Linting TypeScript
The recommended linter for TypeScript code is ESLint which brings a wide range of linting rules that can also be extended with plugins. WebStorm shows warnings and errors reported by ESLint right in the editor, as you type. Learn more from ESLint.
WebStorm highlights errors reported by ESLint in .ts and .tsx files when @typescript-eslint/parser is set as a parser in your project ESLint configuration. Learn more from the readme file in the typescript-eslint repo.
Before you start
Make sure you have Node.js on your computer.
Configure a Node.js runtime in your project as described in Configuring a local Node.js interpreter, in Using Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux, or in Configuring remote Node.js runtimes.
Install ESLint
ESLint version 9 and later
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install --save-dev eslint @eslint/js typescript typescript-eslintpnpm add --save-dev eslint @eslint/js typescript typescript-eslintyarn add --dev eslint @eslint/js typescript typescript-eslint
Learn more from the typescript-eslint official website.
ESLint version 8 and earlier
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install --save-dev @typescript-eslint/parser @typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin eslint typescriptpnpm add --save-dev eslint @eslint/js typescript-eslintyarn add --dev eslint @eslint/js typescript-eslint
Learn more from the typescript-eslint official website.
Configuration file
Depending on the ESLint version you are using, WebStorm recognizes configurations in the following file types:
ESLint version 9 and later
eslint.config.js, eslint.config.mjs, or eslint.config.cjs (flat format), learn more from the ESLint official website.
You can also use configuration files written in TypeScript, such as, eslint.config.ts, eslint.config.mts, or eslint.config.cts. To do that, you need to specify the unstable_ts_config flag.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Select Manual ESLint Configuration.
In the Extra eslint options field, type
--flag unstable_ts_config.Click Apply to save the changes and close the dialog.
ESLint version 8 and earlier
.eslintrc.* (.eslintrc, .eslintrc.json, or .eslintrc.yaml file, or a file in another supported format).
.eslintignore
package.json with a
eslintIgnoreor aeslintConfigproperty. This configuration system is deprecated, learn more from the ESLint official website.
Learn how to switch to the flat format from ESLint configuration migration guide.
Create and edit a configuration file
Open a configuration file or create a new one in the root of your project. Populate the configuration file depending on the ESLint version you are using:
// @ts-check import eslint from '@eslint/js'; import tseslint from 'typescript-eslint'; export default tseslint.config( eslint.configs.recommended, tseslint.configs.recommended, );Learn more from the typescript-eslint official website.
/* eslint-env node */ module.exports = { extends: ['eslint:recommended', 'plugin:@typescript-eslint/recommended'], parser: '@typescript-eslint/parser', plugins: ['@typescript-eslint'], root: true, };Learn more from the typescript-eslint official website.
Configure ESLint in WebStorm
By default, ESLint is configured automatically. You can choose to specify all the configuration settings manually or disable ESLint.
Learn more from ESLint.
Suppress linting TypeScript code with ESLint
If you are already using
@typescript-eslint/parserbut you do not want to check TypeScript code with ESLint, add .ts or .tsx to the .eslintignore file.
Lint your code
When installed and enabled, ESLint activates automatically every time you open a TypeScript file. You can also configure ESLint to detect and fix problems automatically on save.
By default, WebStorm marks detected problems based on the severity levels from the ESLint configuration. See Configuring ESLint highlighting to learn how to override these settings.
Descriptions of the errors detected in the current file and quick-fixes for them are available from the editor and from the File tab of the Problems tool window.
Errors in all previously opened files and quick-fixes for them are shown in the Project Errors tab of the Problems tool window. To open the tool window, click the Inspection widget in the upper-right corner of the editor:
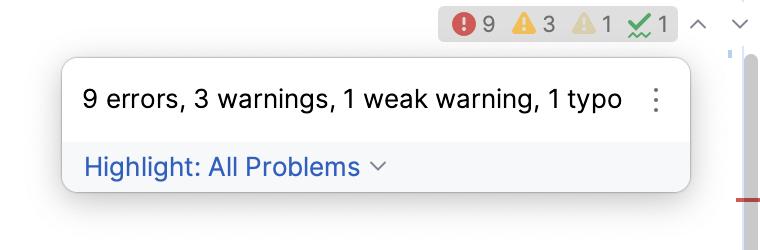
For more information, refer to View problems and apply quick-fixes in the editor and Problems tool window.
