Group by Dominators
The Group by Dominators view lets you understand how memory is retained in your app. For example, you know that the major part of memory in your app is consumed by strings. Nevertheless, most likely, the subject of your optimizations are not these strings by themselves but data structures that store them. The Group by Dominators view answers the "Who retains the memory" question which is extremely important when analyzing ineffective memory usage. To answer this question properly, you should be acquainted with the concept of dominators.
What is a dominator?
The object A dominates the object B if every path to B from application's roots goes through A. In other words, the object B is retained in memory exclusively by the object A: If A is garbage collected, B is also garbage collected. For example, an array is a dominator for its elements (in case there are no other references to array elements).
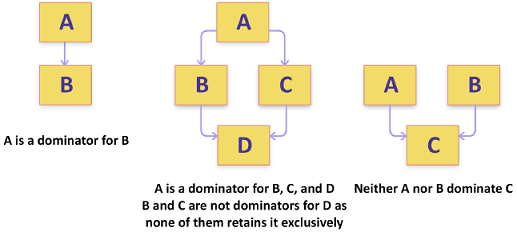
If there are more than one path to an object from app's roots, it is considered as not dominated or not exclusively retained object. For example, if the object C is retained by the objects A and B and A is garbage collected, C will stay in memory (as it is still referenced by B). That's why it is important to understand the difference between the domination path (any object on the path is retained only by one other object) and the retention path (an object on the path may be retained by any number of other objects).
Dominators tree
The list of dominators consists of the following columns:
Name | Description |
|---|---|
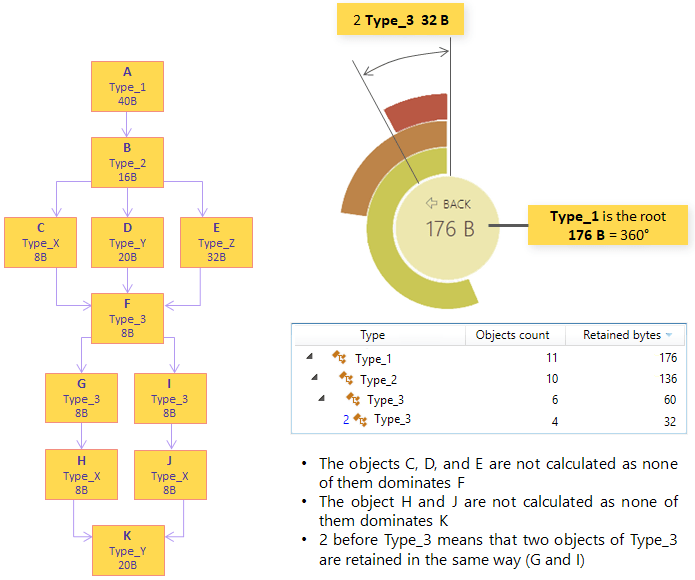
Type | Type name. The number left to the type name shows how many objects of that type are retained that way. For example, elements of some array of integers A are retained in the exact same way (A -> element), but elements of an integer array B have another retention path (B -> element). |
Retained Bytes | The overall size of exclusively retained objects in bytes. |
Retained objects | The number of objects that are dominated by the dominator. |
Example
Filter objects
You can filter out objects that are of no interest to your analysis.
To narrow the list
Start typing the desired type name in the Filter field.
JetBrains Rider will exclude all instances that don't match the pattern.
You can make your search more efficient by using the following tips:
Use CamelHumps. E.g.
fowill return objects of bothSystem.Drawing.FontandMS.Utility.FrugalObjectListtypes.Use special symbols, like wildcards and others. The full list is shown in the table below.
Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Wildcard |
All objects in the set |
All types and namespaces that match the pattern. E.g. | ||
Only namespaces that match the pattern. E.g. | ||
Arrays | ||
| Leave only arrays |
Arrays, containing |
or | Leave only arrays of the specified or higher (if brackets are not closed) dimension |
Arrays with the dimension 3 and higher containing |
Three-dimensional arrays containing | ||
| Exclude arrays from the result |
Objects (excluding arrays) containing |
Generic type arguments | ||
| Leave only types with generic type arguments |
Only objects containing |
Only objects containing | ||
or | Leave only objects with the specified number of generic type arguments |
Objects containing |
Objects containing | ||
| Exclude generic type arguments from the search scope |
Objects (that do not have generic type arguments) containing |
| Search by type, value type, method, or namespace. |
Objects containing |
Select objects for further analysis
In the Group by Dominators view, you can select the following subjects for further analysis:
To open objects retained by a particular dominator
Right-click the dominator and select Open objects retained via this domination path in the context menu.
After this, the Objects retained via [type_name] subject will be added to the analysis path on the left and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.
To open the dominator object set
Right-click the dominator and select Open this object set in the context menu.
After this, the Dominators of [type_name] subject will be added to the analysis path on the left and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.
To select the objects that are exclusively retained by the analyzed objects set
Click the
 Open objects retained by this set button.
Open objects retained by this set button.After this, the Exclusively retained objects subject will be added to the analysis path on the left and the list of desired objects will be displayed in the Group by Types view.