Running and debugging TypeScript
With WebStorm, you can run and debug both client-side TypeScript code and server-side TypeScript code running in Node.js.
note
Debugging of TypeScript client-side code is only supported in Google Chrome and in other Chromium-based browsers.
For more information about running and debugging TypeScript with Angular, refer to Run an Angular application and Debug Angular applications.
Before running or debugging an application, you need to compile your TypeScript code into JavaScript. You can do that using the built-in TypeScript compiler and other tools, including ts-node for running TypeScript with Node.js, used separately or as part of the build process
During compilation, there can also be generated source maps that set correspondence between your TypeScript code and the JavaScript code that is actually executed. As a result, you can set breakpoints in your TypeScript code, launch the application with the run/debug configuration of the type JavaScript Debug (for client-side code) or Node.js, and then step through your original TypeScript code, thanks to generated sourcemaps.
You can write a client-side application in TypeScript, compile the code as described in Compiling TypeScript into JavaScript, and then run and debug your application exactly in the same way as client-side applications written in JavaScript. The only difference is that you can set breakpoints right in the TypeScript code.
In the editor, open the HTML file with a reference to the generated JavaScript file. This HTML file does not necessarily have to be the one that implements the starting page of the application.
Do one of the following:
Choose View | Open in Browser from the main menu or press . Then select the desired browser from the list.
Hover over the code to show the browser icons bar:
. Click the icon that indicates the desired browser.
If your application is running on the built-in WebStorm server, refer to Running a client-side TypeScript application above, you can also debug it in the same way as JavaScript running on the built-in server.
Most often, you may want to debug a client-side application running on an external development web server, for example, powered by Node.js.
Configure the built-in debugger as described in Configuring JavaScript debugger.
To enable source maps generation, open your tsconfig.json and set the
sourceMapproperty totrue, as described in Create a tsconfig.json file.Configure and set breakpoints in the TypeScript code.
Run the application in the development mode. Often you need to run
npm startfor that.Most often, at this stage TypeScript is compiled into JavaScript and source maps are generated. For more information, refer to Compiling TypeScript into JavaScript.
When the development server is ready, copy the URL address at which the application is running in the browser - you will need to specify this URL address in the run/debug configuration.
Go to Run | Edit Configurations. Alternatively, select Edit Configurations from the Run widget on the toolbar.

In the Edit Configurations dialog that opens, click the Add button (
) on the toolbar and select JavaScript Debug from the list. In the Run/Debug Configuration: JavaScript Debug dialog that opens, specify the URL address at which the application is running. This URL can be copied from the address bar of your browser as described in Step 3 above.