To view the description of a problem in the editor, hover over the highlighted code.
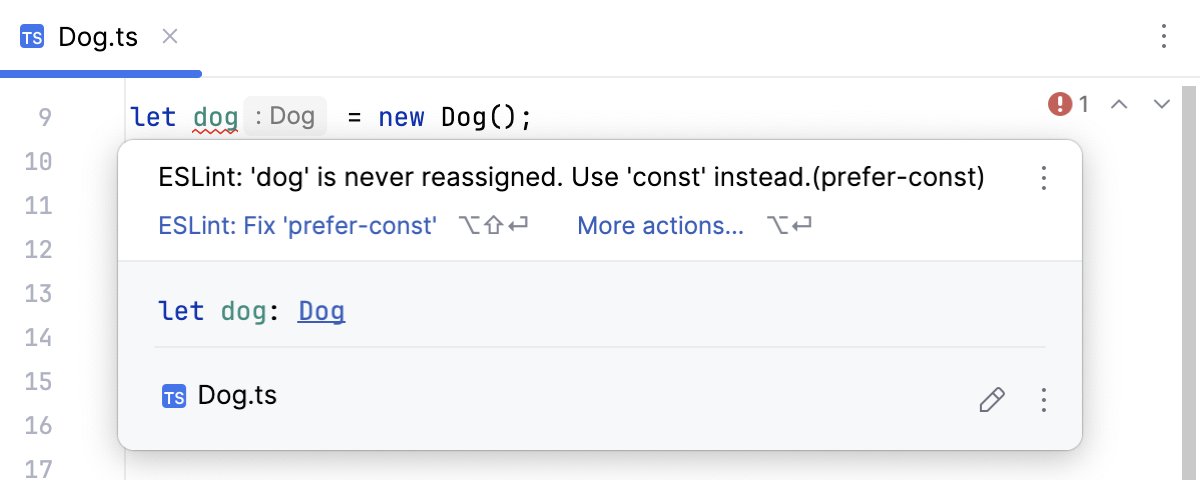
To resolve the detected problem, click ESLint: Fix '<rule name>' or press Alt+Shift+Enter.
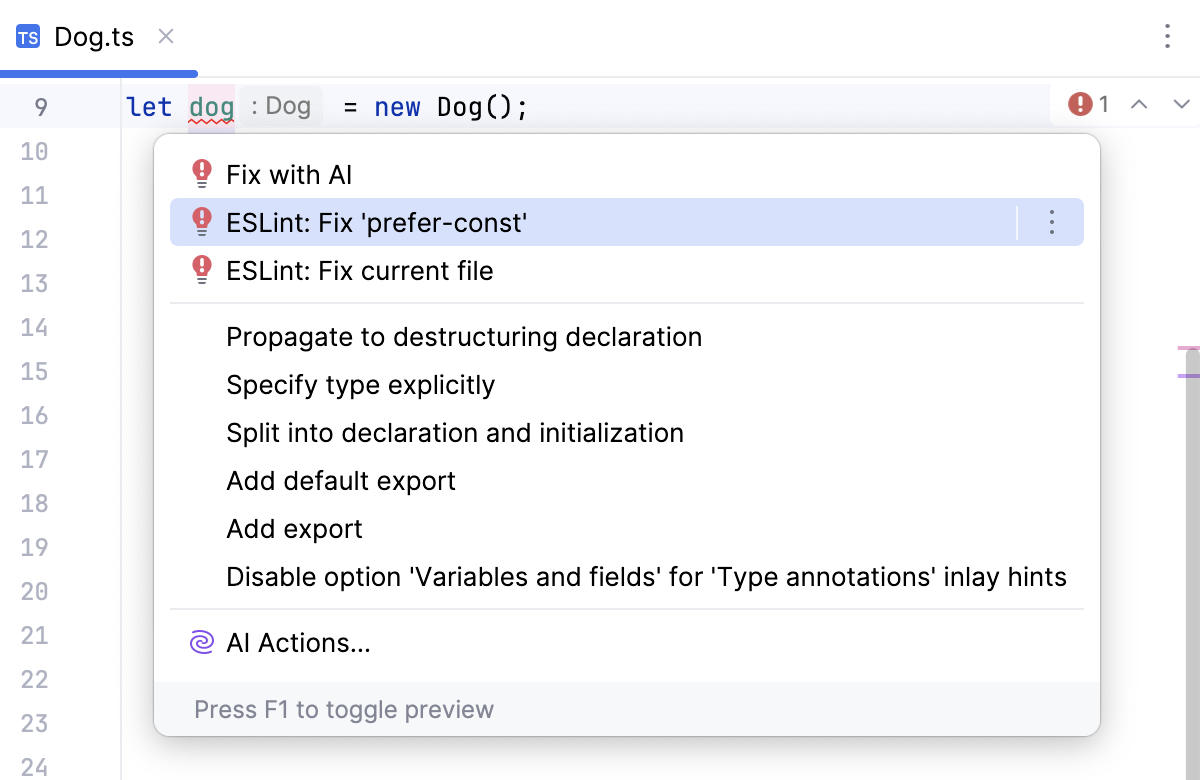
To resolve all the detected problems in the current file, click More actions (Alt+Enter) and select from the list.
