Ruby version managers
The most popular way to install Ruby on Linux or macOS is using a version manager, for example, RVM or rbenv. Version managers allow you to install several Ruby versions on your machine and quickly switch between them. RubyMine automatically detects interpreters installed on a local machine and maintained by the following version managers:
You can switch between Ruby interpreters (and gemsets for RVM and rbenv) on the Ruby Interpreters page for existing projects, and choose the desired interpreter when creating a new project.
Auto-suggested Ruby interpreter/gemset
Version managers support various types of configuration files used to switch a project's Ruby version and gemset. For example, you can set the Ruby interpreter version to 2.6.3 and the gemset to sample_rails_app in one of the following ways:
Using the .ruby-version/.ruby-gemset files
ruby-2.6.3sample_rails_appUsing the .versions.conf file
ruby=2.6.3 ruby-gemset=sample_rails_app
RubyMine will show a notification if there is a mismatch in the interpreter settings for the project's Ruby modules:
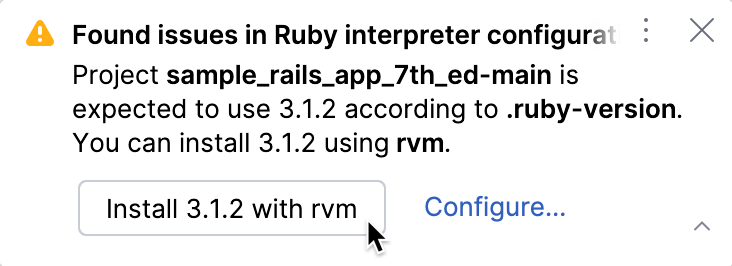
If RubyMine detects the required Ruby version installed on your machine, it will suggest setting it as the interpreter for the current project. Click the button in the notification to switch.

For Linux/macOS only: If the required Ruby version is not found and you use rbenv, RVM, or asdf, RubyMine will suggest installing it using your version manager.
Remote Ruby interpreters
RubyMine allows you to use remote Ruby interpreters maintained using version managers. In this case, you have to specify a path to the version manager executable when configuring a remote interpreter. For instance, the following table lists typical paths for Linux.
Version manager | Executable path |
|---|---|
RVM | Single-user mode: /home/jetbrains/.rvm/bin/rvm (for the jetbrains user) Multi-user mode: /usr/local/rvm/bin/rvm Mixed mode: /usr/share/rvm/bin/rvm |
rbenv | /home/jetbrains/.rbenv/bin/rbenv (for the jetbrains user) /usr/bin/rbenv |
chruby | /usr/local/share/chruby/chruby.sh |
asdf | /home/jetbrains/.asdf/bin/asdf (for the jetbrains user) |
Mise | /home/jetbrains/.local/bin/mise (for the jetbrains user) |
Debug Ruby interpreter detection
If you have issues with detecting local Ruby interpreters maintained by your version manager, follow the steps below to help us determine the cause of the problem:
Open RubyMine and go to in the main menu.
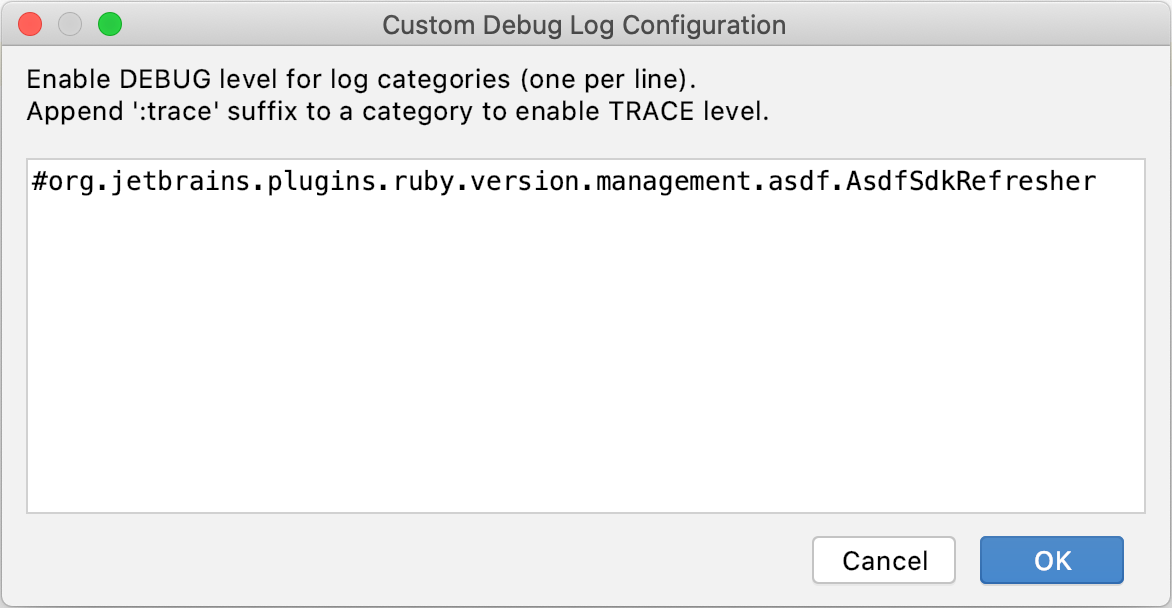
In the invoked dialog, specify a logger identifier for your version manager:
RVM:
#org.jetbrains.plugins.ruby.version.management.rvm.RvmSdkRefresherrbenv:
#org.jetbrains.plugins.ruby.version.management.rbenv.RbenvSdkRefresherchruby:
#org.jetbrains.plugins.ruby.version.management.chruby.ChrubySdkRefresherasdf:
#org.jetbrains.plugins.ruby.version.management.asdf.AsdfSdkRefresherMise:
#org.jetbrains.plugins.ruby.version.management.mise.MiseSdkRefresher
Click OK.
Restart RubyMine.
Open a log file and make sure it contains entries corresponding to your version manager, for example:
2018-07-30 16:57:18,237 [7350] DEBUG - management.asdf.AsdfSdkRefresher - Refreshing sdksCreate an issue and attach the logs.