WSL
WSL (WSL 2) - Windows Subsystem for Linux - is a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables natively on Windows 10. Currently, it supports several Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, OpenSUSE, and SLES.
Configure WSL
Download and install a WSL distribution (for instance, Ubuntu) from Microsoft Store.
For this step, be sure to use Windows 10 with the latest “Fall Creators Update” (minimum version 1709, build 16299.15). See the official guide Install the Windows Subsystem for Linux for instructions.
To work with WSL 2, your Windows version should be 10 build 18917 or later. Follow these instructions to switch the distributive.
Run Ubuntu.
Upon the first launch of Ubuntu, the system may prompt you to enable the Windows optional feature. In this case, you need to do the following:
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator and run
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-LinuxRestart your computer.
(Optional) If your Linux distribution doesn't come with
rsync, you need to install it, for example:apt-get install rsyncyum install rsync
You can create a project and store it in the WSL environment, open one from the WSL file system, and develop your projects further in WSL.
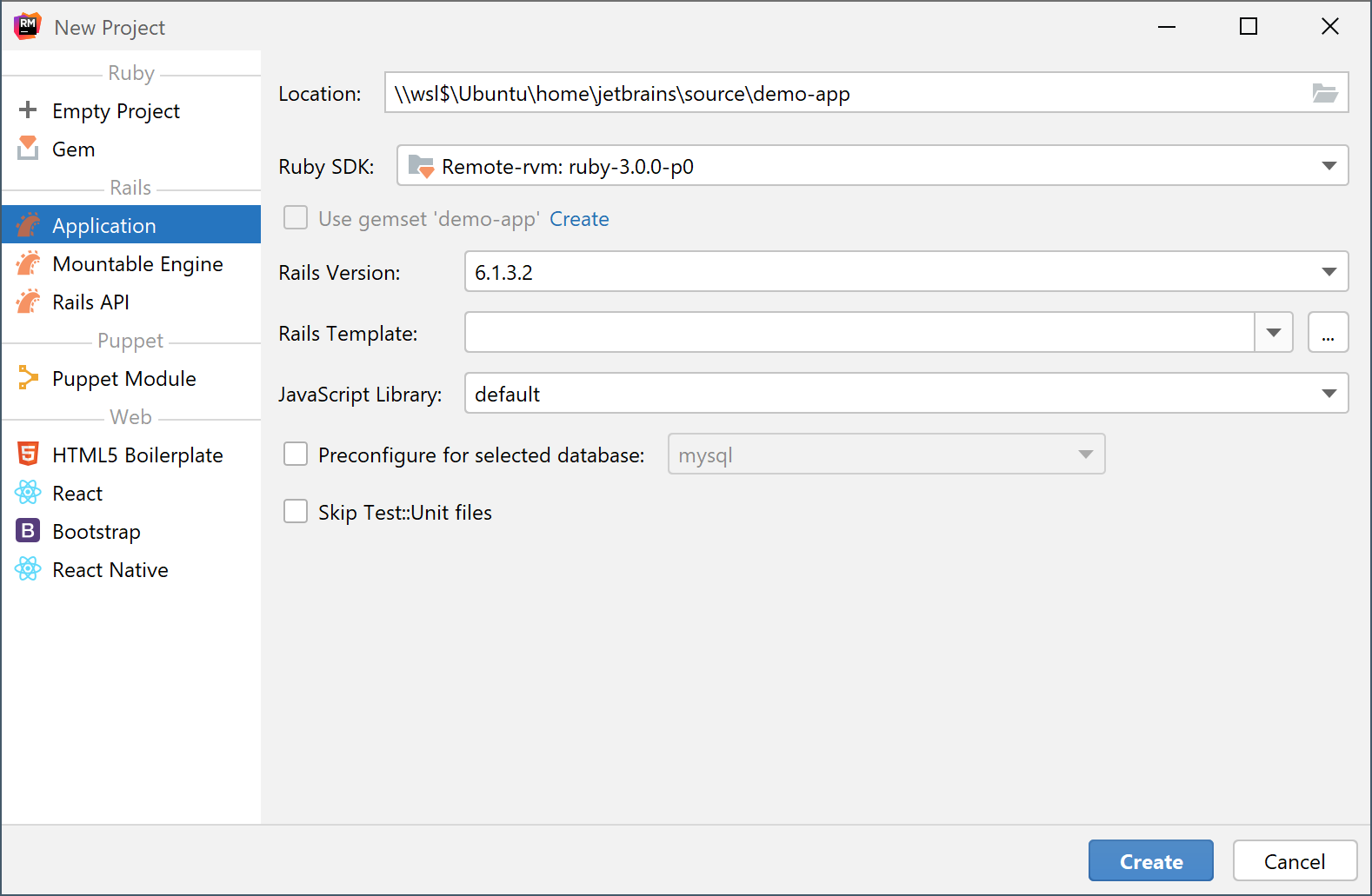
Create a new project in the WSL file system
Install the needed Ruby version to the WSL environment using your favorite SDK manager.