Alternatively, open the File tab of the Problems tool window Alt+6, where you can view problem descriptions, apply quick-fixes, navigate to the fragments in the source code where errors occurred, as well as fix them in the Editor Preview pane without leaving the tool window.
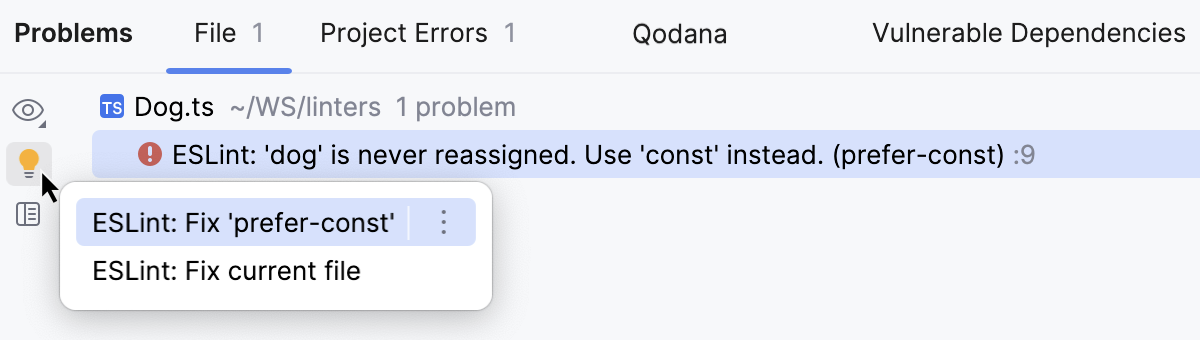
Learn more from Problems tool window.
You can also configure ESLint to fix all the problems in a file when this file is saved. To configure such behavior, select the Run eslint --fix on save checkbox on the ESLint page of the Settings dialog as described in Activating and configuring ESLint in WebStorm.
Learn more from View problems and apply quick-fixes in the editor and from ESLint.
TSLint
You can also use the TSLint code verification tool from inside WebStorm and check your TypeScript code for the most common mistakes without running the application. When the tool is activated, it lints all the opened TypeScript files and marks the detected problems.
To view the description of a problem, hover over the highlighted code. By default, WebStorm marks detected problems based on the severity levels from the TSLint configuration file. See Configuring TSLint highlighting to learn how to override these settings.
