Integrate with a Generic VCS
Follow the instructions on this page to integrate your project with a VCS repository on a hosted version control system.
A generic VCS integration enables you to manually attach commits to issues in YouTrack or add links programmatically using an API.
Prerequisite
YouTrack is accessible to inbound connections. Specifically, you need to make sure that your network doesn't block connections between your VCS server and YouTrack.
Configure the VCS Integration
Next, you need to establish a connection between a project in YouTrack and a repository in your VCS. To connect with your VCS, you need the repository URL.
To connect to a VCS repository:
From the main navigation menu, select
Projects.
From the project list, select a project.
From the project navigation menu, select Version Control.
Click the New VCS Integration button.
The New VCS Integration dialog opens.
For the Server type, select Generic.
Enter or paste the URL that points to your VCS repository into the Repository URL input field. Use
$hash$at the end of the URL as a placeholder for referencing commit hashes.Example:
https://<servername.com>/<user>/<repositoryname>/commit/$hash$
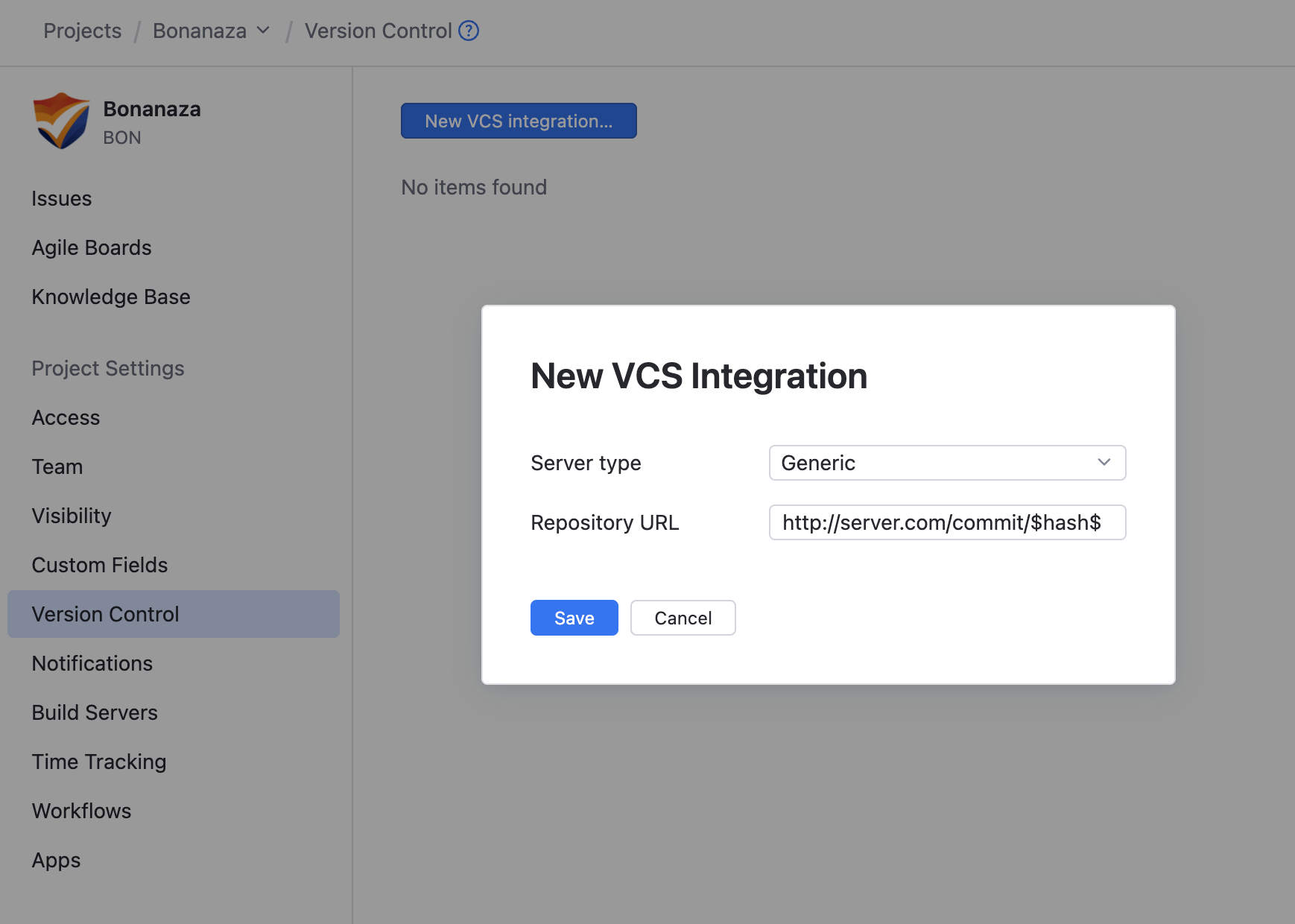
Click the Save button.