On the welcome screen, click New Project.
On the page that opens, select a type of the project you want to create.
In the Location field, specify the project location. The project location for WSL will show the absolute path starting with \\wsl$ to the WSL file system.
In the Ruby SDK field, select the Ruby interpreter or the version manager executable installed in WSL.
Click Create.
RubyMine creates a project located in WSL and you can develop and build your project inside the WSL environment without leaving the IDE.
Open a project stored in the WSL file system
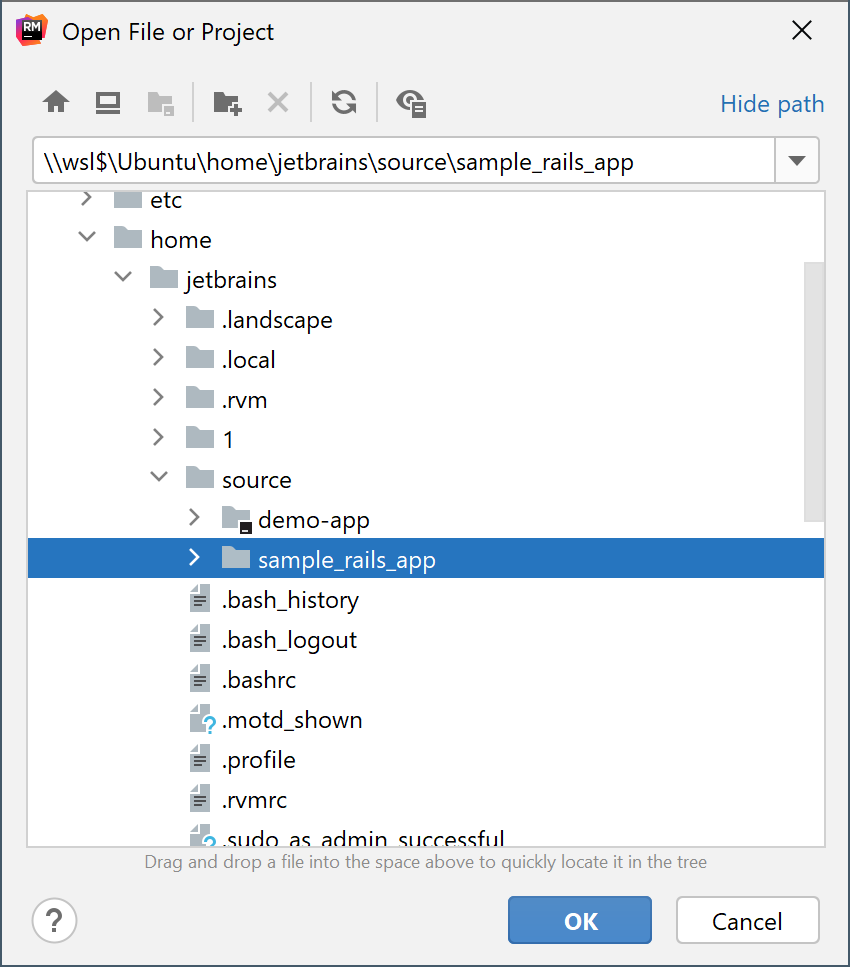
In RubyMine, you can directly open a project stored in the WSL file system and work with it like with any other project.
Click Open on the Welcome screen or select from the main menu.
In the dialog that opens, select the folder in the WSL file system that contains the project to open, or type the path to the \\wsl$ project location manually.
Configure WSL as a remote interpreter
RubyMine allows you to use the remote Ruby interpreter installed on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL and WSL 2) for your local projects.