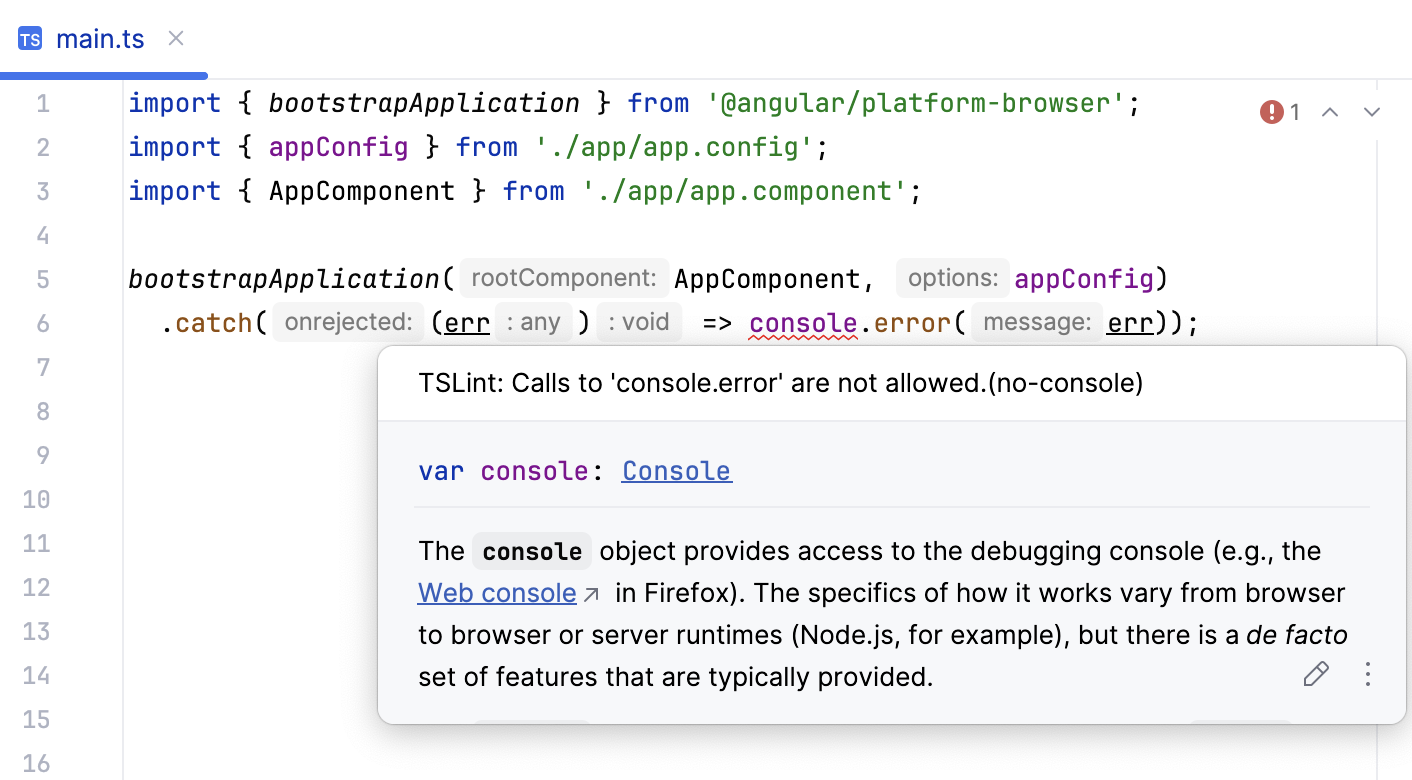
Before you start
Make sure you have Node.js on your computer.
Make sure a local Node.js runtime is configured in your project: open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) and go to . The Node runtime field shows the default project Node.js runtime. Learn more from Configuring a local Node.js interpreter.
Make sure the TSLint bundled plugin is enabled in the settings. Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select . Click the Installed tab. In the search field, type TSLint. For more information about plugins, refer to Managing plugins.
Install TSLint
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
npm install tslint typescript --save-devLearn more from the TSLint official website.
Create TSLint configuration file
In the embedded Terminal (Alt+F12) , type:
cd <project root> tslint --init
Activate and configure TSLint in WebStorm
By default, WebStorm uses the TSLint package from the project node_modules folder and the tslint.json configuration file from the folder where the current file is stored. If no tslint.json configuration file is found in the current file folder, WebStorm will look for one in its parent folders up to the project root.
If you have several package.json files with TSLint listed as a dependency, WebStorm starts a separate process for each package.json and processes everything below it. This lets you apply a specific TSLint version or a specific set of plugins to each path in a monorepo or a project with multiple TSLint configurations.
This behavior is default in all new WebStorm projects. To enable it in a previously created project, go to in the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) and select the Automatic TSLint configuration option.
You can also configure TSLint manually to use a custom TSLint package and tslint.json and specify some additional rules.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to .
Select the Manual Configuration option.
Specify the path to the TSLint package.
In the Configuration File area, appoint the configuration to use.
By default, WebStorm first looks for a tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml configuration file. WebStorm starts the search from the folder where the file to be checked is stored, then searches in the parent folder, and so on until reaches the project root. If no tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml configuration file is found, TSLint uses its default embedded configuration file. Accordingly, you have to define the configuration to apply either in a tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml configuration file, or in a custom configuration file, or rely on the default embedded configuration.
To have WebStorm look for a tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml file, choose the Automatic search option.
