OAuth 2.0 authorization
The HTTP Client supports OAuth 2.0 authorization. You can get an access token and authenticate your request to OAuth 2.0 protected resources. To let you enter the user credentials, the HTTP Client displays the login form in the built-in JCEF browser. This non-modal browser doesn't prevent you from working in the IDE, allowing you, for example, to copy and paste your username and password.
A typical flow includes the following steps:
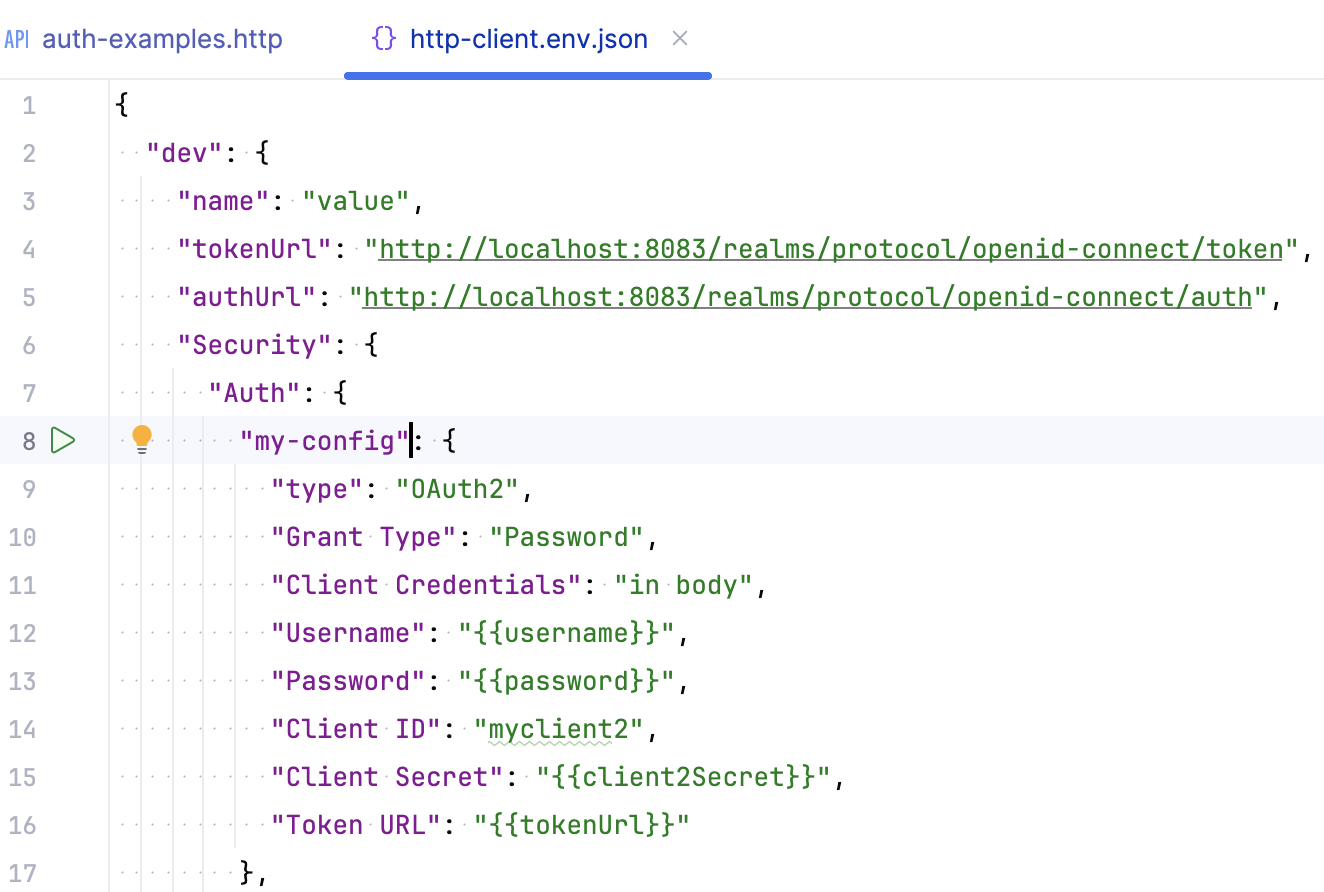
Specify authentication settings, such as the grant type and token URL, in JSON format in a public environment file.
