Structural search and replace
Last modified: 01 July 2022A conventional search process does not take into account the syntax and semantics of the source code. Even if you use regular expressions, WebStorm still treats your code as a regular text. The structural search and replace (SSR) actions let you search for a particular code pattern or grammatical construct in your code considering your code structure.
WebStorm finds and replaces fragments of source code, based on the search templates that you create and conditions you apply.
Search for a target structurally
From the main menu, select Edit | Find | Search Structurally to open the Structural Search dialog.
note
In the Structural Search dialog, you can quickly switch to the Structural Replace dialog. Click
.
In the Structural Search dialog, do one of the following:
Create your own template from scratch.
Select Draft Template from the list of templates.
In the editor area, enter the code template (
$variable$that represents your code), in the dialog's toolbar clickto save it for future use. You can opt to save the template as inspection as well.
WebStorm adds the created template to the existing template list (Recent node).
Use one of the existing templates to act as a prototype.
In the available existing templates list, select the needed template.
Consider the following example class:
class Person { constructor(firstName, lastName, age, eyeColor) { this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; this.eyeColor = eyeColor; this.age = age; } move(distanceInMeters) { console.log(`Person moved ${distanceInMeters}m.`); } sing(a) { console.log(`Person sings ${a}`); } jump (distanceInMeters,heightInMeters) { console.log(`Person jumped ${heightInMeters}m high and ${distanceInMeters}m right.`); } RETIRED(age) { return age >= 60; } }Let's find a certain method in the class.