Your YouTrack project is integrated with the entered repository in from your VCS host.
You can now manually enter commits from your VCS repository that reference an issue in the project. Commit links are displayed in the activity stream of the referenced issue.
The sidebar displays additional settings for configuring the VCS integration.
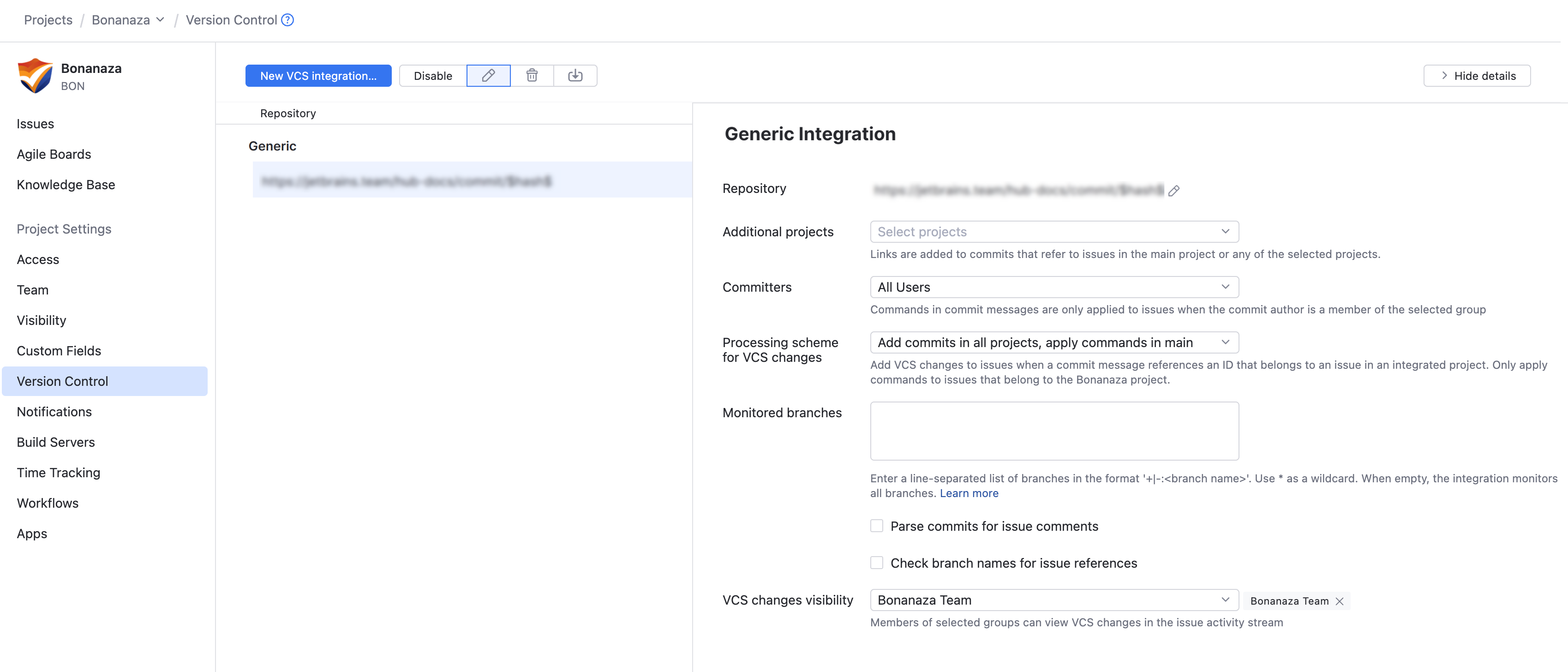
To learn more about these settings, see Integration Settings.
External Integration
Use API calls to authenticate and automatically send information about commits in your VCS repository to YouTrack. When a commit is triggered, an API call is used to send that information to the endpoint YouTrack generates. The call must contain a JSON payload with the commit details that YouTrack expects.
Use the Resource URL generated in the Integration Settings as your POST URL for the API call. The schema for the JSON payload is shown in the example below.
