User Parameters
Depending on the database vendor, the question mark ? is treated as a parameter in SQL statements. On this page, you can specify what other characters and their sequences should be treated as parameters, and in which places.
The patterns for SQL parameters are specified by means of regular expressions.
Running parameterized statements
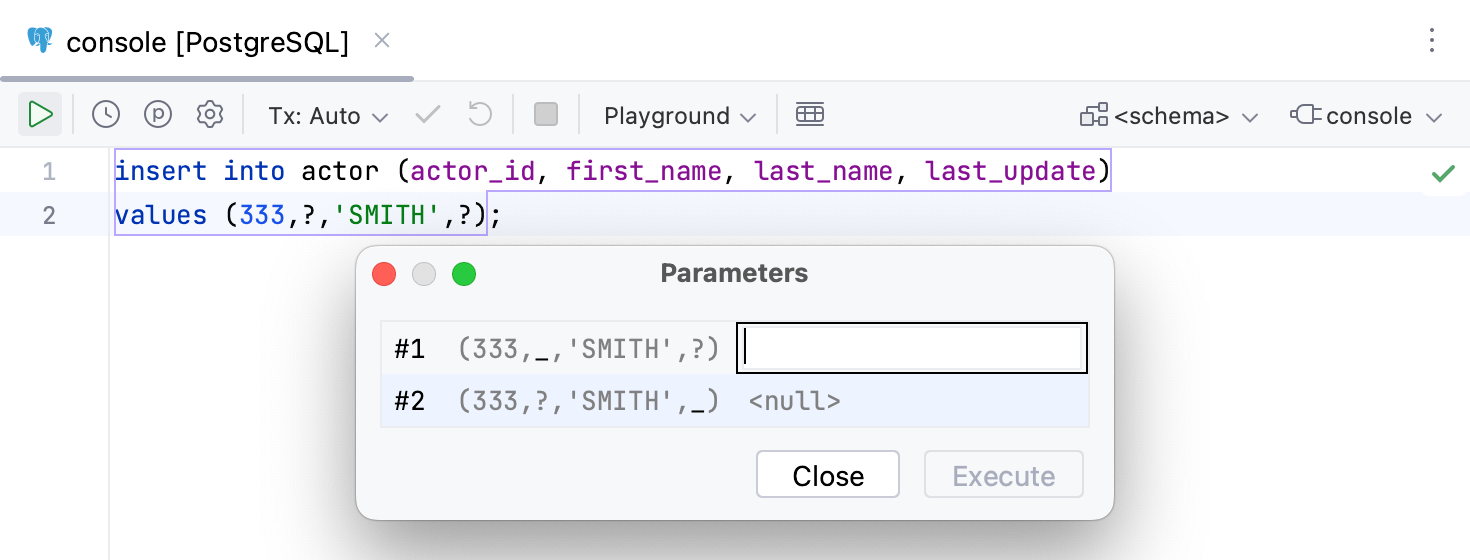
If you have parameters in your statement, you must specify the values of the parameters before you execute the statement.
To execute a parameterized statement, click the Execute button (
) on the toolbar and enter values in the second column. Alternatively, to open the Parameters dialog, click the View Parameters button (
).
Configure settings for user parameters
Open settings by pressing Control+Alt+S and navigate to .
Examples
Array as a parameter
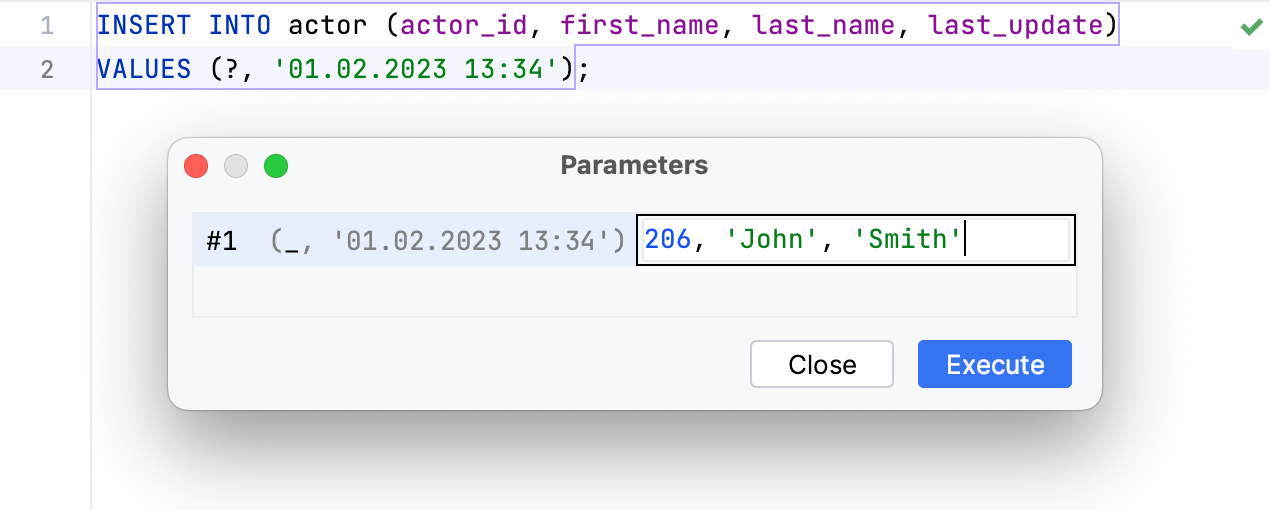
In RubyMine, the replacement of a parameter with a value is straightforward. To use an array as the value, specify your array in the corresponding field.
In the following example, the ? parameter can be replaced with 206, 'John', 'Smith' value:
For further information on parameters, refer to the database documentation.
Parameter pattern
If you have parameters with a specific parameter syntax in your scripts, specify the pattern using a regular expression.
For the following example, the %{2}(\w+_\d+) pattern must be set:
User parameters
Item | Description |
|---|---|
Enable in query consoles and SQL files | Apply parameter patterns to SQL in SQL files and database consoles. You can limit the usage scope at the level of individual patterns. If this checkbox is cleared, the patterns are not used in SQL files and consoles irrespective of the usage scope that is specified for individual patterns. |
Enable in string literals with SQL injection | Apply parameter patterns to string literals injected with SQL. If necessary, you can limit the usage scope at the level of individual patterns. If this checkbox is cleared, the patterns are not used in string literals irrespective of the usage scope that is specified for individual patterns. |
Substitute inside SQL strings | Apply parameter patterns to string literals in the SQL code. For example, consider the following code. SELECT ${column_name}
FROM actor
WHERE actor_id='${actor_id}' If the checkbox is cleared, RubyMine will find only the  But if you select the Substitute inside SQL strings option, the  |
Parameter patterns | List of parameter patterns and their usage scopes. The patterns are specified using regular expressions. Values that start with a colon (
Use To edit a pattern or its usage scope, click the pattern and use the following controls:
|