Refer to this authentication configuration in your HTTP requests using the
$auth.tokenvariable.Run the request. If authentication is successful, you will access the protected resource. You can check the received access token and refresh token in the HTTP Client Authentication Log or in the Services tool window.
You can also manually refresh the access token or re-initialize the authentication procedure by requesting a new token.
In an .http file, in the Run with list, select an environment to which you want to add an authentication configuration.
In the toolbar, click
and select Auth Configuration.
This will add an authentication configuration template to the public environment file, in the
"Auth"object under"Security"of the selected environment. For example:{ "dev": { "Security": { "Auth": { "auth-id": { "Type": "OAuth2", "Grant Type": "", "Client ID": "" } } } } }Replace the placeholder
auth-idwith a meaningful name that you will use to refer to this configuration in your .http file.Specify the authentication parameters. The required parameters depend on the selected
"Grant Type". Use RubyMine coding assistance while filling out the authentication parameters: Start typing a parameter name or press CtrlSpace to get the list of available JSON keys.tip
You can also use the dedicated live template: under
"Auth", start typingauthand press Enter. Depending on the value that you select in"Grant Type", RubyMine will add the required fields to the configuration.If you want to quickly add all parameters available for the authentication configuration, press AltEnter (Show Context Actions) and select Fill-in all properties from JSON-schema.
Once an authentication configuration is created, you can use it to get an access token and authenticate your requests.
Pass the name of an authentication configuration to the
{{$auth.token()}}variable, for example,{{$auth.token("my-config")}}. You can use this variable in the requestAuthorizationheader or in query parameters.Click
to send the request. Before accessing the protected resource, the HTTP Client will send a request to the authorization server to obtain an access token.
When prompted, complete the authentication process. If the authentication is successfully completed, the HTTP Client will access the protected resource.
To quickly add the {{$auth.token()}} variable, you can use live templates: Under the HTTP method, in the header section, start typing AuthorizationToken and select an available authentication from the list of suggestions that appears.
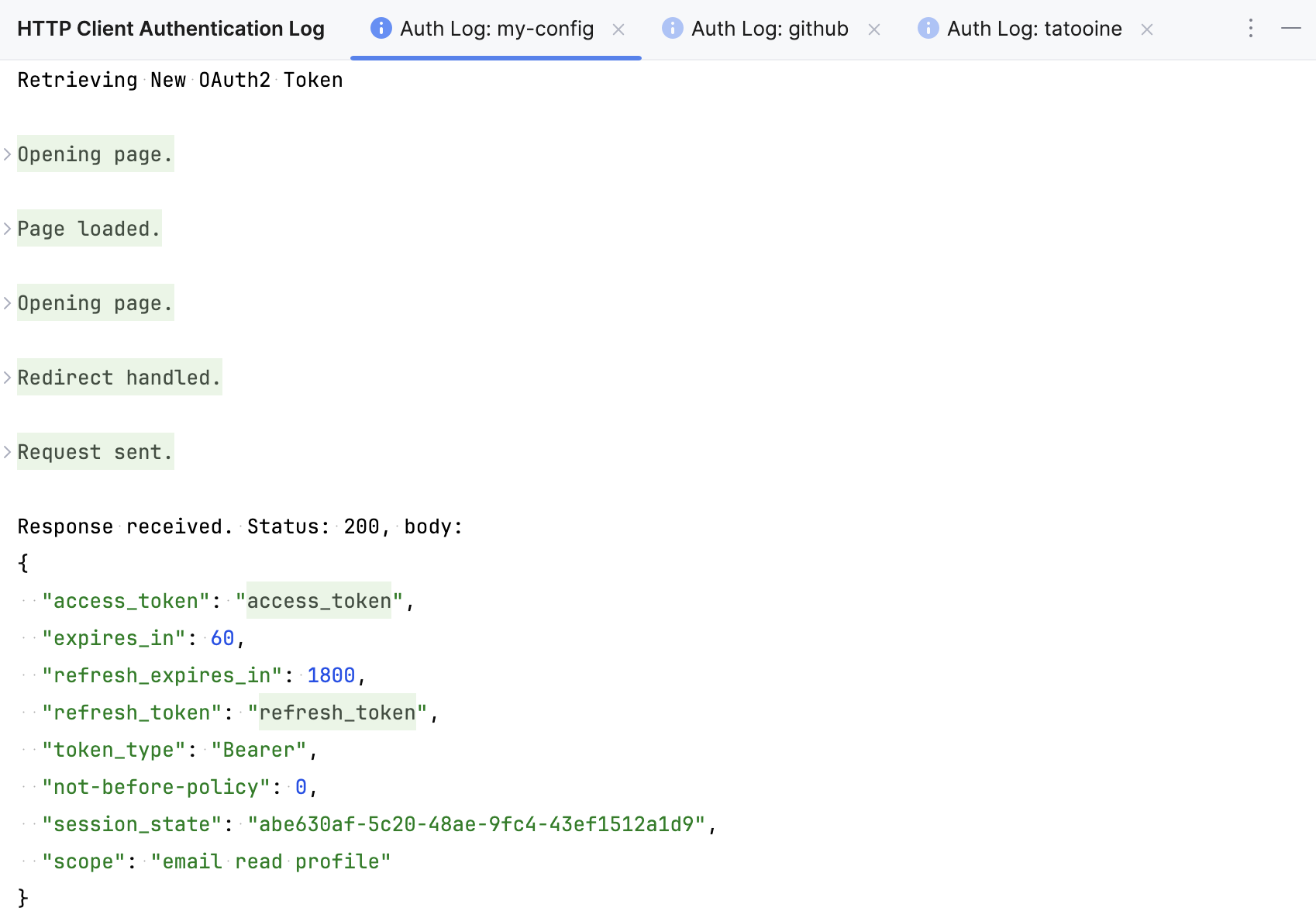
When you run such a request, the Show Auth Log button will be available in the Services tool window. It lets you view the redirect page, access token, and other authentication details.
When you refer to an authentication configuration in an HTTP request, the HTTP Client automatically gets (or refreshes) an access token before accessing the protected resource. If you want to get an access token without sending an actual request to the protected resource, you can acquire the access token manually.
In the http-client.env.json file, click
next to your authentication configuration name.
tip
Alternatively, place the caret on the
$auth.tokenvariable in an HTTP request, press AltEnter (Show Context Actions), and select Acquire or refresh Auth token.If the authentication configuration contains private variables, select a private environment file in the popup that appears.