- Example Request
- POST https://yourserver.youtrack.cloud/api/vcsHooksReceiver/generic/519-6 Accept: application/json Authorization: Basic OLRttN43YBRwnU7= Content-Type: application/json X-YT-Simple-Signature: 1zrYcTh0hAxjbhXrIEoJNagPNqL5wPR7rUx4AQOy4k { "branch":"/refs/head/main", "commits":[ { "version":"48038c4d189536a0862a2c20ed832dc34bd1c8b2", "date":1730130046519, "user":{ "userName":"katie_kelly", "email":"example@gmail.com" }, "comment":"TEST-1 committing code to fix a bug" } ] }
Use the X-YT-Simple-Signature: value from the request as the Auth Header value in the Integration Settings.
Manual Commits in an Issue
After setting up a generic VCS integration for a project, you can add your VCS commits manually to YouTrack issues.
To add a VCS commit manually to an issue:
From the main navigation menu, select
Issues.
Open an issue in preview mode or single issue view.
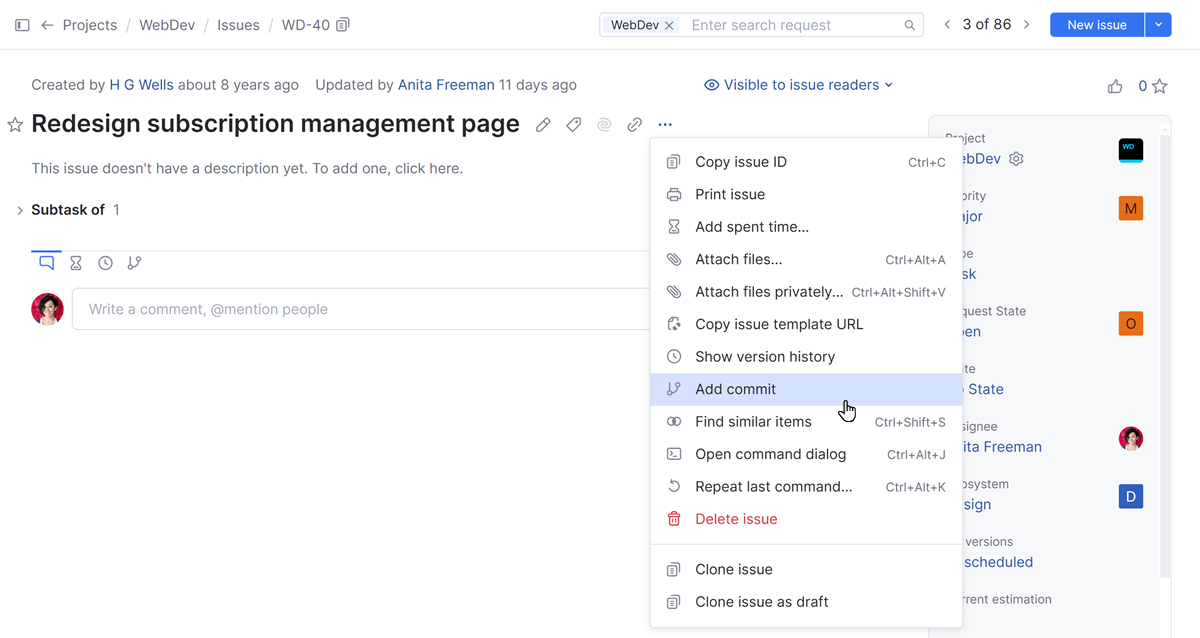
Open the
Show more menu in the toolbar and select
Add commit.
Copy and paste the corresponding commit hash in the URL from your VCS host into the Commit hash field.
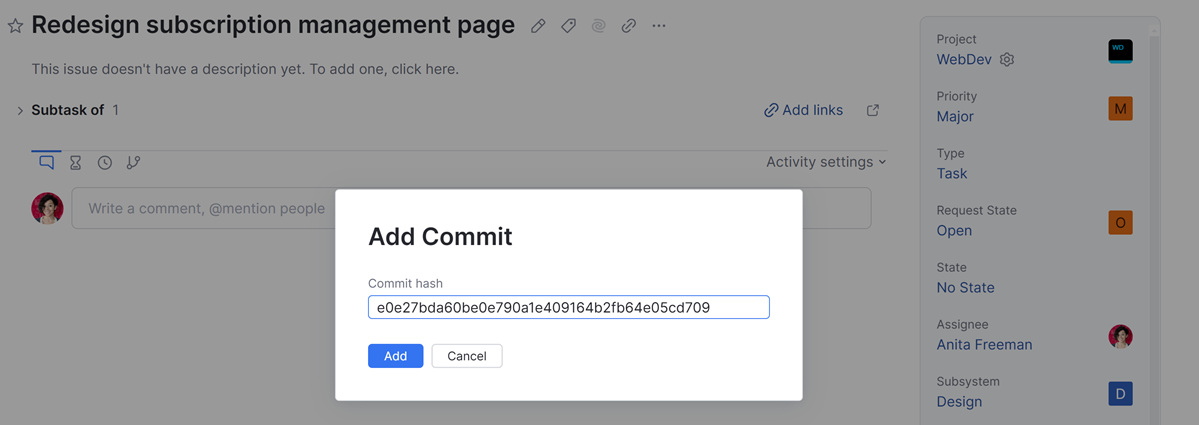
When complete, click the Add button to save the VCS commit in the issue.