In the list of existing templates, click Javascript, expand the General node, and select the Functions template.
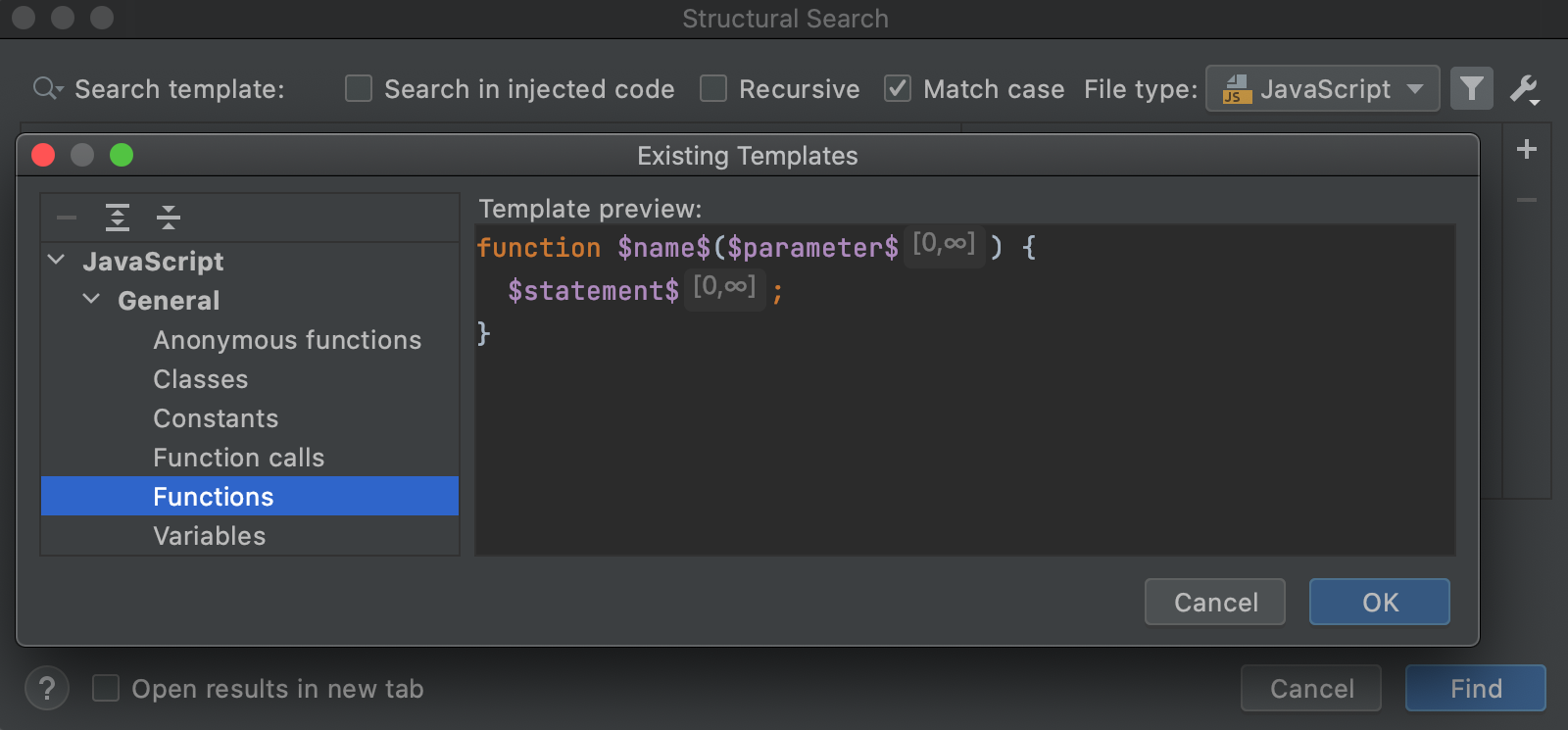
Click Find.
WebStorm instantly highlights the found code occurrences in the editor.
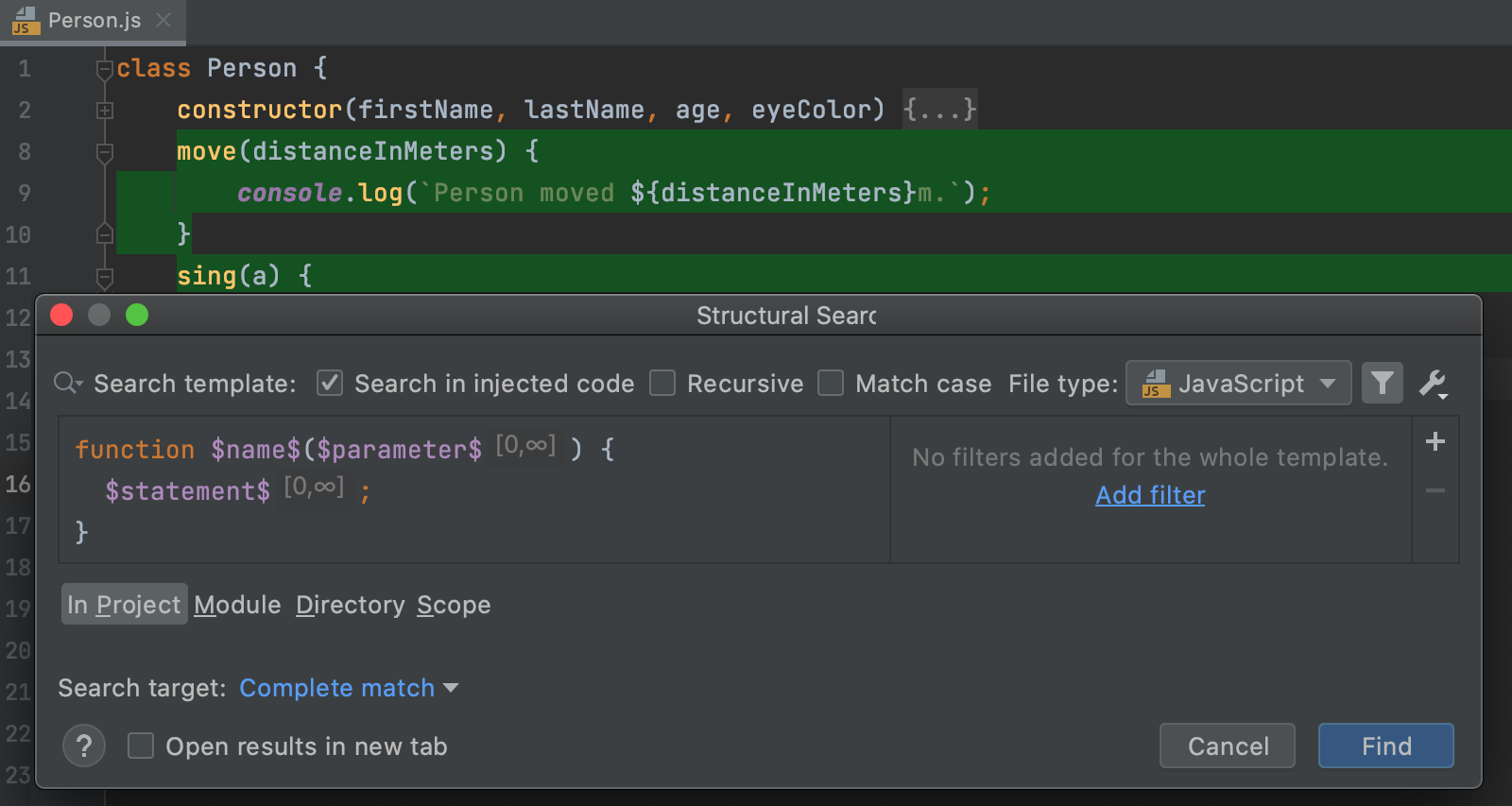
The Structural Search dialog displays the selected template and the values of the filters used in the template. You can edit the existing filters or add new conditions. Place the caret at the code variable and use the filter area to manage filters.
For example, to change the number of parameters in the template, select the
