Integrate with GitHub
Follow the instructions on this page to integrate your project with VCS repositories that are hosted on github.com or a self-hosted GitHub Enterprise installation.
A GitHub integration enables the following features in YouTrack:
Apply commands to YouTrack issues right from a commit comment or a pull request description. For more information, see Apply Commands in VCS Commits.
Track commits that are related to specific issues in the activity stream for the issue in YouTrack. For more information, see View and Edit VCS Changes.
Add links to YouTrack issues in commit messages. For more information, see Link Issues in VCS Commits.
Add links to the GitHub repository by pasting commit hashes into the issue summary, description, comment, or a supplemental text field.
Prerequisites
YouTrack is accessible to inbound connections. Specifically, you need to make sure that your network doesn't block connections between your VCS server and YouTrack.
The user account that you use to generate the personal access token for authorization in GitHub has either Admin or Owner permissions for the repository.
If you're integrating with a GitHub Enterprise installation and want to establish a secure (HTTPS) connection with the server, you may need to import the SSL certificate for your GitHub server into YouTrack.
If your GitHub Enterprise server has a valid certificate that is signed by a well-known certificate authority (CA), the JVM vendor may have already added the root (CA) certificate to the certificate store. You should be able to connect to the server without importing its SSL certificate.
If the certificate for your server is self-signed, you need to import the certificate and public key to establish a secure connection. For security, use this option only when both YouTrack and your GitHub Enterprise server run on a private computer network. This operation is only available to users with Low-level Admin Read and Low-level Admin Write permissions. For details, see SSL Certificates.
Configure the GitHub Integration
The first step is to establish a connection between a project in YouTrack and a repository in GitHub. To connect with GitHub, you need to generate and store a personal access token. This token grants YouTrack access to the repository based on the access that is granted to your GitHub account.
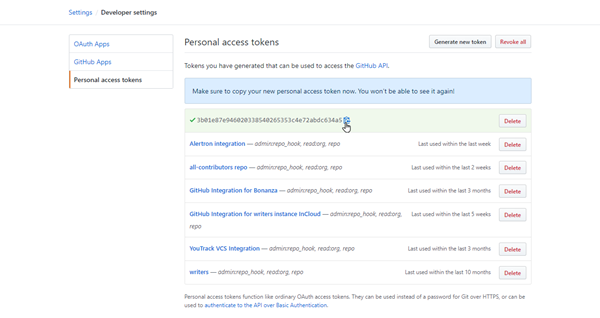
You can use a single access token to set up multiple integrations. If you don't already have a personal access token, you can use the direct link from YouTrack to generate it during this setup procedure.
To connect to a GitHub repository:
Click the Projects link in the header to open the Projects list.
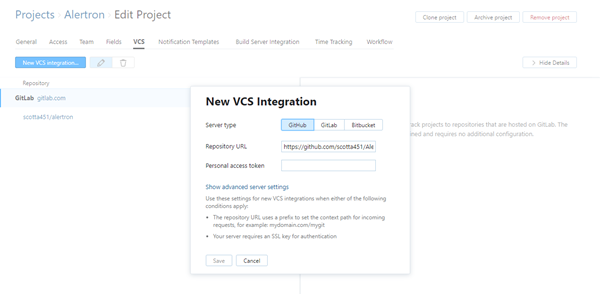
Click the New VCS Integration button.
For the Server type, select GitHub.
Paste the token in the OAuth Token field.
Paste your personal access token into the Personal access token input field. If you don't already have an access token, follow these steps:
Click the Generate token link to open the New personal access token page in GitHub.
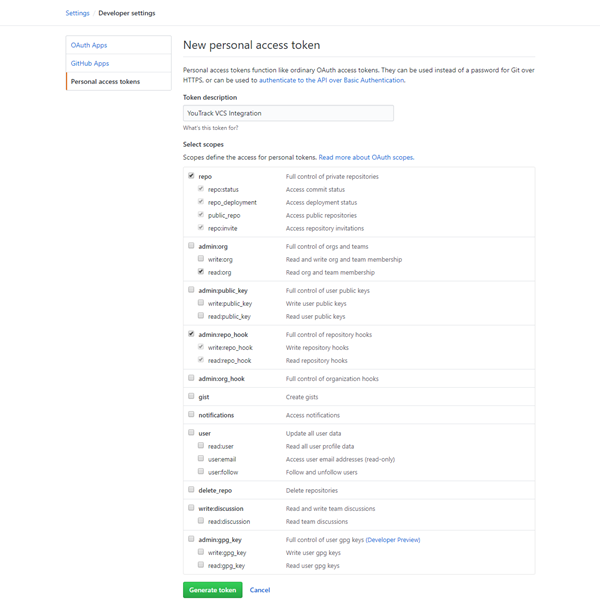
Enter a description for the token.
When you access the New personal access token page using the link from YouTrack, all of the required scopes are selected for you. If you accessed this page directly, select the scopes for
repo,read.org, andadmin:repo_hook.Click the Generate token button.
Switch back to the New VCS Integration dialog in YouTrack and paste the token into the Personal access token field.
Click the Save button.
Your YouTrack project is integrated with the selected repository in GitHub.
Commits from the GitHub repository that reference an issue in the project are displayed in the activity stream of the referenced issue.
The sidebar displays additional settings for configuring the VCS integration.