The VCS commit is displayed in the issue activity feed.
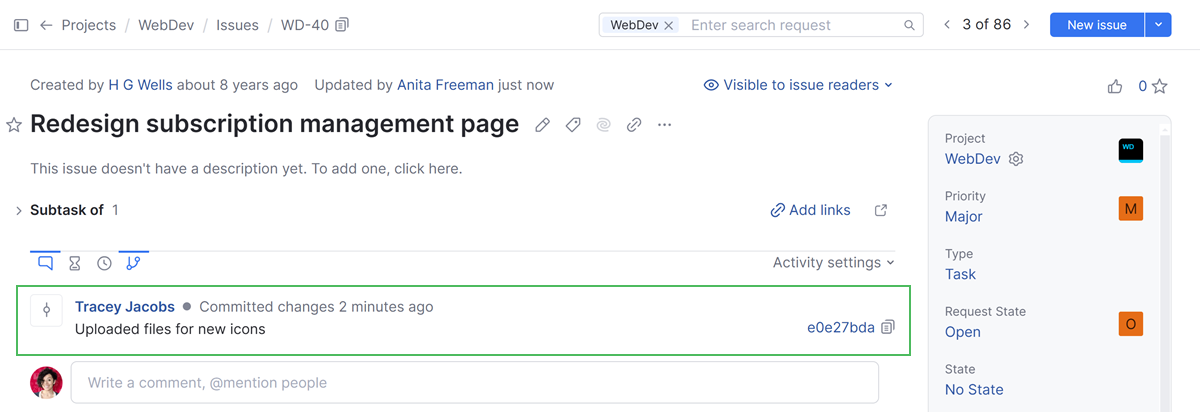
Learn more about how to View and Edit VCS Changes.
Integration Settings
By default, the VCS integration processes changes that are committed to the repository by any user in any branch. Any user who has access to the issue in YouTrack can view these changes in the issue activity stream.
If you only want to process changes by specific users in designated branches or restrict the visibility of VCS changes in YouTrack, you can customize the integration settings. Use the following settings to customize the integration:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Repository | Displays the path to the repository in the integrated version control system. If needed, you can edit the location of the repository after you've set up the integration. For instructions, see Edit Repository Settings. |
Resource URL | The URL used in a |
Auth Header | A hashed value for credentials sent by the VCS host server to YouTrack that can be attached to the API call for authentication. Use the |
Main YouTrack project | Sets the primary project in which the VCS integration is active. |
Additional projects | Integrates the linked repository with one or more additional projects. |
Committers | Restricts the ability to update issues with commands in commit messages to members of the specified group. VCS changes from users who are not members of the selected group are still attached to related issues, but any commands that are specified in their commits are ignored. |
Processing scheme for VCS changes | Choose how to process VCS changes when the commit message references an issue ID. The following options are supported:
|
Monitored branches | Stores the names of the branches that you want to monitor for changes.
|
VCS changes visibility | Restricts the visibility of VCS changes to one or more groups of users in YouTrack. When unrestricted, the list of VCS changes is visible to any user who has permission to read the issue. |
Available Actions
When you select an integrated version control system in the list, the following actions are available in the toolbar:
Action | Description |
|---|---|
Disable | Shuts off the connection between the integrated project and the VCS repository. The configuration is not changed and can be enabled at any time. |
Edit | Opens the integration settings dialog in the sidebar for the selected project and repository. |
Delete | Removes the settings for the integrated project from YouTrack. This action also removes all VCS changes that were added to issues for commits in the linked repository. While the action itself cannot be undone, you can use the Import action to restore VCS changes that were removed accidentally. |
Import commits and open pull requests | Checks the commit history in the linked repository and adds VCS changes to issues that are referenced in commit messages. This option is only available for integrations that are currently enabled. You can use this action to restore VCS changes that were removed when an integration was accidentally deleted or to migrate links to issues in a new project. |