$parameter$variable and specify the appropriate minimum number of them.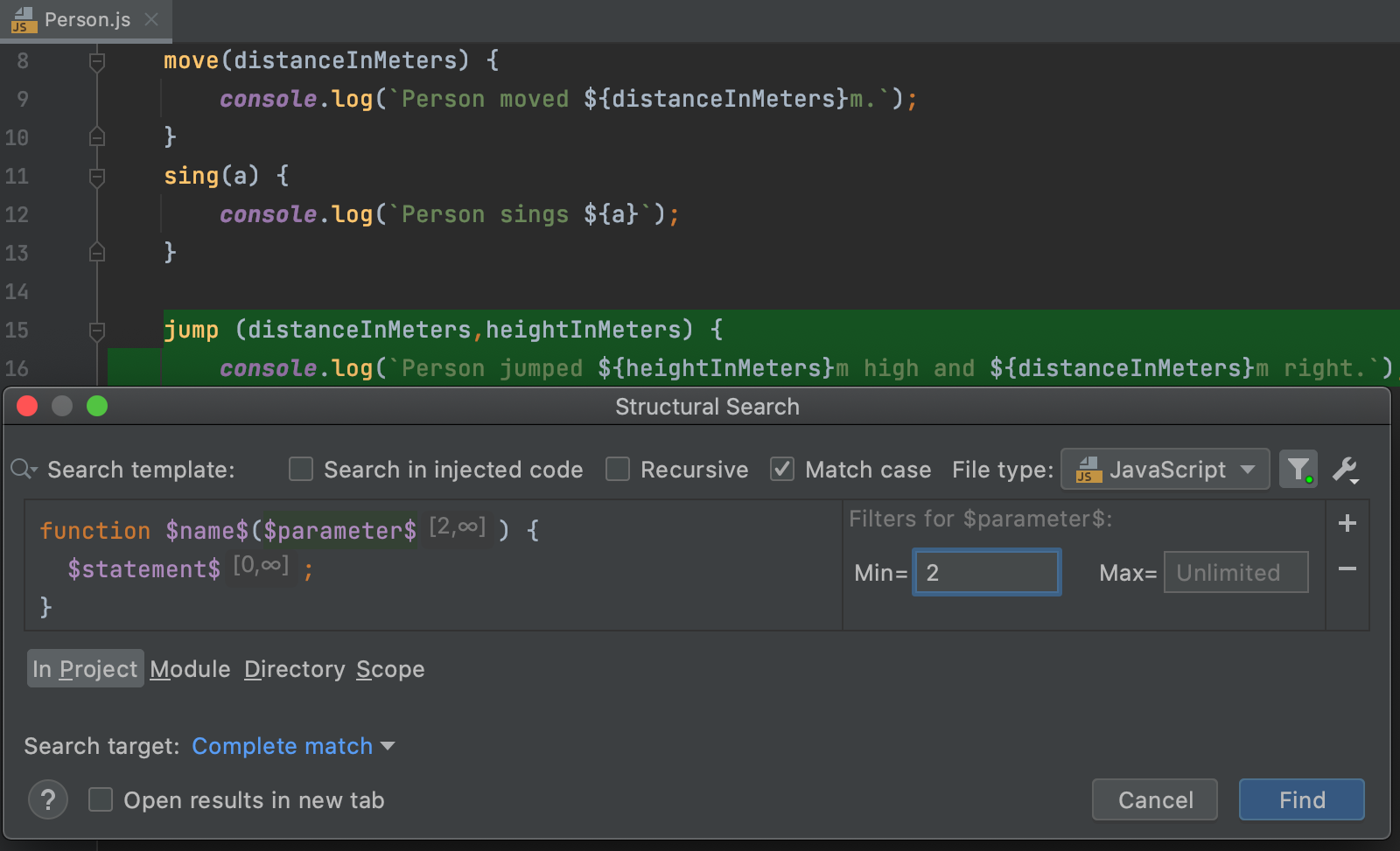
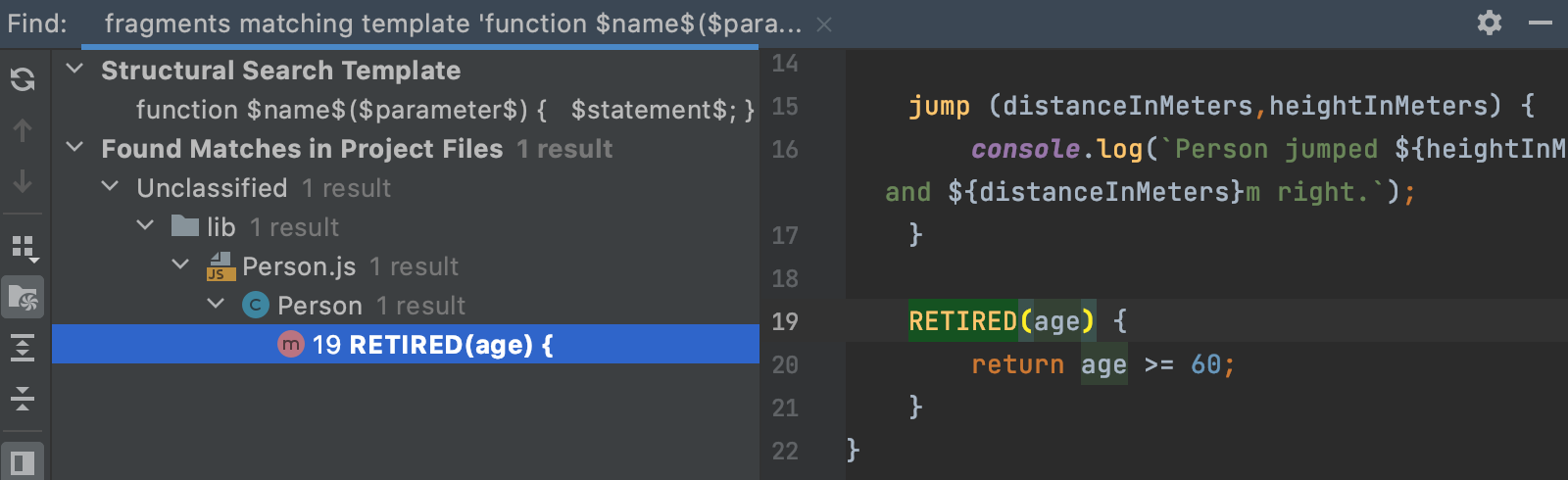
When you click Find, WebStorm opens the Find tool window with a list of methods with two and more parameters, in our example, only
jump (distanceInMeters,heightInMeters) {}is shown.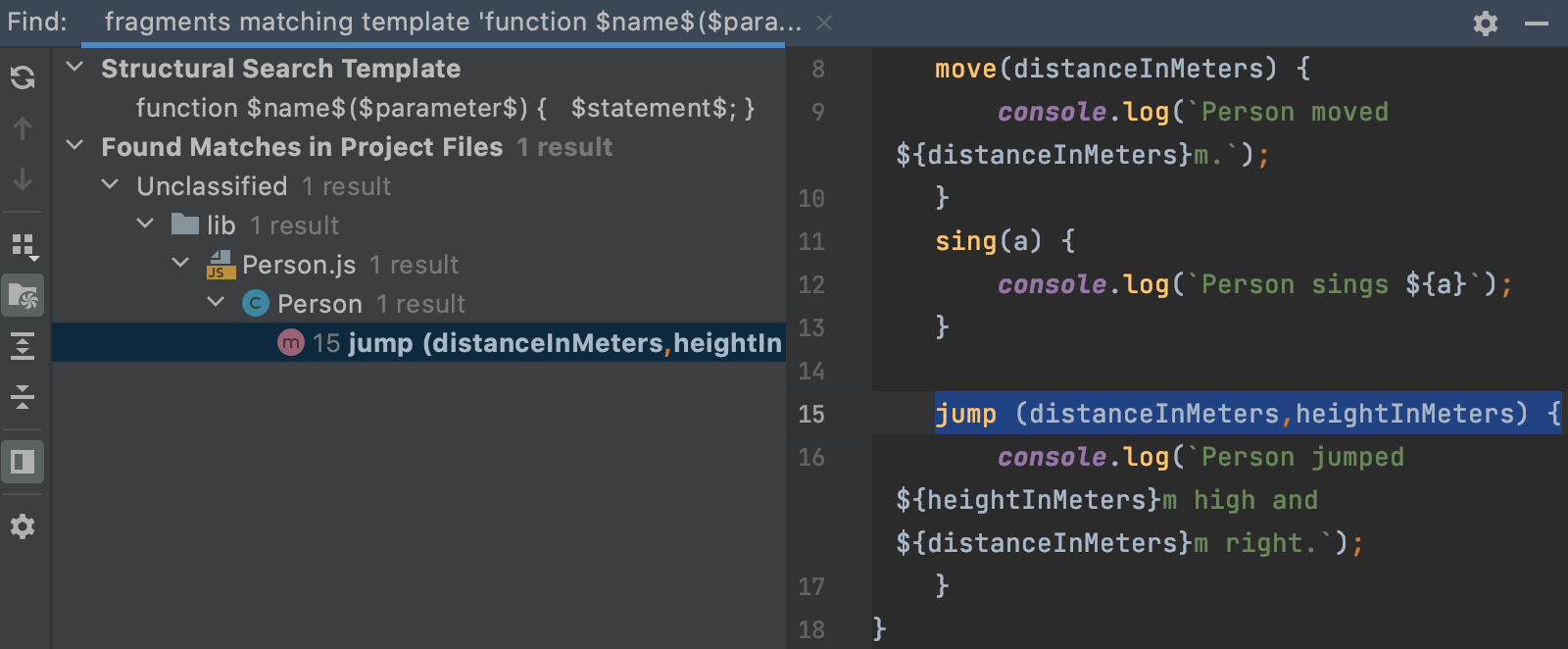
As an example, let's add a condition for the
$name$ variable.In the filter area, click
to add a new condition. If, for example, you need to add a regular expression, select Text. You can also add other conditions depending on your variable.