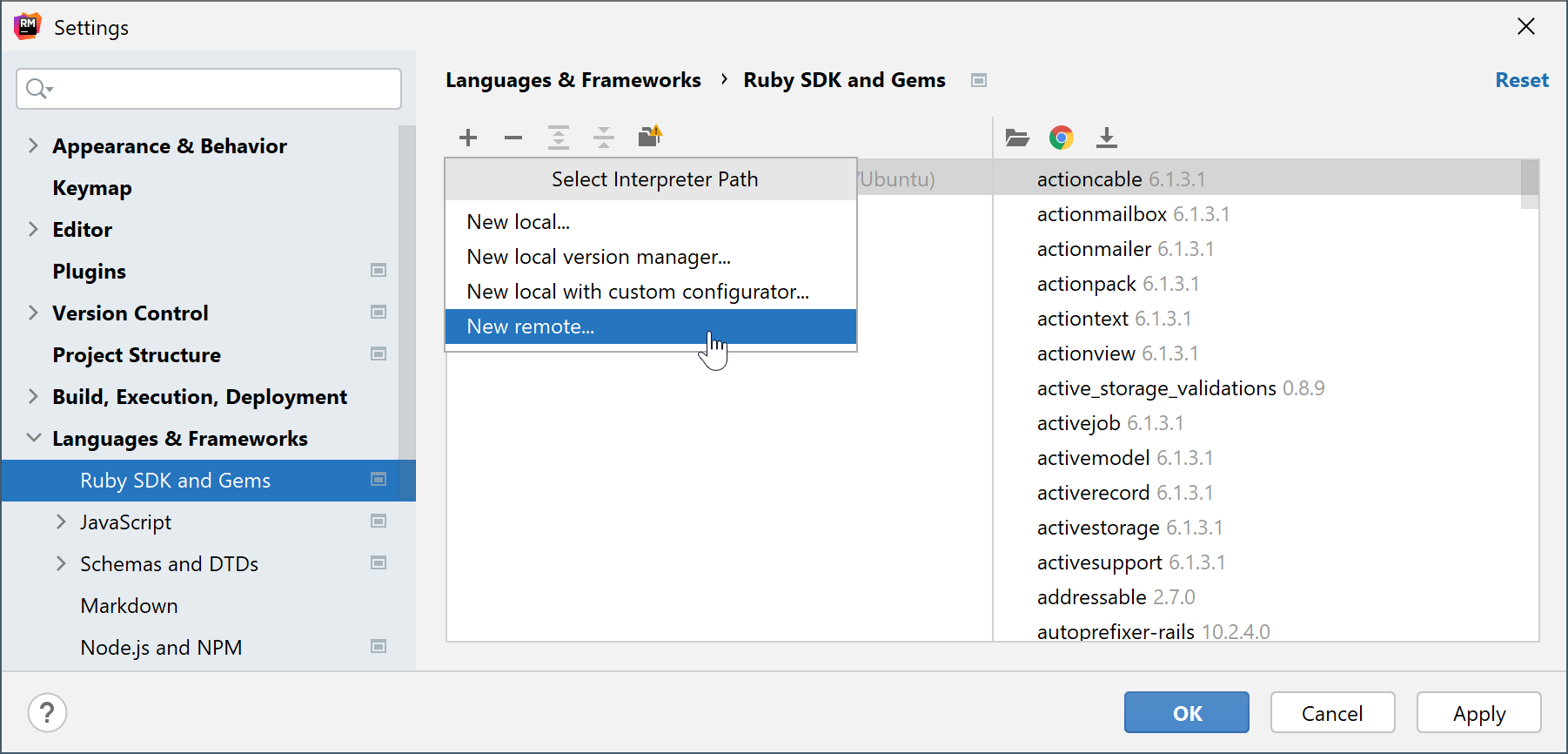
Open the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, go to the Language & Frameworks | Ruby SDK and Gems page.