From the Run widget list on the toolbar, select the newly created configuration and click
next to it. The URL address specified in the run configuration opens in the browser and the Debug tool window appears.
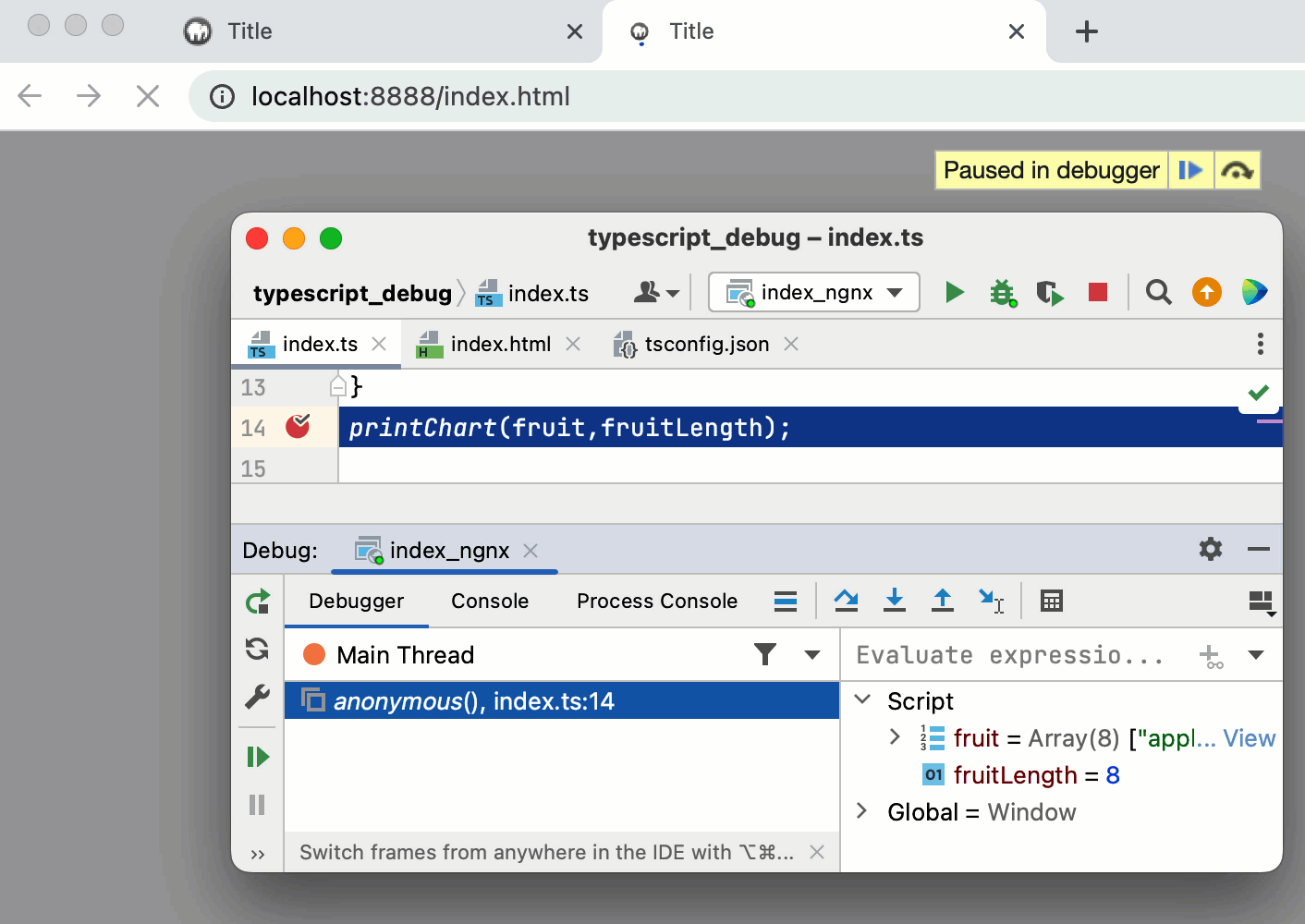
You may need to refresh the page in the browser to get the controls in the Debug tool window available.
In the Debug tool window, proceed as usual: step through the program, stop and resume the program execution, examine it when suspended, view actual HTML DOM, run JavaScript code snippets in the Console, and so on.
With WebStorm, you can run and debug server-side TypeScript code without previously compiling it into JavaScript.
For running and debugging of server-side multiple TypeScript file applications WebStorm uses a built-in loader. When running or debugging a single file, you can turn the loader off by selecting None from the TypeScript loader list in the run/debug configuration.
Make sure you have Node.js 18 or higher on your computer.
Make sure the Node.js plugin is enabled in the settings. Press to open settings and then select Plugins. Click the Installed tab. In the search field, type Node.js. For more information about plugins, refer to Managing plugins.
You can run server-side TypeScript from the Project tool window , from the editor, or from the Run widget.
In the Project tool window , right-click the TypeScript file to run or the starting file of your application and select Run <TypeScript file name> from the context menu.

In the editor, open the TypeScript file to run or the starting file of your application and select Run <TypeScript file name> from the list.

In the editor, open the TypeScript file to run or the starting file of your application. Then from the Run widget on the toolbar select Current file and click
next to it.
Alternatively, from the Run widget select a previously created run/debug configuration and click
next to it.

To run a scratch file, besides the above-mentioned methods, you can also click in the gutter and select the required action from the list.

No matter which way to run server-side TypeScript code you might choose, WebStorm creates a temporary run/debug configuration of the type Node.js which you can save, edit, and reuse for running and debugging.

Learn more from Run/debug configurations.
You can debug server-side TypeScript from the Project tool window , from the editor, or from the Run widget.
Set the breakpoints where necessary.
In the Project tool window, right-click the TypeScript file to debug or the starting file of your application and select Debug <TypeScript file name> from the context menu.

Set the breakpoints where necessary.
In the editor, open the TypeScript file to debug or the starting file of your application and select Debug <TypeScript file name> from the context menu.

Set the breakpoints where necessary.
In the editor, open the TypeScript file to debug or the starting file of your application. Then from the Run widget on the toolbar select Current file and click
next to it.
Alternatively, from the Run widget select a previously created run/debug configuration and click
next to it.

To debug a scratch file, besides the above-mentioned methods, you can also click in the gutter and select the required action from the list.

If you need to run or debug single TypeScript files with Node.js, you can use ts-node instead of compiling your code as described in Compiling TypeScript into JavaScript.
In the embedded Terminal () , type:
npm install --save-dev ts-node
Go to Run | Edit Configurations. Alternatively, select Edit Configurations from the Run widget on the toolbar.