In the field that opens, type your condition.
For example, let's type the following regular expression:
\b[A-Z]+\b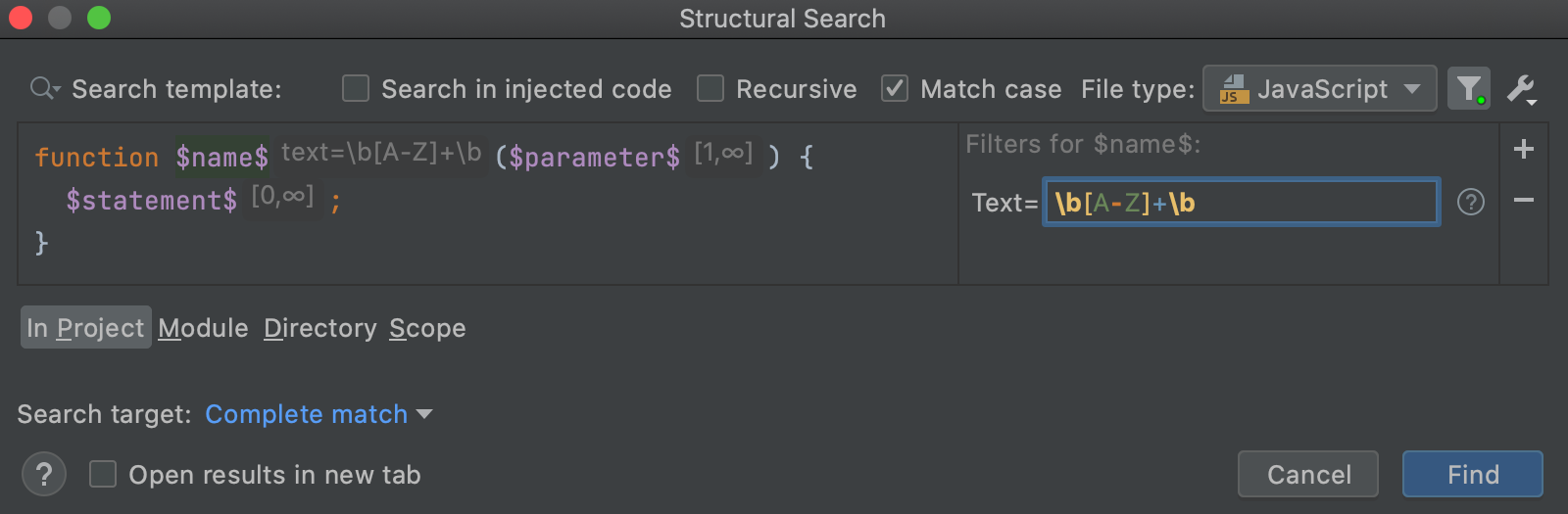
In this case WebStorm will only search for the fields with uppercase characters.
Also note there are different additional options are available depending on the selected language.
For example, check the following options:
Language: use the list to select, which file types should be a part of the search. In our case, it is JavaScript.