Click the
and select New remote in the drop-down:
In the invoked dialog, select WSL:
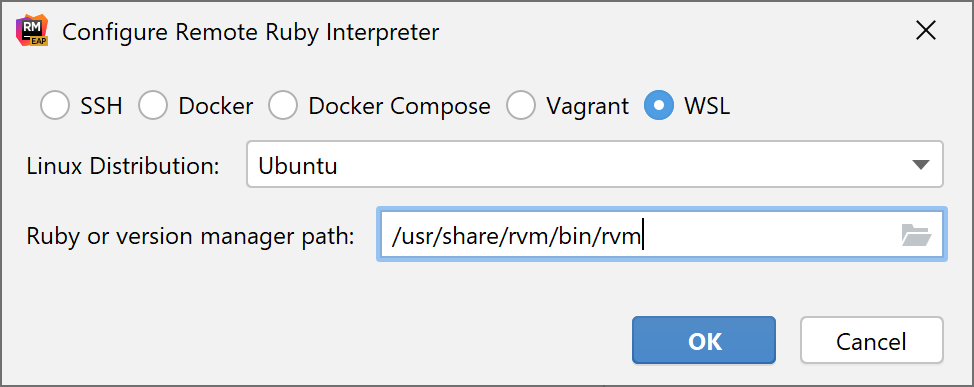
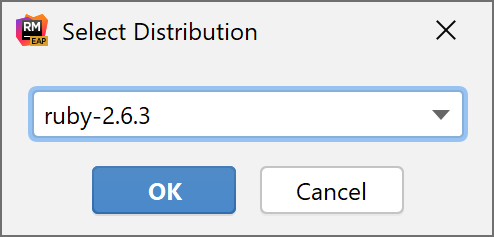
Choose the desired Linux distribution.
In Ruby or version manager path, specify the path to the Ruby interpreter or the version manager executable. Click OK.
(Optional) If you specified a path to the version manager executable in the previous dialog, RubyMine suggests selecting the Ruby interpreter used to run a remote application:
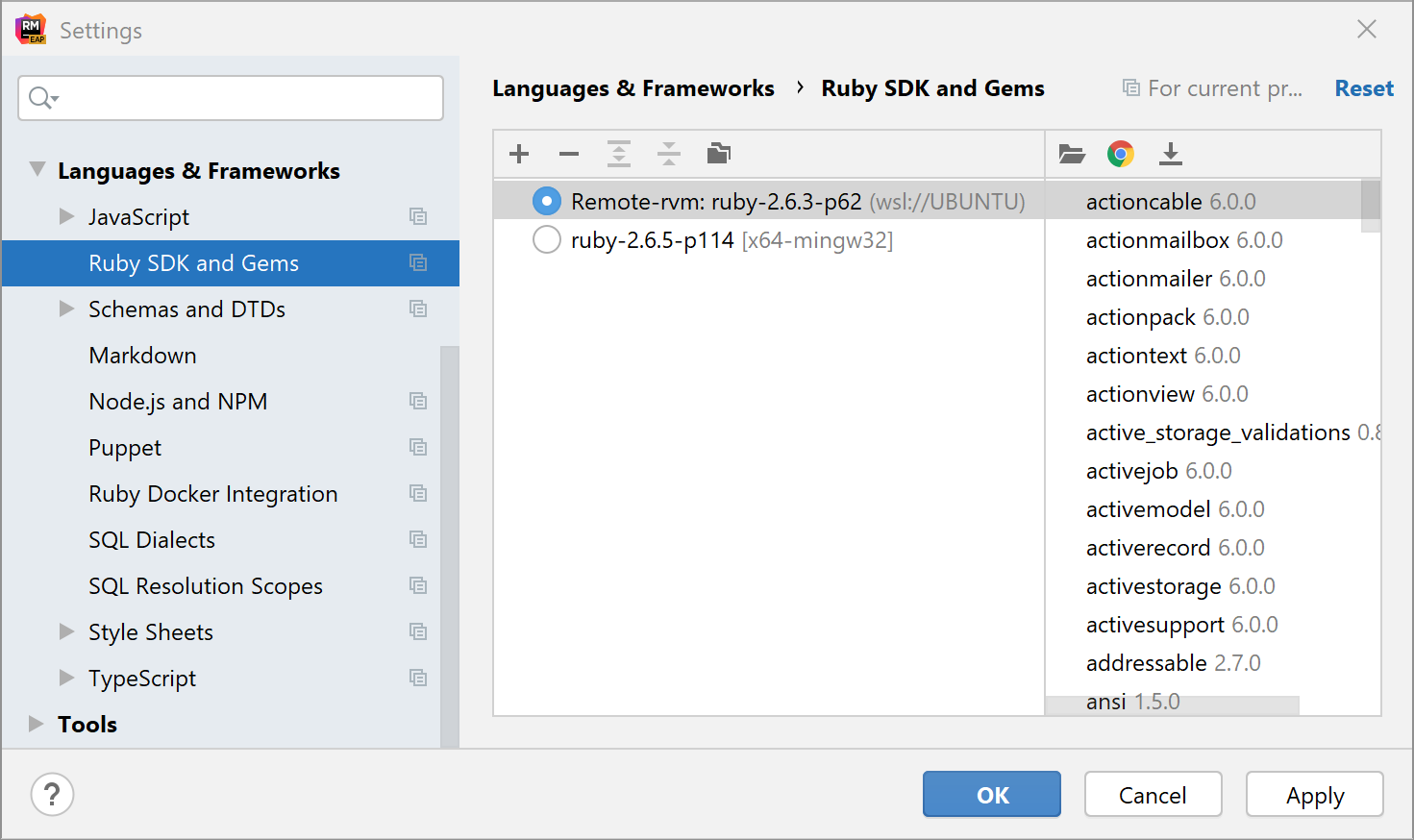
Select the added SDK in the Ruby SDK and Gems page:
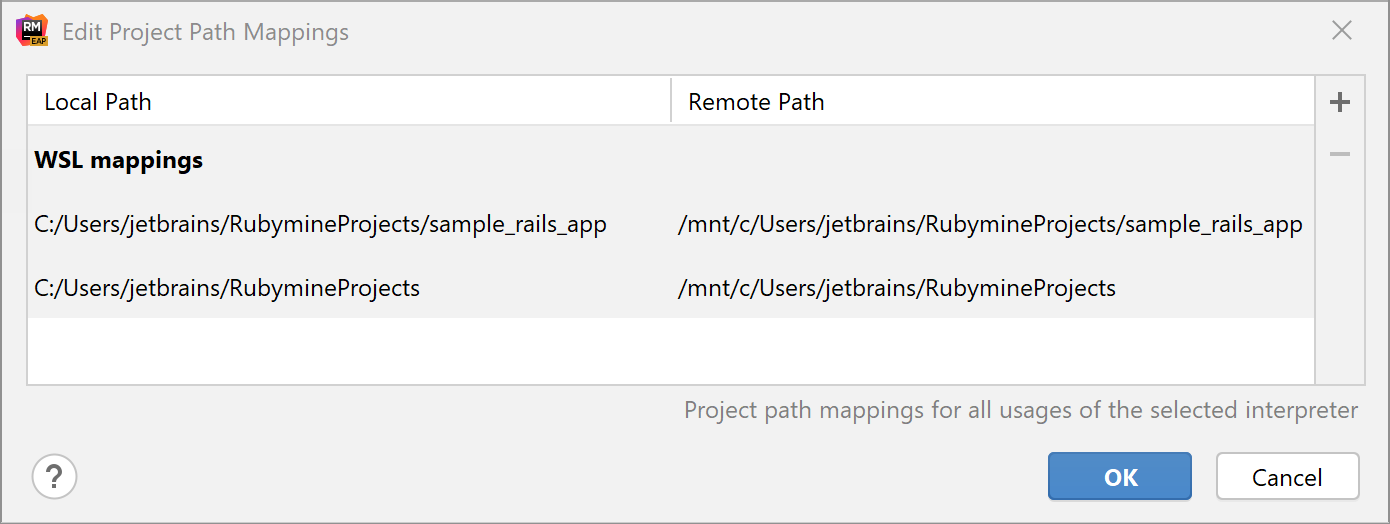
(Optional) If you want to use the added SDK to debug a remote process, specify mappings between files of a local and remote project. To do this, click the Edit Path Mappings
button. In the Edit Project Path Mappings dialog, specify the local and remote project root paths:
Custom WSL distributions
RubyMine allows you to use custom Linux distributions run on WSL. This can be done by editing the wsl.distributions.xml configuration file created by RubyMine automatically after detecting WSL.
Add a custom distribution
Open the %APPDATA%\JetBrains\<product><version>\config\options\wsl.distributions.xml file.
Add the
descriptorelement and provide settings to access your custom distribution. Note that theidvalue should be unique. For example:<!-- ... --> <descriptor> <id>DEBIAN_CUSTOM</id> <microsoft-id>Debian</microsoft-id> <executable-path>debian-custom.exe</executable-path> <presentable-name>Debian GNU/Linux - Custom</presentable-name> </descriptor> <!-- ... -->You can specify
executable-pathin two ways:Specify the executable name of a custom distribution. In this case, RubyMine will find a custom distribution in %LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\WindowsApps.
Specify the absolute path to the custom distribution executable.
Restart RubyMine and add your custom distribution as a remote interpreter.