To use a custom file, choose the Configuration File option and specify the location of the file in the Path field. Choose the path from the list, or type it manually, or click
and select the relevant file from the dialog that opens.
Learn more about configuring TSLint from the TSLint official website.
If necessary, in the Additional Rules Directory field, specify the location of the files with additional code verification rules. These rules will be applied after the rules from tslint.json, tslint.yaml, tslint.yml, or from the above specified custom configuration file and accordingly will override them.
Configure highlighting for TSLint
By default, WebStorm marks the detected errors and warnings based on the severity levels from the TSLint configuration file. For example, errors are highlighted with a red squiggly line, while warnings are marked with a yellow background. For more information, refer to Code inspections and Change inspection severity.
Change the severity level of a rule in the TSLint configuration
In TSLint configuration file, locate the rule you want to edit and set its ID to
warningor toerror. Learn more from the TSLint official website.
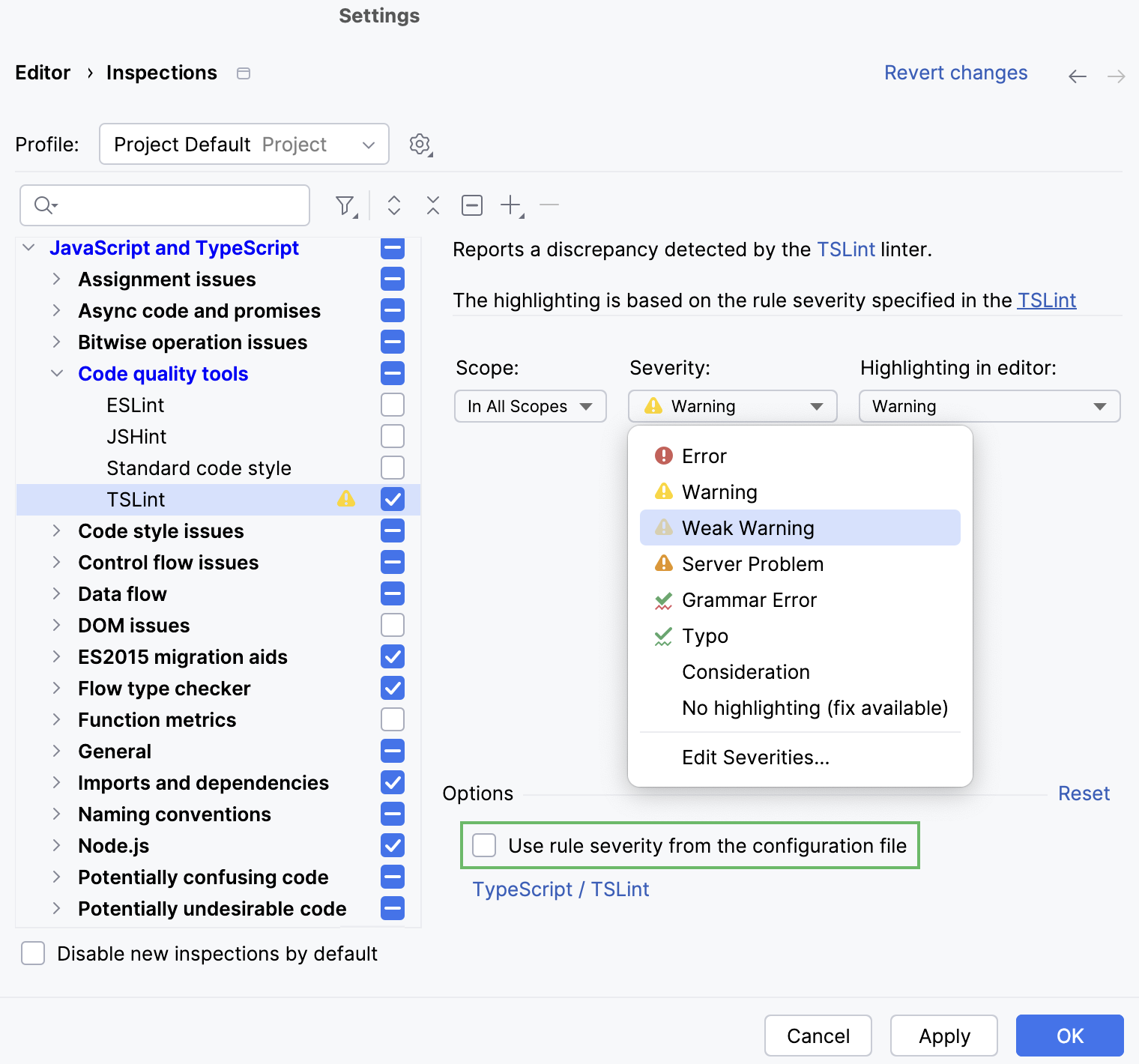
You can override the severities from the TSLint configuration file so that WebStorm ignores them and shows everything reported by the linter as errors, warnings, or in a custom color.