Target: in the list of options, select what item to search for. In our case it is
name).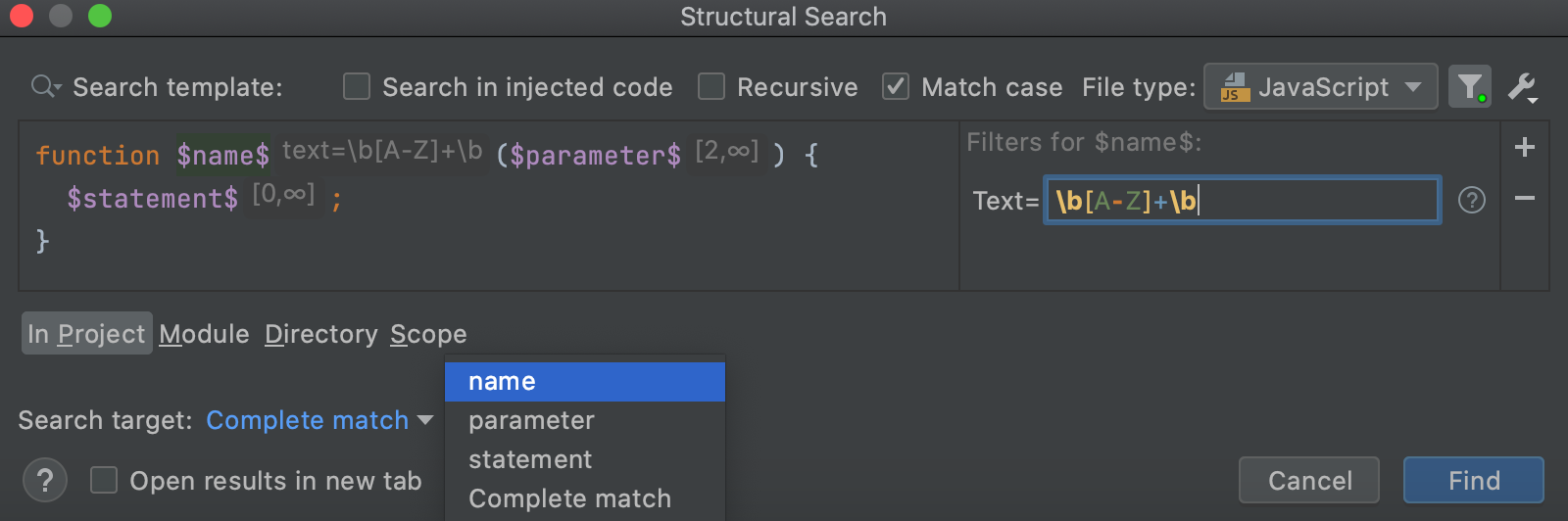
Recursive: if this checkbox is selected, WebStorm performs the recursive search and all nested items will be included in the results. For example, when you search for a method call, with the Recursive option enabled, WebStorm will find nested method calls in
foo(foo(foo())). With the Recursive option disabled, only the outer method call will be found.Injected code: if this checkbox is selected, the injected code such as JavaScript that is injected in HTML code or SQL injected in Java will be a part of the search process.
Match case: if this checkbox is selected, the search result will match the case of a search target.
Specify where to search: in a project, module, directory, or within a custom scope.
Click Find.
WebStorm displays the results in the Find tool window.
Replace a target structurally
From the main menu, select Edit | Find | Replace Structurally.
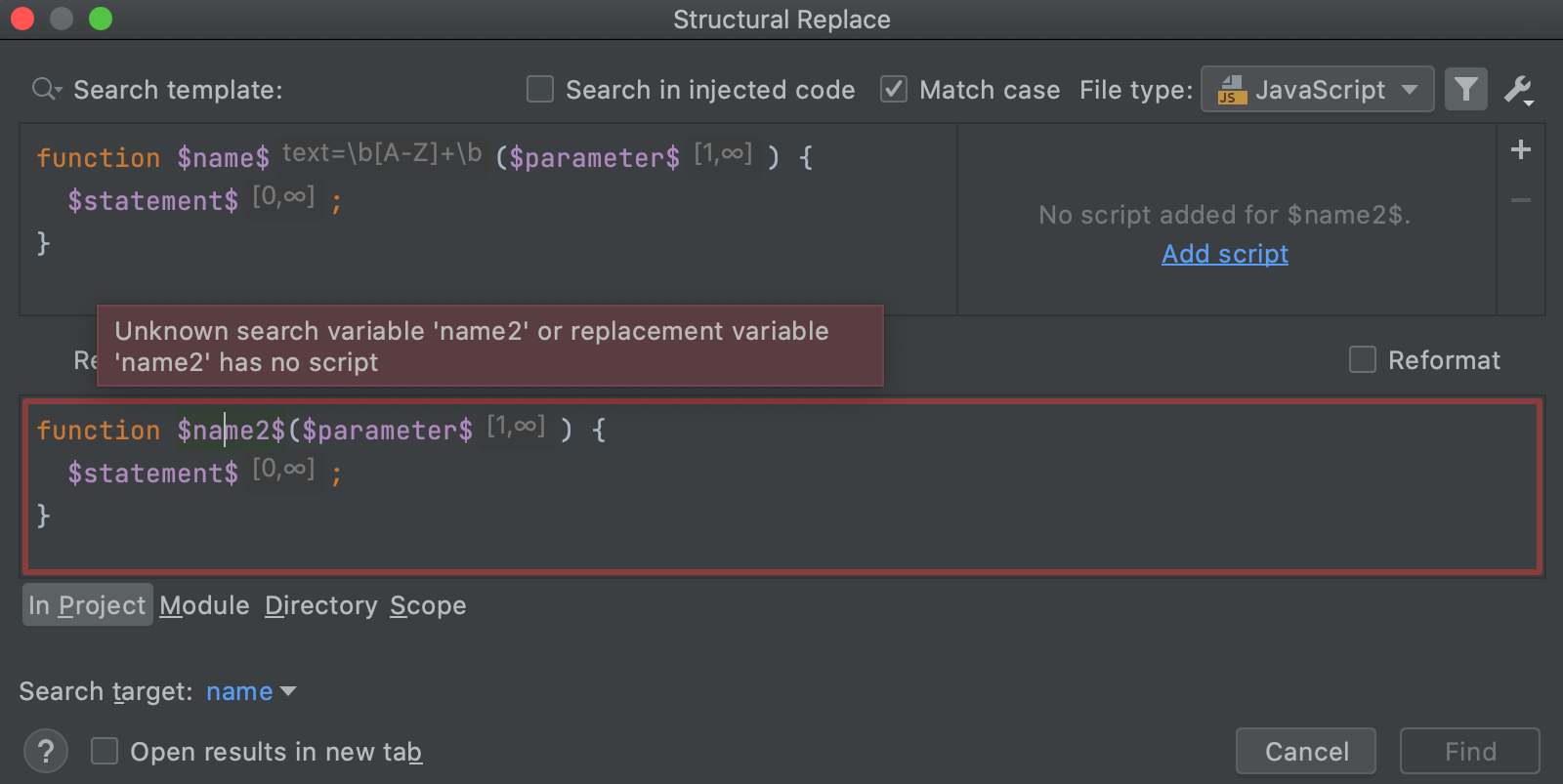
In the Replace Structurally dialog, add new or existing templates to the search and replace template areas. You can save the replace template the same way as the search one.
If you need to add a filter for the variable in the replace template, place a caret at the variable of interest and use the filter area to manage filters.
In the filter area, depending on what you chose as a filter, specify the condition.
To narrow down your replace results, select the following options:
Shorten fully-qualified names - replaces fully qualified class names with short names and imports.
Reformat - automatically formats the replaced code.
Use static import - uses static import in replacement when possible.
After specifying the necessary options, click Find. WebStorm displays the results in the Find tool window.
In the Find tool window, you can work with the results further, replacing found items one by one, or all of them at once, or previewing your potential changes.
Share search templates
You can share a search template with your peers by exporting or importing it.
In the Structural Search dialog (Edit | Find | Search Structurally), create a new search template or use the existing one.
To export a template, click
. WebStorm adds the XML representation of the template to a clipboard (press Ctrl+Shift+V to see the clipboard's content). You can share this representation with other developers in chat, email, or a forum.
To import a template, copy (Ctrl+C) the shared XML code from anywhere (email, chat, or a forum) and in the Structural Search dialog, click
. WebStorm takes the XML code representation and converts it into a template including variables and a scope if it is present.
Thanks for your feedback!