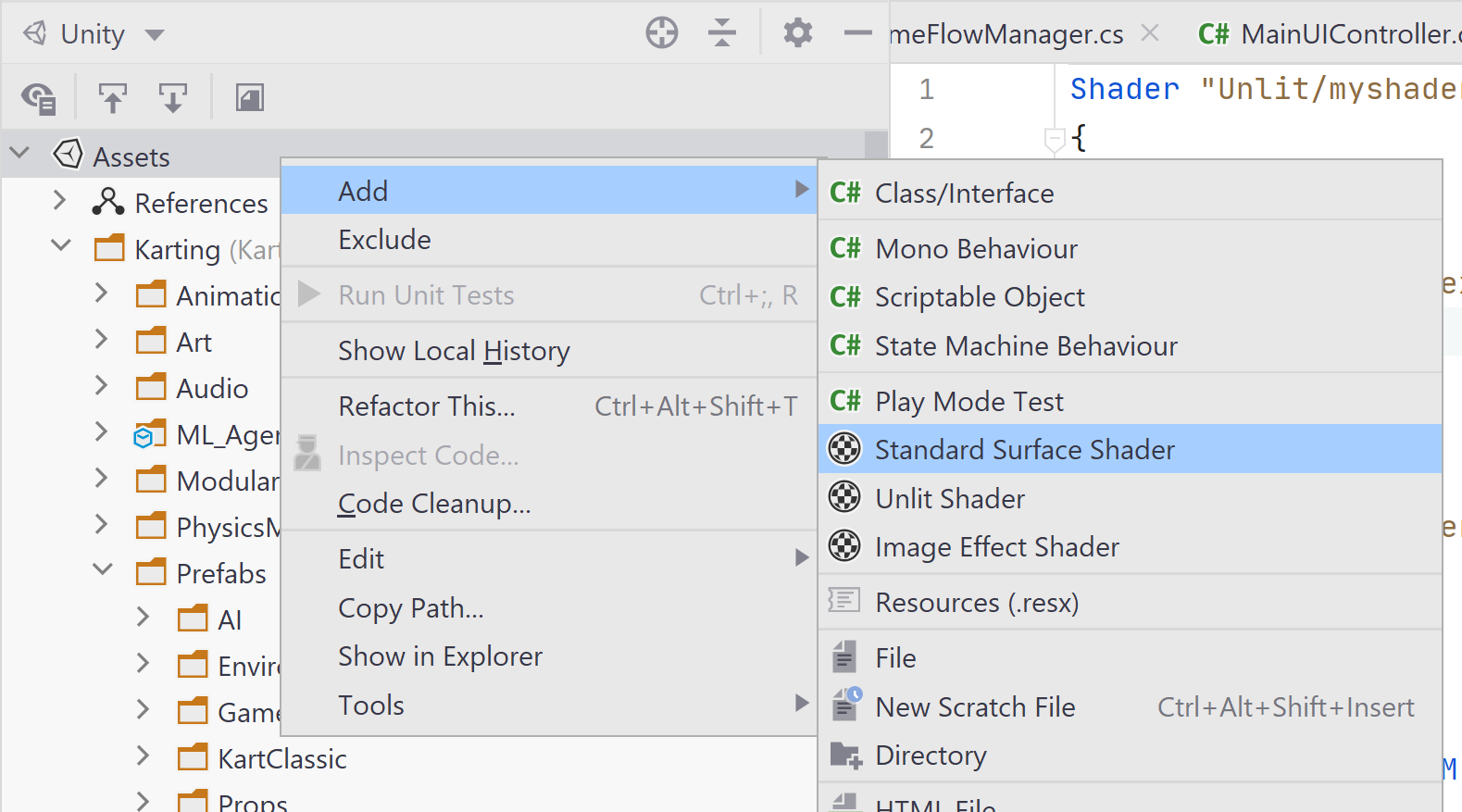
File templates
JetBrains Rider offers a number of file templates for new C# script, tests, and shader files:
Unity logs
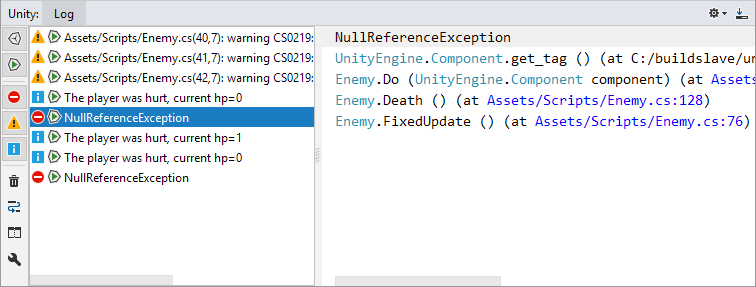
When Rider is connected to the Unity editor, the Unity tool window becomes available. To open the window, select from the main menu or use the Unity-related Actions list on the Unity toolbar.
The Log tab of the Unity tool window brings Unity's Console into Rider. The tab shows Unity log entries and is updated as events are logged in Unity.
The Output part of the window on the right shows the content of the currently selected log entry. Rider makes the content interactive, so that you can navigate to any source file, class, method or property mentioned in the log entry.
Note that log entries can be filtered by event type: events from play or edit mode, warnings, errors, and messages.
UnityYAMLMerge Support
By default, JetBrains Rider uses the UnityYAMLMerge tool for merging all YAML files in Unity projects. You can set additional UnityYAMLMerge parameters in Rider settings in .