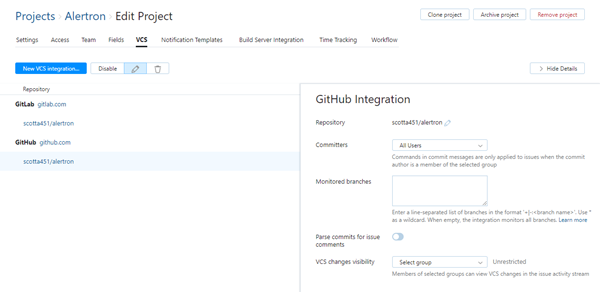
To learn more about these settings, see Integration Settings.
Advanced Server Settings
If you are unable to establish a connection to your repository using the basic settings on the New VCS Integration dialog, click the Show advanced server settings link.
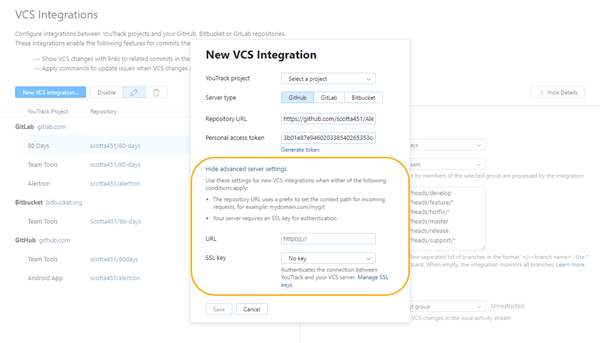
You only need to enter values for these settings when there isn't already a VCS integration with the target server. If you already have a working integration with a single repository on the server, you can add integrations with other repositories without setting these parameters again.
Use the following guidelines to set the values for these settings:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
URL | This setting is not relevant for connections to repositories in GitHub. For integrations with other VCS hosting services, this setting helps to identify the path to the repository. The path to a GitHub repository always consists of two segments. Everything that precedes these two segments in the Repository URL setting is automatically recognized as the path to the server. |
SSL key | If your server environment is set up to require HTTPS authentication, select the keystore that contains the private key for your YouTrack server. This key identifies your YouTrack server when it tries to establish a connection with GitHub. This setting is only used to support HTTPS authentication as required by connections to your internal network. The list only displays SSL keys that are already imported into YouTrack. To learn how to generate keystores files and upload them to YouTrack, see SSL Keys. |
Integration Settings
By default, the VCS integration processes changes that are committed to the repository by any user in any branch. Any user who has access to the issue in YouTrack can view these changes in the issue activity stream.
If you only want to process changes by specific users in designated branches or restrict the visibility of VCS changes in YouTrack, you can customize the integration settings. Use following settings to customize the integration:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Repository | Displays the path to the repository in the integrated version control system. If needed, you can edit the location of the repository after you have set up the integration. For instructions, see Edit Repository Settings. |
Committers | Restricts the ability to update issues with commands in commit messages to members of the specified group. VCS changes from users who are not members of the selected group are still attached to related issues, but any commands that are specified in their commits are ignored. |
Monitored branches | Stores the names of the branches that you want to monitor for changes.
If the address that you entered as the Repository URL when you connected to GitHub points to a specific branch, this branch is automatically added to the list of monitored branches when you set up the connection. |
Parse commits for issue comments | When enabled, specific segments of commit message text are copied to issues as comments. When you copy parts of the commit message to the issue as comments, you can trigger @mention notifications and expose information to users who don't have access to VCS changes. This setting does not affect how commit messages are shown in VCS changes. The entire commit message, including commands and issue comments, is always shown as part of the VCS change record in the activity stream. You should only enable this option when:
To learn more about how YouTrack processes commit messages, see Apply Commands in VCS Commits. |
VCS changes visibility | Restricts the visibility of VCS changes to one or more groups of users in YouTrack. When unrestricted, the list of VCS changes is visible to any user who has permission to read the issue. |
Troubleshooting
Condition — References to issues in VCS commits are not shown as VCS changes in YouTrack.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The webhooks in the integrated VCS don't exist, are disabled, or are otherwise malformed. | Check the webhooks in the settings for your VCS repository. Make sure that the webhooks exist and that they are enabled. If you suspect that there is a problem with a webhook, delete or disable it in the settings for your VCS and set up a new VCS integration in YouTrack. |
Condition — Commands that are specified in VCS commits are not applied to issues in YouTrack.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The users who commit changes to the repository are not members of the Committers group in the integration settings. | Either add the committers to the specified group in YouTrack or modify the selection in the integration settings. |
The users who commit changes to the repository do not have permission to update issues in the connected project. | Either add these users to the project team or grant them a role in the project that includes the Read Issue and Update Issue permissions. |
YouTrack can't find a user account that matches the author of the commit message. | The user must either use the same email address for their accounts in both YouTrack and GitHub or add the value that is stored as the Name in their GitHub profile to the list of VCS user names in their Hub accounts. For more information, see Match Commit Authors and YouTrack Users. |
Condition — You are unable to establish a connection between YouTrack and your GitHub Enterprise server. See if any of the following causes are present.
Cause | Solution |
|---|---|
The external service is unavailable. | Verify that your GitHub Enterprise server is running. |
The connection is blocked by a firewall. | Open the ports in the firewall that are used by YouTrack and the GitHub Enterprise server. |
The connection to the external service is blocked by the proxy server. You are trying to connect over the wrong port. | Set the system properties for your server that let YouTrack connect to other services through the proxy server. For instructions, see Proxy Configuration. |
The GitHub Enterprise server requires a secure connection. | Import the certificate for your GitHub Enterprise server into YouTrack. For instructions, see SSL Certificates. |
Your SSL certificate for the GitHub Enterprise server has expired. | Renew and import the updated certificate into YouTrack. For instructions, see SSL Certificates. |