Ignore the severity levels from the configuration
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to . The Inspections page opens.
In the central pane, go to JavaScript and TypeScript | Code quality tools | TSLint.
In the right pane, clear the Use rule severity from the configuration file checkbox and select the severity level to use instead of the default one.
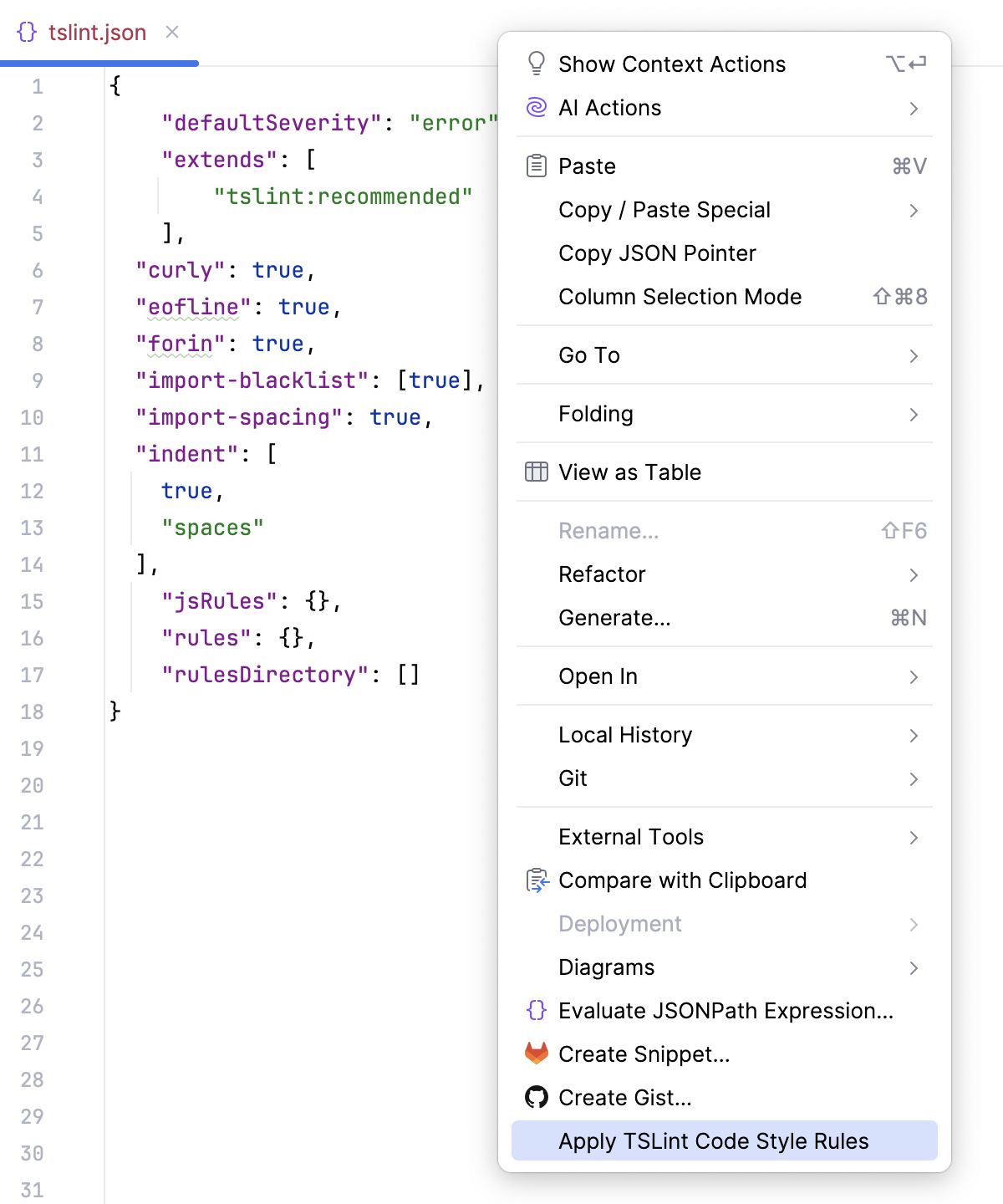
Import code style from a TSLint configuration file
WebStorm understands some TSLint rules that are described in tslint.json, tslint .yaml, or tslint.yml configuration files and lets you apply them to the TypeScript code style configuration in your project.