In the Edit Configurations dialog that opens, click the Add button (
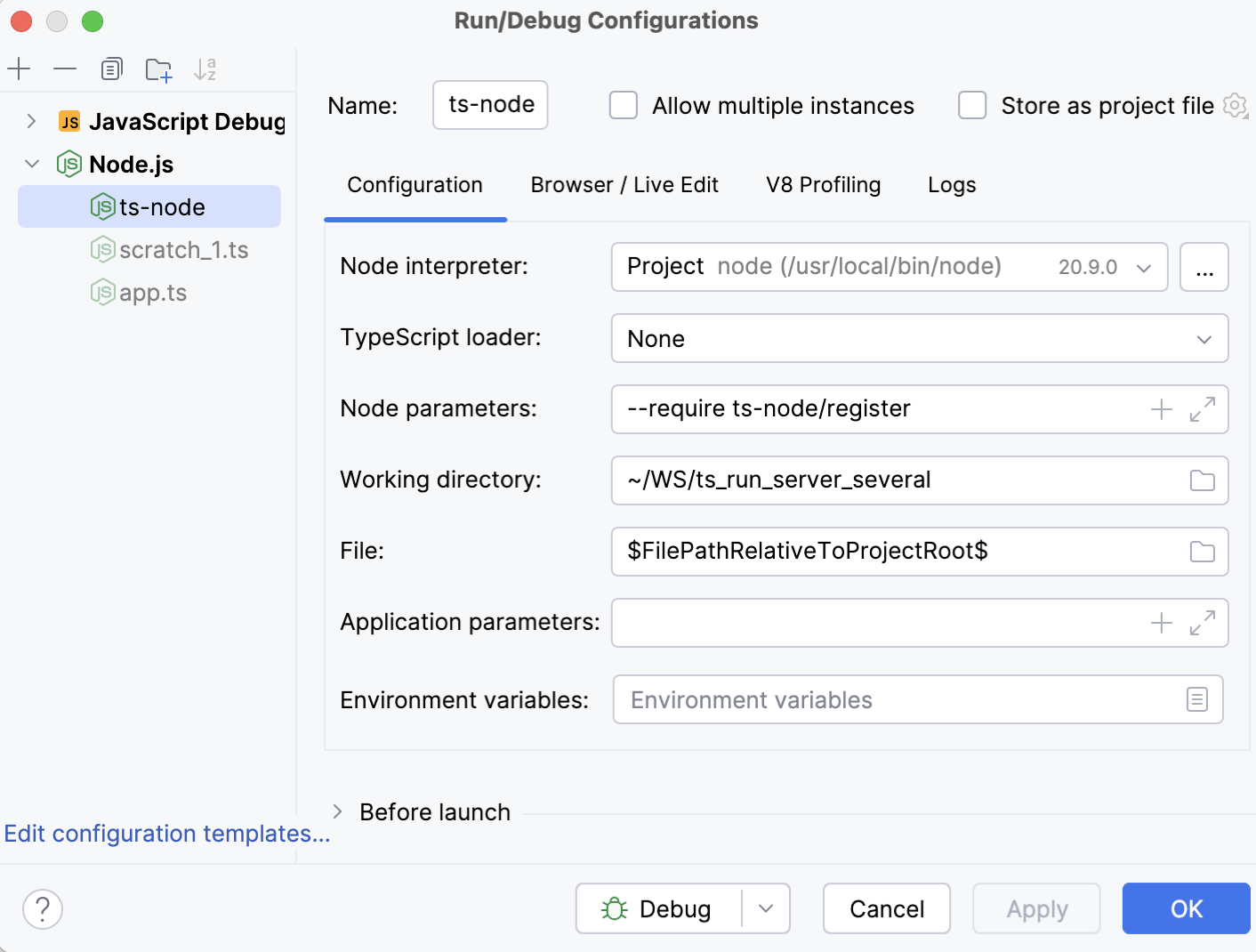
) on the toolbar and select Node.js from the list. The Run/Debug Configuration: Node.js dialog opens.
In the Node Parameters field, add
--require ts-node/register.Specify the Node.js interpreter to use.
If you choose the Project alias, WebStorm will automatically use the project default interpreter from the Node interpreter field on the Node.js page . In most cases, WebStorm detects the project default interpreter and fills in the field itself.
You can also choose another configured local or remote interpreter or click
and configure a new one.
For more information, refer to Configuring remote Node.js interpreters, Configuring a local Node.js interpreter, and Using Node.js on Windows Subsystem for Linux.
In the File field, specify the TypeScript file to run or debug. Depending on your workflow, you can do that explicitly or using a macro.
If you are going to always launch the same TypeScript file, click
and select this file in the dialog that opens. By default, the run/debug configuration gets the name of the selected file.
If you need to launch different files, type
$FilePathRelativeToProjectRoot$. With this macro, WebStorm will always launch the file in the active editor tab.
If necessary, specify any additional parameters for
ts-node(for example,--project tsconfig.json) in the Application parameters field.Save the configuration.
Depending on the way you specified your TypeScript file in the run/debug configuration, do one of the following:
If you typed the filename explicitly, select the required configuration from the Run widget on the toolbar and click
next to the list or press .
If you specified a macro, open the TypeScript file to run in the editor, select the newly created configuration from the Run widget on the toolbar, and click
or press .
WebStorm shows the output in the Run tool window.
In the TypeScript file to debug, set the breakpoints as necessary.
Depending on the way you specified your TypeScript file in the run/debug configuration, do one of the following:
If you typed the filename explicitly, select the required configuration from the Run widget on the toolbar and click
or press .
If you specified a macro, open the TypeScript file to debug in the editor, select the newly created configuration from the Run widget and click
or press .