When prompted, complete the authentication process.
If the authentication is completed successfully, RubyMine will get the access token. If you already have the access token, but it has expired, RubyMine will refresh it.
Besides refreshing the token, you can get a new one by re-authenticating, that is, by repeating the original flow that you used to get the initial access token.
In the http-client.env.json file, place the caret on the authentication configuration name.
Press AltEnter (Show Context Actions), and select Force Acquire Auth Token.
If the authentication configuration contains private variables, select a private environment file in the popup that appears.
You can invoke the same action when your caret is on the $auth.token variable in the .http file. In this case, you don't need to select a private environment file because the HTTP Client will use the one located in the same folder as your .http file.
tip
The authorization server may store your authentication data in cookies of the built-in JCEF browser. In this case, you will be automatically authenticated and won't need to enter user credentials until the cookies expire.
When you refresh or get a new token, the access and refresh token and other authentication details are displayed in the HTTP Client Authentication Log tool window (View | Tool Windows | HTTP Client Authentication Log).
- Grant Type
Method to get access tokens. Possible values:
"Authorization Code","Implicit","Password", and"Client Credentials".- Auth URL
Authorization URL to which the application will redirect the client request to get the auth code.
"Auth URL"is required for Authorization Code and Implicit grant types.- Token URL
The provider's authentication server, to exchange an authorization code for an access token.
"Token URL"is required for Authorization Code, Password, and Client Credentials grant types.- Redirect URL
Client application callback URL to which the request should be redirected after authentication.
- Client ID
Public identifier of your client registered with the API provider. The parameter is required for all grant types.
- Client Secret
Confidential identifier used by a client application to authenticate to an authorization server. The parameter is required for the Client Credentials grant type.
- Client Credentials
Enter one of the following:
"none"if you do not want to specify client credentials in the request."in body"if you want to send client credentials in the request body."basic"to send a Basic authentication request in the request header (default value).
- Scope
A scope to limit an application's access to a user's account. Possible values depend on the service you are trying to access.
- Acquire Automatically
By default, the HTTP Client refreshes or acquires an access token automatically before sending the request. Enter
"Acquire Automatically": falseif you do not want to automatically refresh or acquire an access token before sending the request. You can refresh or acquire manually.- Password
The user's password sent as part of authorization, used with the Password grant type. To avoid sharing your password, you can use a private variable instead of the value, for example,
"Password": "{{password}}".
Thanks for your feedback!