When you open your project for the first time, WebStorm imports the code style from the project tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml automatically.
If tslint.json, tslint.yaml, or tslint.yml is updated (manually or from your version control), open it in the editor and choose Apply TSLint Code Style Rules from the context menu.
TSLint quick-fixes
WebStorm lets you automatically fix some of the issues that TSLint reports.
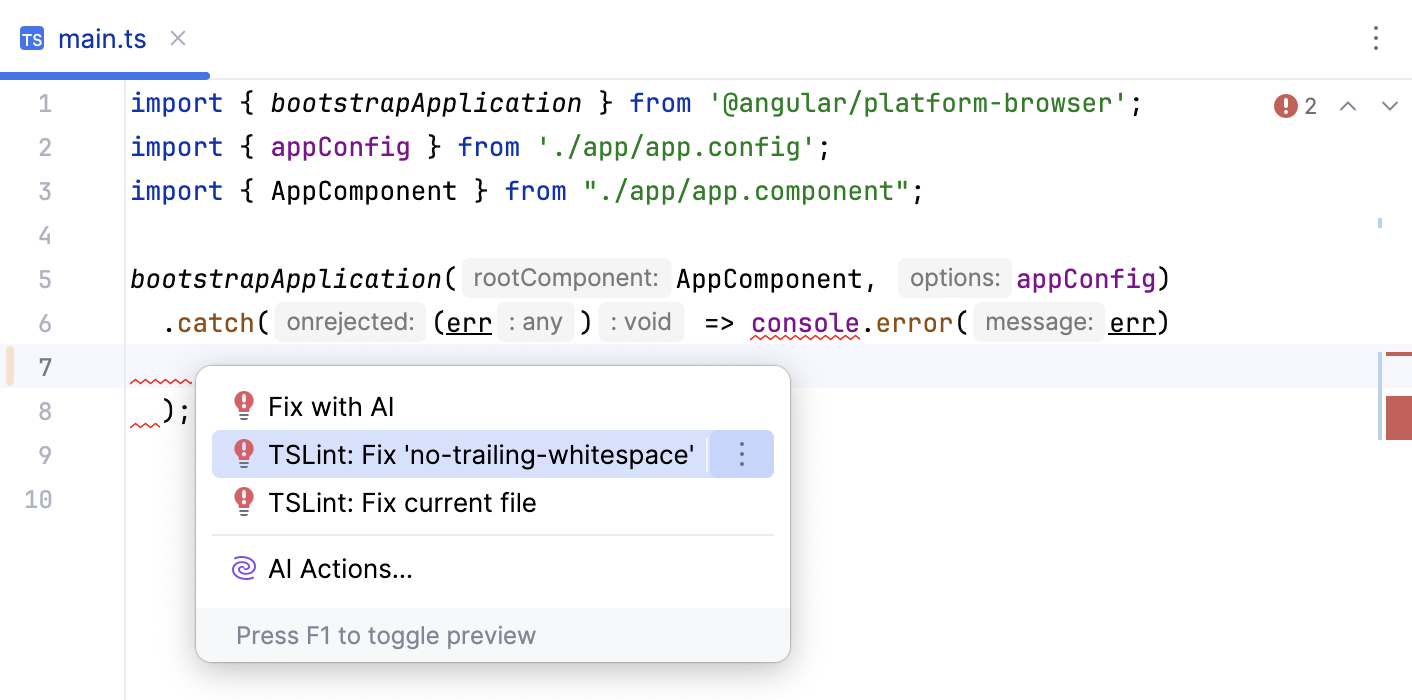
To fix a specific error, place the caret at the highlighted code, press Alt+Enter, and then select TSLint: Fix '<current error>' from the list.
To fix all the issues detected in the file, choose TSLint: Fix current file.
For more information, refer to Applying quick-fixes.
You can suppress TSLint rules for the current file and even for the current line. WebStorm automatically generates disable comments in the format /* tslint:disable:<rule name> or // tslint:disable-next-line:<rule name> and places them on top of the file or above the current line respectively.
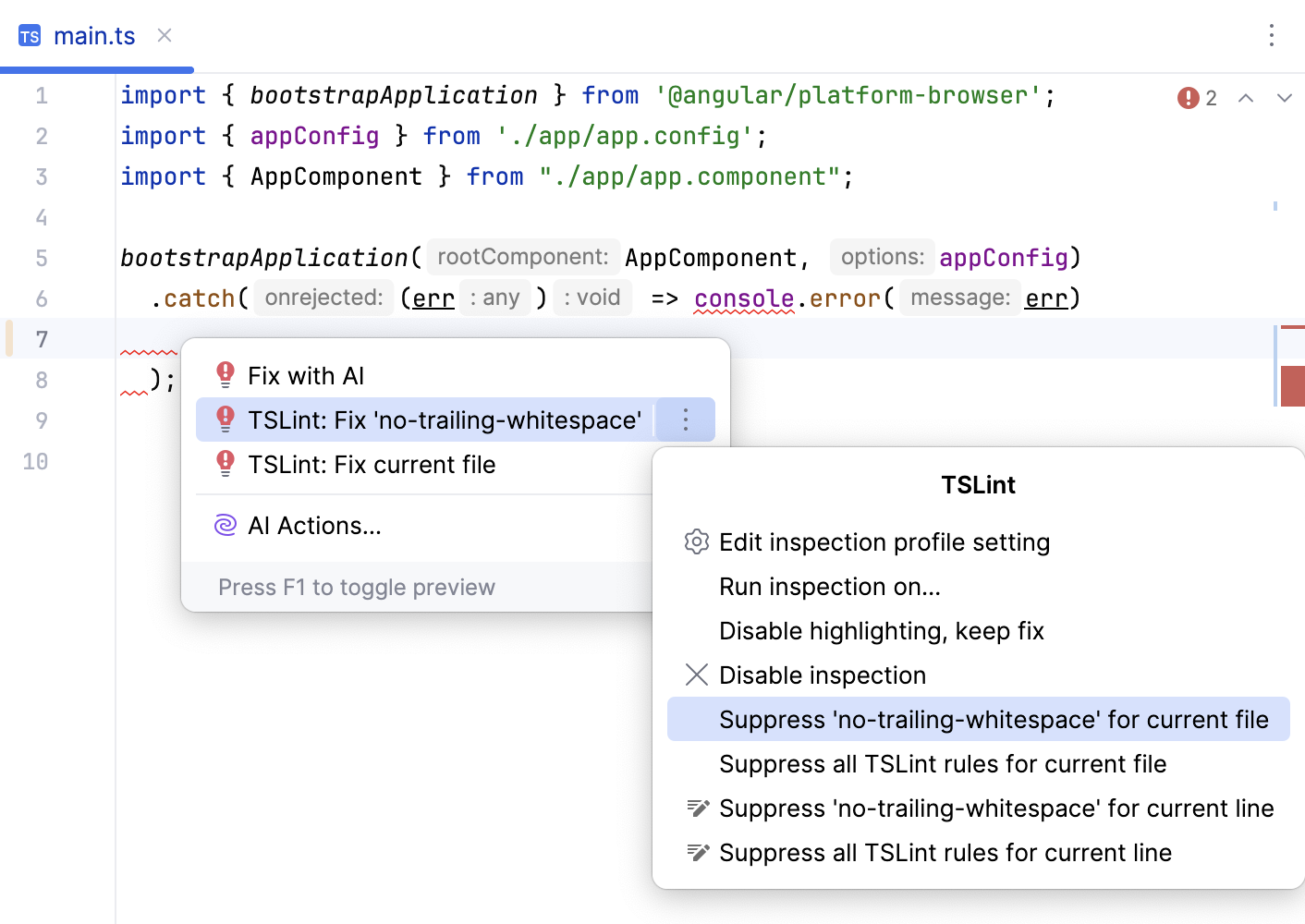
Suppress a TSLint rule on the fly
Place the caret at an error or a warning reported by TSLint and press Alt+Enter.
Select the quick-fix for the rule that you want to disable and press Right.
From the list, select Suppress <rule name> for current file or Suppress <rule name> for current line.